Social Tenure Domain Model (STDM) [Kenia]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Ken Otieno
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
STDM
technologies_3318 - Kenia
- Resumen completo en PDF
- Resumen completo en PDF para imprimir
- Resumen completo en el navegador
- Resumen completo (sin formato)
- Social Tenure Domain Model (STDM): 5 de julio de 2018 (inactive)
- Social Tenure Domain Model (STDM): 7 de mayo de 2019 (public)
- Social Tenure Domain Model (STDM): 28 de junio de 2018 (inactive)
- Social Tenure Domain Model (STDM): 4 de junio de 2018 (inactive)
- Social Tenure Domain Model (STDM): 19 de mayo de 2018 (inactive)
- Social Tenure Domain Model (STDM): 5 de marzo de 2018 (inactive)
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
Especialista MST:
1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
11/12/2017
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
Comentarios:
The technology has demonstrated SLM.
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Social Tenure Domain Model (STDM) is about people and their relationships with land. The tool as applied secures tenure through the recognition of tenure diversity and social contexts. In the management of land and resources use, STDM facilitates proper land use and control to minimize practices that lead to degradation.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
Technology application
Social tenure domain Model technology is applied in relating Natural and human environment as a social tool that defines relationship of persons to Natural resources such as land, their utilization and sharing for sustainable development. To realize optimal resource utilization, the tool enables the direct engagement of the resource users in a collective and participatory way.
Main characteristics of the technology;
The Technology (Social Tenure Domain Model) is a Relational database build on an open source GIS platform called Quontum GIS (QGIS), running on Postgres SQL .This tool was Built by Global Tools Land Network (GLTN) .The technology captures both Spatial information of the resource as well as socio economic aspect of a resource and allows definition of the type of relationship that exist between the resource and the person as well as percentage of tenure or right to use. Therefore the technology enables capturing of bundles of rights that people have/should enjoy in a resource.
The Technology allows generation of reports and performing desired analysis of the information stored within the databases. it is an open source thus available free hence its sustainability.
The purposes/ functions of the Technology
The functions of the technology as have been piloted before has always focused around Land tenure ; to address security of tenure for vulnerable poor communities living within informal settlements and Management of resources such as water and graze lands for improved /increased production of both plants and animal agriculture. However, the technology can be customized to serve other purposes of information storage and management. In securing the use and management of resources, the technology promotes better livelihoods in this case through land management and reduced risks of degradation.
The major activities/ inputs are needed to establish/ maintain the Technology
Major inputs needed in mostly empowerment of local communities through building their capacity to apply the technology on their own initiative. Building community based resource centres and equipping them with computers installed with the softwares, this ensure the technology is centred at the day to day activities of the communities and institutions for sustainability. Partnership with institutions of higher learning so as to include the technology within the curriculum; this will the the ultimate sustainability of the technology and the knowledge sharing from generation to generation.Creating awareness through conferences and workshops by sharing experiences of the pilots where the technology has been applied successfully.
Benefits/ impacts of the Technology
The Technology has left more organised communities in terms of managing land and other resources information.
The technology as assisted local governments to manage issues of Land ownership especially within the context of customary land tenure and ownership. The county governments for instance, have spatial data and information that can help in planning and resources allocation.
in areas where the technology was used in the context of RECONCILE's work, better service and resources can be acquired on accurate information. Improved and sustainable use of natural resources which have a direct impact on production.
Small Dairy Farmers have been able to manage grazing lands, water and salt leeks to improve production of animal products.
Information captured and managed by the technology have enabled communities within informal settlements to negotiate with government authorities to enable land alienation thus security of tenure and improved livelihood.
What do land users like / dislike about the Technology
Likes: The technology is flexible, it can be customized to capture information in any form desired.
It is based on a GIS platform which is easy to manipulated and open source(users can get it for free)
Dislikes: Users sometimes encounter errors that are a result of wrong information entered and these errors are written with programming format thus it required a bit higher knowledge of the technology to fix it.
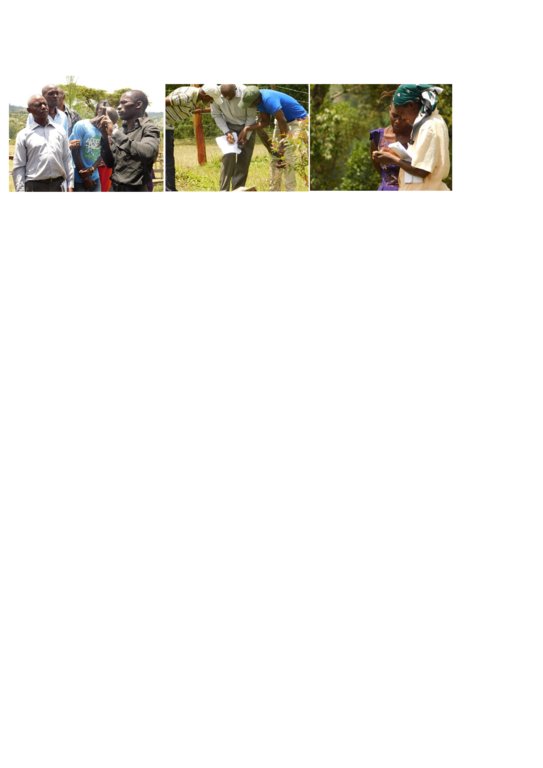
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
Comentarios generales sobre las fotos:
This activity was done to complement the social economic data collected and create the ability to understand the social tenure relationship between farmers and the common resources.
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Kenia
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
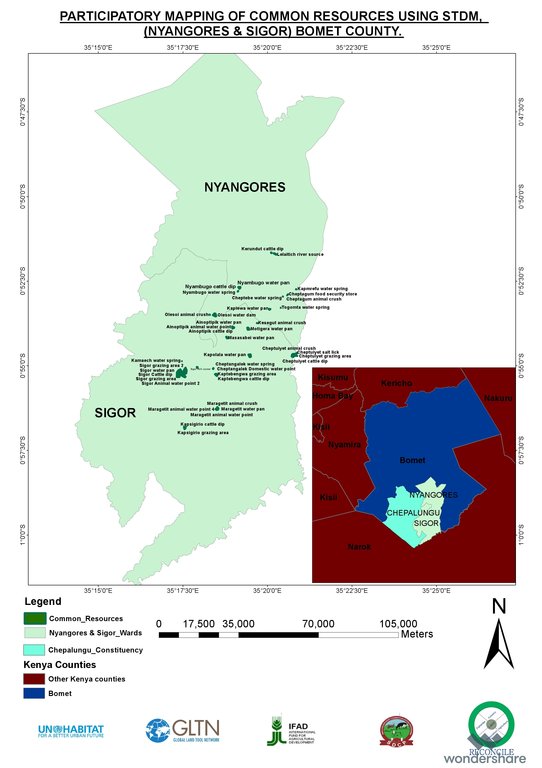
Bomet county
Especifique más el lugar :
Kembu sub-county
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2016
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- conservar el ecosistema
- proteger una cuenca hidrográfica/ áreas corriente abajo – en combinación con otras Tecnologías
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierra de pastoreo
Tierras de pastoreo extensivo:
- Semi-nomadismo/ pastoralismo
Pastoreo intensivo/ producción de forraje:
- Cortar y llevar/ cero pastoreo
Especies y productos animales principales:
The cattle kept in Ndaraweta are mainly up-graded cows from the friesian and Ayrshire. The communitoes are currently in grade 3 of the upgrade but still keeps the short horned zebu cows as well.

Cultivos asociados (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles), incl. agroforestería
- Agropastoreo
Principales productos/ servicios:
The cattle are kept for multi uses including milk, meat, hide and skin. equally, the communities grow hay for local use and sale within.
Comentarios:
The technology did therefore help the communities to appreciate the common resources that support the livestock keeping.
Si el uso de la tierra ha cambiado debido a la implementación de la Tecnología, indique el uso de la tierra antes de la implementación de la Tecnología.
Before the mapping exercise, most common resources were not given much attention. After participatory mapping and documenting these resources and establishment of information, communities have taken up the management of the resources more seriously and therefore increase of tenure security for both rangelands and resources therein.
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 2
Especifique:
April to October and November through March
Densidad del ganado (si fuese relevante):
NA
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- manejo de bosques naturales y seminaturales:
- pastoralismo y manejo de tierras de pastoreo
- manejo de agricultura—ganadería integrada
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente en un área, indique el área aproximada que cubre:
- 10-100 km2
Comentarios:
The technology is applicable in both. It can be customized to fit any use. The best outcome though is total area social enumeration and spatial mapping.
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas de manejo
- M1: Cambio de tipo de uso de la tierra
- M2: Cambio de gestión/ nivel de intensidad
- M3: disposición de acuerdo al entorno natural y humano
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

degradación del agua
- Hs: cambio en la cantidad de aguas superficiales
- Hw: reducción de la capacidad de amortiguación de las áreas humedales

otros
Comentarios:
Land degradation in rangelands is a problem that is being experienced and other challenges especially in the areas where agro-pastoralism is practiced include sustainable land use and management. The mapping process while not having direct response to these issues, it demonstrated that the communities can use sustainable means in land use through land use planning.
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
- adaptarse a la degradación de la tierra
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
The overall space or measurements for the project areas were within the range of 25 to 75 KM2.
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Indique tamaño y unidad de área:
Each project area 25 km2 (Project areas of three Sub-Counties 75 km2)
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- dólares americanos
Indique la tasa de cambio de USD a la moneda local (si fuese relevante): 1 USD =:
101,0
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
between Ksh. 2000 to 3000 depending on the kind of labour required and can go down to a compromised rate of ksh. 1000
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Enumeration of at least 1000 farmers | Otras medidas | 9 months |
| 2. | Mapping of communal resources | Estructurales | 9 months |
| 3. | Mapping of private resources | Estructurales | 9 months |
| 4. | Data Management | Manejo | 3 months |
| 5. | Preparation of data collection including testing of the tools | Otras medidas | 1 month |
| 6. | Dialogue sessions with community leaders | Manejo | 2 months |
| 7. | Negotiations on the methodology for data collection and the kind of information to be collected/asked | Estructurales | 1 month |
| 8. | Technical reviews and reflection with project team and partners | Manejo | 1 month |
Comentarios:
The kind of tasks undertaken in this process is more project oriented combined with advocacy and policy processes.
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Enumerators | persons | 90,0 | 50,0 | 4500,0 | |
| Mano de obra | Consultants | Persons | 6,0 | 1000,0 | 6000,0 | |
| Mano de obra | Technical Staff contribution and time | persons | 5,0 | 750,0 | 3750,0 | |
| Mano de obra | Data processing and management | persons | 24,0 | 60,0 | 1440,0 | |
| Equipo | Data entry and analysis | persons | 20,0 | 40,0 | 800,0 | |
| Equipo | GPS hiring | 120,0 | 55,0 | 6600,0 | ||
| Equipo | GPS purchase | 5,0 | 320,0 | 1600,0 | ||
| Equipo | Computers | 4,0 | 750,0 | 3000,0 | ||
| Equipo | Conferences | 9,0 | 1500,0 | 13500,0 | ||
| Otros | Administrative costs | 9 months | 9,0 | 1400,0 | 12600,0 | |
| Otros | Logistical support | 36,0 | 600,0 | 21600,0 | ||
| Otros | Preliminary activities including targeted dialogue etc | Travels and associated costs | 5,0 | 300,0 | 1500,0 | |
| Otros | Documentation of the project (to be finalized) | Video documentary | 2,0 | 3000,0 | 6000,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 82890,0 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
UNHABITAT, RECONCILE, Smallholder Dairy Commercialization Programme (SDCP)
Comentarios:
The project was supported by the UNHABITAT with contributions from RECONCILE and partners. the community contribution in kind is not included since it has not been tabulated in terms of cash.
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | NA | ||
| 2. | NA | ||
| 3. | NA |
Comentarios:
The project did not have physical structures developed. However, as a result of the work structures like cattle dips have been rehabilitated and are currently being maintained by the the communities themselves. This does not need recurrent costs for maintenance or otherwise by the project.
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
The technology costs are dependent on the size and number of resources targeted by the process. It will therefore define the costs accordingly.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
The area is semi arid
Indique el nombre de la estación metereológica de referencia considerada:
Kenya Meteorological department
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
The average temperature in Bomet is 17.5 °C. Precipitation here averages 1247 mm.
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- no relevante
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
mediana
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
Diversidad de hábitats:
- baja
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
- Semi-nómada
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- grupos/ comunal
- cooperativa
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
- tracción animal
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- jóvenes
- personas de mediana edad
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- comunitaria/ aldea
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- comunitarios (organizado)
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
- comunitarios (organizado)
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de forraje
Comentarios/ especifique:
The production in the farms increased for milk
calidad de forraje
Comentarios/ especifique:
The size of fodder producers also increased. the production trend is stable based on the number of farmers involved.
producción animal
Ingreso y costos
ingreso agrario
Comentarios/ especifique:
Resulting from the proper land use and increased milk production based on more pasture, costs increased.
Impactos ecológicos
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
impactos de sequías
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
disponibilidad de agua
corriente confiable y estable fluye en estación seca
capacidad de amortiguación/ filtrado
impacto de gases de invernadero
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | tipo de cambios climáticos/ climas extremos | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| lluvia anual | disminuyó | moderadamente |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | moderadamente |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
neutral/ balanceado
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- más de 50%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
The technology covered around 500 individual farmers
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, es decir, sin recibir incentivos/ pagos materiales?
- 10-50%
Comentarios:
The technology application did not attract any material gains or incentives but, the process was community centered thus the adoption.
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
Sí
Especifique la adaptación de la Tecnología (diseño, material/ especies, etc.):
The technology was more of the urban oriented tool but had to be modified to adopt to the local demands.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
|
Ability to define spatial space and common and private resources including those resources associated with milk production such as milk coolers, water points, cattle dips, food stores, grazing areas, salt licks, crush, animal corridors, forest e.t.c Establish the carrying capacity of communal shared resources. |
|
Establishment of the Land tenure system of shared communal resources and issues arising. Status (management) of private resources within the rangelands. Production and income generated against household size. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
The nature of the problem required innovative use in the mapping of the land and natural resources. The technology addressed immediate need and provide a foundation for future updates and demands. The technology benefited from the existing data and improved delivery of output without exerting any impediments. |
|
The technology bridged the gap through skills transfer and capacity building and in facilitating dialogue on issues affecting the community (Maps, reports). Ability to adapt the technology in a simplicity manner that the users can relate with and find value in their use contributed immense success Introduced even a more user friendly of the mobile and smartphone use. The quick win could be seen in the transformation of mobile phones into data collection tools and the data can be seen, verified and shared replacing the tedious and manual process which many were struggling with. |
|
STDM database accommodate inclusion of social economic and spatial data that can be maintained, accessed and update by the communities anytime. Provided visual representation of available resources and their distribution and people can relate to spatial information on the map. |
| Ownership of technology by local people who are now leading on data collection, customizing the template, developing reports and innovating on its use. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
|
The design of the tool was a more urban oriented and took time to be adopted for rural use especially where land is communal and customs are key. |
Created more awareness. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
|
Difficult to setup the server environment where no internet is available. Engaging other service providers may be difficult and takes time (Internet service provider need to authorize setting up additional server). Appropriate devices for capturing data may necessity additional budget. |
The internet component remains a challenge Technology is evolving and needs systematic information channels even with the community members. The process requires proper funding in order not to have a break in between. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
900
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
900
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
2
- compilación de informes y otra documentación existente
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
RECONCILE end of project report and other progress reports are available for sharing
Título/ descripción:
Food security in Bomet county
URL:
awsc.uonbi.ac.ke/sites/default/files/chss/arts/.../Bomet-final.doc
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos