Livestock Urine Collection and Use [Etiopía]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: GERBA LETA
- Editores: Kidist Yilma, Julia Doldt, Noel Templer, Tabitha Nekesa, Ahmadou Gaye, Siagbé Golli
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Sally Bunning
Yeshint Madaberya
technologies_6623 - Etiopía
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
usuario de la tierra:
Shone Wachara
Farmer
Etiopía
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
CIAT International Center for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT International Center for Tropical Agriculture) - Kenia1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
Comentarios:
The technology replaces the chemical fertilizer, urea, to restore soil fertility and improve vegetative growth and crop production. Also, it serves as a pesticide to manage insect pests.
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST (documentados usando WOCAT)

Integrated Soil Fertility Management (ISFM) [Etiopía]
The Integrated Soil Fertility Management (ISFM) approach has been adopted under the Integrated Soil Fertility Management Project (ISFM+). It was introduced as a quick-win solution to increase both crop and biomass production through the incremental promotion of varied but complementary technology packages.
- Compilador: GERBA LETA

Farmer-Research-Extension Group (FREG) [Etiopía]
Farmer-Research-Extension Group (FREG) is a grass root level platform aims to bridge gaps on agricultural technology transfer between research and extension linkage and provide a platform of 20-30 members from research, extension and farmer for their joint learning and active participatory role in agricultural technology evaluation and dessimination.
- Compilador: Gizaw Desta Gessesse
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Collection of livestock urine allows resource-poor farmers to capture nutrient-rich livestock waste and use it to substitute urea fertilizer. It is a liquid organic product that restores soil fertility and pest management.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
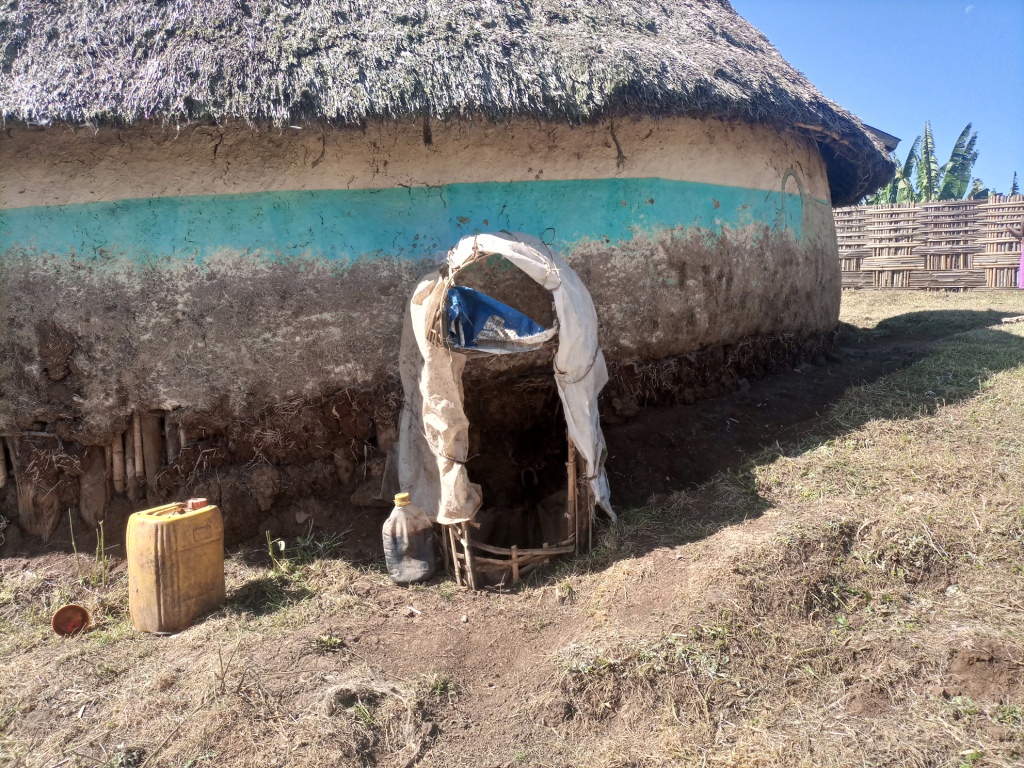
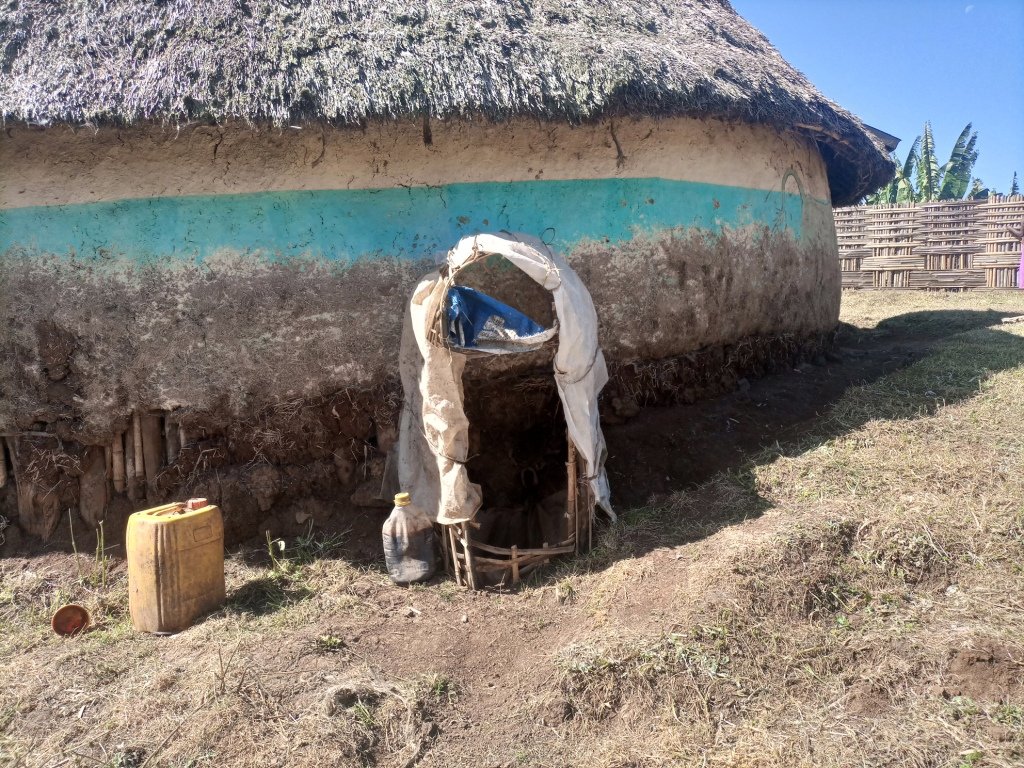
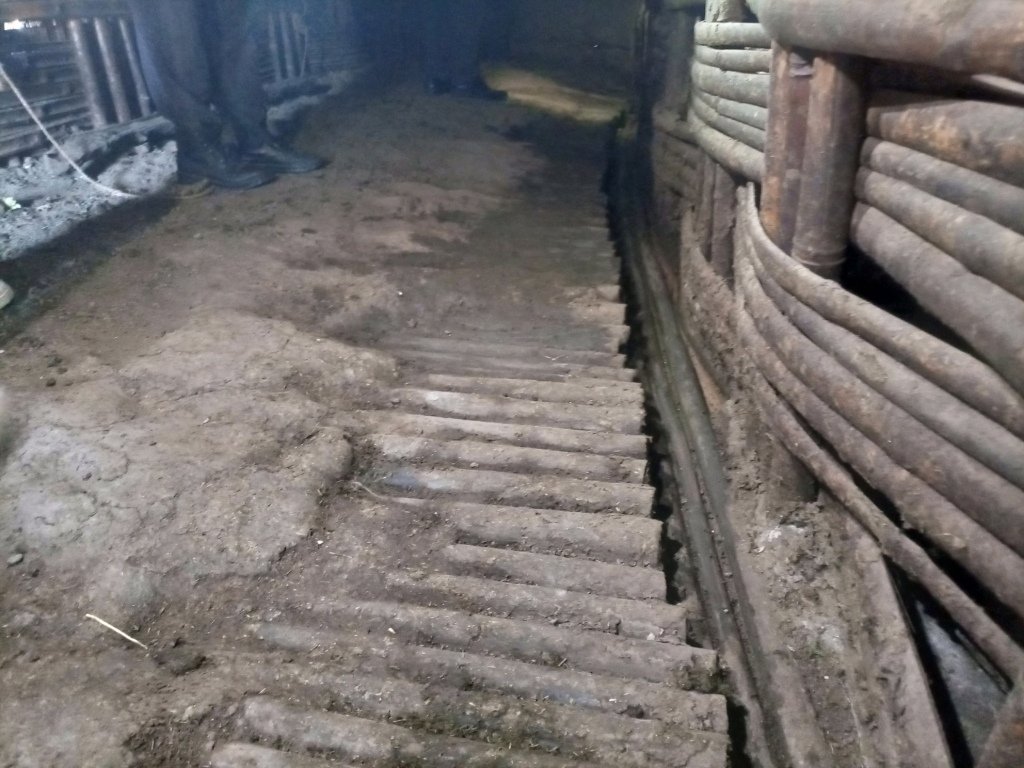
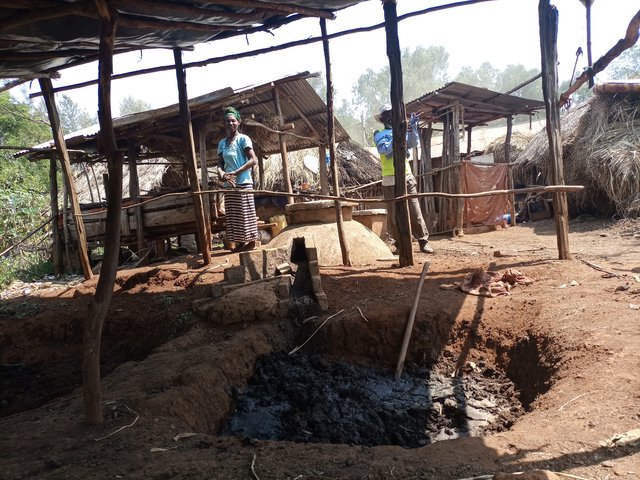
Enset, the “false banana”, is a perennial that grows well under the supply of organic fertilizers (farmyard manure, urine, compost and other household refuse). In the enset farming system, farmers traditionally shelter their livestock behind a partition within the main house. They construct a sloping floor in the livestock stall to allow the urine to drain into a narrow channel that leads to nearby enset and vegetable plots. However, construction of a collection chamber on the outlet side is an innovative approach which allows for better use of the urine. The collected urine fertilizes annual crops such as barley, maize, and vegetables - notably kale, carrots, and onions, via foliar and basal applications. Land users collect and preserve the urine for about 15 days before applying it to the target crops for the intended purposes. The urine is also used for pest management such as aphids and cutworms. According to the land user interviewed about 20 litres a day can be collected from six cattle. This implies the potential to collect about 7 cubic metres a year by a farmer: a considerable resource that should not be lost when there is an urgent need to restore soil fertility given ongoing and severe problems with land degradation. Therefore, urine collection and storage can be a way of reducing substantial investment in chemical fertilizers. To learn and showcase the benefits of urine as a replacement for urea fertilizer, a farmer sprayed 80 litres of urine twice onto 600 m2 of a ISFM+ barley demonstration plot. The sprayed amount replaced the equivalent of 6 kg urea that currently costs about 300 ETB.
Housing animals enables the collection of a reasonable quantity of urine to restore the soil fertility at the homestead and on the farm. Locally available bamboo helps to construct partitions and stall floors for the livestock as well as serving as a pipeline to drain the urine into a collection chamber. The benefits of applying urine goes beyond simply urea replacement, and its potential is merely limited by land users knowledge, skills, and motivation. These can be acquired via training, demonstration, exchange visit, and social learning. Land users like the role of urine in restoring soil fertility and boosting production. Furthermore, urine serves as integrated pest management via targeted application, deterring insects. However, the smell of the urine is unpleasant and may deter farmers from its use as they do not have safety clothes or masks to use when spraying the crop.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
Comentarios generales sobre las fotos:
The photo portrays the floor orientation and the livestock partition/ stall drainage canal that leads urine to the collection chamber outside the house.
2.4 Videos de la Tecnología
Comentarios, descripción breve:
Video for this technology was not captured.
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Etiopía
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Sidama
Especifique más el lugar :
Tuticha Kebele 01
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- aplicada en puntos específicos/ concentrada en un área pequeña
¿El/los sitio(s) de la Tecnología se ubica(n) en un área de protección permanente?
No
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2022
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante la innovación de usuarios de tierras
- como parte de un sistema tradicional (> 50 años)
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
Purely collecting and using urine for target application to the crop as a replacement for urea fertilizer was introduced by ISFM+ of the GIZ. However, land users used to drain slurry of manure and urine from livestock stall to the nearby enset farm. Land users forge spraying vessels and collection pits lined with plastic materials and temporary shade to urine collection points.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación del suelo
- conservar el ecosistema
- preservar/ mejorar biodiversidad
- crear impacto económico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
No

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
- Cultivos perennes (no leñosos)
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cultivos para forraje - pastos
- cereales - cebada
- vegetales - verdura de hojas verdes (ensaladas, repollo, espinaca, otros)
- leguminosas y legumbres - arvejas
- cultivos de raíces/ tubérculos - patatas
- False banana (enset)
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 2
Especifique:
Belg (short rain) and Meher (long rain).
¿Se practica el intercultivo?
No
¿Se practica la rotación de cultivos?
Sí
Si fuera el caso, especifique :
Cereals, like barley, rotate with legumes (such as field peas or faba beans).
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- No (Continúe con la pregunta 3.4)
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Comentarios:
Bimodal rainfall is received twice yearly (short rain Mid-February to Mid-April, and prolonged rain from June to September).
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- manejo de agricultura—ganadería integrada
- manejo integrado de la fertilidad del suelo
- manejo integrado de pestes y enfermedades (incl. agricultura orgánica)
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A2: materia orgánica/ fertilidad del suelo

medidas de manejo
- M7: Otros
Comentarios:
Crop protection: it plays the role of Integrated Pest Management (IPM).
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación del suelo encarados con la Tecnología

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)

degradación biológica
- Bq: reducción de la cantidad/ biomasa
- Bp: incremento de pestes/ enfermedades, pérdida de depredadores
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación del suelo
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- reducir la degradación del suelo
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
Comentarios:
The nitrogen in urine stimulates the growth of various crops and non-crop wild species and restores degraded and potentially degradable lands.
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
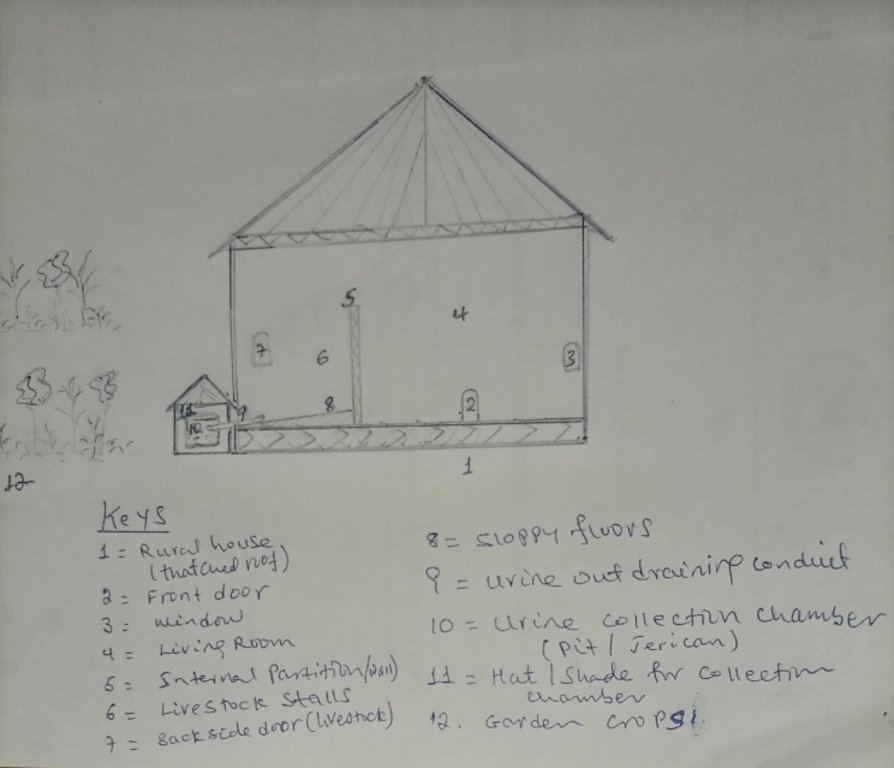
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
The urine collection chamber is set up adjacent to the rural house on the side of livestock stalls. It receives urine that drains out of the sloping floor intentionally constructed using stone or bamboo to drain the liquid wastes through conduit directly to the collection chambers. A ditch that is placed adjacent to the outlet also takes the slurry to the nearby farm/garden. The dimension of the collection chamber and the types of materials used to establish the technology varies depending on resource availability or the number of livestock held by the land user. Other materials such as concrete pits or pits lined by google membranes can be used. Furthermore, jerrican or clay pots are the other alternative tools to collect urine. The different local materials replace the use of expensive materials. Small protective caps over the chamber is recommendable to protect the collected urine from rain and the heat of the sun that triggers the volatilization loss of urea. It is also possible to note additional information from the associated keys to describe the sketch.
Autor:
Gerba Leta
Fecha:
30/03/2023
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por unidad de Tecnología
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
ETB
Si fuera relevante, indique la tasa de cambio de dólares americanos a la moneda local (ej. 1 U$ = 79.9 Reales Brasileros): 1 U$ =:
53,6283
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
500
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construct collection chamber | Dry season |
| 2. | Construct hats or covering lid for the chamber/collection pit | Dry season |
| 3. | Lining drainage line heading to the pit with concrete | Dry season |
| 4. | Storage vessels/barrel | Anytime |
| 5. | Supplying safety clothes (wear, boots, gloves and mask) | In advance |
Comentarios:
Urine collection chambers, lids or roofs, storage vessels, safety wears, and spraying tools are essential for collecting, storing, and further treating urine before use.
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Casual labor | no. | 4,0 | 250,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Carpentering | no. | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 50,0 |
| Equipo | Safety wears (shirt & trousers, gloves, mask, boots) | Lump sum | 1,0 | 3000,0 | 3000,0 | |
| Equipo | Watering cane | no. | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Effective Micro Organism | Litre | 2,0 | 100,0 | 200,0 | 50,0 |
| Material de construcción | Cement | kg | 100,0 | 20,0 | 2000,0 | 50,0 |
| Material de construcción | Stone | m3 | 1,0 | 2000,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Corrugated iron | pcs | 2,0 | 1000,0 | 2000,0 | 50,0 |
| Material de construcción | Posts and nails | Lump sum | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 50,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 13200,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 246,14 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
ISFM+ of the GIZ
Comentarios:
For the model farmer who pilots livestock urine collection for soil amendment and management of pests, supporting the construction of a standard collection chamber and supplying associated kits helps to train and facilitate scaling of the technology in the best way. Effective Microorganisms (EMO) is an input being tested to investigate whether it has the property of changing the stink of the urine collected for storage and use on the farm.
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Effective Microorganisms | Throughout collection and application |
Comentarios:
The use of EMO to change the bad smell of urine, particularly during storage and application needs to be further investigated to prove and use it to reduce the abhorred side of collecting and applying urine for soil amendment and pest management.
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | EMO | Litre | 6,0 | 100,0 | 600,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Family labor | no. | 52,0 | 100,0 | 5200,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 5800,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 108,15 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
NA
Comentarios:
With the assumption that the land user can collect, treat and use about 140 liters of urine per week for different crops, family labor can be used at a lower rate as it is not a full-day operation. Despite our estimation, material and labour costs change in Ethiopia persistently because of market instability and economic crisis that is not uncommon since the outbreak of COVID-19 in 2020.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Economic crisis, spiking inflation, and overall labour and material market cost instability.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Receive bimodal rainfall with a summer maximum.
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
The rainfall distribution is nearly consistent. The temperature is cold typical of highland weather conditions.
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- no relevante
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
The topography is unremitting ups and downs.
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Not available
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
mediana
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
La calidad de agua se refiere a:
agua subterránea y superficial
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
No
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Surface and groundwater quality in the highland areas of Sidama region was not suggested as an issue. Rather, surface water can be polluted by soil erosion before the crops cover the ground.
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
Diversidad de hábitats:
- baja
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
The technology is piloted around the homestead. Agriculture is highly intensified in the area. Hence, only plantation forest or peripheral plants such as Eucalyptus species are the common tree species. This signals medium to lower species diversity that similarly applicable to habitat diversity.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
Género:
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- personas de mediana edad
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
The land user doesn't have off-farm income. He generates his livelihood from 2 hectares of land and a few livestock.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
Comentarios:
Farming is operationalized by hoes (hand-dug) to grow cereal crops. Otherwise, enset culture demands hand digging.
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- estado
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
¿Los derechos del uso de la tierra se basan en un sistema legal tradicional?
Sí
Especifique:
The land was inherited from the family line. However, the adopted national constitution declared land belongs to the state and the users. Thus, usufructs issued by the government to the land user.
Comentarios:
In Ethiopia, the 1995 constitution declared the land as state property but the farmer has usufructs right. As a result, the certificate was issued except in the pastoralist areas of the country. Of course, most people inherited specific plots of land from their lineage, though there was frequent land redistribution during the Derg and early years of the EPRDF regime.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
Comentarios:
Although they mentioned the quality of both ground and surface water is good in the preceding section, the level of sanitation is not significant as the resident use water from the springs for drink and other household activities.
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Cantidad antes de MST:
70 kg from 0.12 hectare of land.
Cantidad luego de MST:
400 kg from the same land.
Comentarios/ especifique:
With the application of ISFM+ approach and urine as a replacement for Urea, a substantial yield increment was achieved.
calidad de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
As the technology is at its early stage of implementation where documentation is not well organized, it was impossible to quantify the harvest and quality of the crop.
manejo de tierras
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Comentarios/ especifique:
As urine complement urea fertilizer, other nutrients from Sulfur, Phosphorus and other micro nutrients remain important.
ingreso agrario
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
situación de salud
oportunidades culturales
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Crop response to urine application is an evidence based for adoption of the SLM technology.
Impactos ecológicos
Suelo
humedad del suelo
cubierta del suelo
pérdida de suelo
acumulación de suelo
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
Not practically measured and documented. Besides, the technology is at earlier phase to judge the real impacts.
acidez
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
Cubierta vegetal
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
diversidad de hábitats
control de pestes/ enfermedades
Comentarios/ especifique:
It has tangible impacts on managing pests.
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
emisión de carbono y gases de invernadero
Comentarios/ especifique:
As a foliar application of urine to the target crops might be subjected to evaporation, if not good hours of the day are not identified, there is a likelihood of emission. However, its amount is very insignificant as the little amount used for foliar feeding.
Especifique la evaluación de los impactos en el sitio (mediciones):
The on-site assessment is made based on conceptual knowledge of the beneficial effects of collecting and applying livestock urine as a replacement to urea fertilizer and the farmer and experts' knowledge on the fertilizer and pesticidal effects of liquid urine. Otherwise, careful documentation of various types of data is commendable to quantify and properly address such comprehensive questions included in the questionnaire.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
inundaciones río abajo
colmatación río abajo
contaminación de aguas subterráneas/ de ríos
Comentarios/ especifique:
The impact has not yet measured.
impacto de gases de invernadero
Especifique la evaluación de los impactos fuera del emplazamiento (medidas):
As an optimum application of urine substitute urea fertilizer, it favors the growth of diverse plant species, positively contributing to the overall ecosystem services and reducing degradations. However, it has not been empirically measured.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| lluvia estacional | estación húmeda/ de lluvias | disminuyó | moderadamente |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | no se sabe |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| período extendido de crecimiento | bien |
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | moderadamente |
Comentarios:
The technology has no direct influence on climate change/climate variability in the short term.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
Post-establishment, the maintenance costs are believed to be very low. This shows the technology is cost-effective to resource-poor farmers.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- 1-10%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
Forty-four (44) farmers are currently piloting this technology. Of these, 30 farmers are innovative and adopted the technology on their own using locally available materials to collect and spray urine as a complement to urea fertilizer to the target crops.
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 51-90%
Comentarios:
Thirty farmers represent the most significant portion who spontaneously took up the technology.
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
Sí
otros (especifique):
Unavailability of the right kits/materials
Especifique la adaptación de la Tecnología (diseño, material/ especies, etc.):
Land users use locally available materials to collect, store and spray the urine on the target crops. Meaning the concept is introduced in a way it matches or complements conventional uses of livestock wastes to improve the fertility of soil on which Enset, a perennial crop is growing. Otherwise, standard designs or types of materials and safety precautions kits have not been associated with the technology. Despite the unavailability of the necessary kits for the establishment of the technology, farmers forge their mechanisms to collect and use urine. This indicates the innovativeness of the land/technology users.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Reduce costs spent on chemical fertilizer. |
| Increase yield per unit of land and land users' income in general. Furthermore, it increases the number of tillers per plant and overall biomass yield. |
| Manage insect pests such as cutworms and aphids. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| It seems a good substitute for chemical fertilizer, urea. It improves farmers' access to wasted resources without being used. |
| It restores the fertility of the soil and improves production and productivity, and species diversity which improves ecological benefits on top of the high return from the most minor investment in fertilizer. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Bad smell of the urine when sprayed on the target crops. | By ensuring access to necessary tools. Otherwise, they will not give up on using it since the benefit outweighs the loss. |
| Lack of spraying materials. | If not accessed spraying tools, the farmer committed to using locally forged ones. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Stinking of the urine while applying to the crop. | Try to test whether using Effective Micro Organism (EMO) can improve urine smell before using it in the field. |
| Lack of safety wear and associated necessary kits. | Improving access to the necessary materials, knowledge, and skills to use the available resources or materials effectively. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
Four (4) persons, including a land user.
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
A farmer
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
Three (3) persons (district expert, regional SLM specialist, and ISFM+ regional advisor).
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
14/01/2023
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Use of Cow Urine in the Field of Agriculture. Singh, R. 2022
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
http://www.pashudhanpraharee.com/use-of-cow-urine-in-the-field-of-agriculture/
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Utilization of urine waste to produce quality cauliflower. Khanal, A., Shakya , S. M., Shah, S. C., Sharma, M. D. 2011.
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
https://www.nepjol.info (Free access)
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
Nitrogen concentration in the urine of cattle, sheep and deer grazing a common ryegrass/cocksfoot/white clover pasture. Doi.org/10.1080/00288233.2010.499899
URL:
https://www.tandfonline.com
7.4 Comentarios generales
Not every question in the questionnaire is relevant to the Livestock urine collection for soil amendment and integrated pest management practices. Urine collection and use does not address every kind of land degradation stated in the questionnaire. However, it directly or indirectly addresses some of the SLM-related issues.
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Integrated Soil Fertility Management (ISFM) [Etiopía]
The Integrated Soil Fertility Management (ISFM) approach has been adopted under the Integrated Soil Fertility Management Project (ISFM+). It was introduced as a quick-win solution to increase both crop and biomass production through the incremental promotion of varied but complementary technology packages.
- Compilador: GERBA LETA

Farmer-Research-Extension Group (FREG) [Etiopía]
Farmer-Research-Extension Group (FREG) is a grass root level platform aims to bridge gaps on agricultural technology transfer between research and extension linkage and provide a platform of 20-30 members from research, extension and farmer for their joint learning and active participatory role in agricultural technology evaluation and dessimination.
- Compilador: Gizaw Desta Gessesse
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos