SLM small grant allocation mechanisms [Tadjikistan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Nandita Jain
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano, Joana Eichenberger
approaches_2453 - Tadjikistan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de l'Approche
Spécialiste GDT:
Mott Jessica
World Bank
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
World Bank (World Bank) - Etats-Unis1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de l'Approche de GDT
2.1 Courte description de l'Approche
Mechanisms to facilitate participatory decision-making about grant allocation among land users and improve transparency and accountability in flow of funds to beneficiaries in small-grant programmes for SLM.
2.2 Description détaillée de l'Approche
Description détaillée de l'Approche:
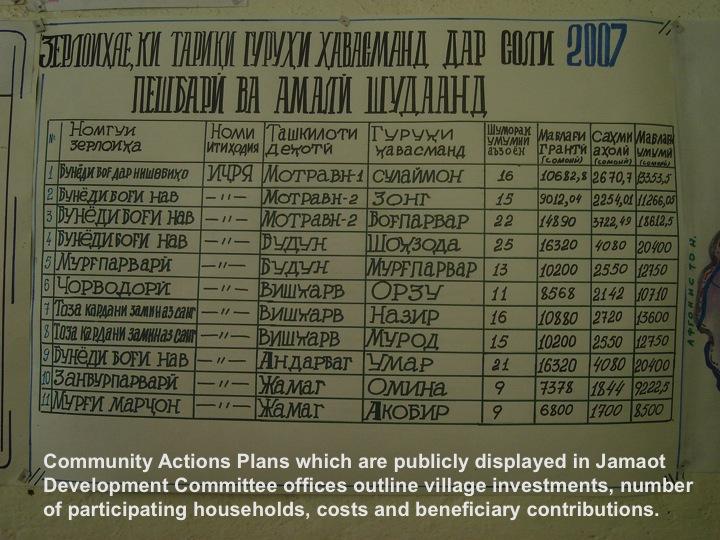
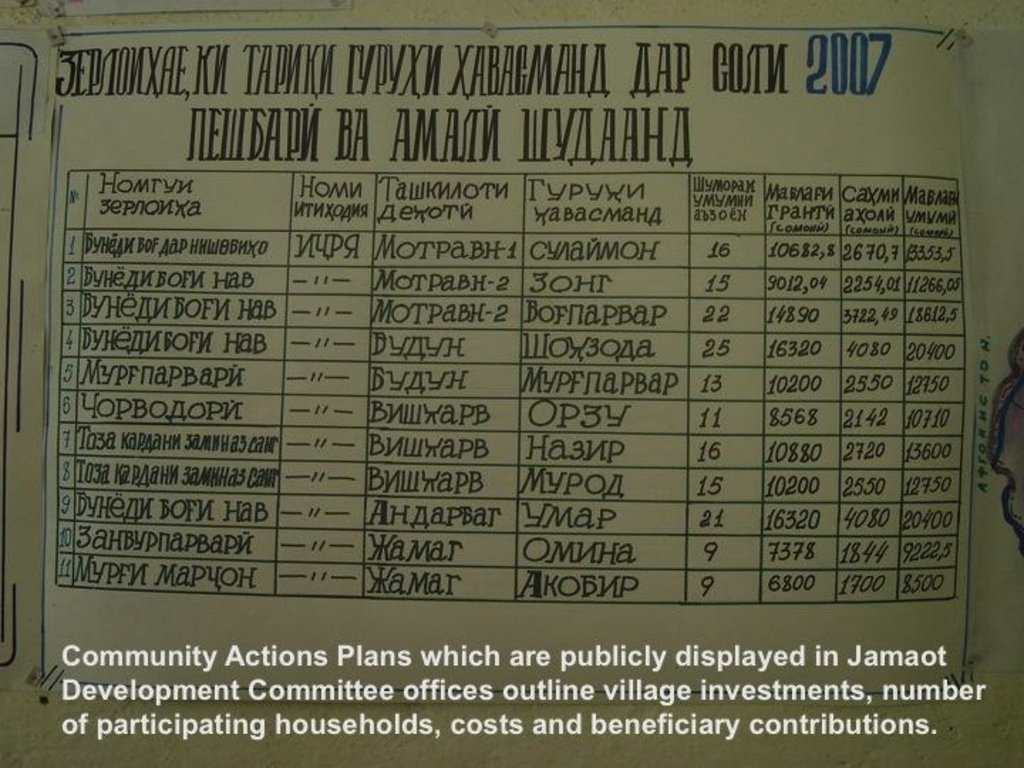
Aims / objectives: As part of the Community Agriculture & Watershed Management Project (CAWMP), this approach helped beneficiaries and project partners allocate grants and manage the flow of funding while promoting fairness, transparency, and ownership. It facilitated appropriate SLM choices across the highly variable agricultural, climatic and geographic conditions. Almost 4000 rural investments including SLM technologies were implemented, resulting in over 96,000ha under improved land management practices and benefits for more than 43,000 households in Tajikistan’s uplands.
Methods: This approach set a fixed budget per village, limited the grant value received per household as well as the total size of any one grant, required minimum levels of beneficiary contributions, and provided grant money to beneficiaries, enabling them to purchase the inputs.
Stages of implementation: Fixed village budget: In their Community Action Plans (CAP) villages assigned priorities to grants within a set budget amount for the entire village. Project guidelines specified a formula for this budget based on amounts per investment type per household excluding beneficiary contributions ($30/household for farm productivity, $74/household for land management, and $30/household for rural infrastructure). The number of households in a village multiplied by these per-household-amounts determined the overall size of the grant funding for that village. Grant allocation limits. The villages were informed of their overall budget as well as the household limits for each category. They chose investments for groups of households (Common Interest Groups, CIGs) and allocated grant funds to subprojects accordingly. The household limits ensured that collectively at least 50% of the families would benefit directly. In practice, about 75%, of a total of about 57000 households in the project sites participated in the farm productivity and land resource management investments, and 60% in rural infrastructure investments. Grant size. Except in a few cases requiring special approval, the Project-financed grants for each subproject were lower than US$5,000, which reduced risks of the funds being used for purposes for unrelated to the Project. Beneficiary Contribution. Beneficiaries were required to contribute a minimum of 25% of the grant amount in labor, materials or cash which increased their stake in the investment, thereby strengthening ownership and sustainability. At least 5% of the grant amount for rural infrastructure had to be contributed in cash at the start in order to demonstrate financial sustainability.
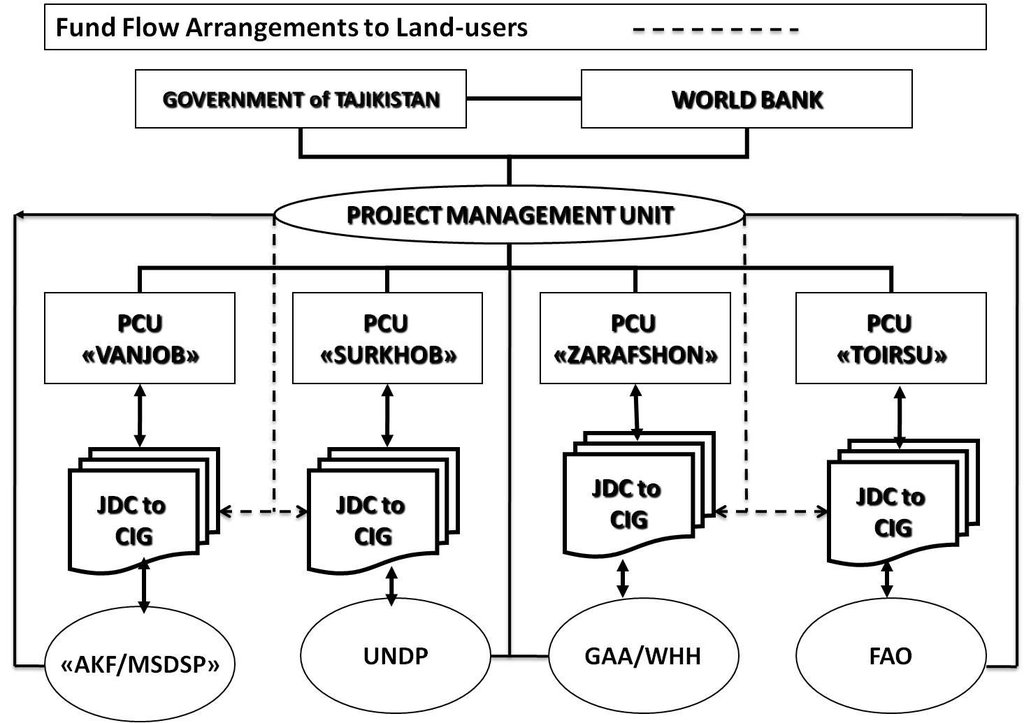
Role of stakeholders: Fund flow. Once a grant proposal was approved, the PMU transferred the grant amount to the local savings bank according to the schedule specified in the agreement between Jamoat Development Committee (JDC) and CIGs. The JDC accountant transferred the funds fromthe bank to the CIGs. The CIGs then had the responsibility for purchasing inputs, which created an incentive for selecting cost-effective inputs.
2.3 Photos de l'approche
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où l'Approche a été appliquée
Pays:
Tadjikistan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Sughd, Region of Republican Subordination, Khatlon, GBAO
Autres spécifications du lieu :
Jirgital, Tajikibad, Vanj, Aini, Matcha, Penjikent, Danghara
Commentaires:
The Community Agriculture and Watershed Management Project was implemented in four project sites/watersheds - Surkhob, Toirsu, Vanjob and Zarafshan - which included 7 districts/raions and 39 sub-districts/jamoats. The total catchment area was 35,000km2. Total arable, farm and pasture land was approximately 319,500ha.
Map
×2.6 Dates de début et de fin de l'Approche
Indiquez l'année de démarrage:
2005
Date (année) de fin de l'Approche (si l'Approche n'est plus appliquée):
2012
2.7 Type d'Approche
- fondé sur un projet/ programme
2.8 Principaux objectifs de l'Approche
The Approach focused mainly on other activities than SLM (small grant programmes, participatory decision-making, village-level, fixed budgets, fund flow arrangements, farmer groups)
Practical and feasible mechanisms for beneficiaries and project partners for: a) grant allocation and fund flow that promote fairness, transparency, and beneficiary ownership in the context of Tajikistan; and b) facilitate appropriate SLM choices across the highly variable agro-climatic and other geographic conditions of the country.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Prior to CAWMP, no practical incentives in donor-funded grant programmes for beneficiaries to consider how to optimise returns according to local conditions. Limited choice of technologies, elite capture of resources, requests for large grants and absence of beneficiary contributions led to inappropriate investments for local agro-climatic conditions, and poor returns and investments not maintained in subsequent years.
2.9 Conditions favorisant ou entravant la mise en œuvre de la(des) Technologie(s) appliquée(s) sous l'Approche
normes et valeurs sociales/ culturelles/ religieuses
- entrave
Grant allocations vulnerable to elite capture and/or political influence. Time taken to address such pressures.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Participatory planning and full disclosure at the start of planning to villagers of available funding and its calculation at village and household levels.
disponibilité/ accès aux ressources et services financiers
- entrave
Beneficiary dependence on donors/implementing agencies since resources given were “in-kind” and not cash.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Adopted “good practice” from other countries with arrangements for direct cash transfers to beneficiaries organised as groups of farmers who then had responsibility for managing financial resources and procurement for chosen investments.
cadre institutionnel
- entrave
Lack of active participation by beneficiaries in decision-making over grant amounts and choice of investments.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Innovative rules about grant allocations enabling villagers to consider various options of grant amounts and types of investments in a participatory manner, taking into account their local conditions.
connaissances sur la GDT, accès aux supports techniques
- entrave
Participatory planning processes lacked consideration of multiple factors, e.g., grant amount, choice of technologies, local context, beneficiary contribution, selection of beneficiaries.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Inclusion of participatory rural appraisal, formulae and rules governing grant allocations in CAP preparation. First 3 proposals for each investment category in project sites reviewed to assess understanding of guidelines. Random review thereafter.
3. Participation et rôles des parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche
3.1 Parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche et rôles
- exploitants locaux des terres / communautés locales
CIGs (Groups of households)
Local cultural and social conditions determined the extent to which women took part in the grant allocation decision-making, and as members of CIGs managing small grant funds. In some more remote communities, it was not generally acceptable for women to be active participants. In other areas, women only CIGs were formed.
Marginal groups within a generally poor upland rural population participated in grant allocation decisions and as CIG members in managing small grant funds. In some villages, vulnerable and poor households were targeted as priority recipients of grants through the allocation mechanism.
Participated grant allocation decision making and fund management
- ONG
JDCs – locally registered NGOs
JDCs managed fund transfers to CIGs based based on formal agreements
- gouvernement national (planificateurs, décideurs)
Project Management Unit
Si plusieurs parties prenantes sont impliquées, indiquez l'organisme chef de file ou l'institution responsable:
Project Management Unit and CIGs
3.2 Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales aux différentes phases de l'Approche
| Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales | Spécifiez qui était impliqué et décrivez les activités | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | aucun | |
| planification | passive | Potential beneficiaries consulted for social assessment conducted during project design which then influenced project approaches. |
| mise en œuvre | interactive | Villagers made grant allocation decisions. CIGs managed grant funds and bought inputs. |
| suivi/ évaluation | interactive | JDCs release grant funds according to benchmarks in formal agreements with CIGs. |
| Research | aucun |
3.3 Diagramme/ organigramme (si disponible)
Description:
CAWMP - Implementation Arrangements and Fund Flow Arrangements to Land-Users
Auteur:
Project Management Unit (Dushanbe, Tajikistan)
3.4 Prises de décision pour la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies
Indiquez qui a décidé de la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies à mettre en œuvre:
- principalement les exploitants des terres soutenus par des spécialistes de la GDT
Expliquez:
Villagers made decisions on grant amounts, types of investments and beneficiaries. SLM specialists from project partners such as FOS and PCUs assisted in choice of SLM technologies to be used for investments.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists. See 2.1.5.1. above - How were decisions on the choice of SLM technologies made. Villagers made decisions on grant amounts, types of investments and beneficiaries. SLM specialists from project partners such as FOS and PCUs assisted in choice of methods for SLM technologies to be used for investments.
4. Soutien technique, renforcement des capacités et gestion des connaissances
4.1 Renforcement des capacités/ formation
Une formation a-t-elle été dispensée aux exploitants des terres/ autres parties prenantes?
Oui
Spécifiez qui a été formé:
- exploitants des terres
- personnels/ conseillers de terrain
- JDCs
Formats de la formation:
- réunions publiques
Thèmes abordés:
Grant allocation mechanisms. Fund flow arrangements and management.
4.2 Service de conseils
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils accès à un service de conseils?
Non
4.3 Renforcement des institutions (développement organisationnel)
Des institutions ont elles été mises en place ou renforcées par le biais de l'Approche?
- oui, modérément
Spécifiez à quel(s) niveau(x), ces institutions ont été renforcées ou mises en place:
- local
Donnez plus de détails:
JDCs received financial support for certain staff, some equipment for their offices, and training (see also TAJ047 for more information on JDC roles in the project). Note-cannot select more than one type of support in the pull-down menu
4.4 Suivi et évaluation
Le suivi et l'évaluation font ils partie de l'Approche? :
Oui
Commentaires:
no. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: Grant allocation – number of beneficiaries
Grant allocation aspects were regular monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: Grant allocation - Estimated costs of rural investments
Fund flow aspects were regular monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: Fund flow - Timeliness of transfers from PMU to JDCs to CIGs,
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Delays in initial fund flow to CIGs due to a lack of details in financial management arrangements. Elaboration of manuals and training addressed this problem.
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Not directly relevant
5. Financement et soutien matériel externe
5.2 Soutiens financiers/ matériels fournis aux exploitants des terres
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils reçu un soutien financier/ matériel pour la mise en œuvre de la Technologie/ des Technologies?
Non
5.4 Crédits
Des crédits ont-ils été alloués à travers l'Approche pour les activités de GDT?
Non
6. Analyses d'impact et conclusions
6.1 Impacts de l'Approche
Est-ce que l'Approche a aidé les exploitants des terres à mettre en œuvre et entretenir les Technologies de GDT?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
The grant allocation mechanism fostered multi-factor decision-making, including consideration of local environmental conditions, by villagers. Fund flow arrangements enabled JDCs to manage about $7.4 million in small grants to about 4000 CIGs for rural production investments.
Est-ce que l'Approche a autonomisé les groupes socialement et économiquement défavorisés?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
The project population is considered generally poor or very poor. Within this population, particularly vulnerable groups participated in rural production investments.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
: Portions of the approach and associated guidelines have been adopted in other donor-funded projects.
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Mechanisms contributed to increased livelihood assets for more than 43,000 households through the implementation of about 4000 small grants.
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Target population generally considered poor or very poor. Assessment of impacts on poverty are included in the project evaluation being conducted in 2011.
6.2 Principale motivation des exploitants des terres pour mettre en œuvre la GDT
- augmenter la production
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
6.3 Durabilité des activités de l'Approche
Les exploitants des terres peuvent-ils poursuivre ce qui a été mis en œuvre par le biais de l'Approche (sans soutien extérieur)?
- oui
Si oui, décrivez de quelle manière:
Grant allocation mechanism was understood and could be used for other sources of financing for groups of households at the village level. Fund flow mechanisms will require a sub-district presence to support transfers to village-based groups.:
6.4 Points forts/ avantages de l'Approche
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| To be added based on project evaluation in 2011 |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Grant allocation mechanism easily understood and perceived to be fair and transparent. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Document application and disseminate widely.) |
| Multiple factors considered in decision-making including grant amount, choice of investment and number of beneficiaries, local conditions. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Improved environmental analyses in participatory planning would lead to more suitable choice of investments.) |
| CIG management of funds contributed to improved accountability and incentives to sustain investments. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Document and disseminate methods and results.) |
7. Références et liens
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
perational Manual for Community Mobilization, Rural Production Investments and Research and Demonstration Grants (2008)
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Project Management Unit
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Operational Manuals for JDCs and CIGs in Financial Management and Procurement (2007)
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Project Management Unit
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
CAWMP: Project Appraisal Document (2005)
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
World Bank website
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé