Early Warning Message Dissemination [Bangladesh]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : TUHIN SAMADDAR
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Alexandra Gavilano, Alvin Chandra
বন্যা পূর্ব-সতর্কবার্তা প্রচার (Bonna Purbo-Satarkabarta Prochar)
approaches_649 - Bangladesh
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de l'Approche
Personne(s) ressource(s) clé(s)
Project staff:
Mustafa Golam
+880 1718770373 / +880 1730799762
pmdrrwash16@gmail.com
Bangladesh Red Crescent Society
Project Manager, DRRWASH Project O⌀ਈce, Shukhsantir Bazar, Dhanghora, Gaibandha, Bangladesh
Bangladesh
Project staff:
Razzak Abdur
+880 1730 799763 / +880 1730 799763
razzak.pe@gmail.com
Bangladesh Red Crescent Society
Project Engineer, DRRWASH Project O⌀ਈce, Shukhsantir Bazar, Dhanghora, Gaibandha, Bangladesh
Bangladesh
Project staff:
Islam Saiful
+880 1730 799746 / +880 1730 799746
saiful644@gmail.com
Bangladesh Red Crescent Society
Field Officer DRR and Training, DRRWASH Project O⌀ਈce, Shukhsantir Bazar, Dhanghora, Gaibandha, Bangladesh
Bangladesh
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
Book project: where people and their land are safer - A Compendium of Good Practices in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) (where people and their land are safer)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
Swiss Red Cross (Swiss Red Cross) - Suisse1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
04/10/2016
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Références au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Technologies de GDT
2. Description de l'Approche de GDT
2.1 Courte description de l'Approche
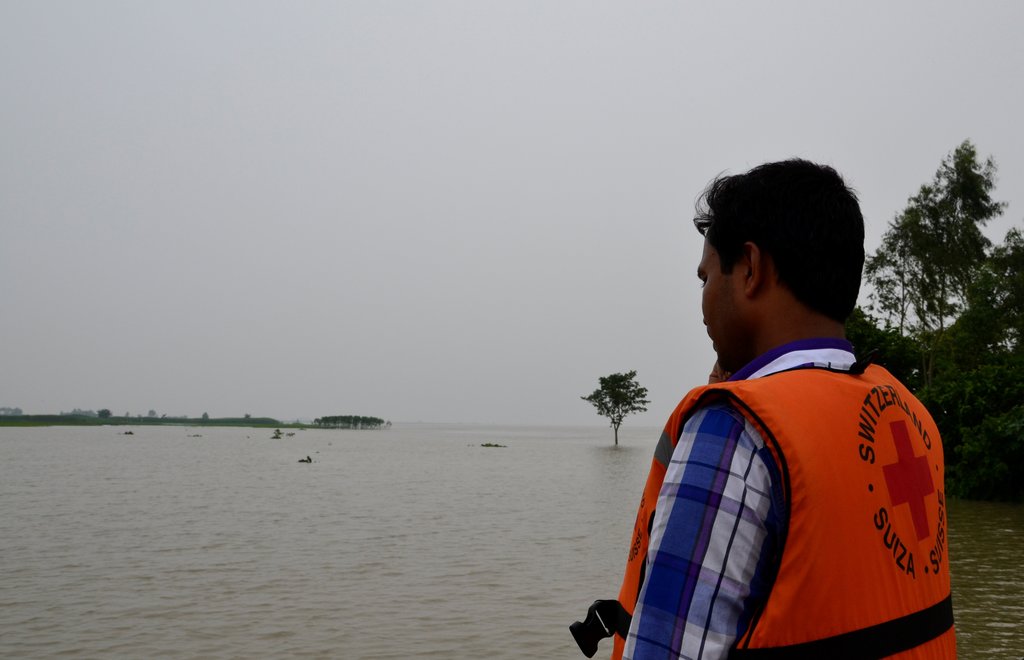
Early warning systems are an essential element in building resilience through effective disaster preparedness and risk mitigation: an effective system for dissemination of early warning messages was established among the vulnerable communities in Chars (riverine sandy islands) of Gaibandha district in order to strengthen their coping mechanisms and reduce loss and damage caused by floods.
2.2 Description détaillée de l'Approche
Description détaillée de l'Approche:
The key characteristics entail linking the intervention units at community level with national and sub-national early warning systems. It also consists of developing the capacity of the local government institutions and organised communities to not only disseminate early warning but to effectively respond to floods. The approach seeks to build upon existing local capacities and systems both in terms of dissemination of early warning and effective response. Merely installing an early warning system is not sufficient to equip communities to cope with recurrent floods; it needs to be linked to broader aspects of disaster preparedness and increased response capacity.
The vulnerability and capacity assessment (VCA) is the basis of all measures oriented at reducing disaster risks. The VCA was carried out with the involvement of local stakeholders, especially the target communities, to understand the vulnerabilities and risks associated with floods as well as to gain insight on existing capacities and capacity gaps that needed to be addressed. The process resulted in a risk reduction action plan which was to be jointly implemented by the target community and local government.
The risk reduction plan pointed to the need of having in place a mix of structural, management and contingency measures. This involved linking local, sub-national and national early warning systems, developing contingency and evacuation plans supported by establishment of safe places where people could move during floods. The risk reduction plan also highlighted the need to support household level protection measures - structurally this meant raising household plinth levels above flood levels. In addition, local early warning system was established through installation of flood markers/pillars, and warning flags at key sites. Capacities were built to internalise, monitor and consequently respond to evolving local flood situation. Building communication channels that linked the local institutions to higher level flood forecasting system resulted in streamlining information from source to destination.
2.3 Photos de l'approche
Remarques générales concernant les photos:
Approach of Early Warning System in DRRWASH project area in Gaibandha district.
2.4 Vidéos de l'Approche
Commentaire, brève description:
Video on Flood 2015 in the DRRWASH project area in Gaibandha including early warning intervention, in Bangla, link:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Os4ZgSMMVyg
Date:
25/10/2015
Lieu:
Gaibandha
Nom du vidéaste:
Tuhin Samaddar and Vabotosh Karmakar
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où l'Approche a été appliquée
Pays:
Bangladesh
Région/ Etat/ Province:
North-Bengal
Autres spécifications du lieu :
Kamarjani and Mollar Char union in Sadar Upazila and Haldia union in Shaghata Upazila of Gaibandha District
Commentaires:
The entire intervention area is divided into 261 clusters. In each cluster, one local volunteer (YRT) has been nominated for preparedness and response operation. 30 Village Disaster Management Committee (VDMC) are actively monitoring the process under the guidance of three Union Disaster Management Committee (UDMC).
Map
×2.6 Dates de début et de fin de l'Approche
Indiquez l'année de démarrage:
2013
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez approximativement quand l'Approche a démarré:
il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
Commentaires:
N/A
2.7 Type d'Approche
- fondé sur un projet/ programme
2.8 Principaux objectifs de l'Approche
To promote resilient communities through improved flood preparedness that reduces loss and damage of vulnerable people's lives and protects their livelihoods in the chars of Gaibandha district.
2.9 Conditions favorisant ou entravant la mise en œuvre de la(des) Technologie(s) appliquée(s) sous l'Approche
normes et valeurs sociales/ culturelles/ religieuses
- favorise
The intervention built upon traditional coping mechanisms and indigenous systems of disaster risk management. The blending of the traditional and indigenous practices with contemporary knowledge and preparedness practices acted as drivers in terms of choice and adoption of technologies.
- entrave
In earlier phases of the intervention, the cultural norm of not abandoning one's household even in extreme crisis hindered timely access to emergency infrastructure.
disponibilité/ accès aux ressources et services financiers
- favorise
The DRR intervention facilitated leveraging of institutional financial resources (Local government budget) and secured cost contribution from target communities.
- entrave
Lack of adequate capacities and resources with local government.
cadre institutionnel
- favorise
The Disaster Management Act and Standing Orders on Disaster of the Govt. of Bangladesh provides for a decentralised disaster management institutional setting from the central level to the local level.
- entrave
In principle a decentralised disaster management structure is in place but due to operational and financial constraints they are unable to perform their mandated function.
collaboration/ coordination des acteurs
- favorise
The initiative built a good coordination with state actors at various levels. From time to time it was also able to secure collaboration from non-state actors around specific thematic areas.
- entrave
Harmonisation of disaster centred initiatives is a time consuming process and very often does not lead to collaborations that harness existing synergies.
cadre juridique (régime foncier, droits d'utilisation des terres et de l'eau)
- favorise
Disaster Management Act, 2012 provides the legal framework for disaster risk management in Bangladesh.
cadre politique
- favorise
A set of policies supports the Disaster Management Act. Government's standing orders on disaster clearly defines the roles and responsibilities of various ministries, line agencies, local govt., mandated committees and other non-state actors in disaster risk management.
- entrave
Policy enforcement across sectors remains weak in Bangladesh.
gouvernance foncière (prise de décisions, mise en œuvre et application des décisions)
- favorise
Traditional rights to land are still accepted in Chars of Bangladesh .
- entrave
Land ownership is complex in Chars given its unstable nature due to high vulnerability to river erosion. Elite capture of land is overwhelmingly practiced in the Chars.
connaissances sur la GDT, accès aux supports techniques
- favorise
Early warning systems have strengthened land management practices.
- entrave
River erosion threats strongly disincentivise investment in SLM.
marchés (pour acheter les intrants, vendre les produits) et prix
- entrave
Market forces are yet to develop properly in Chars which are by nature isolated geographical units, accessed only through time consuming and expensive transportation means.
charge de travail, disponibilité de la main-d'œuvre
- favorise
Higher productivity of land in Chars allow for lower labour engagement in agriculture.
- entrave
Disaster and higher profitability in mainland drives migration leading to labour shortages.
3. Participation et rôles des parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche
3.1 Parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche et rôles
- organisations communautaires
Village Disaster Management Committee (VDMC)
The VDMC is the key actor to perform disaster risk reduction activities in the communities. This covers supporting the conduct of VCA and developing their action plans based on VCA findings. The operationalisation of the plans is anchored in the VDMC and so is leveraging cooperation and collaboration from local government. The VDMC also acts as first responder and as custodian responsible for O&M of built emergency and health infrastructure. Assessing community needs, beneficiary selection, contribution collection and financial management of hardware are their other key responsibilities.
- enseignants/ élèves/ étudiants
Youth Response Team (YRT) members
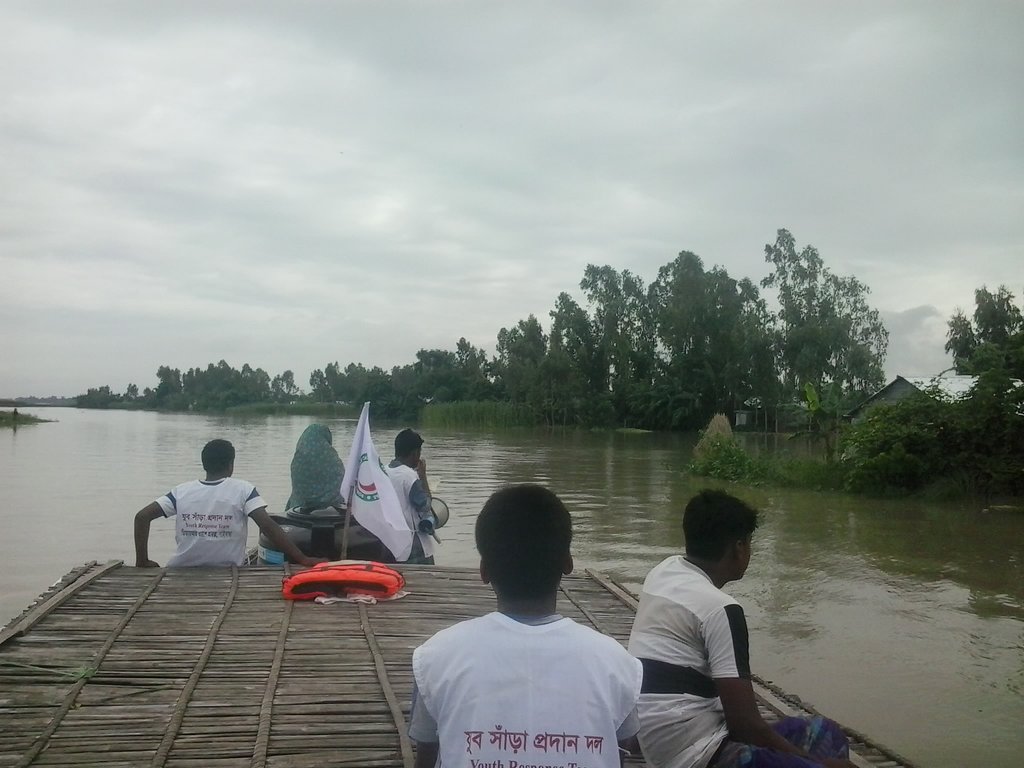
YRT has been developed to promote volunteerism. Their main role is to support response and recovery operations during and after disaster. They are especially trained in Search & Rescue. As they are located in the community, YRTs actively engage in early warning dissemination.
- secteur privé
Enterpreneur of Union Digital Center
The lowest level of local government, the Union Parishad (UP), has a Digital Center to render ICT services to communities. These are run by local entrepreneurs. The entrepreneurs are responsible for monitoring flood forecasts on the internet and updating the UP and CBOs on evolving flood situation. By analysing and interpreting relevant information they play a key role in catalysing the early warning system.
- gouvernement local
Union Disaster Management Committee (UDMC)
The UDMC disseminates forecasts, warnings, and advisories locally. It also performs a lead role in response and recovery operations.
Si plusieurs parties prenantes sont impliquées, indiquez l'organisme chef de file ou l'institution responsable:
UDMC
3.2 Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales aux différentes phases de l'Approche
| Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales | Spécifiez qui était impliqué et décrivez les activités | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | interactive | Key Actors: VDMC/CBOs and Local Government Institutions (UDMC) Activities : Baseline survey, formation of CBOs, reformation of UDMC, VCA and volunteer selection |
| planification | interactive | Key Actors: VDMC/CBOs and Local Government Activities: preparation of risk reduction action plan, preparation of evacuation plan along with route map, contingency plan development, planning of emergency and health infrastructure, Early Warning Systems (EWS) planning |
| mise en œuvre | interactive | Key Actors: VDMC/CBOs and Local Government Activities: Establish Early Warning System, emergency infrastructure, access infrastructure (wooden bridge, roads, etc.), household infrastructure |
| suivi/ évaluation | auto-mobilisation | Key Actors: VDMC/CBOs, Local and Sub-national Government Activities: Developing Quality Assurance System, Community Review Meeting, Site visits/physical verification, quality and financial audit, survey and spot checks, |
| Initiation | auto-mobilisation | Ket Actors: VDMC/CBOs, Local Government and Private Sector: Activities: O&M of built infrastructure and Sanitation Marketing |
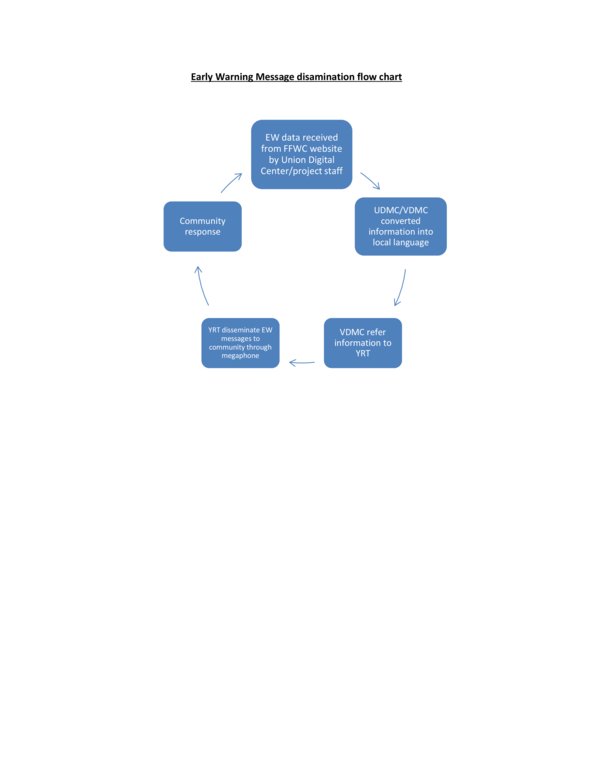
3.3 Diagramme/ organigramme (si disponible)
Description:
The flow chart explains application of the EWS and clarifies local linkages with national flood forecasting and warning centre (FFWC)
Auteur:
Tuhin Samaddar
3.4 Prises de décision pour la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies
Indiquez qui a décidé de la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies à mettre en œuvre:
- tous les acteurs concernés dans le cadre d'une approche participative
Expliquez:
Since participatory approach has been adopted to examine vulnerabilities and capacities, the approach and technology choice to address risk and vulnerabilities was collectively decided.
Spécifiez sur quelle base ont été prises les décisions:
- les résultats de recherches?
- expériences et opinions personnelles (non documentées)
- Government policies and mandates
4. Soutien technique, renforcement des capacités et gestion des connaissances
4.1 Renforcement des capacités/ formation
Une formation a-t-elle été dispensée aux exploitants des terres/ autres parties prenantes?
Oui
Spécifiez qui a été formé:
- exploitants des terres
- personnels/ conseillers de terrain
- Anser-VDP (Village Defence Party) member
Formats de la formation:
- zones de démonstration
- réunions publiques
- cours
Thèmes abordés:
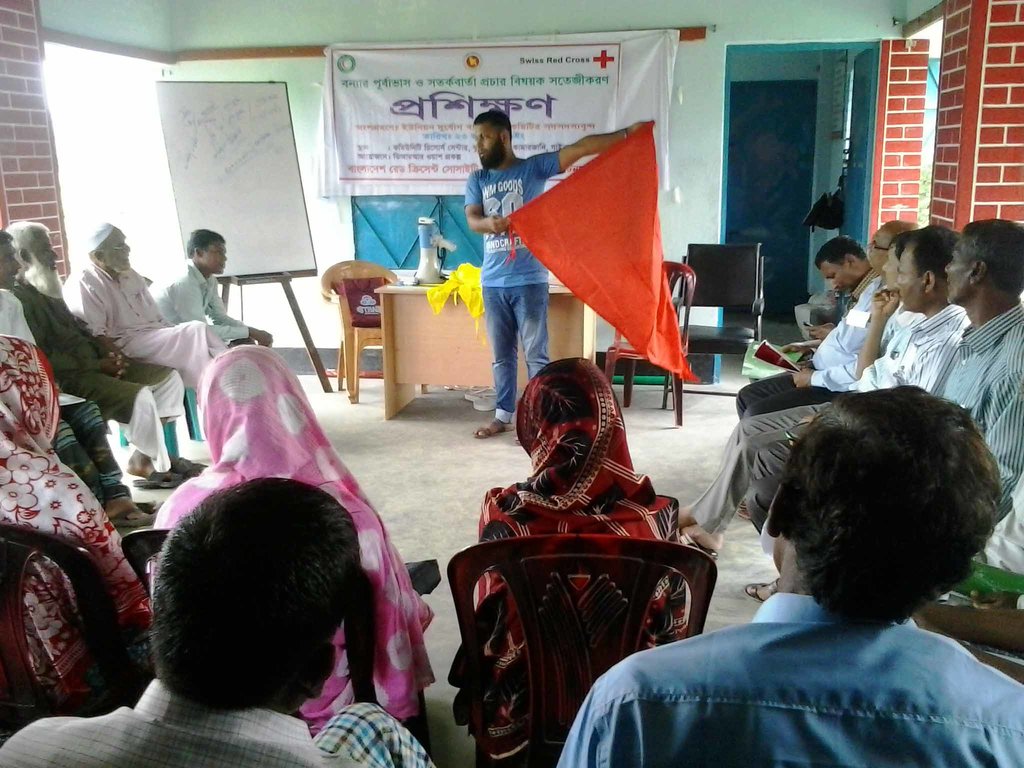
Several training courses and workshops were organised on disaster preparedness and response:
1. Early Warning System (for UDMC/VDMC/ Anser-VDP/YRT/VCRP/Staff): Disaster context in Bangladesh, techniques to identify water levels against standardised danger levels, determining flood intensity by observing pillars and flags, dissemination strategies for early warning messages among the community, and role of stakeholders to warning message dissemination.
2. Evacuation Plan (for VDMC/YRT/VCRP): Response operation, preparing checklist for response, preparing risk and resource map, information collection and analysis, preparing route maps, and roles and responsibilities of respective stakeholders in effectuating evacuation plan
3. Response Plan (for UDMC): Importance of response plan, ke constituents of preparedness and response, interpretation of Early Warning information from FFWC, creating contingency fund, search and rescue, emergency relief and first aid, identifying safe exit route and transportation, damage assessment, launching control room, involving existing manpower and resources in the community and other organisation, and prepositioning of rescue equipments.
Commentaires:
609 VDMC/UDMC members were trained on various DRR topics. 255 local youth volunteers (YRT/VCRP) were also trained on early warning message dissemination, flood forecast interpretation, preparing evacuation plan and route map.
4 mock drill demonstration events were conducted by local government in which 276 community members participated. Refresher training was also organised for newly elected union parishad members on their broad mandate with specific reference to their roles and responsibilities in disaster risk management.
4.2 Service de conseils
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils accès à un service de conseils?
Non
4.3 Renforcement des institutions (développement organisationnel)
Des institutions ont elles été mises en place ou renforcées par le biais de l'Approche?
- oui, beaucoup
Spécifiez à quel(s) niveau(x), ces institutions ont été renforcées ou mises en place:
- local
- régional
Décrivez l'institution, ses rôles et responsabilités, ses membres, etc.
CBOs/Village Disaster Management Committee (VDMC)- on an average each CBO/VDMC has 17 members. Their roles and responsibilities entail assessments, beneficiary selection, developing and implementing RRAPs with special focus on disaster preparedness and response. A key function entails their engagement in EWS and planning and implementation of emergency and health infrastructure, shelter protection, and creating access infrastructure. O&M of all built assets and infrastructure is their responsibility.
Local Government/UDMC: on average it has a 36 members. Standing orders on disaster of the government defines their roles and responsibilities which covers the entire gamut of functions associated with disaster risk management at the local level. Strengthening preparedness and leading effective response is critical to their mandate.
Précisez le type de soutien:
- renforcement des capacités/ formation
- équipement
Donnez plus de détails:
Megaphone, stretcher, Lifejacket, Lifebuoy, Torchlight, Raincoat, Gumboot, Rope and First aid box are some of the equipments that have been given. Further, the YRTs have received whistle, umbrella and apron for early response operation
4.4 Suivi et évaluation
Le suivi et l'évaluation font ils partie de l'Approche? :
Oui
Commentaires:
A joint monitoring team has been formed comprising representative of CBOs, local government and project staff.
Si oui, ce document est-il destiné à être utilisé pour le suivi et l'évaluation?
Non
4.5 Recherche
La recherche a-t-elle fait partie intégrante de l’Approche?
Non
5. Financement et soutien matériel externe
5.1 Budget annuel de la composante GDT de l'Approche
Indiquez le budget annuel de la composante GDT de l'Approche en $ US:
10384,00
Si le budget annuel précis n'est pas connu, indiquez une fourchette:
- 10 000-100 000
Commentez (par ex. principales sources de financement/ principaux bailleurs de fonds):
Swiss Red Cross
Above mentioned amount is for the Early Warning System Implementation approach only
5.2 Soutiens financiers/ matériels fournis aux exploitants des terres
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils reçu un soutien financier/ matériel pour la mise en œuvre de la Technologie/ des Technologies?
Non
5.3 Subventions pour des intrants spécifiques (incluant la main d'œuvre)
- aucun
Si la main d'œuvre fournie par les exploitants des terres était un intrant substantiel, elle était:
- volontaire
Commentaires:
All actions related to dissemination of early warning were performed on a voluntary basis.
5.4 Crédits
Des crédits ont-ils été alloués à travers l'Approche pour les activités de GDT?
Non
5.5 Autres incitations ou instruments
D'autres incitations ou instruments ont-ils été utilisés pour promouvoir la mise en œuvre des Technologies de GDT?
Non
6. Analyses d'impact et conclusions
6.1 Impacts de l'Approche
Est-ce que l'Approche a autonomisé les exploitants locaux des terres, amélioré la participation des parties prenantes?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
The participation of all local stakeholders, especially women, has improved considerably.
Est-ce que l'Approche a permis la prise de décisions fondées sur des données probantes?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
The decision making especially with regard to effectiveness and quality of approach and technologies has been determined by the evidence on the ground.
Est-ce que l'Approche a aidé les exploitants des terres à mettre en œuvre et entretenir les Technologies de GDT?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Since the implementation of technologies and maintenance of built infrastructure has been largely user led, it has improved their capacity to do the same.
Est-ce que l'Approche a mobilisé/ amélioré l'accès aux ressources financières pour la mise en œuvre de la GDT?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
User contribution and govt. contribution was a mandatory component of the project which led to mobilisation of resources that supplemented project resources.
Est-ce que l'Approche a amélioré les connaissances et les capacités des autres parties prenantes?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Implementation of well designed capacity building plan cognizant of the needs of diverse stakeholders has improved the knowledge and capacities of relevant stakeholders.
Est-ce que l'Approche a construit/ renforcé les institutions, la collaboration entre parties prenantes?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
the central element of the approach has been to ensure sustainability of benefits which cannot be attained without strong institutions collaborating around DRM work. Thus, the approach led to improved collaboration between stakeholders and strengthened institutions.
Est-ce que l'Approche a atténué les conflits?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
The approach is based on conflict sensitive programme management. This allowed for pro-active identification of conflicts and tensions followed by measures aimed at their mitigation.
Est-ce que l'Approche a autonomisé les groupes socialement et économiquement défavorisés?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
The extreme poor and socially disadvantaged were especially targeted by the disaster preparedness approach
Est-ce que l'Approche a amélioré l'égalité entre hommes et femmes et autonomisé les femmes et les filles?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Though significant improvements are there as women and girls are much more aware about disaster preparedness in general and flood response in particular, there remains room for further improvement.
Est-ce que l'Approche a conduit à améliorer l'accès à l'eau et l'assainissement?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
As part of strengthening preparedness to health hazards, WASH infrastructure set up by the project has greatly improved access to water and sanitation
Est-ce que l'Approche a amélioré la capacité des exploitants des terres à s'adapter aux changements/ extrêmes climatiques et a atténué les catastrophes liées au climat?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Strengthened DRM capacities include improved climate adaptation and capacities to mitigate climate induced disasters.
6.2 Principale motivation des exploitants des terres pour mettre en œuvre la GDT
- réduire les risques de catastrophe
Early warning system helps people prepare and act before the water level crosses danger level (which denotes the settlement is at risk of inundation)
6.3 Durabilité des activités de l'Approche
Les exploitants des terres peuvent-ils poursuivre ce qui a été mis en œuvre par le biais de l'Approche (sans soutien extérieur)?
- oui
Si oui, décrivez de quelle manière:
Union Digital Center is an information hub that exists in the union where people have easy access. The technology is simple and the approach is easy to understand and has already benefited the targeted community. The anchoring of preparedness in general and EWS in particular in local government and its rolling out in collaboration with communities imparts high probability of sustainability to disaster preparedness measures. During the project cycle, two flood events of significant magnitude have tested the approach and technology and resulted in tangible benefits for the community. At the same time since sustainability considerations are inbuilt in project design and have guided the implementation of the approach and technology, the likelihood of their sustainability is very strong.
6.4 Points forts/ avantages de l'Approche
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Strengths: - A trained group of volunteer is available in the community - Response equipments are in place and ready to use if and when needed - EWS facilitates people's timely access and movement to appropriate emergency infrastructure and protected shelters |
|
Advantages: - Rapid evacuation, especially for physically challenged, children and elderly people, and cattle - Crops are saved due to timely action related to sowing and harvesting. - Means of preparedness, such as boat, banana raft, portable cooker, firewood, ORS, dry food can be collected beforehand |
|
Opportunities: - Balanced representation of community in govt. mandated disaster committees - Coordination/ communication with development actors and local govt./union parishad is more forthcoming |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Strengths: - Sustainability dimensions have been well considered and applied in adopted approach and technologies - Strengthened community institutions are in place to address DRM issues, especially those related preparedness and response mechanisms |
|
Advantages: - Community and local government interface has been strengthened to devise appropriate DM solutions - Decisions on preparedness approach and attendant technologies are taken collectively by stakeholders |
|
Opportunities: - A replicable model of EWS, emergency and access infrastructure has been established |
6.5 Faiblesses/ inconvénients de l'Approche et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| - Long term maintenance of response equipments |
- UDMC should play custodian's role - Local people should contribute towards recurrent cost |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| - Replicability of the model might be difficult due to lack of funds and functionaries available with local government. |
- Support local government in negotiating more resources from higher levels of governance and administration. - Build capacity of local government to utilise resources efficiently and effectively. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
15 - Key Informant Interview (KII)
2- Focus Group Discussion (FGD)
- interviews/ entretiens avec les spécialistes/ experts de GDT
4
- compilation à partir de rapports et d'autres documents existants
6
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Three VCA Reports published by UDMC with support of DRRWASH project
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Bangladesh Red Crescent Society
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes disponibles en ligne
Titre/ description:
Flood Forecasting & Warning Centre (FFWC), Bangladesh Water Development Board (BWDB), SOD
URL:
http://www.ffwc.gov.bd/#, http://ddm.portal.gov.bd/sites/default/files/files/ddm.portal.gov.bd/page/a3f4cc27_7f7d_4c2b_a1b0_166fe6bef73b/udmc.pdf
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé