Spontaneous spread [Kenya]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Ceris A. Jones
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Fabian Ottiger, Deborah Niggli
approaches_2627 - Kenya
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de l'Approche
Spécialiste GDT:
Mwaniki JM
mwanikijm2002@yahoo.com
Ministry of Agriculture/Soil and Water Conservation Branch
Embu
Kenya
Spécialiste GDT:
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock and Fisheries (MoA) - KenyaNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (DEZA / COSUDE / DDC / SDC) - SuisseNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
Agronomica - Royaume-Uni1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Références au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Technologies de GDT

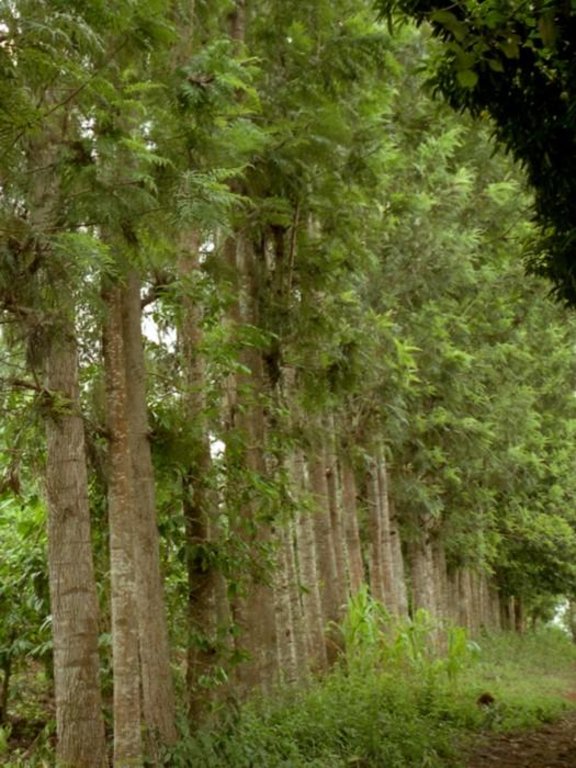
Système agroforestier à Grevillea [Kenya]
Les arbres de Grevillea robusta à usage multiples sont plantés le long les limites des champs, sur les talus des terraces et des fois dispersés dans les champs.
- Compilateur : Ceris A. Jones
2. Description de l'Approche de GDT
2.1 Courte description de l'Approche
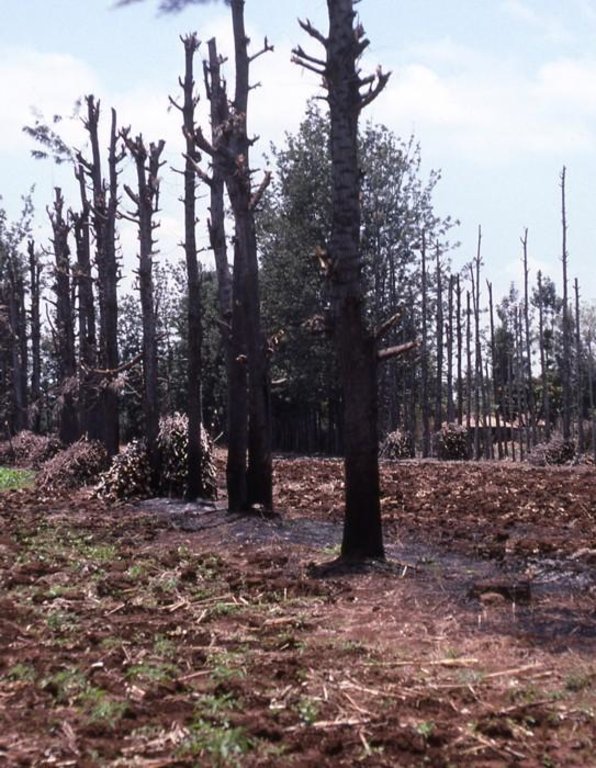
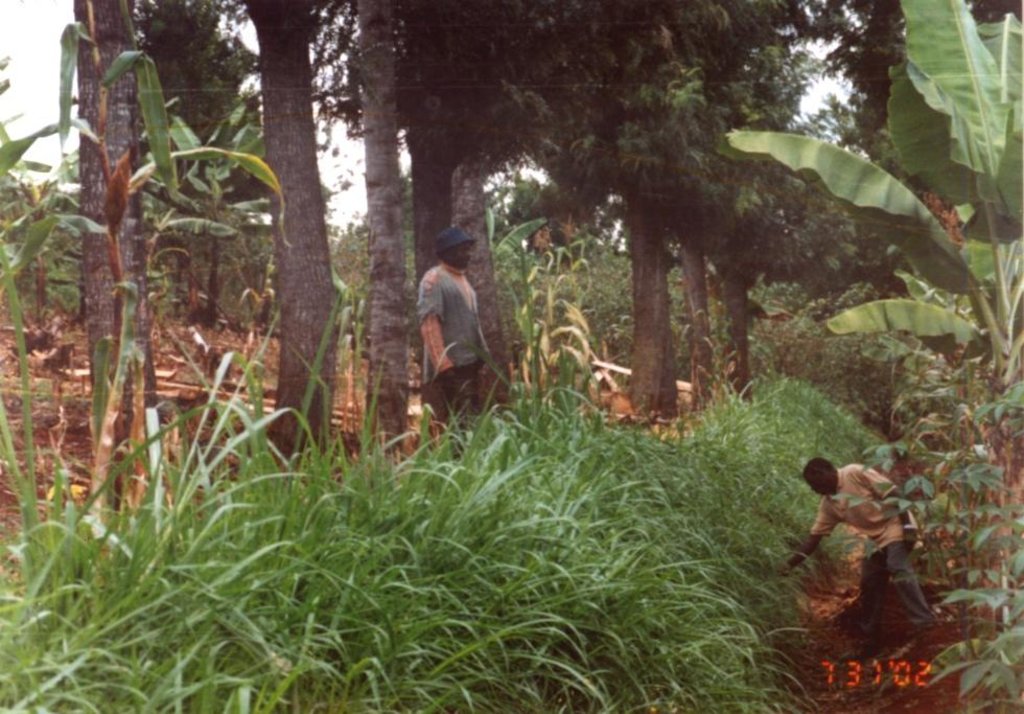
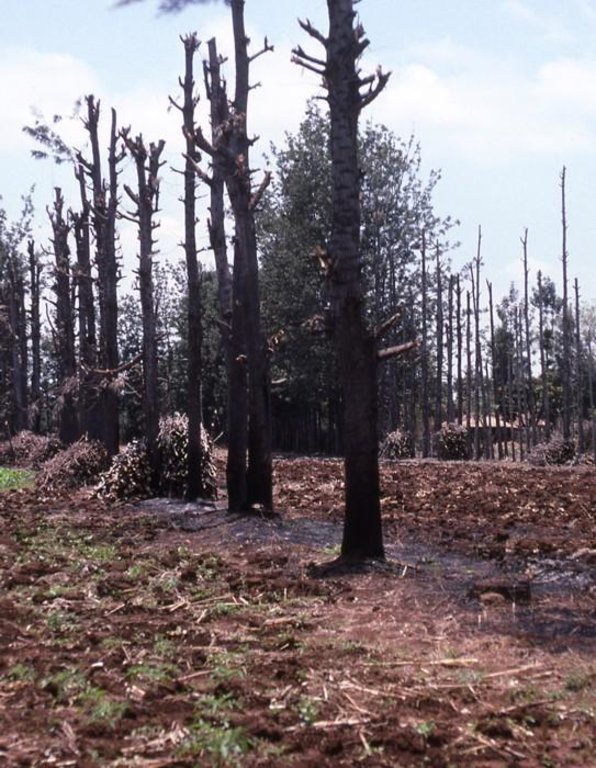
Spontaneous land users' initiative to meet household needs - especially firewood and timber - through planting Grevillea robusta trees as part of an agroforestry system.
2.2 Description détaillée de l'Approche
Description détaillée de l'Approche:
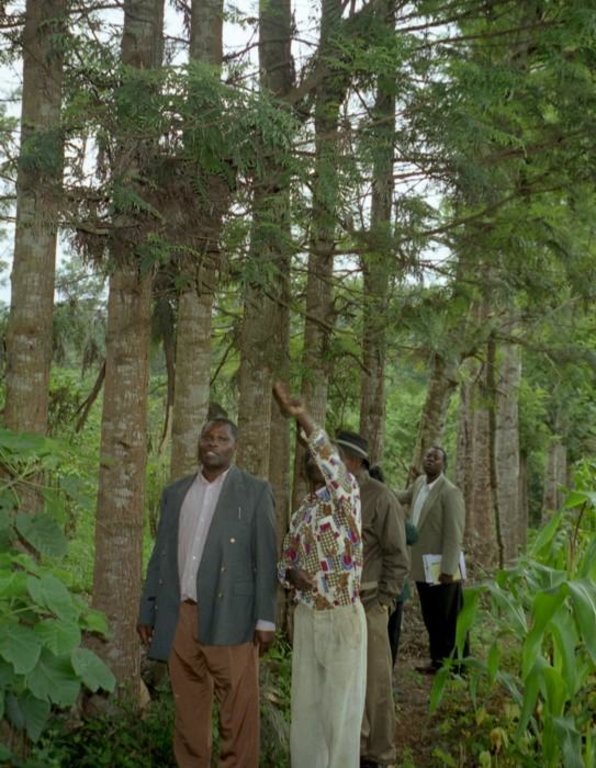
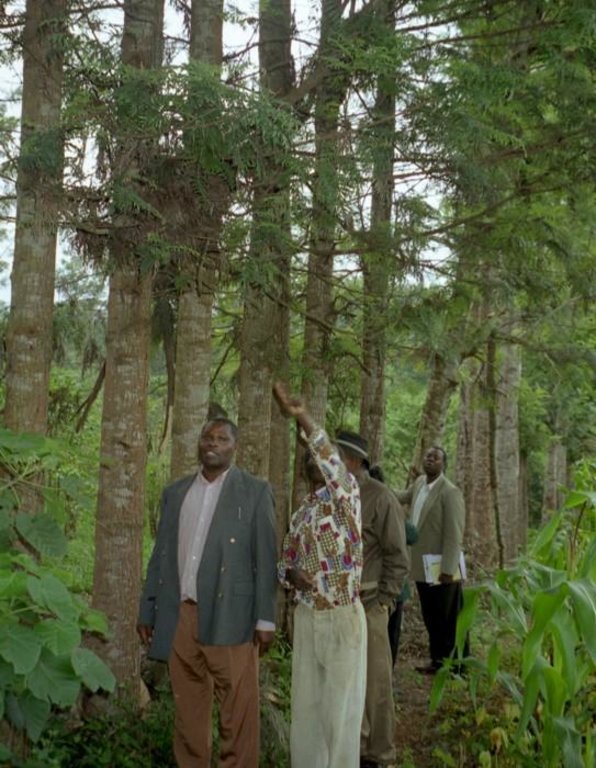
Aims / objectives: Grevillea robusta is a well-known shade tree, used in coffee and tea plantations in East Africa since the early part of the 20th century. While it originates from Australia, it was brought over from India and Sri Lanka by European settlers. Smallholder farmers in the highlands of Kenya noted that there was little or no competition between grevillea and neighbouring crops. Indeed this is one of the reasons it was so successful as a shade tree amongst plantation crops. Responding to the local lack of timber and firewood, due to the expansion of farmland into previously forested areas, smallholders took to planting grevillea, especially as a boundary tree, from the 1970s onwards. While the immediate effect of grevillea planting was to satisfy those needs for wood, the tree also helps in various ways to conserve land and improve the soil. This too was probably a reason for its spontaneous spread.
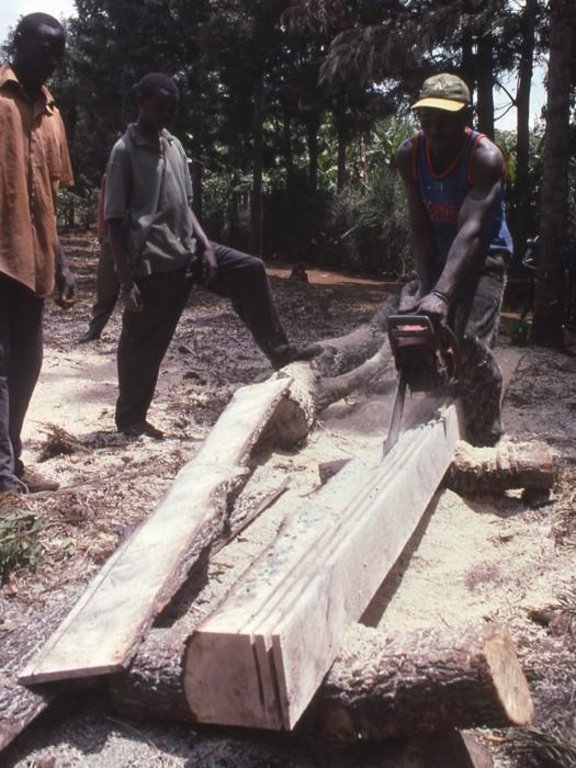
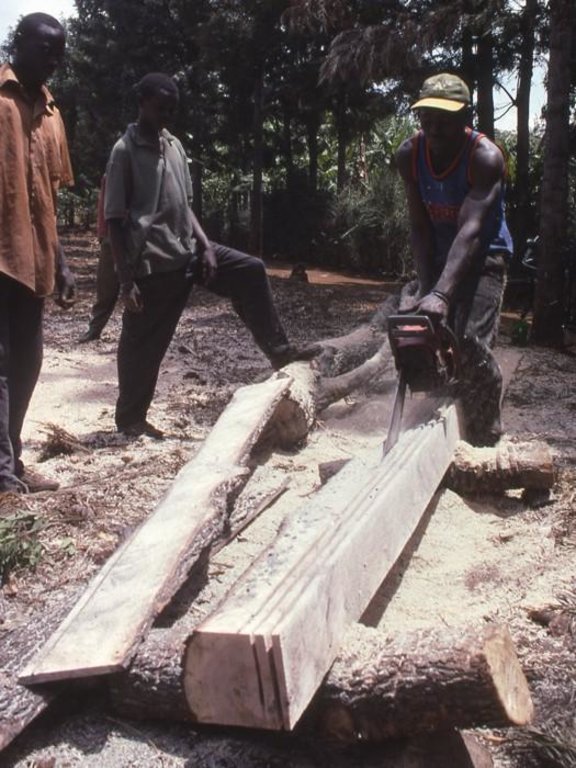
Methods: Because planting of grevillea requires few resources other than tools, even poor land users can readily adopt the technology. Although seedlings can be bought from local Government, NGO or private nurseries, it is also possible to collect ‘wildings’ (naturally generated seedlings) and plant these at minimal cost. The management of grevillea trees, once established, is important to their performance in the field, but the skills of thinning, and pollarding (pruning side branches for use) can be easily learned from neighbours. The success of the spontaneous spread of grevillea, basically through farmer-to-farmer exchange of knowledge, demonstrates that tree planting is not something that has always to be ‘pushed’ by outside agencies. Where smallholders perceive a need for trees and tree products - and an appropriate species is available - they will respond positively. However there is still an important ‘pulling’ role to be played by the Ministry of Agriculture’s extension agents and NGOs, especially through support for tree nurseries and for training to establish private tree nurseries.
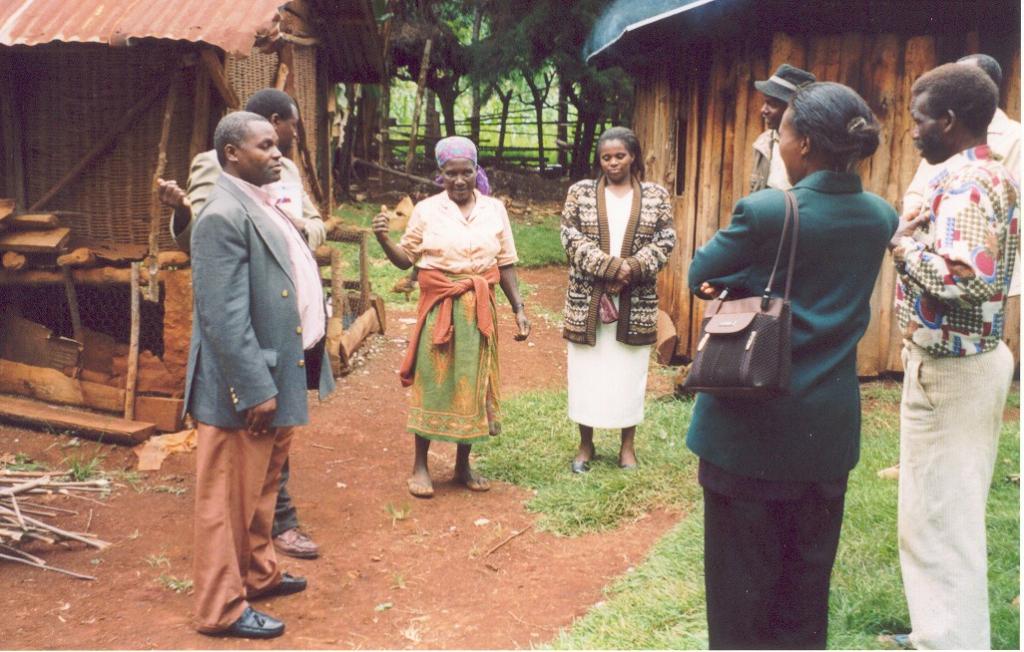
2.3 Photos de l'approche
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où l'Approche a été appliquée
Pays:
Kenya
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Eastern Province
Map
×2.6 Dates de début et de fin de l'Approche
Indiquez l'année de démarrage:
1971
2.7 Type d'Approche
- traditionnel/ autochtone
2.8 Principaux objectifs de l'Approche
The Approach focused mainly on other activities than SLM (Fencing, farm boundary marking, ornamental value, fuel wood supply, building materials provision)
- improve availability of tree products (fuelwood and wood for construction). - demarcate own land easily and cheaply (after land registration). - reduce land degradation. - increase land productivity. - improve household income
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: - shortage of fuelwood and building materials, environmental degradation. - need for farm boundary marking. - lack of simple, widely applicable agroforestry recommendations
2.9 Conditions favorisant ou entravant la mise en œuvre de la(des) Technologie(s) appliquée(s) sous l'Approche
normes et valeurs sociales/ culturelles/ religieuses
- entrave
Gender bias - women not expected to plant trees
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Although not directly related to this approach, intensive campaigns were conducted (by government and NGO's) to encourage gender balance with respect to tree planting
disponibilité/ accès aux ressources et services financiers
- entrave
Shortage of tree seedlings and sourced from long distance
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Setting up of individual on-farm tree nurseries and collection of wildlings
cadre juridique (régime foncier, droits d'utilisation des terres et de l'eau)
- favorise
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: Private land ownership has given farmers confidence to invest the land, and has also been a direct stimulus through the need to mark plot boundaries
connaissances sur la GDT, accès aux supports techniques
- entrave
Shortage of tree seedlings and sourced from long distance
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Setting up of individual on-farm tree nurseries and collection of wildlings.
3. Participation et rôles des parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche
3.1 Parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche et rôles
- exploitants locaux des terres / communautés locales
Working land users were mainly men (It was traditionally the role of men to plant trees. This is however changing ie other groups - women and youth - are now planting trees.)
Land users identified, purchased and planted their species of choice. However, at the same time, Grevillea seedlings were available at institutional (Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources) nurseries.
Traditionally men purchased, collected and planted trees. The men had greater access to and control of decisions on planting. The technology requires few resources, so that even poor land users have easily been able to decide to buy seedlings or collect wildlings and plant
3.2 Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales aux différentes phases de l'Approche
| Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales | Spécifiez qui était impliqué et décrivez les activités | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | auto-mobilisation | innovative individuals planting grevillea |
| planification | auto-mobilisation | informal, individual plans |
| mise en œuvre | auto-mobilisation | |
| suivi/ évaluation | passive | ad hoc observations by MoA; |
| Research | aucun | no activities |
3.4 Prises de décision pour la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies
Indiquez qui a décidé de la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies à mettre en œuvre:
- les exploitants des terres seuls (auto-initiative)
Expliquez:
Land user-driven initiative by shortages/problems
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by by land users* alone (self-initiative / bottom-up). The land user decided on when and how to plant the trees.
4. Soutien technique, renforcement des capacités et gestion des connaissances
4.1 Renforcement des capacités/ formation
Une formation a-t-elle été dispensée aux exploitants des terres/ autres parties prenantes?
Oui
Thèmes abordés:
Some demonstrations of benefits of tree planting by Government at provincial agricultural shows.
4.2 Service de conseils
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils accès à un service de conseils?
Oui
Spécifiez si le service de conseils est fourni:
- dans les champs des exploitants?
Décrivez/ commentez:
Key elements: Informal farmer-to-farmer exchange of ideas and skills. Additionally, on national tree planting days, the government hands out seedlings. Grevillea planting has been encouraged during national campaigns (involving the Ministry of Agriculture, the Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources, and NGOs) to encourage soil and w; 1) Advisory service was carried out through: other: individual land users 2) Advisory service was carried out through: other: individual land users
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; There is collaboration between Government extension service and KARI (Kenya Agricultural Research Institute) to further promote the technology
4.3 Renforcement des institutions (développement organisationnel)
Des institutions ont elles été mises en place ou renforcées par le biais de l'Approche?
- non
4.4 Suivi et évaluation
Le suivi et l'évaluation font ils partie de l'Approche? :
Oui
Commentaires:
technical aspects were ad hoc
economic / production aspects were ad hoc
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored by 0 through observations; indicators: None
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: None
5. Financement et soutien matériel externe
5.1 Budget annuel de la composante GDT de l'Approche
Commentez (par ex. principales sources de financement/ principaux bailleurs de fonds):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (national - Sponsored national tree planting days): 10.0%; other (Individual land user): 90.0%
5.2 Soutiens financiers/ matériels fournis aux exploitants des terres
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils reçu un soutien financier/ matériel pour la mise en œuvre de la Technologie/ des Technologies?
Non
5.3 Subventions pour des intrants spécifiques (incluant la main d'œuvre)
- intrants agricoles
| Spécifiez les intrants subventionnés | Dans quelle mesure | Spécifiez les subventions |
|---|---|---|
| semences | en partie financé | Individual land user. However, labour input was minimal |
Si la main d'œuvre fournie par les exploitants des terres était un intrant substantiel, elle était:
- volontaire
Commentaires:
Individual land user. However, labour input was minimal
5.4 Crédits
Des crédits ont-ils été alloués à travers l'Approche pour les activités de GDT?
Non
6. Analyses d'impact et conclusions
6.1 Impacts de l'Approche
Est-ce que l'Approche a aidé les exploitants des terres à mettre en œuvre et entretenir les Technologies de GDT?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
better soil and water management, increase in soil organic matter levels, nutrient pumping and reduced soil erosion.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Other extension programmes are utilising individual initiative as an entry point
6.3 Durabilité des activités de l'Approche
Les exploitants des terres peuvent-ils poursuivre ce qui a été mis en œuvre par le biais de l'Approche (sans soutien extérieur)?
- oui
Si oui, décrivez de quelle manière:
As land users developed this approach they can continue activities without support.
6.4 Points forts/ avantages de l'Approche
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Strong land user 'ownership' of the approach. |
| Adaptability, flexibilityand simplicity since it is user driven |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Incentives not necessary |
| Valuable lessons from a farmer-driven success for development agencies that promote tree planting and agroforestry systems. |
| Very low inputs (resources) required. However there is still an important 'pulling' role to be played by the Ministry of Agriculture's extension agents and NGOs (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: More support for individual and government tree nurseries.) |
| Self-driven initiative (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: MoA extension staff and land users to encourage other farmers to be self-reliant.) |
6.5 Faiblesses/ inconvénients de l'Approche et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Lack of other stakeholders input | Encourage and inform land users on where to seek additional information consultations with SWC extensionists |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Adoption rates under such approaches depend on the number and efforts of innovators to stimulate others | SWC extensionists (Ministry and NGOs) to undertake more community mobilisation and awareness raising. |
| Approach is dependent on social cohesiveness for dissemination | promote more farmer interaction at community level |
| Poor collaboration and insitutional linkages | Encourage and create forums where stakeholders can share experiences and inform land users about where to seek additional information and assistance. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
NjiruN.N et al. 1998. PRA report of Kiawanja catchmentSee 'Grevillea agroforestry system' case study (QT KEN16) for technical references
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Nembure district
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Système agroforestier à Grevillea [Kenya]
Les arbres de Grevillea robusta à usage multiples sont plantés le long les limites des champs, sur les talus des terraces et des fois dispersés dans les champs.
- Compilateur : Ceris A. Jones
Modules
Aucun module trouvé