Rotational grazing to restore degraded pastures [Afganistán]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Bettina Wolfgramm
- Editores: MIAJAN MAROOFI, Hekmatullah Sharifzai, Roziya Kirgizbekova, Aslam Qadamov
- Revisor: William Critchley
Ploni ba navbat charonidani mol ba khotiri behbudi charogoh
technologies_671 - Afganistán
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Researcher:
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar, Afghanistan (LIPT)Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Potential and limitations for improved natural resource management (NRM) in mountain communities in the Rustaq district, Afghanistan (Rustaq NRM Study)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Terre des Hommes (Terre des Hommes) - SuizaNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (DEZA / COSUDE / DDC / SDC) - SuizaNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suiza1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
17/10/2016
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST

Watershed Associations (WSA) and Natural Resource Management Committees … [Afganistán]
Two Watershed Associations (WSA), in Chaker and Nahristan watershed areas respectively, are registered at the national level with the Ministry of Agriculture Irrigation and Livestock (MAIL) and at the regional level with the Department of Agriculture. Both associations are strong, active, dynamic, and have the capacity to coordinate and support …
- Compilador: Bettina Wolfgramm
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
A plan for rotational grazing has been developed to control pasture use and prevent overgrazing of rehabilitated pastures.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
Livestock keeping is one of the key livelihood strategies in rural Rustaq, in addition to cultivation of cereals. Families rely on their livestock not only for consumption of meat from cattle, goats and sheep, and dairy products such as milk and sour milk, but also as means of transportation (donkeys), labour in agriculture (oxen, donkeys) and as a source of income through sales. Naturally, every family strives to increase their household’s livestock as much as they can, which increases the pressure on the local pastures - leading to extensive overgrazing. The pastures in Jawaz Khana and Sari Joy are characterized by poor vegetation cover, low carrying capacity and severe erosion with deep rills clearly visible. Heavy rains in spring and autumn wash off the topsoil on pastures, resulting in heavy erosion, landslides and gully formation. These severely degraded pastures continue to be used though "open access" - without any management schemes or regulations in place. Some pastures that are not suitable for grazing have been converted to arable lands and tree plantations. The quantity and quality of livestock fodder is insufficient for all the livestock, and this affects animal health.
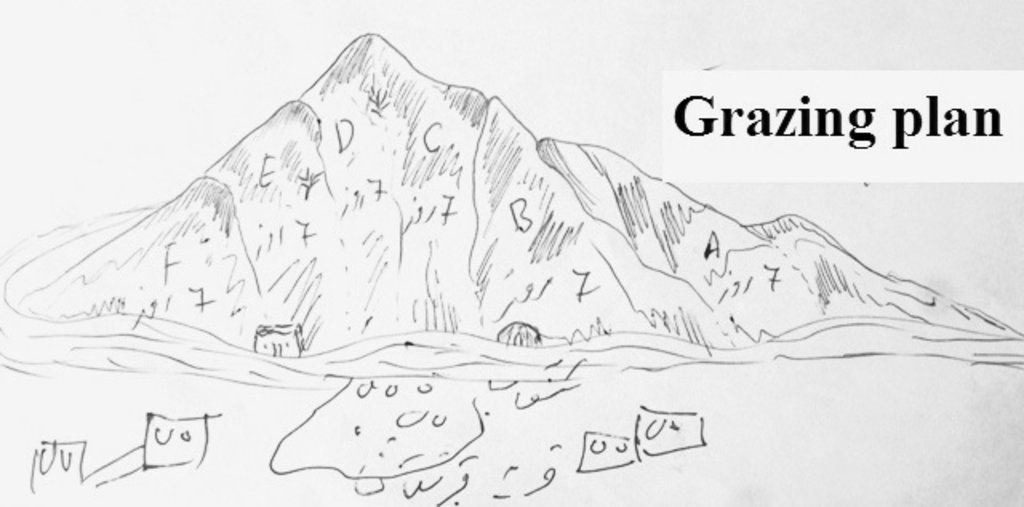
Plans for rotational grazing were prepared for the communities in Sari Joy and Jawaz Khana to organize the use of local pastures and prevent their further degradation. Rotational grazing plans regulate the frequency and intensity of livestock grazing on the pastures. The area is seeded with alfalfa to improve the fodder stock and enhance the quality of the pasture. For up to three years the seeded area is closed to grazing, during which period the community is provided with stocks of hay and straw to feed their livestock as an alternative. After the end of the closure period, the grazing area is divided into 6-7 sections (paddocks) depending on the area of the pasture. The livestock graze the first paddock for 7 days and move to the next paddock. Each paddock is grazed for the period of 7 days during April and May. From the month of May the grazing area is closed for resting. The livestock move to the summer pastures for the rest of the summer months.
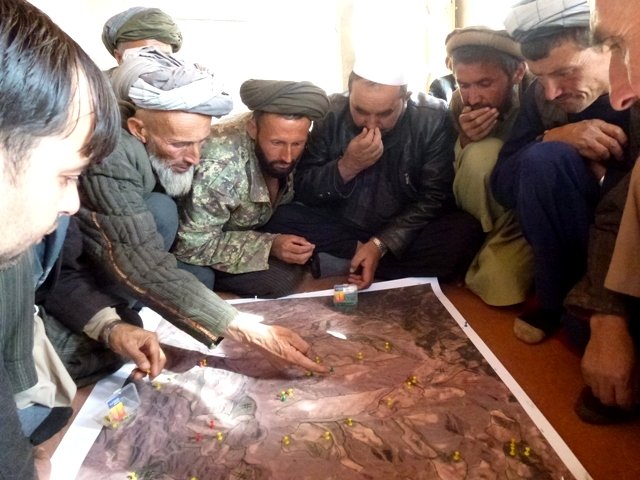
The community is key in preparing the grazing plans and identifying the pastures where these plans will be applied, as well as the conditions which are part of it, such as the frequency of the grazing period. Frequent meetings need to be held with the community livestock holders to explain the purpose of the rotational grazing and how it can be beneficial in pasture improvement. The Natural Resources Management Committee and the technical staff of the Livelihood Improvement Project (LIPT) are in charge of engaging the local pasture users to meet their needs and consider their views accordingly.
The actual implementation of the rotational grazing plans is difficult to assess for the time being. The grazing area is not fully restored and the fodder stock remains low. Many land users do not fully understand the concept behind the rotational grazing plans or their purpose. In an area where there is a severe shortage of livestock fodder and very limited grazing land, accepting and following these plans will require more time and additional support in terms of awareness-raising and support feeding of the livestock during the exclusion period. The villagers have some doubts about the costs and benefits of grazing and rotation. They have no full understanding of the benefits of the rotational grazing for their household and are likely to be not ready to adhere to such schemes.
Women are part of the livestock management system, and are in charge of feeding and taking care of the livestock. However, they are not aware about the plans for rotational grazing in their village and how are these plans are applied in practice.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Afganistán
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Takhar Province, Rustaq District
Especifique más el lugar :
Sari Joy and Jawaz Khana Villages
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2015
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
Livelihood Improvement Project in Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des hommes (Tdh) Switzerland
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierra de pastoreo
Tierras de pastoreo extensivo:
- Semi-nomadismo/ pastoralismo
Pastoreo intensivo/ producción de forraje:
- Pastoreo mejorado
Especies y productos animales principales:
Cow, Sheep, Goat. Alfalfa
Si el uso de la tierra ha cambiado debido a la implementación de la Tecnología, indique el uso de la tierra antes de la implementación de la Tecnología.
Some areas under the Technology are former croplands, which have been completely degraded and no longer suitable for crop cultivation.
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- pastoralismo y manejo de tierras de pastoreo
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente en un área, indique el área aproximada que cubre:
- 0.1-1 km2
Comentarios:
6 ha
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas de manejo
- M2: Cambio de gestión/ nivel de intensidad
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie

erosión de suelos por viento
- Et: pérdida de capa arable

deterioro físico del suelo
- Pc: compactación

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
- Bq: reducción de la cantidad/ biomasa

otros
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
After the end of the exclusion period the grazing area is divided into 6-7 sections (paddocks) depending on the area of the pasture. The livestock graze the first paddock for 7 days and move to the next paddock after 7 days. Each paddock is grazed for the period of 7 days during April and May. From the month of May the grazing area is closed for resting. The livestock move to the summer pastures for the rest of the summer months.
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Indique tamaño y unidad de área:
1 ha
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- dólares americanos
Indique la tasa de cambio de USD a la moneda local (si fuese relevante): 1 USD =:
67,0
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
5.2-5.3 USD
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selection of the pasture area and awareness raising among people | Manejo | Fall |
| 2. | Leveling of the land | Agronómicas | Fall |
| 3. | Sowing alfalfa seed | Agronómicas | Spring |
| 4. | Site under quarantine | Manejo | Three years |
| 5. | Preparation of the grazing plan and community meetings | Manejo | Fall |
| 6. | Protection of the site during quarantine | Manejo | Three years |
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Leveling the land with a rake | person-day | 150,0 | 5,3 | 795,0 | 71,0 |
| Mano de obra | Sowing alfalfa | person-day | 5,0 | 5,3 | 26,5 | 71,0 |
| Mano de obra | Preparation of grazing plan | person-day | 2,0 | 9,0 | 18,0 | |
| Mano de obra | Protection of the site | year | 1,0 | 447,0 | 447,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Shovel | piece | 1,0 | 3,8 | 3,8 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Rope | Meter | 50,0 | 0,15 | 7,5 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Rake | piece | 1,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Alfalfa seed | kg | 17,5 | 0,42 | 7,35 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | DAP | kg | 125,0 | 0,9 | 112,5 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Urea | kg | 125,0 | 0,45 | 56,25 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 1476,9 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des hommes (Tdh) Switzerland
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Community agrees to leave the pasture for resting/ exclusion | Manejo | Three years |
| 2. | Rotational grazing | Otras medidas | Spring/week/grazing plot |
| 3. | Reseeding alfalfa | Vegetativas | After 5 years |
| 4. | Protection of the site | Manejo | Three years |
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Reseeding alfalfa | person day | 5,0 | 5,3 | 26,5 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Protection during exclusion | year | 2,0 | 447,0 | 894,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Alfalfa seed | kg | 17,5 | 0,42 | 7,35 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 927,85 | |||||
Comentarios:
Costs calculated for a Technology area of 1ha was only done for the purpose of the WOCAT documentation. In reality SLM plots are on average 0.4 ha or 2 jiribs. Costs were simply multiplied by 2.5. The actual costs for a 1ha plot might be slightly different.
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Due to the remoteness of the villages where the technology has been implemented, all the inputs for establishment, such as agricultural equipment, plant material, fertilizers, etc., are purchased in Rustaq town. The expenses for traveling and delivering the inputs affect the establishment costs.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Average annual precipitation for the area was calculated with 580 mm, with minimum in dry years (2000 and 2001) of 270 mm and maximum in wet years (2009/2010) of 830 mm. The absolute maximum rainfall was calculated for 1986 with 1024 mm. The data series covers the period from 1979 to 2014.
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- baja (<1%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Local land users differentiate between the following soil types where the technology is implemented:
- Red: shallow; texture medium, coarse; low organic matter
- Light: moderately deep; texture medium; medium, low organic matter
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
mediana
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
Sí
Frecuencia:
frecuentemente
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Floods occur mainly during the rainy seasons in spring and autumn. Availability of surface water differs for the villages of Sari Joy and Jawaz Khana. Sari Joy has good surface water availability. Jawaz Khana has poor water availability as water has to be fetched from a stream lower down.
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- baja
Diversidad de hábitats:
- baja
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Semi-nómada
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- pobre
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- grupos/ comunal
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
Género:
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- personas de mediana edad
- ancianos
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
The land users in the area where the Technology is applied belong to the Uzbek ethnic minority group Qarluq.
Although the men are generally the main land users, women and children also take active part in the related work. The functions of men and women are clearly distinguished within Afghan society. At the same time within the family this division of work and functions also results in men and women working hand-in-hand. An improvement of the family’s livelihood situation is expected to positively affect all family members. While, it is recognized that the involvement of women is key in order to secure basic human rights for everyone, to achieve good governance, sustainable development, and to efficiently contribute to poverty reduction (SDC 2004), it is also clear that a context sensitive approach is of high importance.
Women in rural Afghanistan are involved in many production and income generating activities that contribute to the overall household income, however, very few women own resources such as land and livestock, and their income generating options are fewer in comparison to that of men.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- escala mediana
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- comunitaria/ aldea
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- comunitarios (organizado)
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
Comentarios:
Those who own land and use water for irrigation are obliged to pay for the water. The payment is made both in kind and in cash to the Mirob - the person in charge of distributing water in the community. The amount of the payment varies from village to village.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
producción de forraje
producción animal
producción de madera
producción de productos forestales no madereros
diversidad de producto
área de producción
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
escurrimiento superficial
Suelo
pérdida de suelo
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
Cubierta vegetal
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
inundaciones río abajo
colmatación río abajo
capacidad de amortiguación/ filtrado
Comentarios acerca de la evaluación del impacto:
These comments apply to 6.1 and 6.2:
- Socio-economic impacts: Individual SLM implementers were asked to rate the benefits from the technology. They were asked to indicate production increase of crops; fodder; animals; wood; non-wood forest products; increase in prduct diversity; or production area. The most important increase they rated with 3, the second most with 2, others with 1 point. Averages of the points given by all terrace implementers are reflected here.
- Similarly for the "ecological impacts" and on "off-site impacts": Individual SLM implementers were asked to rate the on-site and off-site impacts of the technology on water; soil; and vegetation. They were asked to indicate the strength of impacts with three, two or one points. Averages of the points given by all terrace implementers are reflected here.
- Socio-cultural impacts: This section is answered by the scientists, based on information collected during focus group discussions, and interviews conducted with persons from the 3 villages where the LIPT project implemented the technology.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | muy bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Comentarios:
SLM implementers from three villages were asked to jointly discuss and rate how much the SLM technology reduced the lands vulnerability to drought and local rainstorms. Only vulnerability to the most prevalent climate extremes (drought and local rainstorms) was discussed. SLM technologies were rated as reducing vulnerability poorly, well, or very well. The average points reflected here are from multi-criteria matrixes compiled in three villages where the SLM technology had been implemented.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
SLM implementers from three villages were asked to jointly discuss and rate the SLM technologies short term (1-3 years) and long-term (10 years) return. As most of the technologies have only been implemented 1-2 years ago, it is too early to compare benefits to maintenance costs. Farmers have little experience so far on the actual benefits of the SLM technologies. The ratings are mostly based on expected benefits and not on actual benefits.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- casos individuales / experimentales
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
6 ha
Comentarios:
Rotational grazing plans are developed for common lands used by the whole village. There is one common grazing plan for each village.
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
No
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| If implemented according to the plan and the pasture area is allowed to rest, the quality and quantity of the fodder will be enhanced. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The land users have no full knowledge about the plans for rotational grazing and how they should be applied | Increase awareness raising among the land users |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
Focus group discussions were organized to collect information from SLM implementers in Sari Joy and Jawaz Khana.
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
Close collaboration took place during the compilation of this material with the technical staff of the LIPT project in Rustaq.
- compilación de informes y otra documentación existente
Information provided in the reports of Tdh LIPT Project in Rustaq served as an initial source of information during the preparatory phase and also solidifying the description of the technology and area of implementation. Other background papers on Afghanistan were referred to for general information on agriculture and natural resource management in Afghanistan.
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Guidelines for Focus Groups Discussions
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Methods section of the Rustaq NRM study
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Watershed Associations (WSA) and Natural Resource Management Committees … [Afganistán]
Two Watershed Associations (WSA), in Chaker and Nahristan watershed areas respectively, are registered at the national level with the Ministry of Agriculture Irrigation and Livestock (MAIL) and at the regional level with the Department of Agriculture. Both associations are strong, active, dynamic, and have the capacity to coordinate and support …
- Compilador: Bettina Wolfgramm
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos