Strip Tillage Conservation Farming [Zambia]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Silenga Wamunyima
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1187 - Zambia
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Ndandula Sharon
Golden Valley Agricultural Research Trust
Zambia
Especialista MST:
Katoweji Alfred
Golden Valley Agricultural Research Trust
Zambia
Especialista MST:
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Golden Valley agricultural research trust (Golden Valley agricultural research trust) - Zambia1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST (documentados usando WOCAT)

Participatory Research and Development [Zambia]
This is a collaborative process between researchers and farmers for developing and adapting new technologies that focus on incorporating the perspectives and inputs from the farmers into the development process.
- Compilador: Arthur Chomba
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
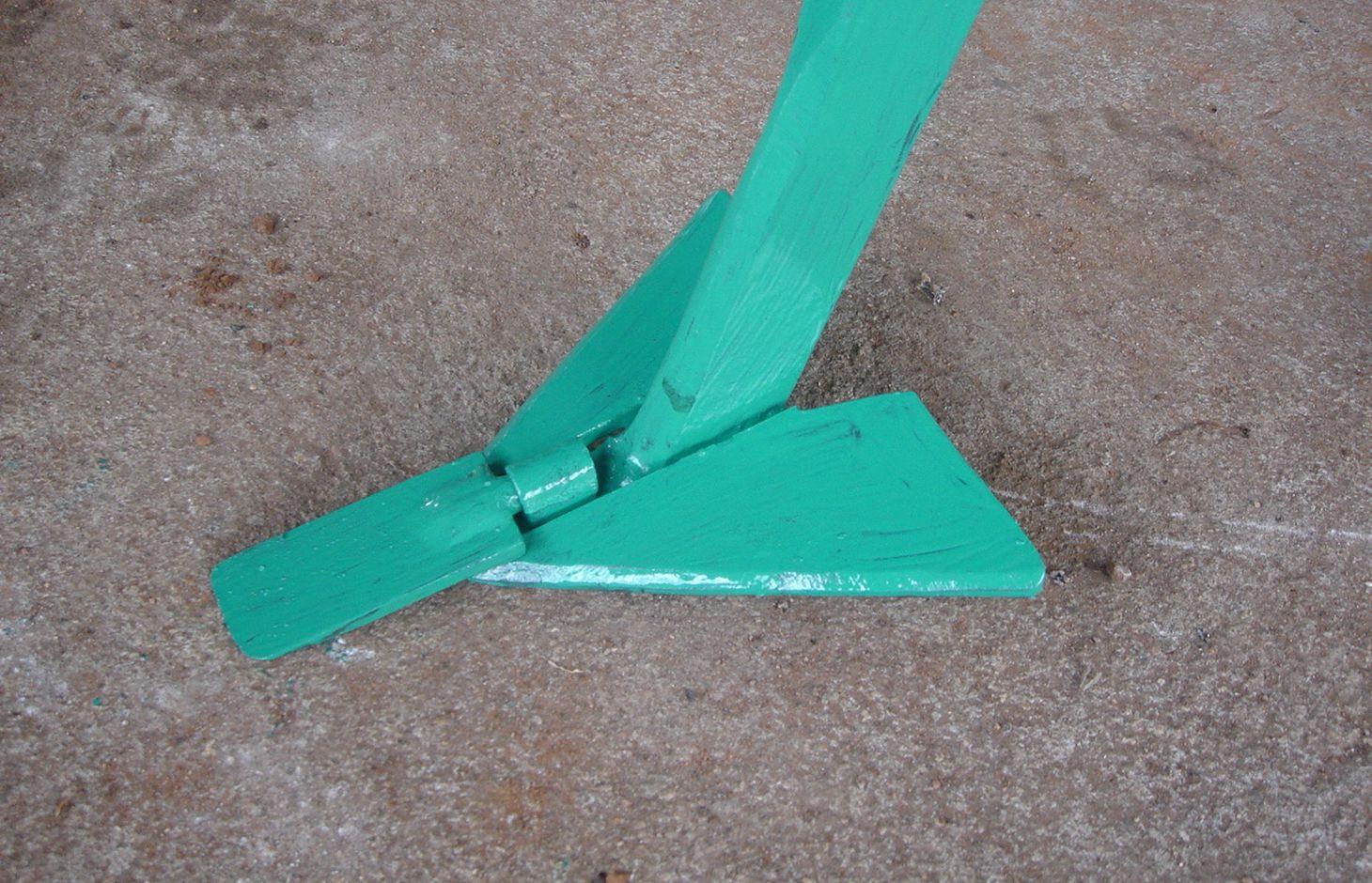
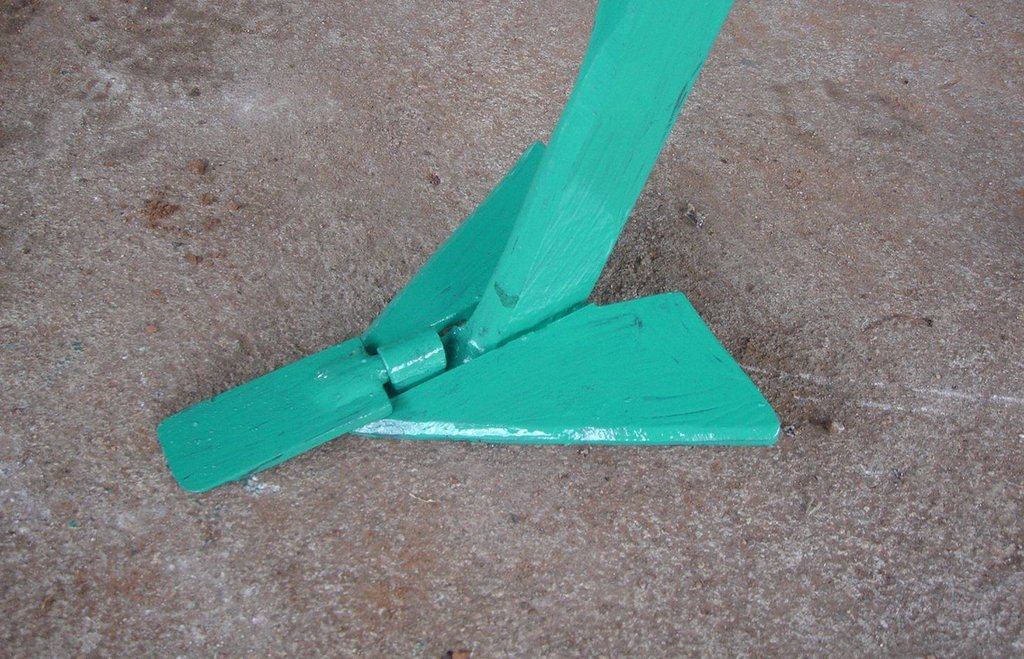
Strip Tillage Conservation Farming is an animal draft reduced tillage method that involves loosening a strip of soil with a strip tillage tool so as to reduce soil disturbance and improve soil and water conservation.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
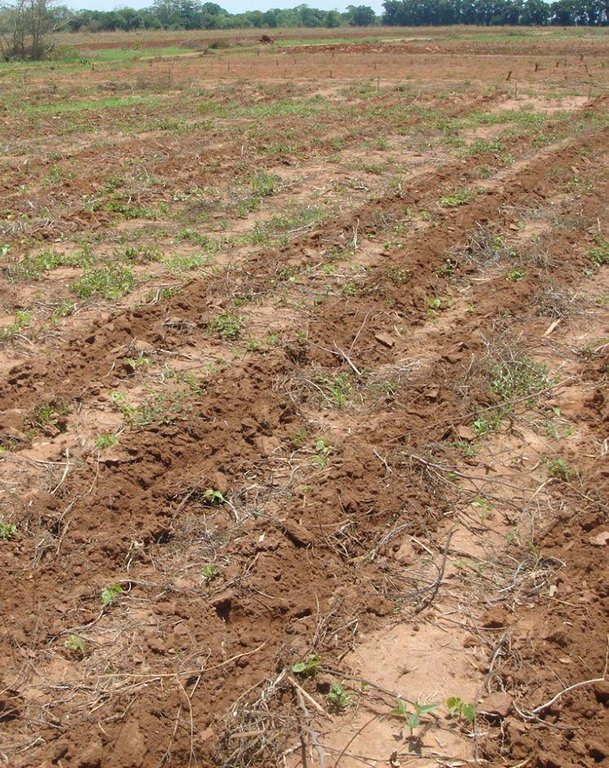
The strip tillage tool is an adaptation of a Magoye Ripper but is meant to be used in moist soil. In the strip tillage tool, sub-surface wings are attached to the ripper tine to increase the width of soil disruption which the ripper will be unable to achieve in moist soil. The sub-surface wings loosen the soil by lifting it slightly and letting it fall in place without inverting it. In this way, a strip of soil with a width of around 20cm is tilled up to 20cm deep and this is where the crop will be planted. The region between the strips is maintained as a no-till region for soil and water conservation.
Purpose of the Technology: The strip tillage tool is meant to be a transitional technology for farmers intending to adopt Conservation Agriculture (CA) in degraded soils. These soils will need routine loosening while the biological activities allow the soil structure to recover sufficiently until tillage is no longer required. Strip tillage is able to achieve deeper soil loosening with much less draft force, wear of tines and soil disturbance than ripping. The untilled region between the strips enables the benefits of soil cover such as improved infiltration, soil water storage and increased soil organic matter. Soil loosening by strip tillage does not produce large clods like ripping does but instead produces a fine seedbed that enables uniform emergence of the crop, and this together with the deep penetration results in early plant vigour. The strip tillage implement is also designed to allow the attachment of a planter unit to enable tillage and planting in one operation.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The establishment of strip tillage based conservation agriculture mainly involves the purchase of the strip tillage implement and the replaceable tines. Liming acidic soils (low pH soils) followed by a final ploughing will be required to correct the soil PH which otherwise will be difficult to correct once conservation tillage has been established. Maintenance activities include strip-tilling the soil which may or may not include planting and fertilizing in the same operation. Weeding should preferably include the use of herbicides, implying that the major operations will include spraying. In addition to the normal conventional inputs, herbicides will also become a major input and cost.
Natural / human environment: The strip tillage technology is most suited to the bigger small-scale farmers with a capacity of 5ha to about 20ha. The strip tillage tool together with the planter will require a relatively substantial investment and only the bigger farmers will fully utilize its capacity. The strip tillage action will not be very effective in wet soils especially in the heavier soils, soil disruption is best achieved when the soil is slightly moist but not too dry as to require to high draft forces. Strip tillage is useful in soil with poor structure that will require routine loosening to maintain yields while the soil is being rehabilitated.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Zambia
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Zambia/Southern Province
Especifique más el lugar :
Mazabuka/Magoye
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si se desconoce el área precisa, indique el área aproximada cubierta:
- 0.1-1 km2
Comentarios:
The strip tillage technology is only in its second year of promotion and 7 farmers had adopted the technology in the 2011/12 season. The field sizes range from 1ha to 30ha.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- durante experimentos/ investigación
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
Development of the strip tillage technology began in 2008 in response to farmers’ feedback from the promotion of another conservation agricultural technology, the Magoye Ripper. The technology was introduced to the farmers in 2011.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
Sí
Especifique el uso combinado de tierras (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles):
- Agropastoralismo (incluyendo cultivo-ganado integrados)

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cereales - maíz
- cultivos para producción de fibras - algodón
- cultivos de semillas oleaginosas - maní
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 135; Longest growing period from month to month: Mid November to end of March

Tierra de pastoreo
Tipo de animal:
- ganado - lechero
- cabras
- aves de corral

Bosques
Comentarios:
Livestock density (if relevant):
1-10 LU /km2
Principaux problèmes d'utilisation des sols (opinion du compilateur): perte de structure du sol et perte de fertilité du sol
Principaux problèmes d'utilisation des terres (perception des utilisateurs fonciers): sécheresses et périodes de sécheresse
L'élevage pèche sur les résidus de récoltes
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- perturbación mínima del suelo
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A2: materia orgánica/ fertilidad del suelo
- A3: Tratamiento de superficie del suelo
- A6: Manejo de residuos
- A7: Otros
A3: Diferencie sistemas de labranza:
A 3.1: Sin labranza
A6: Especifique manejo de residuos:
A 6.1: quemado
Comentarios:
Specification of other agronomic measures: Zero till, Crop Residue
Type of agronomic measures: early planting, mulching, manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, soil conditioners (lime, gypsum), rotations / fallows, breaking compacted topsoil, minimum tillage, non-inversion tillage, breaking compacted subsoil
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)

deterioro físico del suelo
- Pc: compactación
- Pk: desmoronamiento y encostramiento
- Pi: sellado de suelo

degradación biológica
- Bl: pérdida de la vida del suelo
Comentarios:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: soil management (over ploughing, soil nutrient mining), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Monocropping of Maize), overgrazing (overgrazing of crop residues), poverty / wealth (Charcoal burning, under application of fertilizer)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (charcoal burning, openning up new land for agriculture), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (high intensity storms resulting in soil erosion and leaching), land tenure (over-exploitation of communal land), governance / institutional (lack of credit facilities)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
Comentarios:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
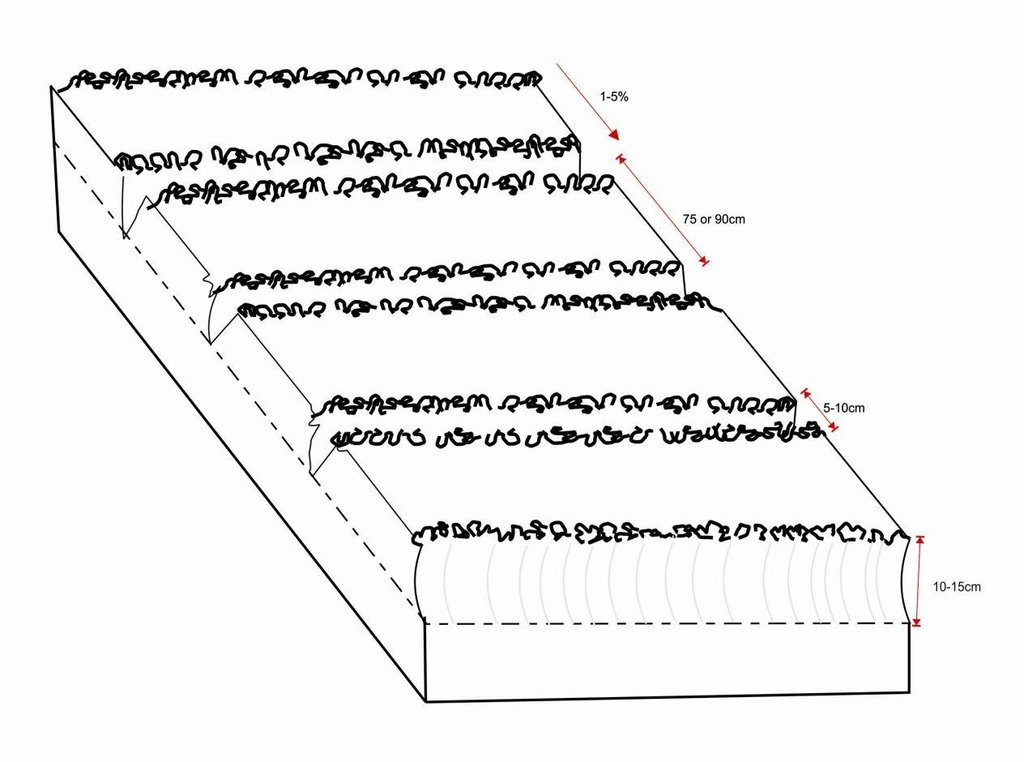
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
Planting lines are done at a depth of 15-20cm with inter row of 75 or 90cm. The width of the open furrow is 5-10cm wide. Planting rows are done across the slope to reduce runoff, these planting rows may be made in the dry season or during the rainy season when the soil is moist.
Location: Magoye. Mazabuka/Southern Province/Zambia
Date: 2014-06-29
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (must be able to troubleshoot and advise the farmers on how to adapt the technology to fit into their production systems.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (knowledge of soil health management required when adopting the practice)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, water harvesting / increase water supply
Early planting
Material/ species: Maize, Cotton
Quantity/ density: 44,000 pla
Remarks: 25cm intra row x 75cm
Mulching
Material/ species: Crop residues
Quantity/ density: 3ton/ha
Remarks: Uniformly spread
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: crop residues
Quantity/ density: 3ton/ha
Remarks: uniformly spread
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: basal and top dressing
Quantity/ density: 800kg/ha
Remarks: spot application
Soil conditioners (lime, gypsum)
Material/ species: lime
Quantity/ density: 1ton/ha
Remarks: every 2-3 years
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: rotations of maize, cotton, cowpeas
Breaking compacted topsoil
Material/ species: strip tillage
Quantity/ density: 20cm deep
Minimum tillage
Material/ species: strip tillage
Non-inversion tillage
Material/ species: strip tillage
Breaking compacted subsoil
Material/ species: strip tillage
Autor:
Silenga Wamunyima, Box 670577, Mazabuka, Zambia
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- USD
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
2.40
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Strip Tillage implement | |
| 2. | Knapsack Sprayer |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipo | Strip Tillage implement | pieces | 1,0 | 500,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Knapsack Sprayer | pieces | 1,0 | 80,0 | 80,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 580,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 580,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Slashing and spreading crop residues | May-June yearly after harvest |
| 2. | Liming soil | Nov-Dec every 3 years |
| 3. | strip tillage, planting and fertilizing | Nov-Dec at onset of rain |
| 4. | Chemical weeding | 3 times per season |
| 5. | Harvesting | April-May |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Slashing and spreading crop residues | persons/day/ha | 8,0 | 2,5 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Liming soil | persons/day/ha | 2,0 | 2,5 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Strip tillage, planting and fertilizing | persons/day/ha | 4,0 | 2,5 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Chemical weeding (sprayers) | persons/day/ha | 24,0 | 1,0 | 24,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Animal traction | ha | 1,0 | 40,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Seeds | kg/ha | 20,0 | 2,5 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Fertilizer | kg/ha | 400,0 | 0,8 | 320,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Herbicides | l/ha | 5,0 | 6,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Lime | kg | 1000,0 | 0,042 | 42,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Labour: Chemical weeding (sprayers) | persons/day/ha | 10,0 | 4,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Labour: Harvesting | persons/day/ha | 10,0 | 4,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 621,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 621,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
Machinery/ tools: Strip tillage planter
Calculations are for 1 ha of maize under strip tillage based conservation tillage and costs are for the Zambia situation in Magoye as of August 2012.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
The weed control method employed is the main determinate factor depending on whether the farmer uses hand hoe or herbicides for weeding. Weed densities are higher in unploughed fields increasing the labour requirements/costs by a factor of about 5 if hand weeding is used instead of herbicides. Another major recurrent cost is that of fertilizer which makes up about half the cost hence the total cost will vary significantly depending on fertilizer cost.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Summer rains from November to March
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
Thermal climate class: subtropics. 3 distinct seasons – summer, winter and one rainy season
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- baja (<1%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil fertility is low - medium and low fertility caused mainly by poor soil management practices, otherwise soils are inherently fertile.
Topsoil organic matter: Due to excessive ploughing and under fertilization
Soil drainage / infiltration is good - medium. Soils are naturally well drained but become less so after compaction due to ploughing
Soil water storage capacity is medium. Soils mostly loam to sandy loam with medium storage capacity
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
> 50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
mediana
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de mala calidad (requiere tratamiento)
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Ground water table: Hand wells are <20m but reliable boreholes are > 50m
Availability of surface water: Mostly seasonal streams and dams
Water quality (untreated):Good when from communal hand-pumps and poor when from hand-dug wells.
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- muy pobre
- pobre
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
- tracción animal
Género:
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: The technology is applied mostly by men since most households are headed males and animal traction operation are reserved for men. Planting and weeding operations are the domain of women and children
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
8% of the land users are rich and own 15% of the land (own more than 10 cattle).
8% of the land users are average wealthy and own 15% of the land (own 5 - 10 cattle).
16% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land (less than 5 cattle).
68% of the land users are poor and own 40% of the land (do not own cattle).
Off-farm income specification: sale of rainfed crops makes up about half of their income, the remainder coming from sale of livestock, petty trading, hiring out labour and remittances
Market orientation of production system: Livestock, maize and legumes for home consumption/subsistence and sale of excess maize and cotton, dairy products (mixed).
Level of mechanization: Manual labour only for small backyard fields. Families without cattle borrow or hire
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
Comentarios:
Cropland: 1-2 ha (families without oxen), 2-5 ha (families with one pair of oxen), 5-15 ha (families with over five oxen)
Grazing land: 5-15 ha, 15-50 ha, 50-100 ha
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- comunitaria/ aldea
- individual, sin título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
- individual
- Apportioned by traditional rulers
Derechos de uso de agua:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
- Apportioned by traditional rulers
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Cantidad antes de MST:
3tons/ha
Cantidad luego de MST:
5tons/ha
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to early planting
producción de forraje
Comentarios/ especifique:
Residues needed for soil cover
riesgo de fracaso de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
Better resistance
área de producción
Cantidad antes de MST:
2-3ha
Cantidad luego de MST:
>10ha
Ingreso y costos
ingreso agrario
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to increased production area and improved yield
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
Comentarios/ especifique:
More time and labour freed for other activities
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to mechanised planting and herbicide use
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to incresed yields
situación de salud
Comentarios/ especifique:
Improved nutrition due to crop diversification
oportunidades recreativas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Less time spent on farm operations
instituciones comunitarias
Comentarios/ especifique:
Farmers trained through cooperatives
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to incresed soil Carbon, crop residues to reduce run off, and capacity building
mitigación de conflicto
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to competition with neighbours cattle for crop residues
livelihood and human well-being
Comentarios/ especifique:
The technology was only introduced recently and not yet widely adopted to make an impact. However the few farmers that have adopted have been able to multiply their production capacities and incomes.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cosecha/ recolección de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to better soil cover
escurrimiento superficial
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to better soil cover
drenaje de agua en exceso
Comentarios/ especifique:
Improved soil structure
nivel freático/ acuífero
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to good drainage
evaporación
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to better soil cover
Suelo
humedad del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to better soil cover
cubierta del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to non-inversion tillage
pérdida de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
encostramiento/ sellado de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
compactación de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to deep tillage
ciclo/ recarga de nutrientes
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
salinidad
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to good drainage
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
diversidad animal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to soil organic matter (SOM) buildup
control de pestes/ enfermedades
Comentarios/ especifique:
Resistance to chemical weed control
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
emisión de carbono y gases de invernadero
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to Carbon (C) sequestration
Otros impactos ecológicos
Ground water contamination
Comentarios/ especifique:
Some chemicals get carried down the profile
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
disponibilidad de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
Only if applied over an extensive area
corriente confiable y estable fluye en estación seca
Comentarios/ especifique:
Only if applied over an extensive area
inundaciones río abajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Only if applied over an extensive area
colmatación río abajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Only if applied over an extensive area
daño a campos de vecinos
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | no se sabe |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | bien |
| tormenta de viento | no se sabe |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | no muy bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | no se sabe |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
Timely and quicker planting enables larger areas to be planted and with less labour in the short term. Improved soil structure and soil fertility leads to higher yields and better resilience to droughts in the long term.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- > 50%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
7 households in an area of 0.1 - 1 km2 (field size 1 ha - 30 ha)
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 91-100%
Comentarios:
7 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: These farmers heard of the technology by word of mouth and solicited for the technology even before it could be officially promoted
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Even before promotion, inquiries to purchase the strip planter have been overwhelming. This is most likely due to the ability to till, plant and fertilizer in one operation.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
|
Enables early planting How can they be sustained / enhanced? acquire more than one strip tillage implement |
|
Quicker planting enables planting of larger areas How can they be sustained / enhanced? Plant the seed and apply the fertilizer in one opperation |
|
Lighter to pull enabling deeper penetration of the tillage tool increasing the rooting depth How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use in moist soils |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
Enables early planting How can they be sustained / enhanced? Plant with the first heavy rain in November |
|
Quicker planting enables planting of larger areas How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use herbicides because without them, the capacity to weed will limit the production capacity |
|
Preserves soil cover and reduces soil disturbance How can they be sustained / enhanced? Training in residue management (No Burning) and use of zero tillage implement |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The purchase price of the strip tillage planter | subsidizing the strip tillage implement |
| Excessive weeds and lack of information on herbicide use | More training on herbicide use |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The purchase price is high making it affordable only to the larger small-scale farmers | It is already by far the cheapest planter available but mass production can lead to significant reduction in purchase price |
| Benefits are more evident on a scale larger than many farmers capacity especially when used in combination with herbicides | Support farmers to increase capacity |
| Difficult to control weeds in the absence of herbicides | make herbicides more available at a lower cost |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Social-economic analysis of conservation agriculture in southern Africa, FAO, 2011
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
FAO
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Conservation farming in Zambia, Steven Haggblade, Gelson Tembo, October 2003
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
INDABA project, Michigan State University
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
Conservation farming in Zambia, Conservation farming unit (CFU), 2011
URL:
cfu@zamnet.zm
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Participatory Research and Development [Zambia]
This is a collaborative process between researchers and farmers for developing and adapting new technologies that focus on incorporating the perspectives and inputs from the farmers into the development process.
- Compilador: Arthur Chomba
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos