Land reclamation by agave forestry with native species [México]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Christian Prat
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
Recuperación de tierras degradadas por agaveforestería con especies locales de agaves, arboles y herbaceas (Spanish)
technologies_1114 - México
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Martínez Palacios Alejandro
(443) 334-0475
apalacios56@gmail.com
Instituto de Investigaciones Agropecuarias y Forestales, Universidad Michoacana de San Nicolás de Hidalgo
km 9.5 carr. Morelia-Zinapecuaro, Tarímbaro, Michoacán 58330
México
Especialista MST:
Ríos Patrón Eduardo
(443) 322-6017
eduardo.rios@semarnat.gob.mx
Delegación de SEMARNAT en Michoacán, Unidad de Planeación y Política Ambiental
Morelia, Michoacán
México
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
DESIRE (EU-DES!RE)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Instituto de Investigaciones Agropecuarias y Forestales (IIAF) - MéxicoNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Institut de recherche pour le développement IRD (Institut de recherche pour le développement IRD) - FranciaNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
SECRETARÍA DE MEDIO AMBIENTE Y RECURSOS NATURALES (SECRETARÍA DE MEDIO AMBIENTE Y RECURSOS NATURALES) - MéxicoNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Universidad Michoacana de San Nicolás de Hidalgo (UMSNH) - México1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
01/10/2010
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST

Participative actions for economic benefits of agave forestry [México]
Land reclamation with local agave (to produce Mezcal) associated with trees, shrubs and grasses planted through participative actions for economic benefit.
- Compilador: Christian Prat

Land reclamation by agave forestry with native species [México]
Land reclamation with local agave (to produce mezcal) associated wotj trees, shrubs and grasses planted through participative actions for economic benefit.
- Compilador: Christian Prat
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Agave forestry land reclamation system with native agaves, trees, shrubs and grasses planted through participatory action for a sustainable production of mezcal and other products in order to generate high incomes for farmers.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
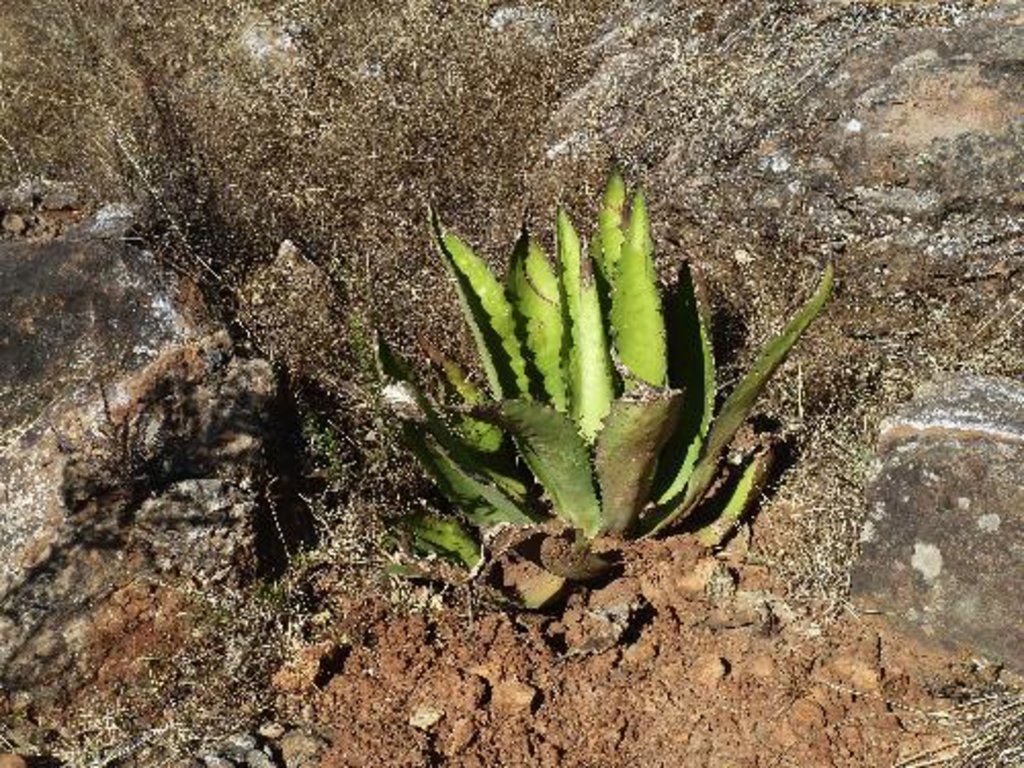
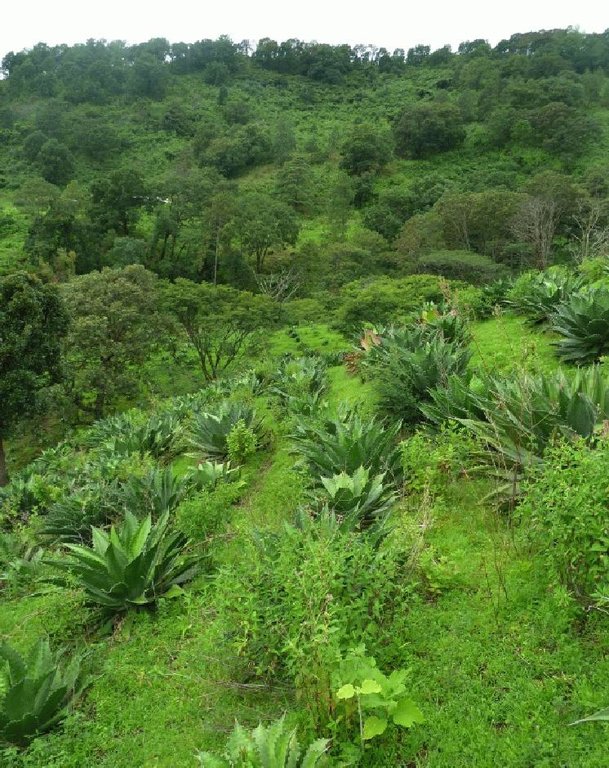
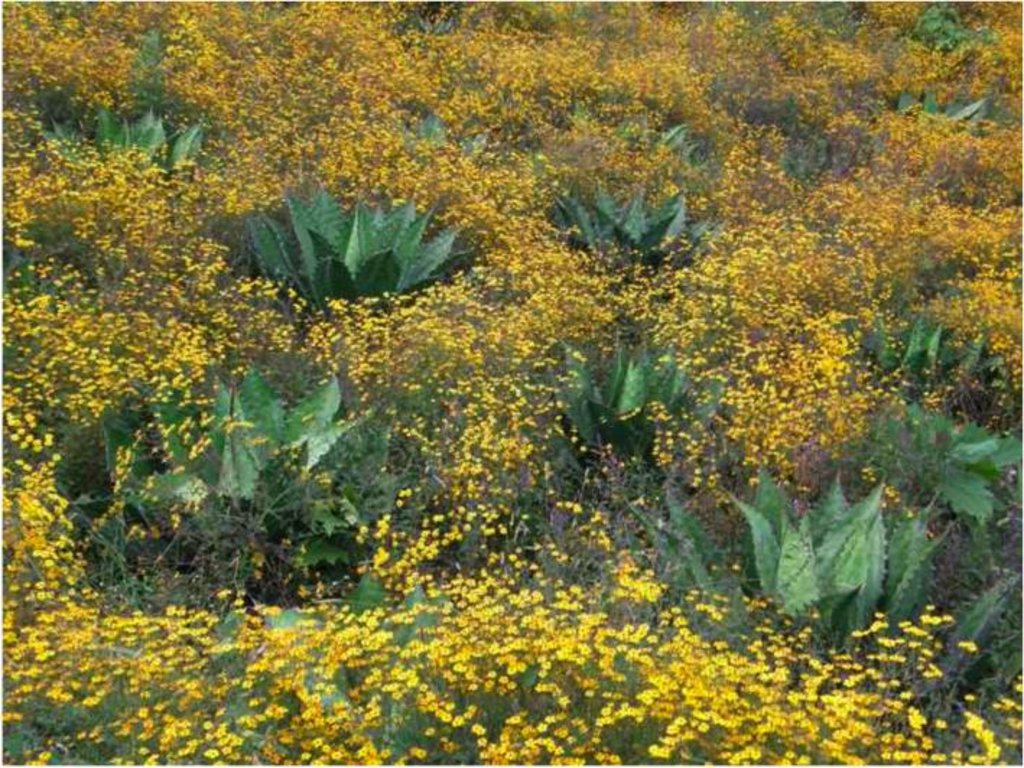
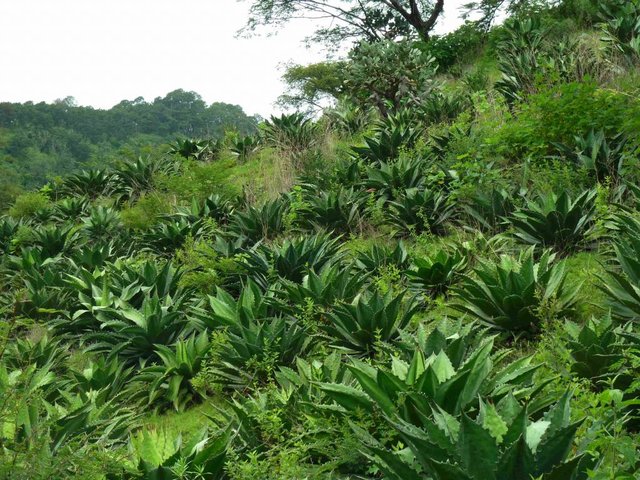
Rehabilitation of degraded land is achieved using native agave (Agave inaequidens), trees and/or fruit trees, shrubs and grasses to create, over the medium-term (7-10 years), sustainable production of a traditional alcoholic drink (mezcal) made from agave and/or cosmetic and medicinal products, and/or fibres and/or fodder for cattle and/or wood. Between the agave plants, native vegetation is managed or planted for use as food, fodder and/or medicinal products. Depending on the slope and the level of land degradation, continuous planted rows of agave provide a ’green’ barrier that controls soil erosion and runoff.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose is to achieve sustainable land rehabilitation while generating a high income for the farmer. This allows reducing the amount of livestock and overgrazing, which is the main cause of soil erosion in this region. The production of mezcal gives local farmers high incomes. Trees, shrubs and grasses for medicinal uses, food, and fodder are complements of agave production and are processed mainly by women, while agave harvesting is a male activity. As it is very attractive financially, farmers stay in the communities instead of emigrating to cities or abroad. Biodiversity is preserved and increased using native plants (agaves, trees, shrubs, grasses). These plant associations are effective at controlling plant pests and diseases. Turning eroded into productive soil sequesters carbon and increases water availability as a result of the new soil cover.
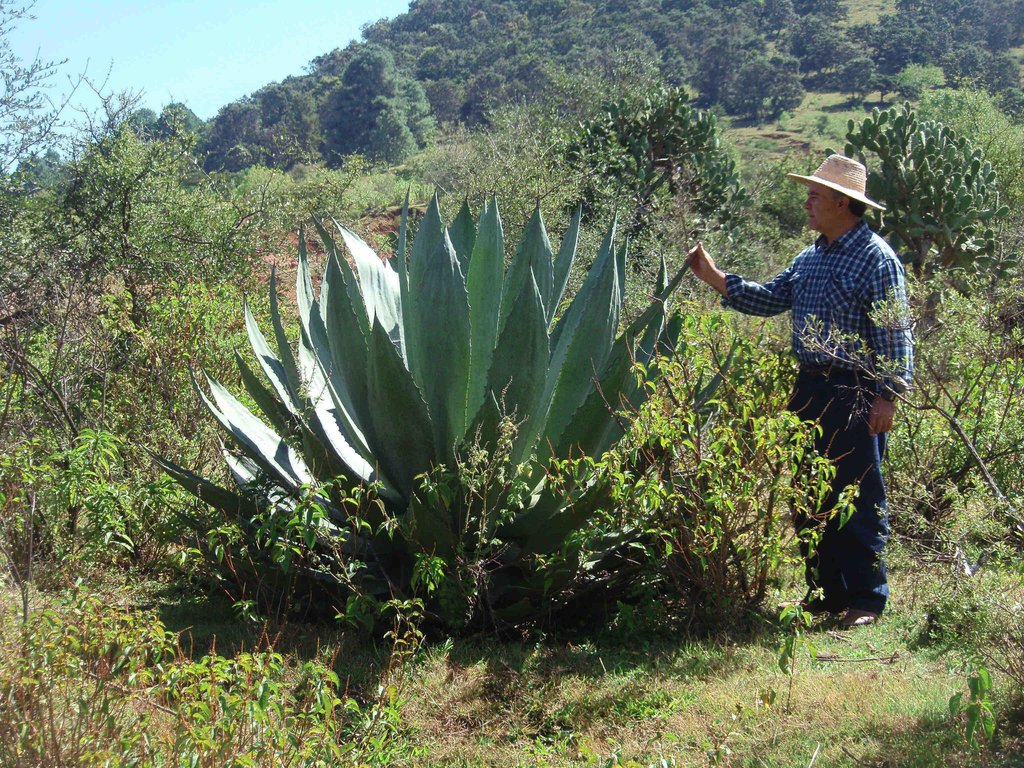
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Unlike most agave, Agave inaequidens reproduces from seed, which requires harvesting the seeds from native plants in the fields. One plant generates 80,000 seeds with a 90% success rate of germination, which is enough to cover 25 ha of agave forestry plantations set up to control soil erosion. After harvesting seeds from native agaves, trees and shrubs, seedlings and small plants are raised in a greenhouse and nursery managed by the owners and tenants of the land in the first year. At the beginning of the rainy season, these are planted in plots protected from cattle grazing for at least the first two years after planting. The harvesting activity for trees, shrubs and grasses is done annually, but for the agaves only once every 7 to 12 years depending on the degree of soil degradation. Some months before harvesting, the flower from the stem has to be cut. The leaves are then cut and left in the plot while the 50 kg heart of the agave (“piña”) is removed. Mezcal is produced from the heart and requires an average of three weeks and at least two men to process 25 agave plants (1.5 tonnes), which produces about 300 litres of mezcal.
Natural / human environment: Poverty levels in the area are medium to high and the income from agriculture accounts for only 10 to 20% of the total family budget. People, therefore, do not have time to install soil erosion protection systems in the fields. Cattle graze freely everywhere and the number of animals is increasing annually, which also increases soil erosion. Locals know how to produce mezcal, but they prefer to buy it from other people who take wild plants from their lands to process them. The proximity of the site to the Michoacán of Ocampo state capital and the recognition of the designation of origin for mezcal by the authorities will enhance its value for future production.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
México
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Mexico/Michoacán state
Especifique más el lugar :
Morelia municipality
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- 10-50 años atrás
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
10 years ago, at Titzio, close to Cointzio basin, A. Martinez developped the culture of a wild native agave (Agave Cupreata) for alcohol production which was done traditionnaly for local consumming. We are following this project and objectives, but we are improving it for land remediation and soil erosion control too with a new species of native Agave (A. inaequidens)
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- crear impacto económico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Cultivos asociados (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles), incl. agroforestería
- Agropastoreo
- Agro-silvopastoralismo
Principales productos/ servicios:
semi perennial cropping (7-10 years): Agave inaequidens
annual: Herbaceous
tree cropping: Wood, fodder and fruits
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Mainly overgrazing due to uncontrolled grazing by cattle.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion by water due to the storms and improper land use.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Yes
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, grazing / browsing, other forest products / uses (honey, medical, etc.), nature conservation / protection
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
Si el uso de la tierra ha cambiado debido a la implementación de la Tecnología, indique el uso de la tierra antes de la implementación de la Tecnología.
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 190; Longest growing period from month to month: June to November
Densidad del ganado (si fuese relevante):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- cobertura de suelo/ vegetal mejorada
- medida de pendiente transversal
- variedades vegetales/ razas animales mejoradas
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente en un área, indique el área aproximada que cubre:
- 0.1-1 km2
Comentarios:
630 km2 is the area of the Cointzio watershed. Untill now (2010), 10 ha have been managed with this technics and from 2011, 50 ha/year will be done (at least)
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A1: vegetación/ cubierta del suelo

medidas vegetativas
- V1: Cubierta de árboles y arbustos

medidas estructurales
- S11: Otros

medidas de manejo
- M3: disposición de acuerdo al entorno natural y humano
Comentarios:
Secondary measures: agronomic measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, mixed cropping / intercropping, contour planting / strip cropping, cover cropping, retaining more vegetation cover, breaking compacted topsoil, contour ridging, breaking compacted subsoil
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie
- Wg: erosión en cárcavas

deterioro físico del suelo
- Pu: pérdida de la función bioproductiva a causa de otras actividades

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
- Bq: reducción de la cantidad/ biomasa
- Bs: reducción en la calidad y composición/ diversidad de las especies

degradación del agua
- Hs: cambio en la cantidad de aguas superficiales
Comentarios:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Pu: loss of bio-productive function due to other activities, Bq: quantity / biomass decline, Hs: change in quantity of surface water
Main causes of degradation: soil management (System of one year culture/one year fallow with cattle), overgrazing (THE real cause of soil erosion here), poverty / wealth (Cattle is used as a "bank on 4 feet")
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Untill 30 years ago, some wood was used for carbon used for cooking), population pressure
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
Comentarios:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
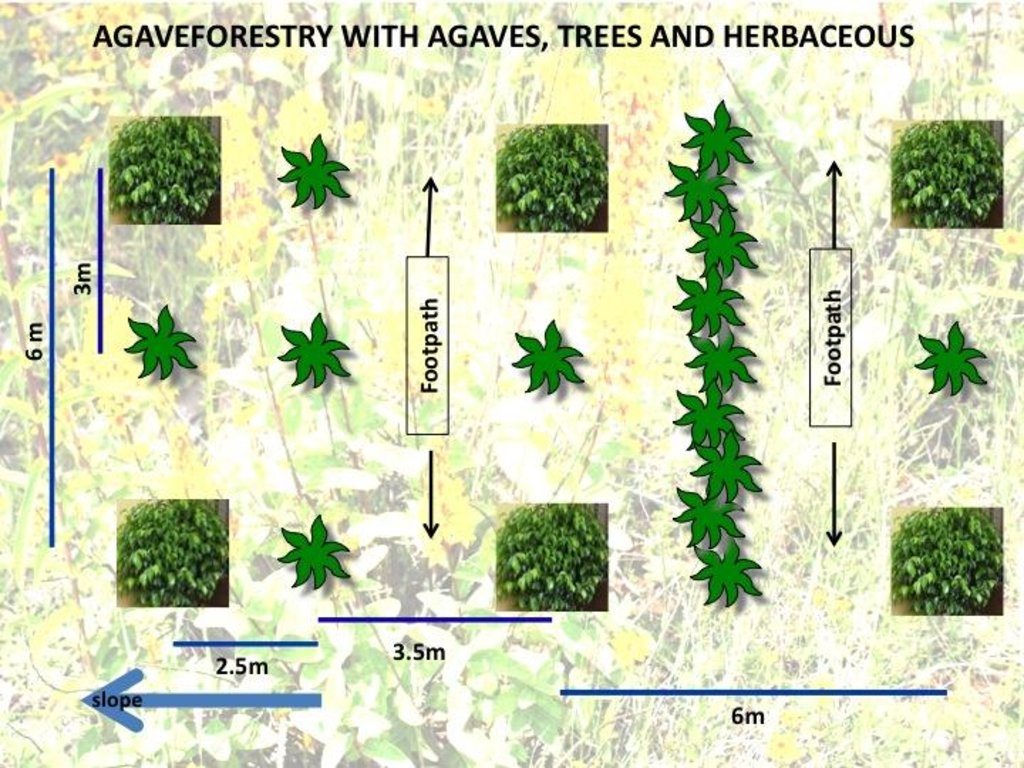
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
Agave production is based on planting them with trees along the contour. Herbs are maintained / planted or sown between the plants. Depending on the slope, one or more dense lines of agaves (1 plant every 25 cm) is planted for control of soil erosion and runoff, including a lateral gradient to the gully which will evacuate the excessive runoff. Footpaths are planned for the maintenance of the plantation
Location: Michoacán. Mexico
Date: 2010
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (low for reproduction, plantation and cultivation and middle for alcohol production)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (low for reproduction, plantation and cultivation and middle for alcohol production)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase of infiltration, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase of surface roughness, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Better crop cover
Material/ species: Agave inaequidens+native trees+herbaceous
Quantity/ density: 830/270
Remarks: Agaves/Trees per ha
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Agave inaequidens+native trees+herbaceous
Quantity/ density: 830/270
Remarks: Agaves/Trees per ha
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: Agave inaequidens+native trees+herbaceous
Quantity/ density: 830/270
Remarks: Agaves/Trees per ha
Cover cropping
Material/ species: Native trees+herbaceous
Agronomic measure: Herbaceous
Material/ species: Native herbaceous
Agronomic measure: Leafs from trees
Material/ species: Native trees
Quantity/ density: 270
Remarks: Trees per ha
Breaking compacted topsoil
Material/ species: Agave inaequidens+native trees+herbaceous
Quantity/ density: 830/270
Remarks: Agaves/Trees per ha
Contour ridging
Material/ species: Agave inaequidens+native trees+herbaceous
Quantity/ density: 830/270
Remarks: Agaves/Trees per ha
Breaking compacted subsoil
Material/ species: Agave inaequidens+native trees+herbaceous
Quantity/ density: 830/270
Remarks: Agaves/Trees per ha
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Number of plants per (ha): 1200
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 30
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0,25
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: O : other
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Perennial crops species: Agave inaequidens (mature between 7 to 14 years)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 30%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Layout change according to natural and human environment: Natives plants are used, planted according to the slopes and the rest of vegetation still existing
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Indique tamaño y unidad de área:
100 ha
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
mexican pesos
Indique la tasa de cambio de USD a la moneda local (si fuese relevante): 1 USD =:
13,0
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
160
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selection and collect Agave and tree seeds | Vegetativas | 1 week |
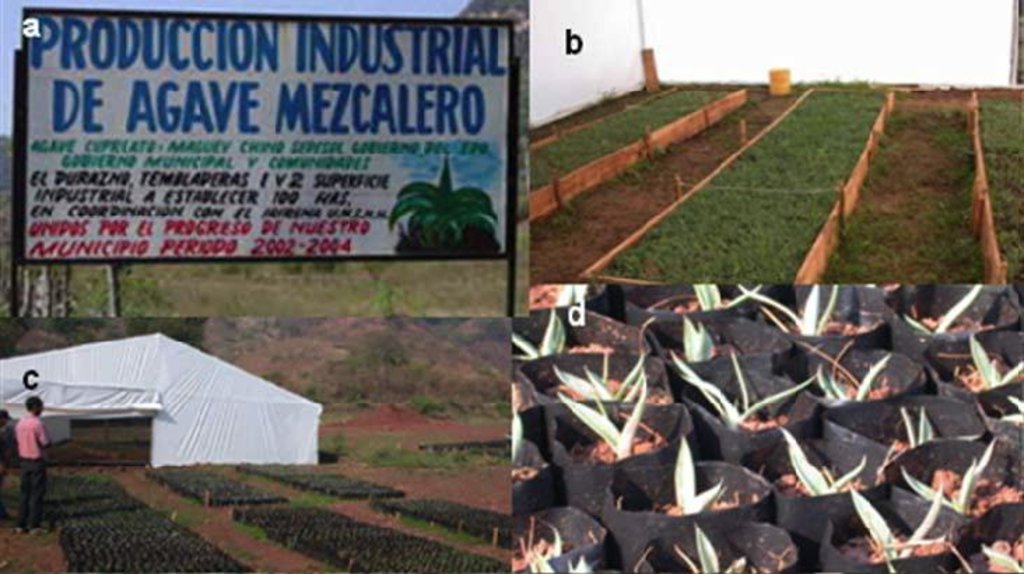
| 2. | Building of greenhouses incl. soil and organic matter | Vegetativas | 1 month |
| 3. | Fencing of greenhouses with barbed wire, poles and nails (0.5 ha | Vegetativas | |
| 4. | Seeding & maintaining in greenhouses | Vegetativas | 3 monthes |
| 5. | Installation of a nursery for agaves and trees and transplantation of seedlings in plastic bags | Vegetativas | 2 weeks |
| 6. | Plant care and maintaining in nursery (9 months) | Vegetativas | 9 monthes |
| 7. | Transportation of plants in plastic bags | Vegetativas | |
| 8. | Plantation of plants (agaves and trees) | Vegetativas |
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Building of greenhouses | persons/day | 21,0 | 523,8095 | 11000,0 | |
| Mano de obra | Seeding & maintaining in greenhouses | persons/3 months | 2,0 | 5000,0 | 10000,0 | |
| Mano de obra | Installation of a nursery for agaves and trees | persons/day | 14,0 | 1071,4285 | 15000,0 | |
| Mano de obra | Plant care and maintaining in nursery | persons/9months | 2,0 | 15000,0 | 30000,0 | |
| Material para plantas | Selection and collect Agave and tree seeds | plants | 5,0 | 100,0 | 500,0 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Materials for plant care | months | 9,0 | 2777,7777777 | 25000,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Materials for greenhouse | trees | 60000,0 | 0,056666666 | 3400,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Materials for greenhouse | agave | 200000,0 | 0,035 | 7000,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Materials for fences | m | 1500,0 | 2,4 | 3600,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Materials for nurserys | trees | 60000,0 | 1,5 | 90000,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Materials for nurserys | agaves | 200000,0 | 0,2 | 40000,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 235500,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning around plants to give them space the first 3 years (For 1 person 10 days) | Agronómicas | 1 time/year |
| 2. | Cutting the scape before the harvest (For 1 person 15 days) | Agronómicas | 1 time in agave life (between 7-14 years) |
| 3. | Weeding around plants to give them space during the first 3 years (10 person days) | Vegetativas | 1 time/year |
| 4. | Cutting the stalk before the harvest (15 person days) | Vegetativas | 1 Agavelife time (7 to 14 years old) |
| 5. | Replanting of agaves after 7 to 14 years (restarting of a new cycle of production, see establishment activities) | Vegetativas |
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Weeding around plants | persons/day | 10,0 | 160,0 | 1600,0 | 10,0 |
| Mano de obra | Cutting the stalk before the harvest | persons/day | 15,0 | 150,0 | 2250,0 | 10,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 3850,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
Calculations are for the plantation of 200,000 plants (agaves and trees) which correspond to the numbers of plants for 100 ha in the agave forestry example presented here. The main portion of these plants is planted by the community on the own land; the rest is given or sold to other communities or private people. The lifetime of the greenhouse, nursery and fencing installations are around 10 years.
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
The most important factors determining the costs are: 1) the materials to build a greenhouse and the personal to take care of young plants; 2) the difficulties to make holes in the indurated soils, which takes time and efforts; and 3) the distance between the nursery and the field requires time and efforts (truck carrying the plants).
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Rainy season from june to october
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
Thermal climate class: subtropics
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- no relevante
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Slopes on average: Also steep, very steep and moderate
Altitudinal zone (2000-2500 m a.s.l.) : The Agave inaequidens grows is this conditions but other spieces of Agaves grow in other agroclimatic conditions
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
- baja (<1%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil depth on average: For Agaves and herbaceous no problems, for trees much more difficult
Soil texture (topsoil): For Agaves, trees and herbaceous no problems
Soil fertility is very low - medium: For Agaves, trees and herbaceous no problems
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium - poor: For Agaves and herbaceous no problems, but some difficulties for some tree species
Soil water storage capacity is very low - medium: For Agaves and herbaceous no problems, but some difficulties for some tree species
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
mediana
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
solo para uso agrícola (irrigación)
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Ground water table: Also > 50 m and for Agaves, trees and herbaceous no problems
Availability of surface water: Also poor/ none and for Agaves and herbaceous no problems, but some difficulties for some tree species
Water quality (untreated): Also unusable
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- elevada
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
Use of native species
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- > 50% de todo el ingreso
Individuos o grupos:
- grupos/ comunal
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
- mecanizado/motorizado
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Men for hard works: digging holes during the plantation and carrying plants during the harvest
Women and men, do the rest of the activities
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
Relative level of wealth: average, poor, very poor
34% of the land users are average wealthy.
33% of the land users are poor.
33% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: off farm incomes represent between 80 to 90% of the annual incomes! This money is obtain through an "external" job, business, trade, or by money send by family from the USA
Market orientation of production system: 90% commercial but some plants (fruit trees, some herbaceus) can be consummed.
Level of mechanization: Manual labour for seed collect, greenhouse, digging holes, plantation, cleaning and harvesting and in some case, tractor can pass to make sub soiling for the plantation of Agave lines to control soil erosion.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
Comentarios:
Also 15-50 ha
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- comunitaria/ aldea
- individual, con título
- ejido
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- comunitarios (organizado)
- individual
- ejido
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
- individual
- ejido
Comentarios:
"ejido" is the community organisation in Mexico: land belongs to the state but it is managed by the community. Some areas can be used by everybody; others are assigned to the land user families.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
producción de forraje
calidad de forraje
producción animal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduction number of animals but improvement of meat production
producción de madera
diversidad de producto
área de producción
Ingreso y costos
ingreso agrario
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
situación de salud
Comentarios/ especifique:
Directly by plants , indirectly with the money earned, it is possible to buy medecinal products.
If producers sell their alcohol production abroad, no problems, if not problems!
oportunidades culturales
oportunidades recreativas
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios/ especifique:
Huge beneficts can create great conflicts!
mitigación de conflicto
situación de grupos en desventaja social y económica
impact on the community due to the huge beneficts
Comentarios/ especifique:
It can be positive as well as negative (may induce corruption, violence)
livelihood and human well-being
Comentarios/ especifique:
The production of alcohol beverage (certified Mescal) from agaves, and/or in medicinal products, will generate very high Incomes for stakeholders. Life will change drastically. This allows the farmer's sons to stay in the community and work in the fields.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cosecha/ recolección de agua
escurrimiento superficial
nivel freático/ acuífero
Suelo
humedad del suelo
cubierta del suelo
pérdida de suelo
encostramiento/ sellado de suelo
compactación de suelo
ciclo/ recarga de nutrientes
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
diversidad vegetal
diversidad animal
diversidad de hábitats
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
riesgo de incendio
velocidad de viento
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
disponibilidad de agua
corriente confiable y estable fluye en estación seca
inundaciones río abajo
colmatación río abajo
contaminación de aguas subterráneas/ de ríos
capacidad de amortiguación/ filtrado
daño a campos de vecinos
daños a infraestructura pública / privada
biodiversity
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | tipo de cambios climáticos/ climas extremos | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | bien |
| tormenta de viento | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | bien |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
That is why, state institutions fund the installations of this system meanwhile the production did not start. After that, benefits generated will be enough to motivate people to increase by themselves, the surface to remediate, without economical helps.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- 1-10%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
50 households covering 10 percent of the stated area
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, es decir, sin recibir incentivos/ pagos materiales?
- 0-10%
Comentarios:
50 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The program just start in 2010, so it is too early to reduce the experience at few hectares!
As the land users belongs to the same comunity ("ejido"), formally, all the inhabitants are involved in some way by this experience
Comments on spontaneous adoption: As the program just started in 2010, it is impossible to have an exact overview of the results now (end of 2011). As the land users belong to the same community ("ejido"), formally, all the inhabitants are involved in some way
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: It is too early to identify an adoption trend.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
Remediation of degraded land turning it to a sustainable production generating very high incomes in the medium term How can they be sustained / enhanced? life will change drastically and not necessarily for the better. Transparency and communication regarding benefits and land use are necessary. |
|
Project done in a participative way where different kind of stakeholders are involved: administrations, politics, scientists and people. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintain workshops dynamic between stakeholders, present results to other authorities and forum |
|
Low-cost project but need to be funded and supported with technical and institutional advice to initiate the first cycle of the project. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Farmers can start to produce their mezcal from the wild agaves to sell them to wholesalers and use this money to pay for the project. |
|
As a result of the economical benefits, young people will stay in the communities. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Involve the young to guarantee the future: develop the marketing, the diversification of the products, the quality of production, etc. |
|
It will hopefully reduce the number of cattle, which are the main cause of soil erosion, as farmers lose interest in cattle raising. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Authorities need to monitor this and inform the farmers about the ecological impact of too much free cattle grazing. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Obligation to find external funds to pay the first steps of the system (greenhouse, planting, etc.) due to the lack of incomes amongst farmers. | Involve all stakeholders in the project |
| Be sure that alcohol production will not be consummed in excess in the community | Control of the volume of the production, and the sufficiently high selling price should avoid "losing" the production at local scale |
| Risk that the benefits will be captured by few people | Transparency and stakeholder communication in accounting for the benefits |
| Marketing and selling the products | Authorities help the farmers to contact sellers. The formation of communities of producers, leading to products conforming to regulations that maintain good quality and provide certification. |
| Owing to the high incomes, life will change drastically and not necessarily for the better. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Colunga-García Marín P., D. Zizumbo-Villareal, J.T. Martínez. 2007. Tradiciones en el aprovechamiento de los agaves mexicanos: una aportación a la protección legal y conservación de su diversidad biológica y cultural. In: En lo Ancestral hay Futuro: del Tequila, los Mezcales y otros Agaves. P. Colunga-GarcíaMarín, L. Eguiarte, A. Larqué, D. Zizumbo-Villarreal (eds). CICY-CONACYT-CONABIO-SEMARNAT-INE. México D.F., pp. 85-112.
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
DESIRE project Mexico partner (IRD 22)
URL:
http://www.desire-project.eu/
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Participative actions for economic benefits of agave forestry [México]
Land reclamation with local agave (to produce Mezcal) associated with trees, shrubs and grasses planted through participative actions for economic benefit.
- Compilador: Christian Prat

Land reclamation by agave forestry with native species [México]
Land reclamation with local agave (to produce mezcal) associated wotj trees, shrubs and grasses planted through participative actions for economic benefit.
- Compilador: Christian Prat
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos