Combined cut-and-carry and fruit-production system with terraces [Tayikistán]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Christian Wirz
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Зина бох (tajik for terrace garden)
technologies_1406 - Tayikistán
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - SuizaNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - Kirguistán1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST (documentados usando WOCAT)

State-controlled research territory for orcharding [Tayikistán]
Cultivation of an orchard with research activities and research staff with food for work.
- Compilador: Christian Wirz
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
A combination of fruit- and nut-trees together with seminatural trees and shrubs on one side with grass-communities on the other side provide for a diversified production system.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
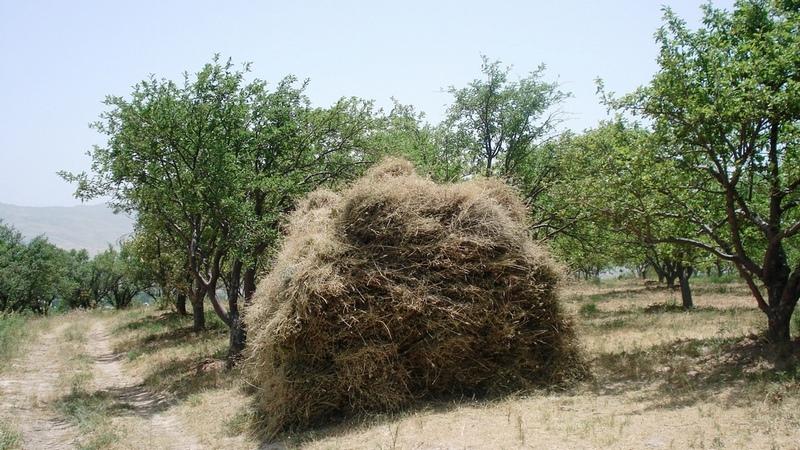
Fruit- and nut-trees give the production system the characteristics of an orchard, whereas sour cherry trees rather provide for a jungle atmosphere. They spread very quickly once they are planted. Hayproduction substitutes other uses of the lowest vegetation layer, since grazing is forbidden. The whole territory is concipied as a research station.
Purpose of the Technology: In general trees act against erosion: By their stabilising function they prevent soil from being washed out. Especially nut-trees with their 20 to 25 m long roots preserve soil moisture and by that consolidate soil structure. Terraces contribute to this moisture-preserving and production-enhancing function. They are very important in order to make rather steep land exploitable by reducing slope. Haymaking does not damage soils, but is only allowed after the end of June so that grasses can reproduce before.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Both the establishment of terraces and the planting of trees on such a big surface are costly in terms of labour and money. Maintenance means taking care of trees, taking measures against diseases and conserving soil fertility. Fertilisers are very costly and therefore dung has been substituting them in the last years.
Natural / human environment: From the two research stations of the orchard institute - one in the upper hill-zone and one close to the village Karsang - only the second one is assessed. This area is surrounded by two rivers in the West and in the East, with its main exposition to the South. It is in direct competition for irrigation water, especially needed for the trees, with the village. The orchard is situated on a ridge that is in the haymaking area, but is accessible for animals from the village.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Tayikistán
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Region of Republican Subordination
Especifique más el lugar :
Faizabad
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si se desconoce el área precisa, indique el área aproximada cubierta:
- 0.1-1 km2
Comentarios:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.7 km2.
Of the 70 hectares nearly half of the surface can be considered as unproductive with protective functions against erosion (many sour cherry trees planted).
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- 10-50 años atrás
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante la innovación de usuarios de tierras
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
1961 the national orchard institute began with developing a research area in Karsang, which should be further enlarged from 1975 onward.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha de árboles y arbustos
Cultivos de matorrales y arbustos - Especifique cultivos:
- frutas, otros
- frutas de hueso (durazno, albaricoque, cerezos, ciruelas, etc)
- frutos secos (castañas, pistachos, nuez, almendras, etc.)
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 270 Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Jul

Tierra de pastoreo
Pastoreo intensivo/ producción de forraje:
- Cortar y llevar/ cero pastoreo
- Access for livestock forbidden.
Comentarios:
Livestock density (if relevant):
< 1 LU/km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The main problems are arid conditions and the loss of fertility, mainly by processes of water erosion.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Gully erosion by water and wind erosion together with droughts are the main problems. Gullly erosion may also be caused by
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: Access for livestock forbidden.
Grazingland comments: People have goats, sheep and cows and 1-2 donkeys, if they can afford.
Type of grazing system comments: People have goats, sheep and cows and 1-2 donkeys, if they can afford.
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Comentarios:
Water supply: post-flooding
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- cobertura de suelo/ vegetal mejorada
- variedades vegetales/ razas animales mejoradas
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas vegetativas
- V1: Cubierta de árboles y arbustos

medidas estructurales
- S1: Terrazas

medidas de manejo
- M2: Cambio de gestión/ nivel de intensidad
Comentarios:
Main measures: vegetative measures, management measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie
- Wg: erosión en cárcavas

erosión de suelos por viento
- Et: pérdida de capa arable

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)

deterioro físico del suelo
- Pc: compactación
- Pk: desmoronamiento y encostramiento
- Pi: sellado de suelo

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
Comentarios:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Et: loss of topsoil
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Pc: compaction, Pk: sealing and crusting, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: change of seasonal rainfall (According to agronomist and elderly persons steady decrease of rainfall Causing aridification..), droughts (No considerable precipitation for one and a half years. Causing compaction, crusting and aridification.), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (The lack of fertilisers and other inputs is a consequence of the breakdown of URSS.)
Secondary causes of degradation: floods (Causing gully erosion and loss of topsoil by water.), war and conflicts (Many trees were chopped illegally during war to have energy (charcoal mines were occupied by armed men)), Unsuitable soils especially in the upper part (loe (Causing compaction, crusting and loss of topsoil by wind.), Steep topography with high sun inclination angle (Causing compaction.)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
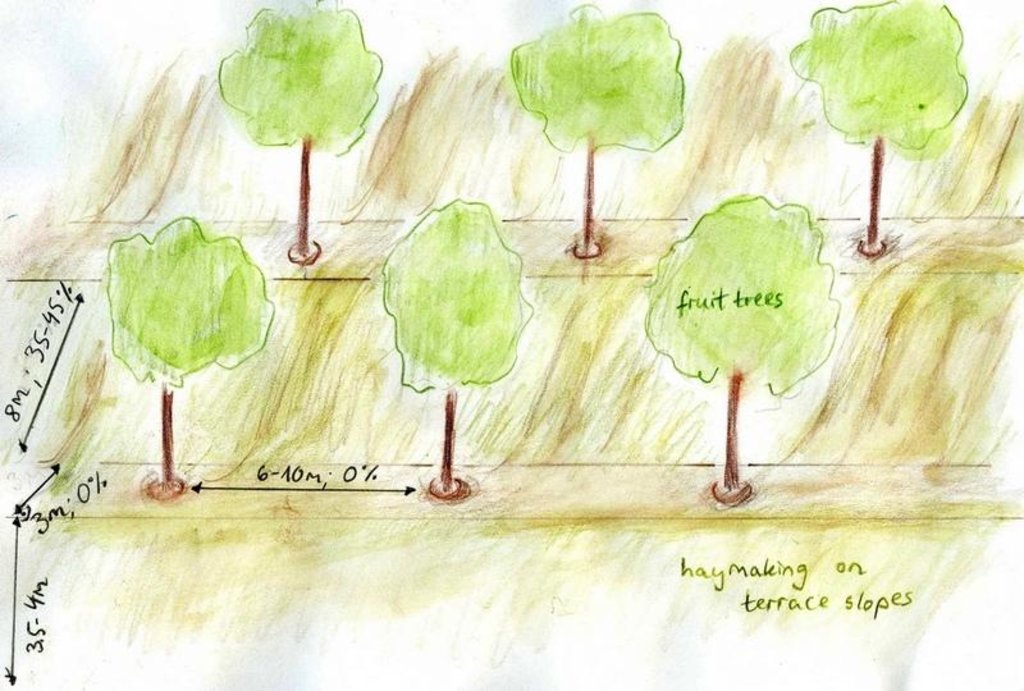
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
Terraces with fruit trees.
Location: Karsang. Faizabad / Tajikistan
Date: 25.08.09
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Cutting trees and maintaining tree nurseries)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Fieldwork such as haymaking)
Technical knowledge required for Research coordinator: high (Carrying out of workshops)
Main technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, reduction in wind speed, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity), control of fires, trees protect from snow
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 120
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 9
Trees/ shrubs species: Apple, apricot, almond, walnut, quince, pear, peach trees
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Sour cherries, mostly through vegetative growth
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 45.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.00%
Terrace: bench level (earth)
Vertical interval between structures (m): 2.5
Spacing between structures (m): 11
Construction material (earth): endogenous material used
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 33-45%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 0%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Strictly regulated haymaking, only after the end of June.
Autor:
Christian Wirz, Switzerland
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- USD
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
0.70
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting of trees with provenance from Russia and Ukraine | Tree plants |
| 2. | Tree-planting, grafting, giving dung | 20 persons for 3 years |
| 3. | Terrace establishment | 2 tractor drivers for 1 year |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Tree planting | ha | 1,0 | 714,0 | 714,0 | |
| Material para plantas | seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | |
| Otros | Terrace establishment | ha | 1,0 | 614,0 | 614,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 1428,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 1428,0 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
research stations of the orchard institute
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 36 month(s)
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Yearly replacement of fruit-trees (10-15% per year) | 10 persons plus brigadier, always employed |
| 2. | Aerating soils around trees, each spring | 10 workers, fix employment |
| 3. | Applying animal dung and / or fertilisers | 10 workers, fix employment |
| 4. | Seasonal workers for harvesting | 10 workers, additionally |
| 5. | Planning of activities | 1 director |
| 6. | Haymaking | 1 month |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Maintenance | ha | 1,0 | 93,0 | 93,0 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 28,0 | 28,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 121,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 121,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
The data on the establishment of the orchard are an estimation of the director. The recurrent costs are based on the director's and other person's declarations and are rather a rough estimation than a precise list of the costs.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
The costs today are strongly determinated by labour input, whereas during establishment and till the end of USSR costs for pesticides, fertilisers, new trees and equipment were very high.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
In the long-term average, 600-650 l, but in the years 2007 / 2008 only 200 l, since no rains in autumn.
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Altitudinal zonation: The orchard is located between 1300-1500 m.
Landforms ridges: A part of the area surrounds a ridge
Landforms hill slopes: Generally slopes are of moderate steepness.
Slopes on average gentle: The terraces themselves are quite flat.
Slopes on average hilly: A great share of the area are slopes, either natural ones or from terraces.
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
- baja (<1%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil depth on average shallow: In the higher part stony soils prevail.
Soil fertility low: When gypsum and loess soils.
Soil fertility medium: In the lower part soils with little humus.
Soil drainage / infiltration good: 3-4 m infiltration capacity.
Soil water storage capacity medium: Thanks to trees not low.
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
pobre/ ninguna
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Availability of surface water: Insufficient: only permitting to irrigate 5 ha of totally 30 ha classified as "irrigated cropland"
Water quality (untreated): According to expert, water contains iodine, but is otherwise "light" and clean, without calcium carbonate
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- elevada
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
Typical plants of the foothills can be found in the area.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Ingresos no agrarios:
- > 50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- empleado (compañía, gobierno)
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
100% of the land users are average wealthy and own 100% of the land (all smallholders owning additional income by the work for the institute).
Off-farm income specification: Nearly all people have family members (mostly sons) in Russia, who send remittances.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
Comentarios:
The employees produce hay on maximally 7 ha.
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- estado
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- comunitarios (organizado)
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
Comentarios:
Whereas land use rights are restricted to those employed by the research institute, water use is negotiated between the research institute and the village authorities.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
The reason is the decision not to plant wheat anymore, partly because of droughts and partly because of the trees having reached a critical height (shadow).
producción de forraje
calidad de forraje
Comentarios/ especifique:
Animals eating this fodder give more milk.
producción de madera
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua para irrigar
Comentarios/ especifique:
On the neighbour-ridge no irrigation water.
demanda de agua para irrigar
Comentarios/ especifique:
Trees require more water than simple pastures, especially in the establishment period.
Ingreso y costos
ingreso agrario
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Comentarios/ especifique:
Especially fruit production is important, to make jams, dried fruits etc. for winter.
situación de salud
Comentarios/ especifique:
The milk is of better quality and leads to less sicknesses
mitigación de conflicto
Comentarios/ especifique:
The institue is in conflict with the village for irrigation water.
Open-access pasture-area
Comentarios/ especifique:
No strong effect, because it is a research territory.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
escurrimiento superficial
Comentarios/ especifique:
Is especially a function of cover and infiltration capacity
Suelo
humedad del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Plants are greener and less dusty thanks to moisture
cubierta del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Plants are taller, wider and denser.
pérdida de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Thanks to strongly reduced erosion, organic matter is conserved
encostramiento/ sellado de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Less crusting than without technology, but more than without droughts.
salinidad
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to lacking drainage system
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
More nutrients given, for example by the trees' leaves.
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
diversidad vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
More than 50 pasture species
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
riesgo de incendio
Comentarios/ especifique:
Forest administration considers the proportion of trees to be one of the decisive factors of fire-risk.
velocidad de viento
Comentarios/ especifique:
High proportion of trees leads to longer snow cover and thus soil protection in spring
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
sedimentos transportados por el viento
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | bien |
| tormenta de viento | no muy bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | no muy bien |
Comentarios:
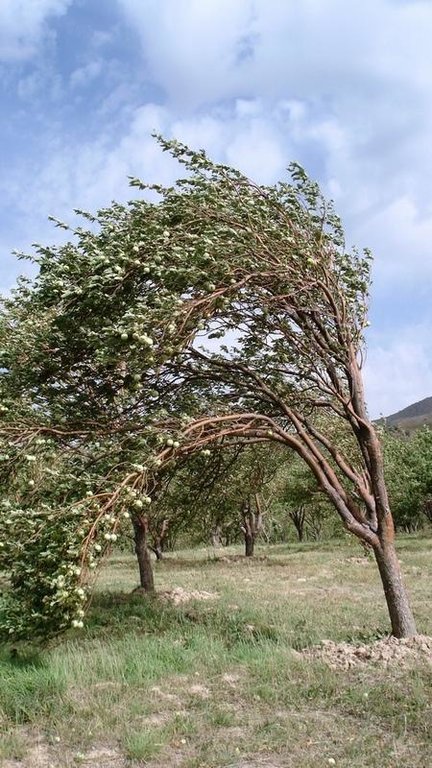
No damages by heavy rainfall in the orchard, whereas next to it there is damage. Especially winds cause damages by covering vegetation with dust and impeding them from making fotothynthesis. Plants can die therefore.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- casos individuales / experimentales
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 0-10%
Comentarios:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The government wants more people to adopt the technology and their has effectively been an increase of such initiatives over the last years.
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

State-controlled research territory for orcharding [Tayikistán]
Cultivation of an orchard with research activities and research staff with food for work.
- Compilador: Christian Wirz
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos