Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank [Tayikistán]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Sa'dy Odinashoev
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
Чамоварии оби борон
technologies_1460 - Tayikistán
- Resumen completo en PDF
- Resumen completo en PDF para imprimir
- Resumen completo en el navegador
- Resumen completo (sin formato)
- Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank: 21 de agosto de 2019 (inactive)
- Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank: 2 de noviembre de 2021 (public)
- Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank: 4 de abril de 2018 (inactive)
- Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank: 21 de julio de 2017 (inactive)
- Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank: 6 de mayo de 2017 (inactive)
- Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank: 16 de marzo de 2017 (inactive)
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
CARITAS (Switzerland) - SuizaNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
CAMP - Central Asian Mountain Partnership (CAMP - Central Asian Mountain Partnership) - KirguistánNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - Kirguistán1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
27/04/2011
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
The roof top rain water harvesting system using a concrete tank was designed to improve household access to water for irrigation of kitchen garden plots during the hot and dry summer months.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
A 16 cubic metre concrete tank situated in the shadow of the house constructed to retain rainwater that collects in the roof guttering.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of the tank is to retain water to be used for drinking, sanitation and irrigation during the hot and dry summer months. The retained water allows for the irrigation of kitchen garden plots and more diverse crops, and hence should improve the livelihoods of households involved.
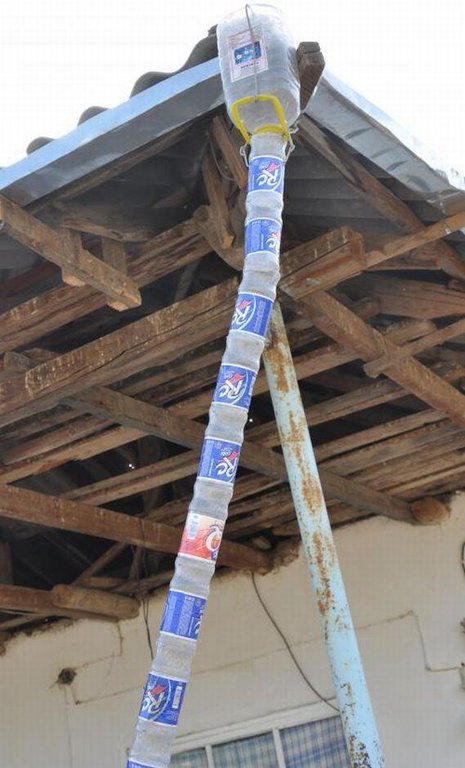
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: There are three main elements to the construction of the rainwater harvesting system. The first is the construction of a metal gutter on wooden supports around the perimeter of the roof; second, the construction of a concrete pool in the shadow of the house; and finally the provision of a connection pipe between the gutter and the pool. The pool needs to be cleaned periodically to prevent contamination and build up of algae around the edge the pool.
Natural / human environment: During the Soviet period the water supply for the village was supplied through a concrete storage tank located at the foot of the hills above the village. After the collapse of the Soviet Union the concrete tank and its associated infrastructure fell into disrepair. As a result the inhabitants were faced with water shortages, especially during the hot dry summers. In response to this issue the residents invested time, finance and resources into constructing rainwater collection systems.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Tayikistán
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Tajikistan
Especifique más el lugar :
Rudaki, Boshkengash
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- 10-50 años atrás
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante la innovación de usuarios de tierras
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
The land owner built the concrete tank in 2010, however numerous other tanks have been constructed during the last 10 years.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- access to water
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
- Cosecha de árboles y arbustos
Cosechas principales (comerciales y de subsistencia):
Major food crop: Legumes, fruit trees

asentamientos, infraestructura
- Asentamientos, edificios
Comentarios:
Urban areas with small kitchen gardens.
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The village has 600mm/yr of precipitation, but it only falls during two months of the year. The land within the village is becoming increasingly dry and thus more denuded and unsuitable for cultivation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Lack of water at critical times of the year.
Forest products and services: fruits and nuts
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: It is household garden plots that benefits from the water supply. These plots tend to be fruit trees intercropped mainly with onions, potatoes, carrots.
Constraints of settlement / urban: Use of land for concrete tank could be used to grow crops.
Si el uso de la tierra ha cambiado debido a la implementación de la Tecnología, indique el uso de la tierra antes de la implementación de la Tecnología.
Forests / woodlands: Fo: Other
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 220Longest growing period from month to month: March - November
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- cosecha de agua
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente en un área, indique el área aproximada que cubre:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentarios:
A roof top rainwater harvesting system that channels water into a concrete collecting tank has been replicated in numerous houses within the village.
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A6: Otros

medidas estructurales
- S5: Diques, hondonadas, estanques
Comentarios:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación del suelo encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie

erosión de suelos por viento
- Et: pérdida de capa arable
Comentarios:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (The domestic plots were over used due to poor water supply.)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (This occured previously and the trees were not replaced.), other human induced causes (specify) (After the collapse of the Soviet Union the concrete tank and it's associated infrastructure fell into disrepair.), change of seasonal rainfall (Less rainfall at critical times impacted on cultivation activity.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Lack of vegetation results in higher losses of soil erosion during heavy rainfall events.), droughts (Longer dry periods in the summer months.), population pressure (The population and number of houses in the village is increasing.)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación del suelo
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- reducir la degradación del suelo
Comentarios:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
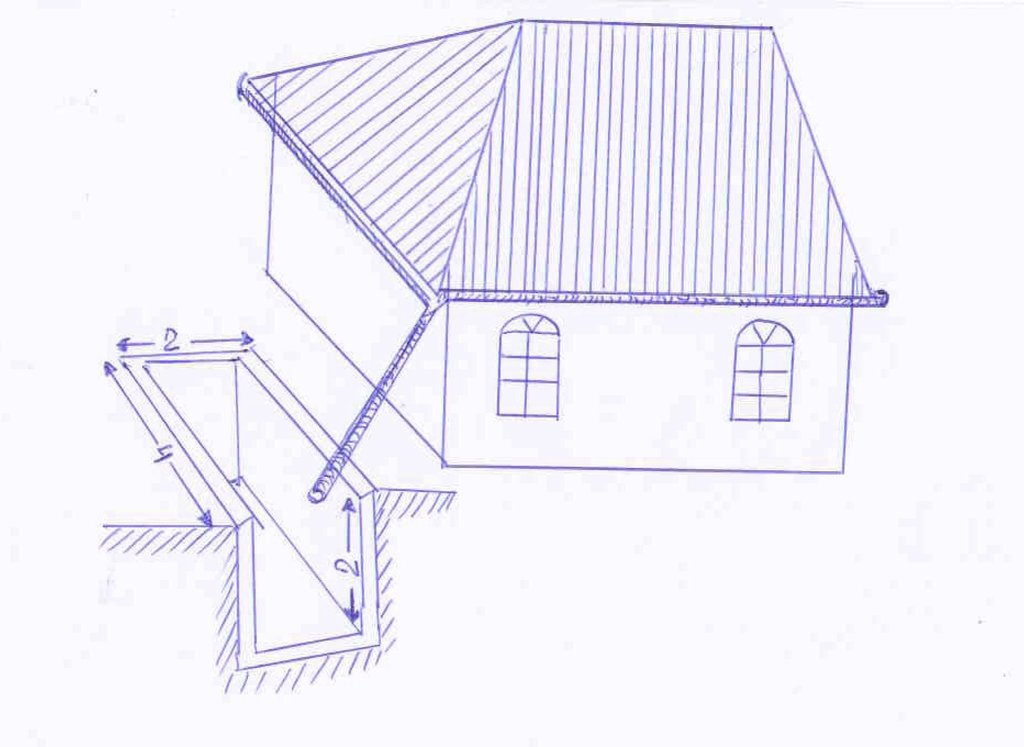
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
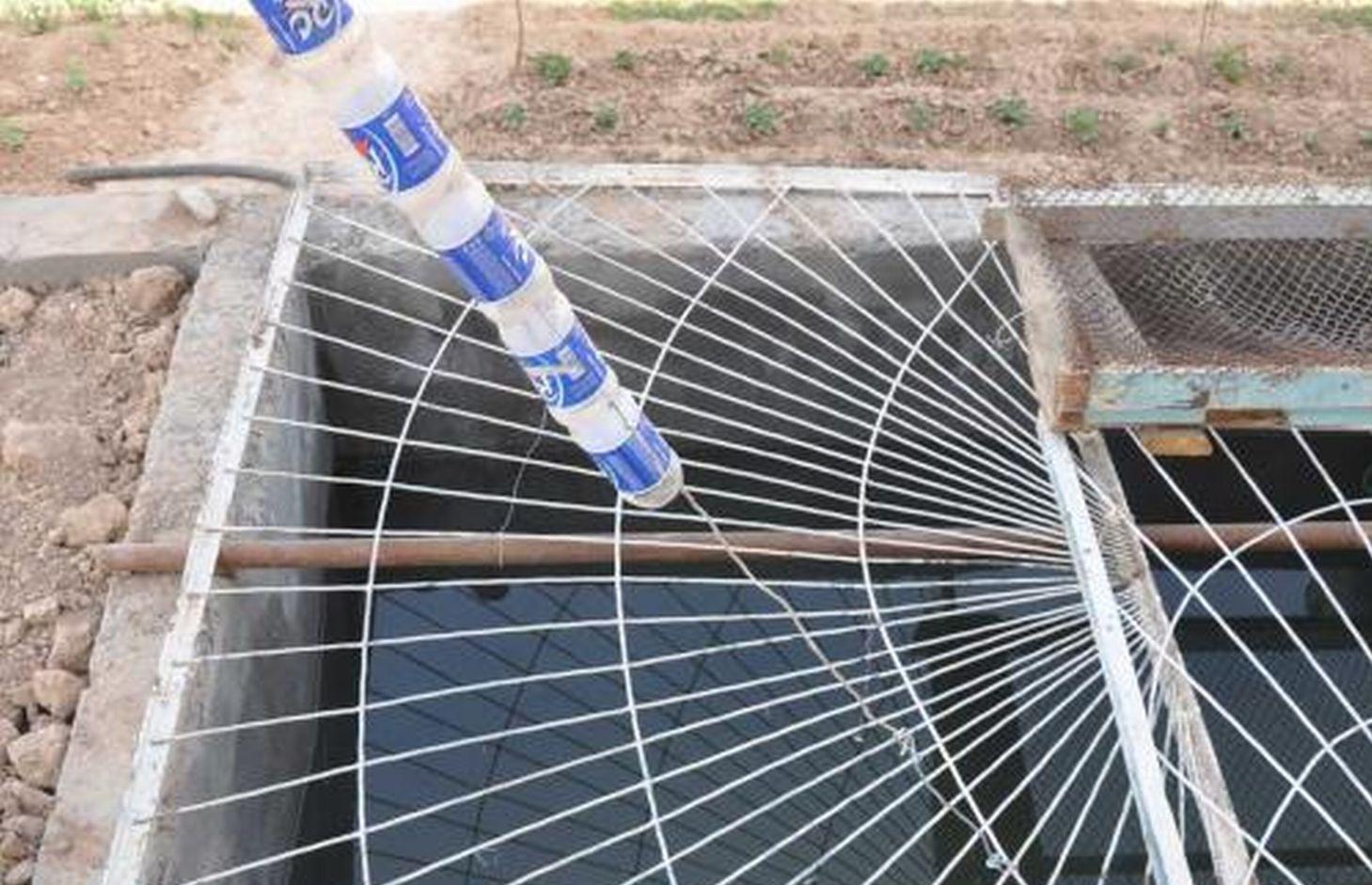
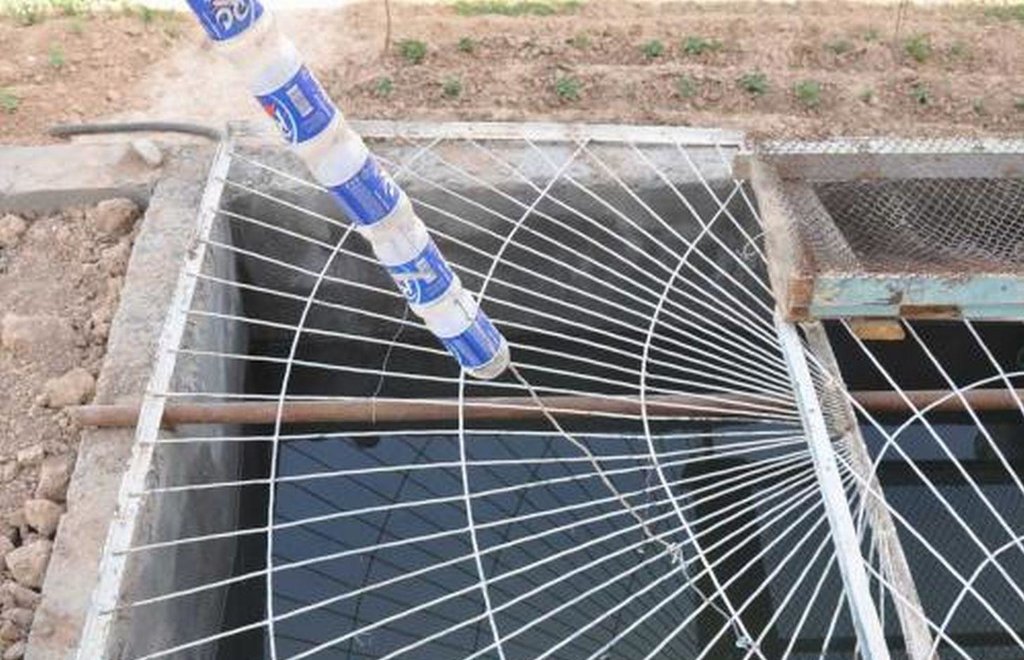
The drawing shows the metal guttering (0.15m) wide around the perimeter of the roof top. The guttering collects the rainwater run off from the roof, and through a plastic pipe made of old plastic bottles stitched together by thin wire it drains into a concrete tank. In this example the tank is 4m long, 2 wide and 2 metres deep and is located within the shadow of the house to reduce evaporation rates. In this example the tank is located on a slope and is partially buried on the upslope. The tank is covered for safety reasons and to prevent external contamination.
Location: Boshkengash.. Rudaki, Tajikistan
Date: 20011-05-06
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Some technical knowledge is required or else the structure will collapse.)
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Dam/ pan/ pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 4
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 16m3
Catchment area: 20 m sqm2
Beneficial area: 0.2 h.am2
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Material: Other
Slope of dam wall inside: 0%;
Slope of dam wall outside: 0%
Dimensions of spillways: 0m
Other specifications: tank size 2*2*4m
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:0.5
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
Somoni
Indique la tasa de cambio de USD a la moneda local (si fuese relevante): 1 USD =:
4,5
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
10.00
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | construction of concrete tank and guttering | Estructurales | spring |
| 2. | None | None |
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Construction of concrete tank and guttering | Persons/day | 20,0 | 22,5 | 450,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Tools | pieces | 6,0 | 11,1666666 | 67,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Concrete sand, stone | tons | 2,0 | 337,5 | 675,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Metal guttering | tons | 0,5 | 900,0 | 450,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Wood | tons | 0,5 | 240,0 | 120,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Plastic pipes | pieces | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 1772,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning | Estructurales | annually |
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Cleaning | Person/day | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 25,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
The costs were calculated based on 2010 prices per tank.
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Labour, tools and piping can be provided by the land user and stone for the foundation is locally available, however, there is an initial outlay of $300 for the cement, wood and metal guttering. In this example the money for the initial outlay was collected by family members working in Russia and from local salaries.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Estimated to be at the lower end of the range
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Altitudinal zone = 800m
Slopes on average: The village is located on a flat plain at the foothill of a slope.
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil texture: Loess soils.
Soil fertility has a potential to be high when cultivated under good conditions.
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium but can be reduced under dry conditions. i.e crusts.
Soil water storage capacity is low-medium since loess material does contain some clay soils.
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
mediana
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Availability of surface water is good during spring rains and poor/none in the summer months.
Water quality (untreated) is good drinking water during winter and spring (snow and rainfall), but poor during summer.
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
Mixture of vegetables and orchards being grown.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
15% of the land users are rich.
70% of the land users are average wealthy (for the land user used for this example).
15% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: The residents do not have a significant income from their garden plots.
Market orientation of production system: The water is for personal use.
Level of mechanization: All work is done by hand.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- estado
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- individual
Comentarios:
In regards to the water in the tank, household plots are allocated by the local government. All land is owned by the state.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to access to water in the summer months
producción de madera
Comentarios/ especifique:
From the increased number of fruit trees.
riesgo de fracaso de producción
diversidad de producto
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua potable
Cantidad luego de MST:
16 cub m
Comentarios/ especifique:
Readily available especially in the summer months.
disponibilidad de agua para ganado
Cantidad luego de MST:
16 cub m
Comentarios/ especifique:
Dramatically increased, in the summer months.
disponibilidad de agua para irrigar
Cantidad luego de MST:
16 cub m
Comentarios/ especifique:
During the drought periods.
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Comentarios/ especifique:
In some households water had to be purchased.
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
No collection of water from distant sources.
Otros impactos socioeconómicos
Potential debt issues if finance is borrowed for the initial outlay
Comentarios/ especifique:
Initial outlay in the region of $400
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Comentarios/ especifique:
Able to grow more and of a better quality.
mitigación de conflicto
Comentarios/ especifique:
Previously residents had to wait at water points.
Hygiene and sanitation
Comentarios/ especifique:
Constant access to water dramatically improves sanitation levels in the village.
Livelihood and human well-being
Comentarios/ especifique:
Permanent access to water has dramatically improved the sanitation and hygiene levels, and increased crop quality and diversification. It has also improved the quality of and access to drinking water, and therefore has significant health benefits.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cantidad de agua
Cantidad luego de MST:
16 cub m
Comentarios/ especifique:
Readily available water supply.
calidad de agua
Cantidad luego de MST:
16 cub m
cosecha/ recolección de agua
Cantidad luego de MST:
16 cub m
Comentarios/ especifique:
The technology concentrates on harvesting water.
evaporación
Comentarios/ especifique:
Tank is built in the shadow of the house.
Suelo
humedad del suelo
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
diversidad vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Able to grow crops at different times of the year.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
disponibilidad de agua
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | tipo de cambios climáticos/ climas extremos | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | no muy bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | bien |
Comentarios:
In times of heavy rainfall and prolonged summer drought the size of the tank could be increased.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
If it is constructed to a reasonable standard then it will not need any significant maintenance.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- más de 50%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
900 household (70 percent of the area covered)
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, es decir, sin recibir incentivos/ pagos materiales?
- 90-100%
Comentarios:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The urban roof top rainwater harvesting has been replicated by many members of the community without external support.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: People observed, and experienced the benefits, and decided that it was worth the initial investment.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Improved the standard of living, and the increased access to water allowed the households to have more automony over what that grow and eat. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
Improves the provision of irrigated water for the hot dry summer periods. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further dissemination to other households. |
|
Allowed for the improvement and expansion of kitchen gardens. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Training on keeping a kitchen garden. |
| Improved the quality and quantity of fruit yields |
|
Improved the access of water for sanitation and drinking water purposes How can they be sustained / enhanced? Education on sanitation methods. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The perception was that the water was not clean in the concrete pool. | However, it was tested and proved to be safe to use. This provided reassurance to the household members. It would be a major benefit if the water tank remains covered and is cleaned periodically. |
| The initial outlay may be considered expensive for some families. | Many families have adopted this, possibly if many were built at once the material costs would be reduced. The technology could be tied in with micro finance activities. |
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos