Reduced pressure on forest resources by improved thermal insulation in private houses [Tayikistán]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Roziya Kirgizbekova
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Alexandra Gavilano, Deborah Niggli, Joana Eichenberger
Central Asian Countries Initiative for Land Management (CACILM/ИСЦАУЗР)
technologies_1459 - Tayikistán
- Resumen completo en PDF
- Resumen completo en PDF para imprimir
- Resumen completo en el navegador
- Resumen completo (sin formato)
- Reduced pressure on forest resources by improved thermal insulation in private houses: 4 de enero de 2017 (inactive)
- Reduced pressure on forest resources by improved thermal insulation in private houses: 19 de julio de 2017 (inactive)
- Reduced pressure on forest resources by improved thermal insulation in private houses: 20 de agosto de 2019 (inactive)
- Reduced pressure on forest resources by improved thermal insulation in private houses: 2 de noviembre de 2021 (public)
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Zevarshoev Rustam
Retail Cooperative "Zindagi"
Tayikistán
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Central Asian Countries Initiative for Land Management (CACILM I)Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST (documentados usando WOCAT)

Access to thermal insulation through micro loans [Tayikistán]
Provision of small scale loans for private households to ensure access to thermal insulation (in the frame of CACILM).
- Compilador: Roziya Kirgizbekova
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
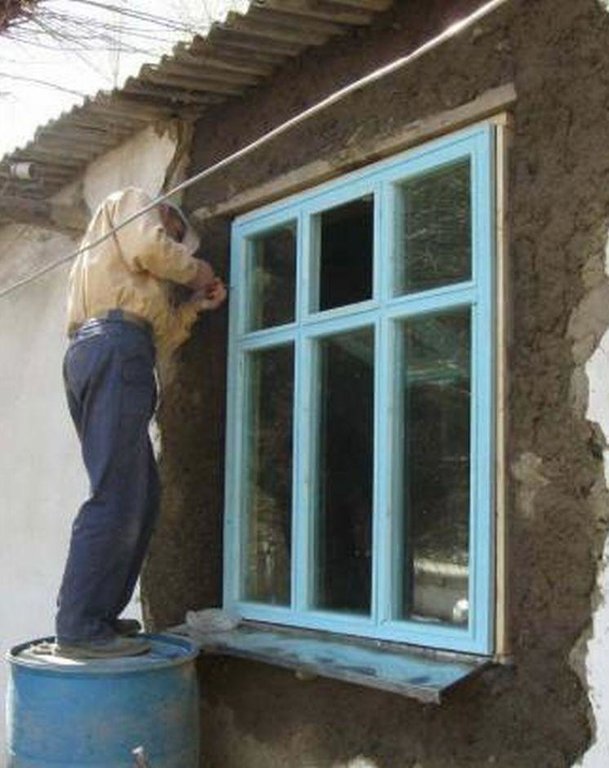
Thermal insulation of private houses with energy efficient products to reduce the fuel-wood demand and pressures on the natural environment.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
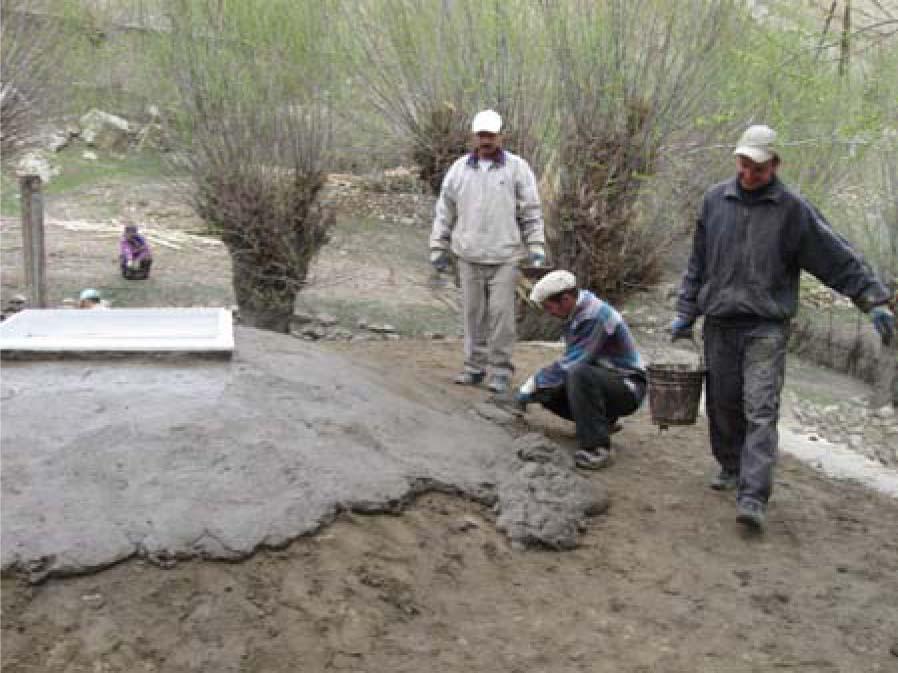
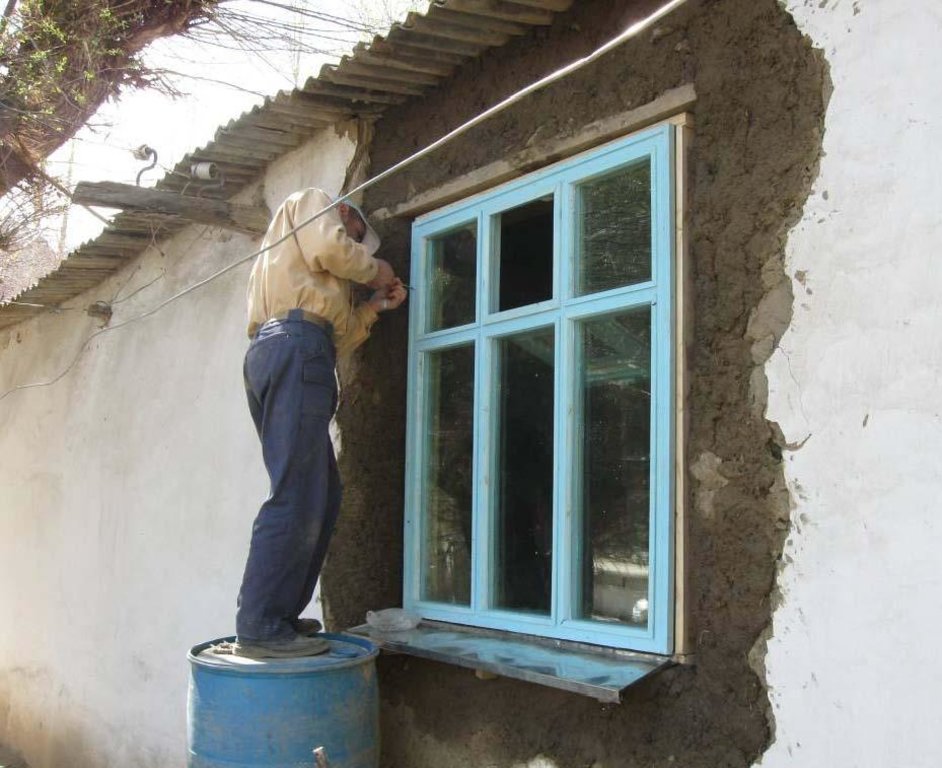
Well insulated doors and windows are installed together with thermal insulation of the ceilings and floors in houses in the remote villages of the Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Region. Improved quality windows and doors, as well as improved thermal insulation of the houses contribute to retain the heat inside, which is one of the main problems in many of these traditionally built houses. The quality of the materials used to produce the products as well as the quality of the product itself and its installation process are ensured through using locally trained craftsmen. Local available organic materials such as sawdust, straw, water plants, leaves and others can be used as thermal insulation material for walls, floors and ceilings. The materials should be dry and free of insects. The local labour market plays a crucial role in the technical accurate performance of the thermal insulation measures. Therefore the local labour market has to be analysed and training needs for the craftsmen have to be defined, e.g. for producing double-glazed windows and improved doors, as well as insulating walls, ceilings or floors, and the installation of windows and doors in accordance to the defined and standardised thermal insulation measu
Thermal insulation contributes to the reduction of heat exchange between indoors and outdoors and therefore may have two main effects: Less fuel may be needed to heat the houses, or using the same quantities of fuel the temperature indoors can be significantly increased. A reduction in fuel consumption means a reduction either of financial expenses or of labour, so the saved money or time can be used for other purposes - ideally for making investments and creating additional income sources. Higher and more constant indoor temperatures can contribute to a reduction in health risks and to increased quality of life during the winter period. Going beyond the level of the individual household, a reduction in fuel consumption means less pressure on natural resources: The less firewood that is used for heating, the less trees will be cut down and the less the forests will degrade. Also the less manure that is burnt in the stoves means more of it can be used as fertilizer on the arable land. In this framework many of the economical, social and environmental problems could be mitigated if houses were properly insulated.
A technical assessment of the identified house for thermal insulation is carried out to investigate which materials are used for the construction of the house, and to identify measures and materials that could be used for thermal insulation purposes, in order to be able to offer the most technically appropriate solution, which is adapted to the local cultural and climatic conditions. The organic thermal insulation material should be prepared in advance to make sure it is dry and clean. The designated area whether it is the floor, ceiling or walls should be cleared of furniture and other things items. Electric wires should be safely removed, or covered adequately for safety reasons to prevent fire. In the case of the roof, the insulation material is laid out evenly on the surface to a thickness of 15-20 cm depending on the type of organic material which is used. The lime is then spread out over the organic insulation material. For 1 m2 about 1-1.5kg of lime is required. The material is thoroughly tamped down to reduce subsidence of the protective cover, which will be put over the insulation material. A mixture of clay, straw and water is prepared to form a substance with a solid consistency to prevent the surface from cracking when it dries. This clay and straw mixture is then spread evenly on the surface about 4-6 cm thick, ensuring that the whole insulation material is covered. The surface should dry in 24 hours after which some cracks might appear and if this happens then a liquid mixture of clay and sand is used to flatten the area left to dry again. The same process is applied to the floors, and the more complex roof thermal insulation materials where roof felt is used as a basis for the organic insulation material as it is moisture proof. The windows and doors as well as these insulated areas in the house should be properly maintained. It should be ensures that there are no leaks in the roof so that the ceiling insulation is kept dry.
Riparian forests in the Western parts of Gorno-Badakhshan and Teresken shrubs on the high plains in the Eastern parts are almost completely destroyed due to their excessive use as a fuel for heating and cooking, and their overuse as areas for pastures. Manure, as one important natural fertilizer for agriculture, is no longer available in large quantities and so the fertility of soil has decreased. In the Eastern Pamirs, although the area is scarcely populated, Teresken shrubs have been used excessively as a fuel and are no longer found within 70km around the only major settlement of Murgab, which has resulted in massive soil erosion and degradation of pastures in this area. The situation is worsened by the fact that the local, mostly traditionally built houses are poorly insulated, low quality doors and windows do not preserve the heat inside during severe cold temperatures. Constant heating is thus necessary meaning households burn large amount of natural fuel resources to keep their houses warm. The thermal insulation technology should contribute to ease the pressure on the natural resources in the GBAO area and allow natural regeneration of forests and Teresken shrubs.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Tayikistán
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Tajikistan, Gorno Badakhshan Autonomous Oblast (GBAO)
Especifique más el lugar :
Roshtkala, Shugnan, Murgab and Ishkashim
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si se desconoce el área precisa, indique el área aproximada cubierta:
- 100-1,000 km2
Comentarios:
The technology was implemented in several regions of GBAO.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
The technology was developed and introduced through GIZ project. Gradually Retail Cooperative "Zindagi", established by GIZ is taking the project over.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- crear impacto económico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Bosques
- Bosques/ zonas boscosas (semi) naturales
Bosques/ zonas boscosas (semi-) naturales: Especifique tipo de manejo:
- Tala selectiva
Productos y servicios:
- Madera
- Leña
- Frutos y nueces
- Pastoreo/ ramoneo

asentamientos, infraestructura
- Energía: gasoductos, líneas eléctricas
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Due to a shortage of energy sources, wood, teresken and manure are extensively used for heating private houses; natural resources are therefore severely overused, which has resulted in degraded land, destroyed forests and lack of natural fertilizer for agriculture; poor thermal insulation of houses also leads to increased demand for fuel.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Unable to heat their houses properly during cold winters; shortage of fuel for cooking and heating; during cold winters, fire wood becomes so scarce that even fruit trees are cut down.
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?

asentamientos, infraestructura
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- tecnologías de eficiencia energética
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas vegetativas
- V5: Otros

medidas estructurales
- S11: Otros

medidas de manejo
- M2: Cambio de gestión/ nivel de intensidad
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
- Bq: reducción de la cantidad/ biomasa
- Bs: reducción en la calidad y composición/ diversidad de las especies
Comentarios:
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Exploiting forest resources for heating and cooking.), poverty / wealth (Most people can't afford to buy other fuel such as coal or gas.), Lack of finances
Secondary causes of degradation: change in temperature (Extremely cold winters force people to cut down excessive amounts of wood for fuel), change of seasonal rainfall (Less precipitation), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Heavy periods of rainfall), population pressure (Population growth leads to increasing demand for wood for fuel.), Destroyed infrastructure
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
This diagram with photos shows the different thermal insulation measures.
Location: Ishkashim. Ishkashim, GBAO, Tajikisatan
Date: 26-02-2011
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (Increased technical knowledge)
Technical knowledge required for craftsmen: high (Increased skills in producing well insulated doors and windows.)
Technical knowledge required for construction workers: high (Advanced skills in installation of thermal insulation products.)
Main technical functions: increase of biomass (quantity), Reduced heat loss from houses, Reduced fuel consumption
Secondary technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Change of land use practices / intensity level
Autor:
Tajikistan
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
somoni
Si fuera relevante, indique la tasa de cambio de dólares americanos a la moneda local (ej. 1 U$ = 79.9 Reales Brasileros): 1 U$ =:
4,6
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Installation of window 1.40x1.30 | Any time |
| 2. | Installation of door 2.00x0.90 | |
| 3. | Thermal insulation |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | labour | ha | 1,0 | 17,0 | 17,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | door | ha | 1,0 | 133,0 | 133,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | window | ha | 1,0 | 126,0 | 126,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Isolation material | ha | 1,0 | 126,0 | 126,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 402,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 87,39 | |||||
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
Comentarios:
The labour costs are indicated for installation of one window/door. With regards to the thermal insulation the labour costs are higher, so they are calculated per square metre of the area where thermal insulation will be applied.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
The costs for the installation of windows and doors depends on their size and also whether additional work has to be done to fit the door or window hatch to the required size. With regards to the thermal insulation the costs are estimated based of the size of the area in square metres, whether it is the floor, ceiling or wall.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
In Murghab District annual rainfall is below 200mm. Around Khorog annual rainfall is 480mm.
Zona agroclimática
- árida
Thermal climate class: temperate, boreal
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
- baja (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
bueno
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- elevada
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- > 50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- pobre
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3% (If creditworthy, they can participate through micro-loans schemes.).
Off-farm income specification: The majority of households rely heavily on remittances from Russia.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- estado
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- arrendamiento
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de forraje
calidad de forraje
producción animal
Ingreso y costos
ingreso agrario
Comentarios/ especifique:
Save money from buying fuel and electricity
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
Comentarios/ especifique:
Income of craftsmen increased.
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Less time needed for fire wood collection
Impactos socioculturales
situación de salud
Comentarios/ especifique:
Warmer houses reduce health risks.
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios/ especifique:
Improved knowledge on energy efficiency and insulation measures.
mitigación de conflicto
situación de grupos en desventaja social y económica
Comentarios/ especifique:
Opportunity to improve living conditions and save money.
contribution to human well-being
Comentarios/ especifique:
In general, people save money on energy sources and spend less time collecting wood and animal dung from the field. Houses are warmer, which can be beneficial for the family's health.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
escurrimiento superficial
evaporación
Suelo
humedad del suelo
cubierta del suelo
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
Up to 45% less wood used for fuel.
diversidad vegetal
diversidad de hábitats
Comentarios/ especifique:
In Murghab District teresken used as fire wood is the main fodder for wild animals (e.g. deer, gazelles)
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
corriente confiable y estable fluye en estación seca
Comentarios/ especifique:
Protection of riparian forests.
inundaciones río abajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Protection of riparian forests.
capacidad de amortiguación/ filtrado
sedimentos transportados por el viento
daño a campos de vecinos
daños a infraestructura pública / privada
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | bien |
| tormenta de viento | no se sabe |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | no se sabe |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | bien |
| Extreme cold temperatures | bien |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
Comentarios:
168 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
The households take a micro loan with an affordable low interest rate to install thermal insulation products. The micro loan is not provided in the form of cash, but in kind, i.e. the products and installation.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: When one household installs quality windows or doors or has its house insulated, the effects are visible not only to that given household but also to neighbours and other visitors. As a result the number of people interested in installing such technology to their homes is increasing.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Costs of firewood reduced |
| Warm and comfortable houses |
| Reduced workload |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| If implemented on a larger scale can prevent overuse of natural resources for fuel. |
| Incentives in form of micro loans to make the technology more accessible to local people. |
| Reduced workload and costs spent on buying fuel. |
| Imported timber used to produce doors and windows. |
| More fertilizer available. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Lack of skilled craftsmen | Improved professional craftsmen education through training courses. |
| Lack of modern equipment to produce wooden products | Financial support to supply the local craftsmen with modern equipment to further improve the quality of the products and increase the rate the production process. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
24/01/2011
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Access to thermal insulation through micro loans [Tayikistán]
Provision of small scale loans for private households to ensure access to thermal insulation (in the frame of CACILM).
- Compilador: Roziya Kirgizbekova
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos