Irrigation of uplands through Hydraulic Flange Pump [Afganistán]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Aqila Haidery
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Alexandra Gavilano, David Streiff
Aabyari zamin hai boland Aaba thawasut Pump_e_Aabi_Charkhdar
technologies_1731 - Afganistán
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Especialista MST:
Especialista MST:
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
People in Need (PIN) (People in Need (PIN)) - Afganistán1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
18/05/2016
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Technology for lifting water to uplands: hydraulic flange pump, reservoir and pipe scheme.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
This technology is documented by the Sustainable Land Management Project, implemented by HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation and funded by the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC), with close support and cooperation of People in Need.
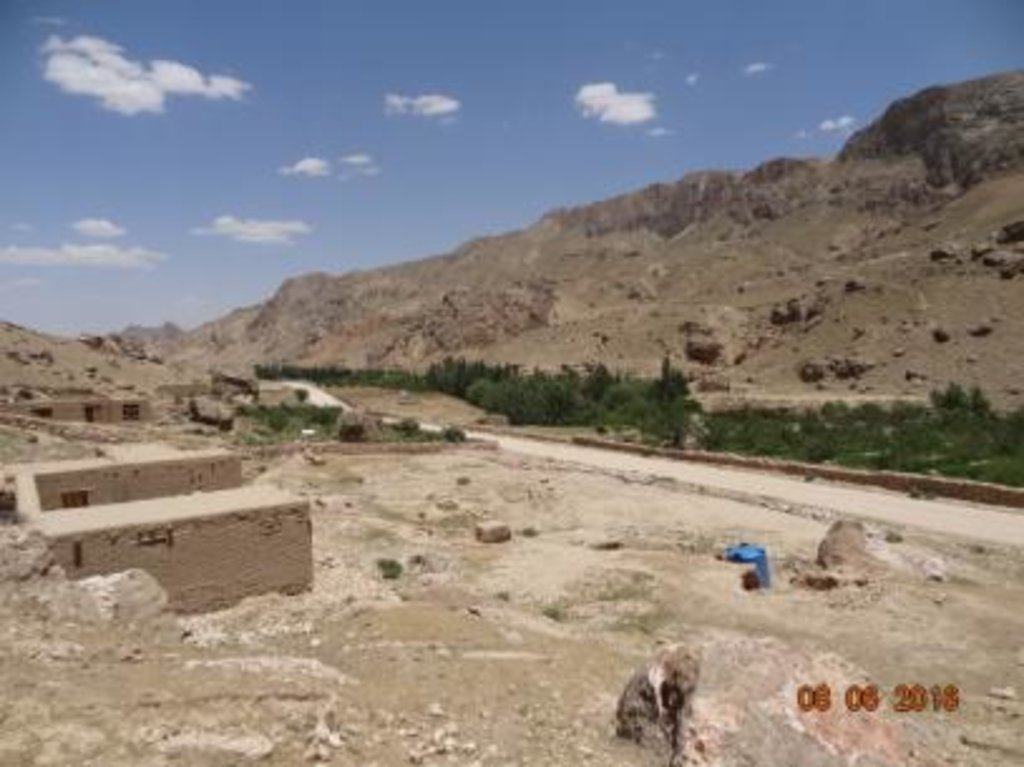
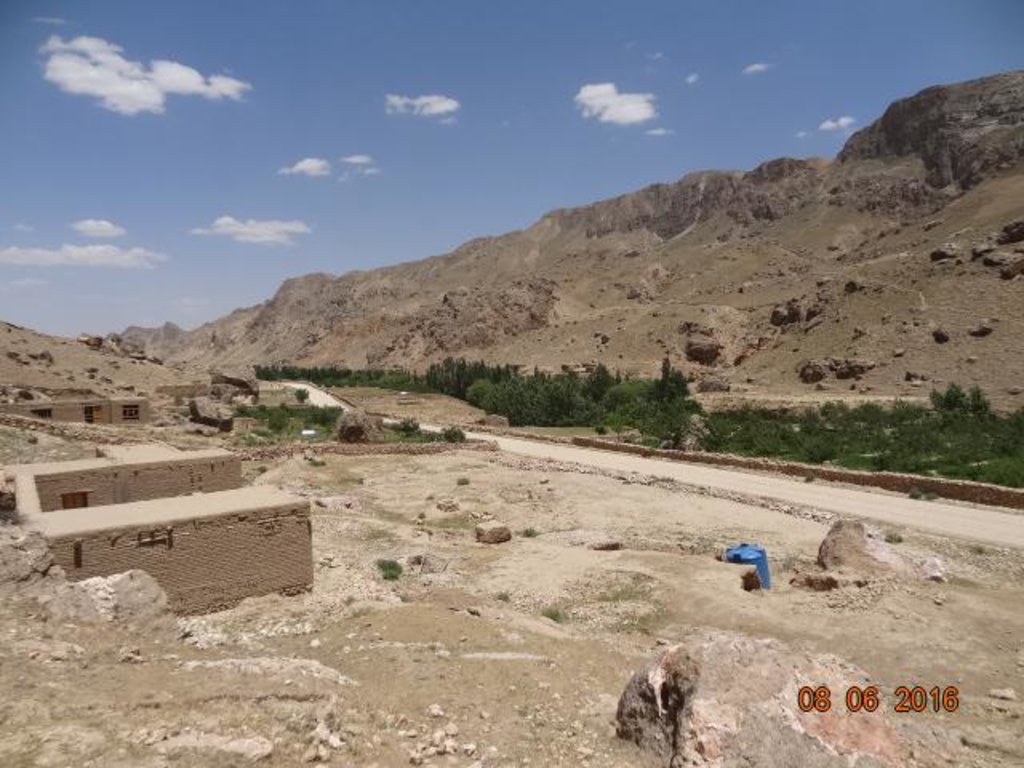
Samangan, Khuram wa Sarbagh district, Klor-e-Bala village is situated in a mountainous region where the greatest limiting factor to agricultural production is water. Arable lands are located far away from water sources. Lack of technology to exploit these lands prohibits villagers to cultivate their land to make a livelihood. Therefore, families are compelled to leave their village during summer.
Purpose of the Technology: To address this problem, People in Need (PIN), with financial support from GIZ and the Czech Embassy (CzDA) introduced irrigation through hydraulic flange pump. The hydraulic flange pump provides water to 30 orchards of Klor-e-Bala village, drinking water to the 43 village households, the mosque and the school of 500 students.
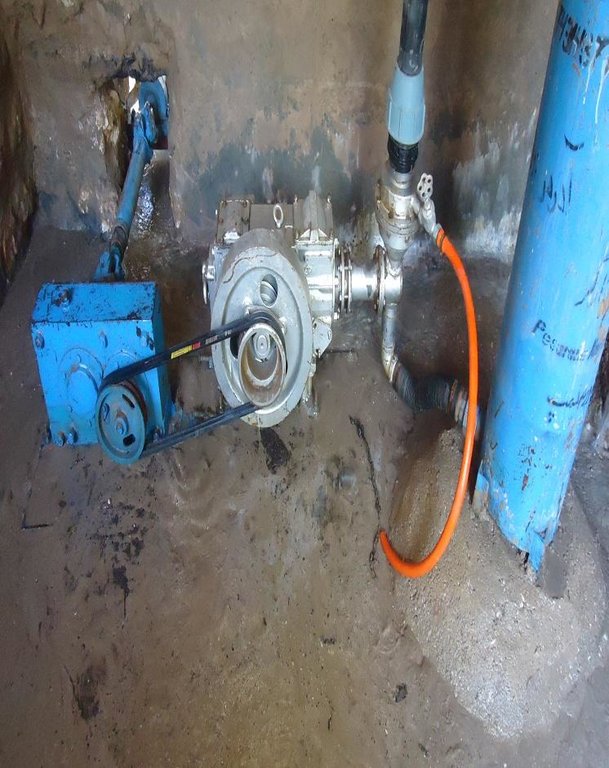
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The main water source which starts and runs the hydraulic flange pump is the Khuwaja Hayat spring. The spring water arrives to the hydraulic flange pump from 1.8 meter height on a 12 percent slope in 200 meters distance from the water source. The water flow passes through the intake and moves towards the water wheel which starts/runs the hydraulic flange pump. The water is then pumped through three pipes of one inch to the reservoir. The hydraulic flange pump has the capacity of lifting water up to 250 meters.
The reservoir’s storage capacity is 25,600 liters of water with the dimensions as follows: 4.9 meter length; 2.9 m width; and 1.8 m height. It has two outlets: a spill way fitted with three pipes of one inch at the top of the reservoir and two outlets fitted with two pipes of three inches at the bottom. The lower outlet leads water to the orchards by diverting water after 40 meters into two pipes which are 1,000 meters long. Each orchard is connected to one of these two pipes by a T-connector and the water flows into a tin water tank with the capacity of 1,000 liters for each orchard. The two pipes are extended as far as the school which is located near the orchards and has been equipped with a 2000 liters tin water tank.
The hydraulic flange pump is made locally in Taloqan city, Takhar province of Afghanistan in the Baradaran-e- Kargar workshop. The pump costs 140,000 Afghani/ 2,200 US$, including installment. The estimated cost of the construction of the reservoir and the pump’s room including the hydraulic flange pump is 19,000 US$. The pipe scheme of the project was installed by the Community Development Council (CDC) with technical support from PIN’s engineering team. Community members contributed 10 percent of the costs as labor. As Klor-e-Bala village is situated in flood prone area and flooding is a common occurrence, PIN, with funding from the GIZ, constructed in 2015 two protection walls, 45 m and 55 m in length, on both sides of the river, to minimize erosion and protect the pump’s intake from floods. The protection walls were built through cash for work programme, but community members provided 10 percent contribution through labor and by providing stones for construction. The total estimated cost of the hydraulic flange pump, reservoir and pipe scheme technology amounted to 37,000 US$.
Furthermore, in order to maintain the technology, a caretaker, who lives close to the pump’s room has been appointed. The caretaker was trained by the technician who installed the hydraulic flange pump and has voluntarily taken the responsibility of maintenance activities; changing the oil and cleaning of the hydraulic flange pump's room and changing of the pipes in case of need. The owners of the orchards have to cover for all maintenance costs and the chairman of the Community Development Council (CDC) has the responsibility of managing the money for maintenance and other recurrent activities.
The flange pump technology contributed to the economic growth of the community members by increasing the orchards’ yields. Currently, the hydraulic flange pump irrigates 12 jireb/2.4 ha (30*800m2) orchards of apple, apricot, almond, pear and cherry trees. In addition to the orchards, alfalfa, potato, vegetables and other crops are as well cultivated on these lands. Furthermore, the pump supports the community members to settle year-round in their villages and prevents from their seasonal displacement. Moreover, the flange pump enables the provision of drinking water to the whole community and the school.
Natural / human environment: Samangan is one of the northern provinces of Afghanistan. Wheat, melons, pistachio,
almonds, potatoes, onions and caraway are important crops and Karakul sheep
and goats the main livestock for meat, dairy, and wool production. Rugs are the
main handicraft of this area. Khuram-wa-Sarbagh district in Samangan has two growing
seasons, the longest of which is 150 days from February to June and the second is 90
days from June to September. The average rainfall is below 500mm and the climate semi-arid.
The community members have limited access to off farm employment, market, energy,
financial services, roads and transportation and moderate access to health and education.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Afganistán
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Samangan
Especifique más el lugar :
Khuram-wa-Sarbagh district, Klor_e_Bala village
2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- access to water
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
- Cosecha de árboles y arbustos

Tierra de pastoreo
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Lack of safe drinking and irrigation water which makes agricultural activities difficult.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Lack of cultivation due to the scarcity of water. High workloads and small incomes.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
Si el uso de la tierra ha cambiado debido a la implementación de la Tecnología, indique el uso de la tierra antes de la implementación de la Tecnología.
Other: Ow: Waterways, drainage lines, ponds, dams
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 2
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: February - June; Second longest growing period in days: 90; Second longest growing period from month to month: June - September
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- manejo de bosques naturales y seminaturales:
- agroforestería
- Manejo de irrigación: (incl. provisión de agua, invernaderos)
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente en un área, indique el área aproximada que cubre:
- 1-10 km2
Comentarios:
The technology area which is considered here is the distance from the water area where the machine exists to the reservoir and reservoir to the orchard and crop land.
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas estructurales
- S5: Diques, hondonadas, estanques
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
- Bq: reducción de la cantidad/ biomasa
Comentarios:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bq: quantity / biomass decline
Main causes of degradation: disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff), droughts, education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
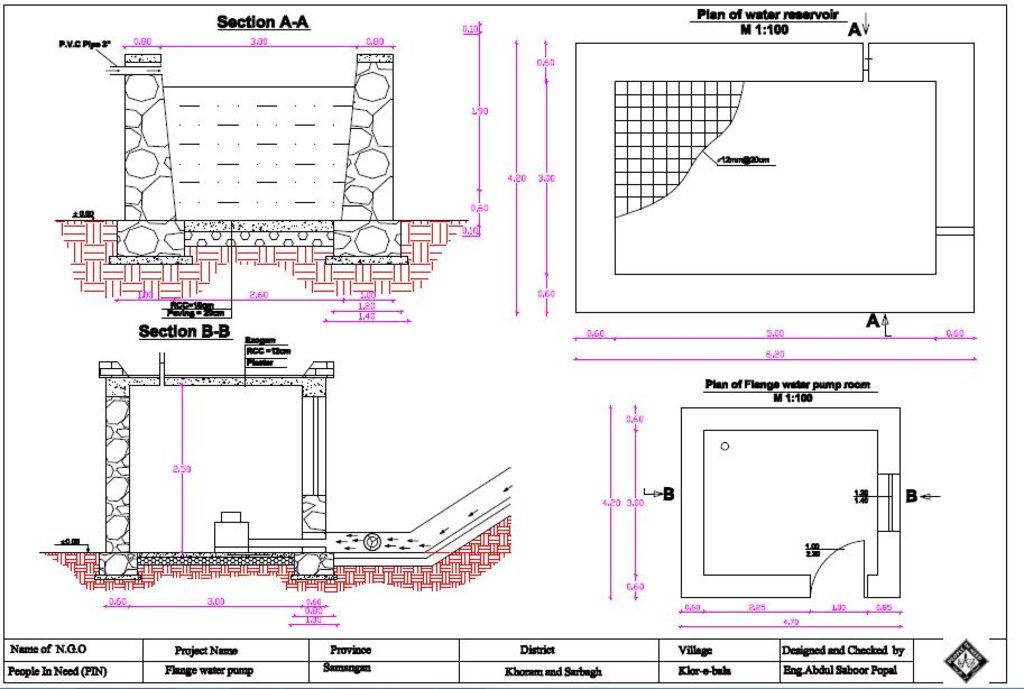
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
A detailed technical drawing of the hydraulic flange pump and the reservoir, Klor-e-Bala village, Khuram-wa-Sarbagh district, Samangan province.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- dólares americanos
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
7.00
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Excavation of the foundation | Estructurales | |
| 2. | Construction activities,Stone masonry foundation and wall: | Estructurales | |
| 3. | a:P.C.C concrete foundationb:R.C.C concretec:Iron shattering for walls, roof and floord:External and internal pointing | Estructurales | |
| 4. | a:Plasteringb:Steel barsc:Door and window | Estructurales | |
| 5. | Pipe scheme:a:Pipesb:Water tanksc:other equipmentd:Skilled and unskilled labor | Estructurales | |
| 6. | Procurement of the Hydraulic flange pump | Estructurales |
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Excavation of the foundation | square meters | 50,0 | 2,88 | 144,0 | 10,0 |
| Mano de obra | Excavation of the foundation | cubic meters | 161,0 | 2,4037 | 387,0 | 10,0 |
| Mano de obra | Skilled and unskilled labor | persons/day | 343,0 | 9,47521 | 3250,0 | 10,0 |
| Equipo | Water tanks | pieces | 39,0 | 98,615384 | 3846,0 | 10,0 |
| Equipo | Pipes | meter | 2900,0 | 2,9241379 | 8480,0 | 10,0 |
| Equipo | Other equipment | all | 1,0 | 2424,0 | 2424,0 | 10,0 |
| Equipo | Procurement of the Hydraulic flange pump | pieces | 1,0 | 2200,0 | 2200,0 | 10,0 |
| Material de construcción | Concrete foundation | cubic meters | 12,23 | 96,64758 | 1182,0 | 10,0 |
| Material de construcción | Concrete | cubic meters | 8,4 | 114,0476 | 958,0 | 10,0 |
| Material de construcción | Iron shattering for walls, roof and floor | cubic meters | 110,0 | 4,86363 | 535,0 | 10,0 |
| Material de construcción | External and internal pointing | square meters | 226,0 | 2,85398 | 645,0 | 10,0 |
| Material de construcción | Plastering | square meters | 32,0 | 5,9375 | 190,0 | 10,0 |
| Material de construcción | Steel bars | square meters | 364,4 | 1,21844 | 444,0 | 10,0 |
| Material de construcción | Door and window | square meters | 3,98 | 28,8944 | 115,0 | 10,0 |
| Material de construcción | Stones | square meters | 244,0 | 50,0 | 12200,0 | 10,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 37000,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 7 month(s)
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Changing of the pipes | Estructurales | Once a year |
| 2. | Cleaning of the flange pump room | Estructurales | Six times a year |
| 3. | Changing of the hydraulic flange pump oil | Estructurales |
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Changing of the pipes | persons/day | 1,0 | 7,0 | 7,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Cleaning of the flange pump room | persons/day | 1,0 | 7,0 | 7,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Changing of the hydraulic flange pump oil | persons/day | 1,0 | 7,0 | 7,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Pipes | meter | 20,0 | 0,65 | 13,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Oil | times/year | 4,0 | 4,5 | 18,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 52,0 | |||||
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Labor, stone and equipment are the main fundamental factors which need high initial investments.
After a couple of years pipes may need to be changed.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- baja (<1%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
mediana
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
Diversidad de hábitats:
- mediana
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Nómada
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- pobre
Individuos o grupos:
- grupos/ comunal
Género:
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly disadvantaged land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Constructional activities which are done outside of the houses and compounds are mainly applied by men in Afghanistan.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
100% of the land users are poor.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- comunitaria/ aldea
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- comunitarios (organizado)
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
producción de forraje
calidad de forraje
diversidad de producto
área de producción
manejo de tierras
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua potable
disponibilidad de agua para ganado
calidad de agua para ganado
disponibilidad de agua para irrigar
calidad de agua para irrigar
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
ingreso agrario
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
carga de trabajo
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
situación de salud
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
mitigación de conflicto
Comentarios/ especifique:
In case the owner of the first orchard do not obey the water use right
livelihood and human well-being
Comentarios/ especifique:
The pump improved households’ economy through increasing agricultural yieIds and by decreasing the need for a generator pump. It has as well reduced the workload of the community members
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cosecha/ recolección de agua
evaporación
Suelo
humedad del suelo
cubierta del suelo
encostramiento/ sellado de suelo
compactación de suelo
salinidad
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
diversidad vegetal
diversidad animal
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
impactos de inundaciones
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
disponibilidad de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
It has decreased the water flow only in the place where the hydraulic flange pump is installed.
corriente confiable y estable fluye en estación seca
contaminación de aguas subterráneas/ de ríos
capacidad de amortiguación/ filtrado
daño a campos de vecinos
daños a infraestructura pública / privada
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | tipo de cambios climáticos/ climas extremos | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien | |
| lluvia anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | no se sabe |
| tormenta de viento | no muy bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación repentina | no muy bien |
Otros extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
| otros (especifique) | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? |
|---|---|
| length of growing period | bien |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
ligeramente positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
neutral/ balanceado
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- 10-50%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
98 households covering 50 percent of the stated area
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, es decir, sin recibir incentivos/ pagos materiales?
- 0-10%
Comentarios:
98 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Due to high expenses of the implementation of the technology, it has not been applied without any external support.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The technology is of a high cost and needs external support to be established.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
|
Application of the technology has reduced the workload for the families. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Greater awareness on water management can be created by training/workshop for the water users. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
The technology has supported the community members economically by increasing agricultural yields. Moreover, it contributes to reduce the costs of water during the summer season. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The land users should try to plant local and native trees and cultivate the crops which are adapted to the land.Community members should actively participate in maintenance activities. |
|
Provides safe drinking water to the 43 households and the school at low cost. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Pipe scheme and cover of the reservoir, should be cleaned regularly. If any leakages occurs in the pipes or reservoir, they should be sealed. Water taps and water tanks should be properly maintained. |
|
This technology has been applied in a low slope/latitude where the water flows with a very low speed and the application of other technologies was difficult. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Protect from sedimentation. |
|
The hydraulic flange pump is produced locally. Procurement and installment of the pump contributes therefore to local economic growth and private sector development. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Link the company to the other potential buyers. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Social conflicts can occur during the distribution of water | The water in keeper/maintainer can be introduced by CDCs for the distribution of water. |
| Electricity cannot be produced by applying this technology. The slope and latitude of the location where the flange pump is installed is too small. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
|
It is difficult to apply the technology without any external and financial support. |
Locally available materials should be used to reduce costs. |
| High level of technical knowledge is required for the establishment of the technology. | The technical knowledge should be transferred to the extension workers or local people to provide technical support in the future. |
|
This technology needs regular maintenance and the reservoir has to be properly cleaned after heavy rainfalls. |
The CDC should monitor maintenance activities by the caretaker as well as manage funds for maintenance costs. |
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos