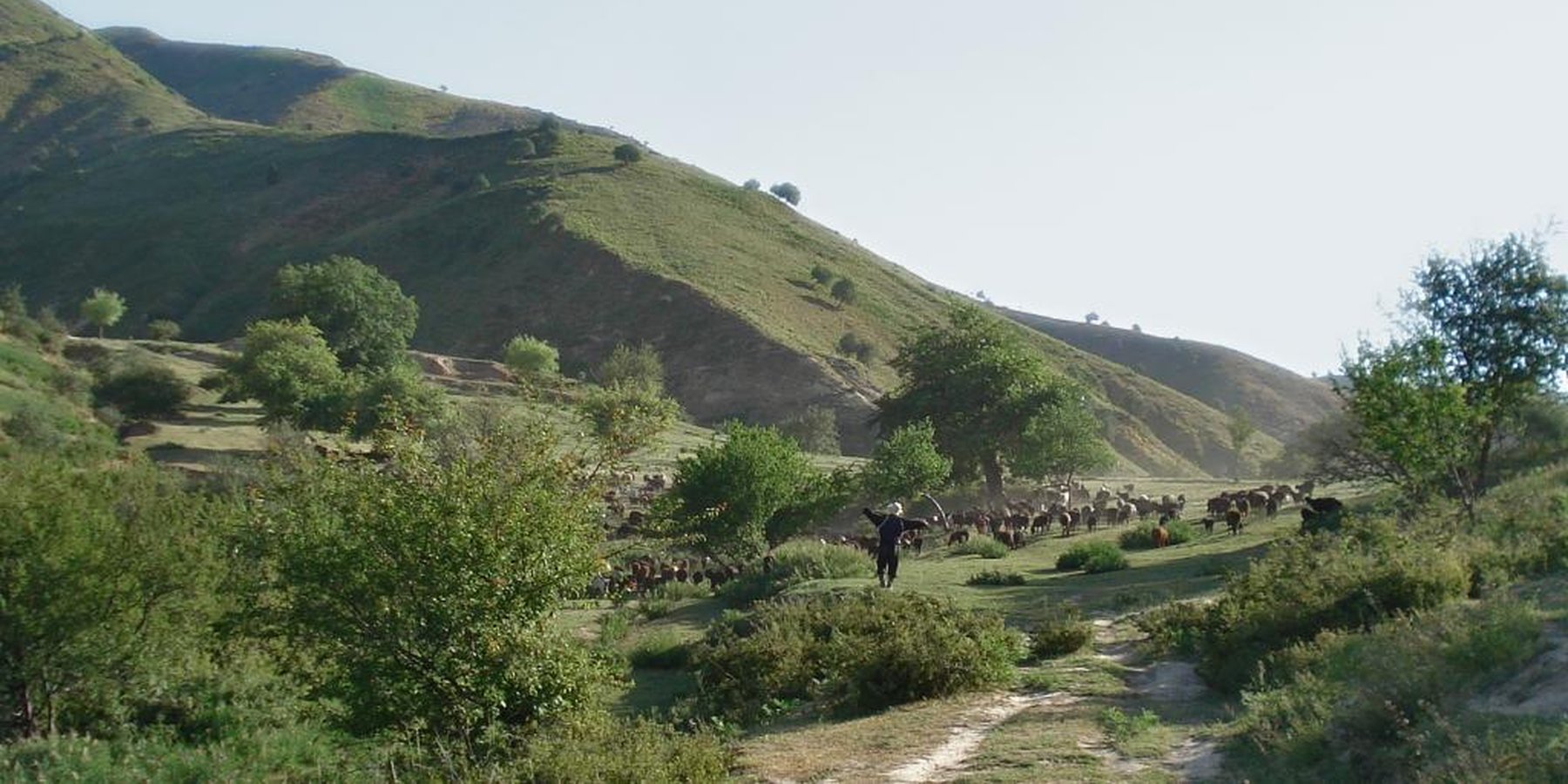
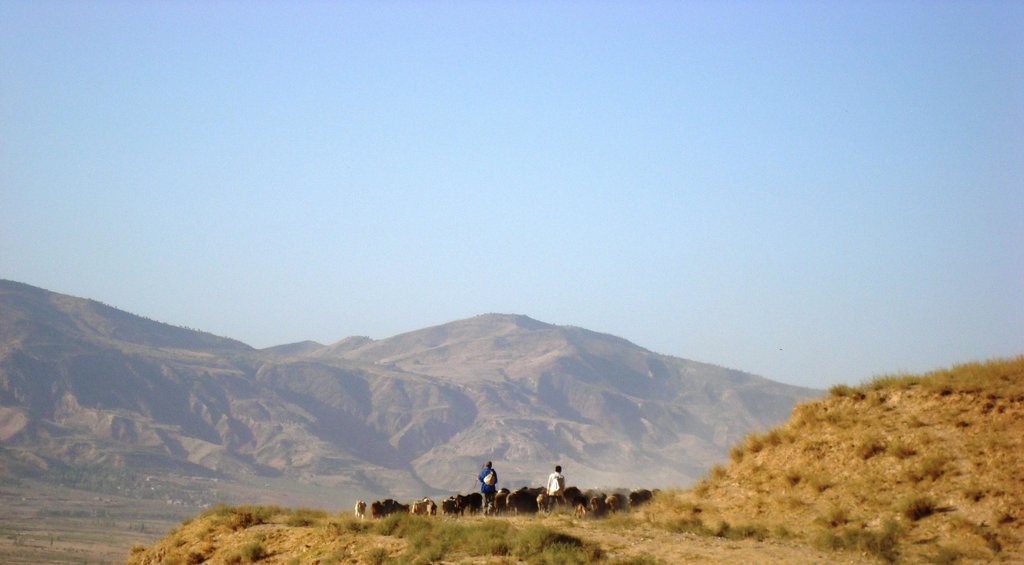
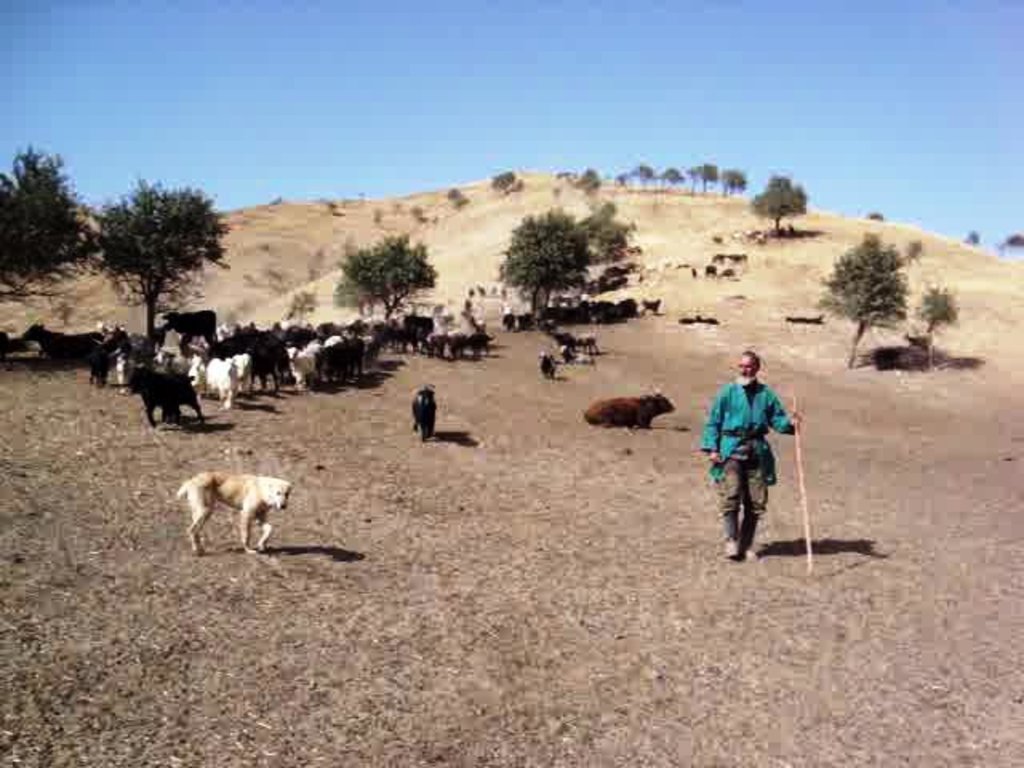
Seminomadic individual herding [Tadjikistan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Christian Wirz
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : David Streiff
Chupon / Dajmardei Khaspi (professional herding)
approaches_2565 - Tadjikistan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de l'Approche
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suisse1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
15/08/2008
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Références au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Technologies de GDT

Daily and seasonal rotation on grassland [Tadjikistan]
Extensive grazing of sheep and goats by the means of a precise rotational scheme
- Compilateur : Christian Wirz
2. Description de l'Approche de GDT
2.1 Courte description de l'Approche
Pasture management by a single herder, assisted either by an employee or by his own grandchildren, in collaboration with the habitants of the nearby village Karsang.
2.2 Description détaillée de l'Approche
Description détaillée de l'Approche:
Aims / objectives: The herder chooses his territory by the criteria of biomass, vegetation cover and availability of surface water. In his work he gives special attention to fattening the animals, to not losing any of them and to giving back the right animals to the right tenant at the end of the season. For him it is important to be sincere with the tenants and to pay for lost animals.
Methods: Every method applied serves the target of having an obeying herd. The herder works with lots of patience. In the first two weeks he pays very much attention to keeping the herd together, so the animals get used to each other. The rotational grazing scheme also fulfills the requirement of fattening the animals. Grazing the animals by night-time is a method to make the animals obey better. Part of the work is the daily control of the herd to identify sick animals and treat them.The animals are by the way not led by the herder, but rather accompanied by him.
Stages of implementation: After apprenticeship the herder is entrusted with animals from the village and with the generated income can then gradually build up his own herd.
Role of stakeholders: The herder is responsible for the relation with his animals, with the villagers and with the forest department (contract).
2.3 Photos de l'approche
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où l'Approche a été appliquée
Pays:
Tadjikistan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Region of Republican Subordination
Autres spécifications du lieu :
Faizabad
Map
×2.6 Dates de début et de fin de l'Approche
Indiquez l'année de démarrage:
1987
2.7 Type d'Approche
- traditionnel/ autochtone
2.8 Principaux objectifs de l'Approche
The Approach focused mainly on other activities than SLM (The focus of this approach is providing the own family with income and meat, by herding own and animals of other herders. It is very important for the herder to keep the animals healthy and to give them all back (the fattest possible) to their tenants.)
The herder's motivation to continue his father's work was that it enabled him to nourish his family. In his work he pays attention to fatten the animals enough to make them survive winter and to give them all back.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: The inhabitants of the village give the herder their animals because they know that the animals will be more healthy on the more natural pastures frequented by him compared with village pastures and because the animals get more reserves for winter-time. The herder claims that the animals need 50% less hay and fodder in winter than the animals grazed near the villages.
2.9 Conditions favorisant ou entravant la mise en œuvre de la(des) Technologie(s) appliquée(s) sous l'Approche
normes et valeurs sociales/ culturelles/ religieuses
- entrave
Being unable to go to parties and weddings.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: As it is not a problem for the herder (but perhaps for his wife and family?) the problem is not tackled.
disponibilité/ accès aux ressources et services financiers
- entrave
Paying for lost animals.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: As long as the herder can find the lost animal, even if it is dead, he will not have to pay for it.
cadre institutionnel
- entrave
It is necessary to have good relations to obtain land from the forest administration.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: As M. worked for the forest department for many years, it was not a problem for him to lease land.
cadre juridique (régime foncier, droits d'utilisation des terres et de l'eau)
- favorise
If tenure were more secure and land use free, M. would divide the rented land into pasture zone, orchard and cropland. This would ensure more self-sufficiency, but probably less income, because he could keep less animals on the reduced pasture area
- entrave
autre
- entrave
For M. the principal problem are bears (and wolves) killing animals.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Since he is not allowed to have a rifle to kill wild animals he has to chase them away with his dogs. This means that in summer, when the bears descend to lower areas for fruit in the orchards, he often has to keep awake by night.
3. Participation et rôles des parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche
3.1 Parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche et rôles
- exploitants locaux des terres / communautés locales
The herder himself is the protagonist. In some years he employed and educated young herders.
Si plusieurs parties prenantes sont impliquées, indiquez l'organisme chef de file ou l'institution responsable:
The herder himself implements the approach
3.2 Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales aux différentes phases de l'Approche
| Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales | Spécifiez qui était impliqué et décrivez les activités | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | auto-mobilisation | Deciding to be a herder |
| planification | aucun | |
| mise en œuvre | auto-mobilisation | Once M. knew how to treat the animals he could begin work with an own herd. |
| suivi/ évaluation | aucun | |
| Research | aucun |
3.4 Prises de décision pour la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies
Indiquez qui a décidé de la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies à mettre en œuvre:
- les exploitants des terres seuls (auto-initiative)
Expliquez:
The herder learnt his profession during an apprenticeship of one year
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by by land users* alone (self-initiative / bottom-up). M. learned all the technologies from his father, but says, that he only does his job half as well as his father.
4. Soutien technique, renforcement des capacités et gestion des connaissances
4.1 Renforcement des capacités/ formation
Une formation a-t-elle été dispensée aux exploitants des terres/ autres parties prenantes?
Oui
Spécifiez qui a été formé:
- personnels/ conseillers de terrain
Si pertinent, spécifiez le genre, l'âge, le statut, l'ethnie, etc.
Young men and boys.
Formats de la formation:
- sur le tas
Thèmes abordés:
Teaching of herding method: He tells his assistants not to beat the animals, not to shout at them, to treat animals fairly so they obey and to nourish them sufficiently so they don't walk away by night.
4.2 Service de conseils
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils accès à un service de conseils?
Non
4.4 Suivi et évaluation
Commentaires:
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: None
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: None
5. Financement et soutien matériel externe
5.1 Budget annuel de la composante GDT de l'Approche
Si le budget annuel précis n'est pas connu, indiquez une fourchette:
- < 2 000
Commentez (par ex. principales sources de financement/ principaux bailleurs de fonds):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: local community / land user(s) (All costs): 100.0%
5.2 Soutiens financiers/ matériels fournis aux exploitants des terres
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils reçu un soutien financier/ matériel pour la mise en œuvre de la Technologie/ des Technologies?
Non
5.3 Subventions pour des intrants spécifiques (incluant la main d'œuvre)
Si la main d'œuvre fournie par les exploitants des terres était un intrant substantiel, elle était:
- vivres-contre-travail
Commentaires:
Also paid in cash: Whereas his grandsons help him and get food therefore, the herder sometimes employs assistants who are paid.
5.4 Crédits
Des crédits ont-ils été alloués à travers l'Approche pour les activités de GDT?
Non
6. Analyses d'impact et conclusions
6.1 Impacts de l'Approche
Est-ce que l'Approche a aidé les exploitants des terres à mettre en œuvre et entretenir les Technologies de GDT?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
More biodiversity, less fertility decline, less cover reduction (compared to the grazing method used near the villages)
Est-ce que l'Approche a autonomisé les groupes socialement et économiquement défavorisés?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Young men herding in Faizabad area, one of them only a few ridges in the east of M.
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Whereas in the villages every family has to send someone as a herder once per month, M. earns money for his job and breeds his own animals. On the other hand the family structure is disrupted by the c
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
In finacial terms, it did (by generating income), But in terms of education, it did not help.
6.2 Principale motivation des exploitants des terres pour mettre en œuvre la GDT
- augmenter la production
Animals get fatter than on the common pastures
- conscience environnementale
The herder somehow has a consciousness of only taking from nature for what he has paid
6.3 Durabilité des activités de l'Approche
Les exploitants des terres peuvent-ils poursuivre ce qui a été mis en œuvre par le biais de l'Approche (sans soutien extérieur)?
- oui
Si oui, décrivez de quelle manière:
The herder intends to continue his work as long as physically possible. He though wants to take less animals in the following year and instead more cows and less sheep and goats. He says that cows are easier to keep and in addition, he is paid four times more for a cow than for a sheep or a goat.
6.4 Points forts/ avantages de l'Approche
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Each tenant has animals with their own comportment. M. only has to deal with a little number of tenants (and thus animal comportments), whereas the village herds are composed by animals of much more tenants. |
| animals can get used to each other. The composition of the big village herd is not always the same. |
| The herder is always the same and treats the animals fairly: he leads the animals slowly and doesn't shout at them or beat them. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| With around 600-700$ per season, the work as a professional herder is quite well-paid (for rural areas). (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: As soon as work in the foreigner (especially Russia) becomes scarce, herding will be more attractive again.) |
| For people with a tight relationship to nature and god (in the case of M.) this area is a good place, since remote. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: There will probably continue to be religious, nature-bound young people.) |
6.5 Faiblesses/ inconvénients de l'Approche et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The trees damaged by the animals are a problem from the herder's point of view. | He sees the main problem in the past civil war, when lots of trees were chopped illegally. He says that tree-planting would not be a solution, because then grazing would not be possible anymore either. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The way of living is not modern in the young peoples' eyes: They prefer social and urban to rural, solitary life. | As long as poverty predominates in the villages and cities cannot offer enough jobs to young people, agriculture and herding will stay interesting. Though, new (old) forms of herding might appear, such as herding in groups. |
| Night grazing makes sheep eat impalatable (poisonous) plants and than become sick (according to a specialist from CARITAS). | Training and workshops could be a platform for the discussion of such critical aspects. |
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Daily and seasonal rotation on grassland [Tadjikistan]
Extensive grazing of sheep and goats by the means of a precise rotational scheme
- Compilateur : Christian Wirz
Modules
Aucun module trouvé