Strip Tillage Conservation Farming [Zambie]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Silenga Wamunyima
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1187 - Zambie
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Ndandula Sharon
Golden Valley Agricultural Research Trust
Zambie
Spécialiste GDT:
Katoweji Alfred
Golden Valley Agricultural Research Trust
Zambie
Spécialiste GDT:
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Golden Valley agricultural research trust (Golden Valley agricultural research trust) - Zambie1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)

Participatory Research and Development [Zambie]
This is a collaborative process between researchers and farmers for developing and adapting new technologies that focus on incorporating the perspectives and inputs from the farmers into the development process.
- Compilateur : Arthur Chomba
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Strip Tillage Conservation Farming is an animal draft reduced tillage method that involves loosening a strip of soil with a strip tillage tool so as to reduce soil disturbance and improve soil and water conservation.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
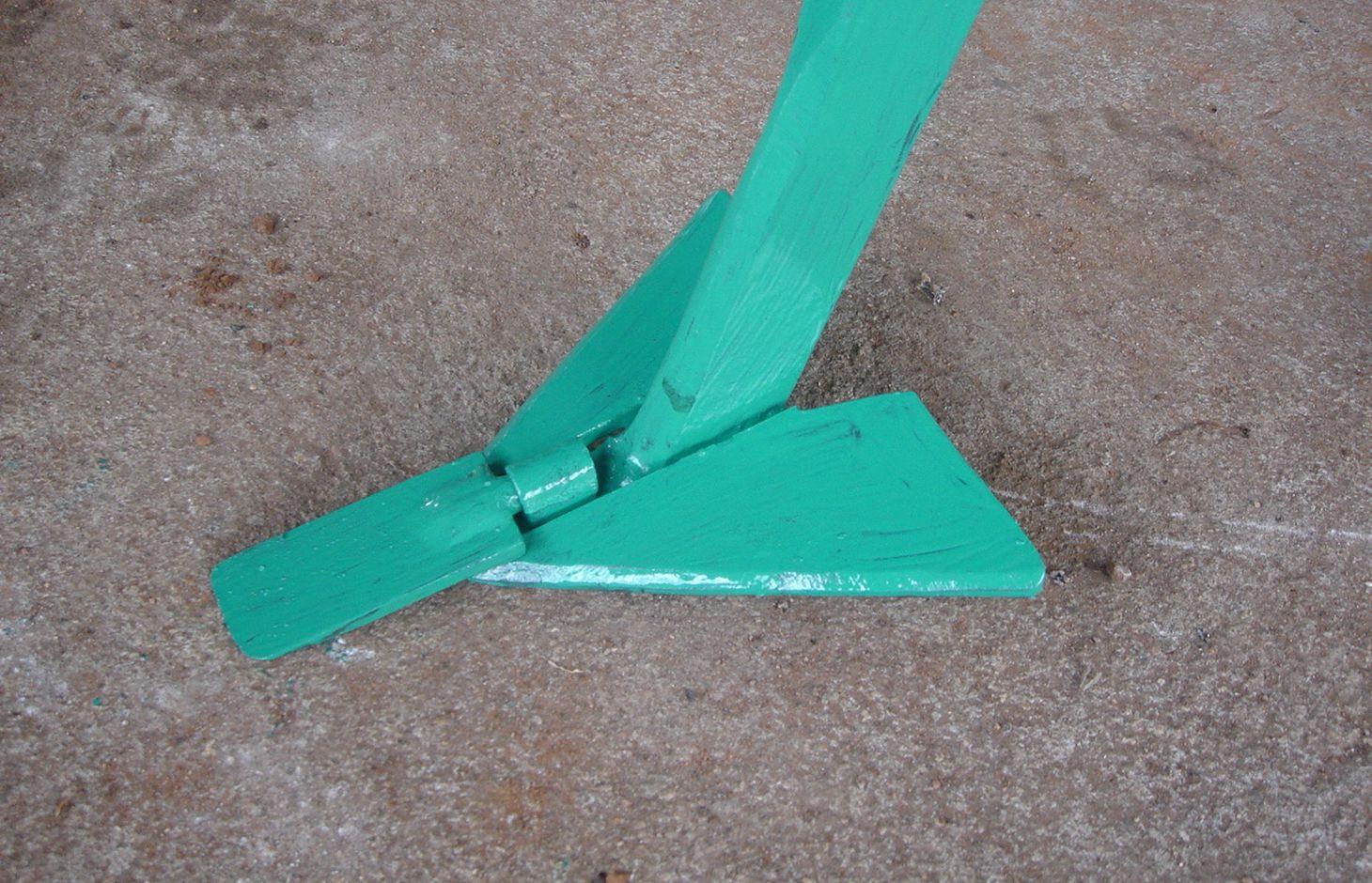
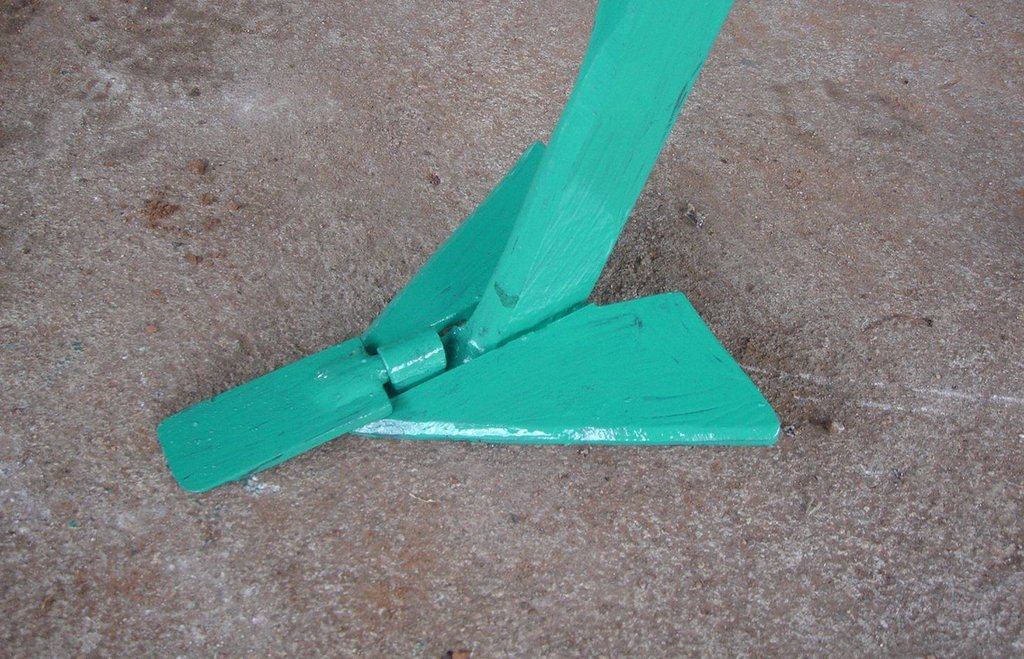
The strip tillage tool is an adaptation of a Magoye Ripper but is meant to be used in moist soil. In the strip tillage tool, sub-surface wings are attached to the ripper tine to increase the width of soil disruption which the ripper will be unable to achieve in moist soil. The sub-surface wings loosen the soil by lifting it slightly and letting it fall in place without inverting it. In this way, a strip of soil with a width of around 20cm is tilled up to 20cm deep and this is where the crop will be planted. The region between the strips is maintained as a no-till region for soil and water conservation.
Purpose of the Technology: The strip tillage tool is meant to be a transitional technology for farmers intending to adopt Conservation Agriculture (CA) in degraded soils. These soils will need routine loosening while the biological activities allow the soil structure to recover sufficiently until tillage is no longer required. Strip tillage is able to achieve deeper soil loosening with much less draft force, wear of tines and soil disturbance than ripping. The untilled region between the strips enables the benefits of soil cover such as improved infiltration, soil water storage and increased soil organic matter. Soil loosening by strip tillage does not produce large clods like ripping does but instead produces a fine seedbed that enables uniform emergence of the crop, and this together with the deep penetration results in early plant vigour. The strip tillage implement is also designed to allow the attachment of a planter unit to enable tillage and planting in one operation.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The establishment of strip tillage based conservation agriculture mainly involves the purchase of the strip tillage implement and the replaceable tines. Liming acidic soils (low pH soils) followed by a final ploughing will be required to correct the soil PH which otherwise will be difficult to correct once conservation tillage has been established. Maintenance activities include strip-tilling the soil which may or may not include planting and fertilizing in the same operation. Weeding should preferably include the use of herbicides, implying that the major operations will include spraying. In addition to the normal conventional inputs, herbicides will also become a major input and cost.
Natural / human environment: The strip tillage technology is most suited to the bigger small-scale farmers with a capacity of 5ha to about 20ha. The strip tillage tool together with the planter will require a relatively substantial investment and only the bigger farmers will fully utilize its capacity. The strip tillage action will not be very effective in wet soils especially in the heavier soils, soil disruption is best achieved when the soil is slightly moist but not too dry as to require to high draft forces. Strip tillage is useful in soil with poor structure that will require routine loosening to maintain yields while the soil is being rehabilitated.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Zambie
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Zambia/Southern Province
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Mazabuka/Magoye
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- 0,1-1 km2
Commentaires:
The strip tillage technology is only in its second year of promotion and 7 farmers had adopted the technology in the 2011/12 season. The field sizes range from 1ha to 30ha.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- au cours d'expérimentations / de recherches
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Development of the strip tillage technology began in 2008 in response to farmers’ feedback from the promotion of another conservation agricultural technology, the Magoye Ripper. The technology was introduced to the farmers in 2011.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agropastoralisme (y compris les systèmes culture-élevage intégrés)

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - maïs
- cultures de plantes à fibres - coton
- cultures oléagineuses - arachide
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 135; Longest growing period from month to month: Mid November to end of March

Pâturages
Type d'animal:
- bétail - laitier
- caprine
- volailles

Forêts/ bois
Commentaires:
Livestock density (if relevant):
1-10 LU /km2
Principaux problèmes d'utilisation des sols (opinion du compilateur): perte de structure du sol et perte de fertilité du sol
Principaux problèmes d'utilisation des terres (perception des utilisateurs fonciers): sécheresses et périodes de sécheresse
L'élevage pèche sur les résidus de récoltes
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- perturbation minimale du sol
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A2: Matière organique/ fertilité du sol
- A3: Traitement de la couche superficielle du sol
- A6: Gestion des résidus des cultures
- A7: Autres
A3: Différenciez les systèmes de travail du sol:
A 3.1: Systèmes de culture sans travail du sol
A6: Précisez la gestion des résidus des cultures:
A 6.1: Résidus brûlés
Commentaires:
Specification of other agronomic measures: Zero till, Crop Residue
Type of agronomic measures: early planting, mulching, manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, soil conditioners (lime, gypsum), rotations / fallows, breaking compacted topsoil, minimum tillage, non-inversion tillage, breaking compacted subsoil
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)

dégradation physique des sols
- Pc: compaction
- Pk: scellage et encroûtement
- Pi: imperméabilisation des sols

dégradation biologique
- Bl: perte de la vie des sols
Commentaires:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: soil management (over ploughing, soil nutrient mining), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Monocropping of Maize), overgrazing (overgrazing of crop residues), poverty / wealth (Charcoal burning, under application of fertilizer)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (charcoal burning, openning up new land for agriculture), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (high intensity storms resulting in soil erosion and leaching), land tenure (over-exploitation of communal land), governance / institutional (lack of credit facilities)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
Commentaires:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
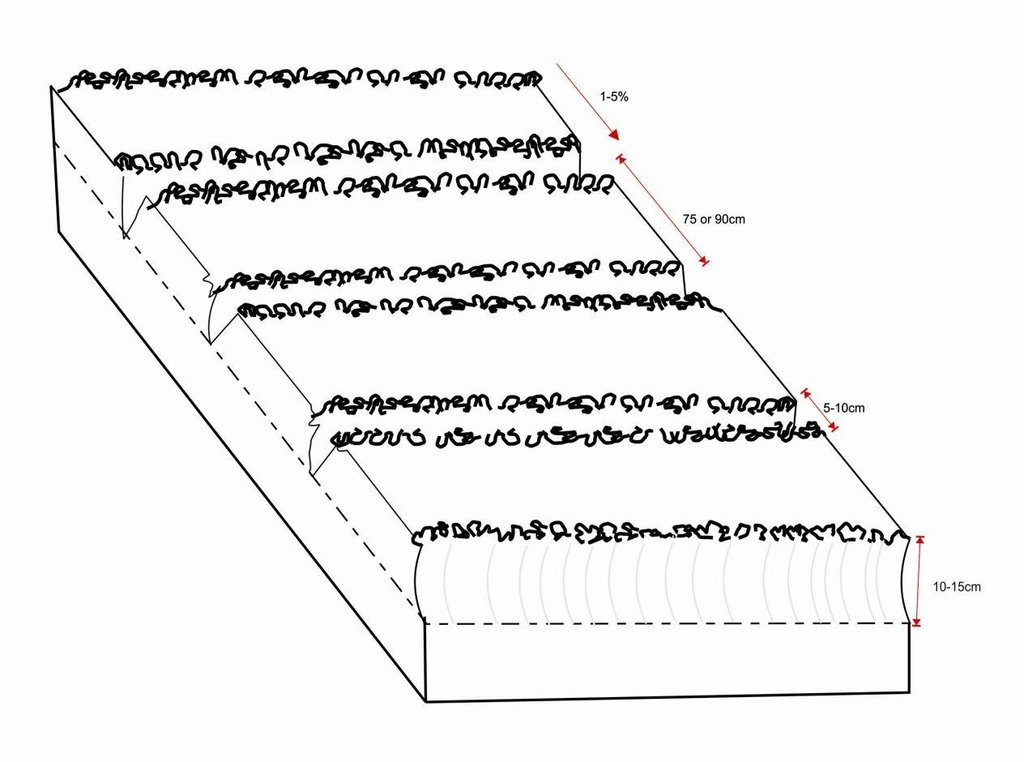
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Planting lines are done at a depth of 15-20cm with inter row of 75 or 90cm. The width of the open furrow is 5-10cm wide. Planting rows are done across the slope to reduce runoff, these planting rows may be made in the dry season or during the rainy season when the soil is moist.
Location: Magoye. Mazabuka/Southern Province/Zambia
Date: 2014-06-29
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (must be able to troubleshoot and advise the farmers on how to adapt the technology to fit into their production systems.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (knowledge of soil health management required when adopting the practice)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, water harvesting / increase water supply
Early planting
Material/ species: Maize, Cotton
Quantity/ density: 44,000 pla
Remarks: 25cm intra row x 75cm
Mulching
Material/ species: Crop residues
Quantity/ density: 3ton/ha
Remarks: Uniformly spread
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: crop residues
Quantity/ density: 3ton/ha
Remarks: uniformly spread
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: basal and top dressing
Quantity/ density: 800kg/ha
Remarks: spot application
Soil conditioners (lime, gypsum)
Material/ species: lime
Quantity/ density: 1ton/ha
Remarks: every 2-3 years
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: rotations of maize, cotton, cowpeas
Breaking compacted topsoil
Material/ species: strip tillage
Quantity/ density: 20cm deep
Minimum tillage
Material/ species: strip tillage
Non-inversion tillage
Material/ species: strip tillage
Breaking compacted subsoil
Material/ species: strip tillage
Auteur:
Silenga Wamunyima, Box 670577, Mazabuka, Zambia
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars américains
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
2.40
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Strip Tillage implement | |
| 2. | Knapsack Sprayer |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipements | Strip Tillage implement | pieces | 1,0 | 500,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Knapsack Sprayer | pieces | 1,0 | 80,0 | 80,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 580,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 580,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Slashing and spreading crop residues | May-June yearly after harvest |
| 2. | Liming soil | Nov-Dec every 3 years |
| 3. | strip tillage, planting and fertilizing | Nov-Dec at onset of rain |
| 4. | Chemical weeding | 3 times per season |
| 5. | Harvesting | April-May |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Slashing and spreading crop residues | persons/day/ha | 8,0 | 2,5 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Liming soil | persons/day/ha | 2,0 | 2,5 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Strip tillage, planting and fertilizing | persons/day/ha | 4,0 | 2,5 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Chemical weeding (sprayers) | persons/day/ha | 24,0 | 1,0 | 24,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Animal traction | ha | 1,0 | 40,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds | kg/ha | 20,0 | 2,5 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Fertilizer | kg/ha | 400,0 | 0,8 | 320,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Herbicides | l/ha | 5,0 | 6,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Lime | kg | 1000,0 | 0,042 | 42,0 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Labour: Chemical weeding (sprayers) | persons/day/ha | 10,0 | 4,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Labour: Harvesting | persons/day/ha | 10,0 | 4,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 621,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 621,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: Strip tillage planter
Calculations are for 1 ha of maize under strip tillage based conservation tillage and costs are for the Zambia situation in Magoye as of August 2012.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The weed control method employed is the main determinate factor depending on whether the farmer uses hand hoe or herbicides for weeding. Weed densities are higher in unploughed fields increasing the labour requirements/costs by a factor of about 5 if hand weeding is used instead of herbicides. Another major recurrent cost is that of fertilizer which makes up about half the cost hence the total cost will vary significantly depending on fertilizer cost.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Summer rains from November to March
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Thermal climate class: subtropics. 3 distinct seasons – summer, winter and one rainy season
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility is low - medium and low fertility caused mainly by poor soil management practices, otherwise soils are inherently fertile.
Topsoil organic matter: Due to excessive ploughing and under fertilization
Soil drainage / infiltration is good - medium. Soils are naturally well drained but become less so after compaction due to ploughing
Soil water storage capacity is medium. Soils mostly loam to sandy loam with medium storage capacity
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
> 50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
faiblement potable (traitement nécessaire)
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Ground water table: Hand wells are <20m but reliable boreholes are > 50m
Availability of surface water: Mostly seasonal streams and dams
Water quality (untreated):Good when from communal hand-pumps and poor when from hand-dug wells.
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- très pauvre
- pauvre
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- traction animale
Genre:
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: The technology is applied mostly by men since most households are headed males and animal traction operation are reserved for men. Planting and weeding operations are the domain of women and children
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
8% of the land users are rich and own 15% of the land (own more than 10 cattle).
8% of the land users are average wealthy and own 15% of the land (own 5 - 10 cattle).
16% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land (less than 5 cattle).
68% of the land users are poor and own 40% of the land (do not own cattle).
Off-farm income specification: sale of rainfed crops makes up about half of their income, the remainder coming from sale of livestock, petty trading, hiring out labour and remittances
Market orientation of production system: Livestock, maize and legumes for home consumption/subsistence and sale of excess maize and cotton, dairy products (mixed).
Level of mechanization: Manual labour only for small backyard fields. Families without cattle borrow or hire
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
Cropland: 1-2 ha (families without oxen), 2-5 ha (families with one pair of oxen), 5-15 ha (families with over five oxen)
Grazing land: 5-15 ha, 15-50 ha, 50-100 ha
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- communauté/ village
- individu, sans titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- accès libre (non organisé)
- individuel
- Apportioned by traditional rulers
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- accès libre (non organisé)
- Apportioned by traditional rulers
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Quantité avant la GDT:
3tons/ha
Quantité après la GDT:
5tons/ha
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to early planting
production fourragère
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Residues needed for soil cover
risque d'échec de la production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Better resistance
surface de production
Quantité avant la GDT:
2-3ha
Quantité après la GDT:
>10ha
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to increased production area and improved yield
diversité des sources de revenus
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
More time and labour freed for other activities
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to mechanised planting and herbicide use
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to incresed yields
situation sanitaire
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Improved nutrition due to crop diversification
possibilités de loisirs
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Less time spent on farm operations
institutions communautaires
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Farmers trained through cooperatives
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to incresed soil Carbon, crop residues to reduce run off, and capacity building
apaisement des conflits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to competition with neighbours cattle for crop residues
livelihood and human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The technology was only introduced recently and not yet widely adopted to make an impact. However the few farmers that have adopted have been able to multiply their production capacities and incomes.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
récolte/ collecte de l'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to better soil cover
ruissellement de surface
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to better soil cover
drainage de l'excès d'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Improved soil structure
nappes phréatiques/ aquifères
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to good drainage
évaporation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to better soil cover
Sols
humidité du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to better soil cover
couverture du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to non-inversion tillage
perte en sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
encroûtement/ battance du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
compaction du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to deep tillage
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
salinité
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to good drainage
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
diversité animale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to soil organic matter (SOM) buildup
contrôle des animaux nuisibles/ maladies
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Resistance to chemical weed control
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
émissions de carbone et de gaz à effet de serre
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to Carbon (C) sequestration
Autres impacts écologiques
Ground water contamination
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Some chemicals get carried down the profile
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
disponibilité de l'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Only if applied over an extensive area
flux des cours d'eau fiables et stables en saison sèche
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Only if applied over an extensive area
inondations en aval
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Only if applied over an extensive area
envasement en aval
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Only if applied over an extensive area
dommages sur les champs voisins
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | pas connu |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | bien |
| tempête de vent locale | pas connu |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | pas connu |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
Timely and quicker planting enables larger areas to be planted and with less labour in the short term. Improved soil structure and soil fertility leads to higher yields and better resilience to droughts in the long term.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- > 50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
7 households in an area of 0.1 - 1 km2 (field size 1 ha - 30 ha)
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 91-100%
Commentaires:
7 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: These farmers heard of the technology by word of mouth and solicited for the technology even before it could be officially promoted
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Even before promotion, inquiries to purchase the strip planter have been overwhelming. This is most likely due to the ability to till, plant and fertilizer in one operation.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Enables early planting How can they be sustained / enhanced? acquire more than one strip tillage implement |
|
Quicker planting enables planting of larger areas How can they be sustained / enhanced? Plant the seed and apply the fertilizer in one opperation |
|
Lighter to pull enabling deeper penetration of the tillage tool increasing the rooting depth How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use in moist soils |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Enables early planting How can they be sustained / enhanced? Plant with the first heavy rain in November |
|
Quicker planting enables planting of larger areas How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use herbicides because without them, the capacity to weed will limit the production capacity |
|
Preserves soil cover and reduces soil disturbance How can they be sustained / enhanced? Training in residue management (No Burning) and use of zero tillage implement |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The purchase price of the strip tillage planter | subsidizing the strip tillage implement |
| Excessive weeds and lack of information on herbicide use | More training on herbicide use |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The purchase price is high making it affordable only to the larger small-scale farmers | It is already by far the cheapest planter available but mass production can lead to significant reduction in purchase price |
| Benefits are more evident on a scale larger than many farmers capacity especially when used in combination with herbicides | Support farmers to increase capacity |
| Difficult to control weeds in the absence of herbicides | make herbicides more available at a lower cost |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Social-economic analysis of conservation agriculture in southern Africa, FAO, 2011
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
FAO
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Conservation farming in Zambia, Steven Haggblade, Gelson Tembo, October 2003
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
INDABA project, Michigan State University
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes en ligne
Titre/ description:
Conservation farming in Zambia, Conservation farming unit (CFU), 2011
URL:
cfu@zamnet.zm
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Participatory Research and Development [Zambie]
This is a collaborative process between researchers and farmers for developing and adapting new technologies that focus on incorporating the perspectives and inputs from the farmers into the development process.
- Compilateur : Arthur Chomba
Modules
Aucun module trouvé