Transport of freshwater from local streams [Grèce]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : John Gkiougkis
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Fabian Ottiger
Μεταφορά γλυκού από γειτονικά αρδευτικά κανάλια
technologies_1042 - Grèce
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Pechtelidis Alexandros
Democritus University of Thrace
Vasilissis Sofias 12, Xanthi 671 00, Greece
Grèce
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Democritus University of Thrace (Democritus University of Thrace) - Grèce1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
10/06/2011
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Approches de GDT

Combating Soil Salinization [Grèce]
Use of freshwater to combat soil salinization.
- Compilateur : John Gkiougkis
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
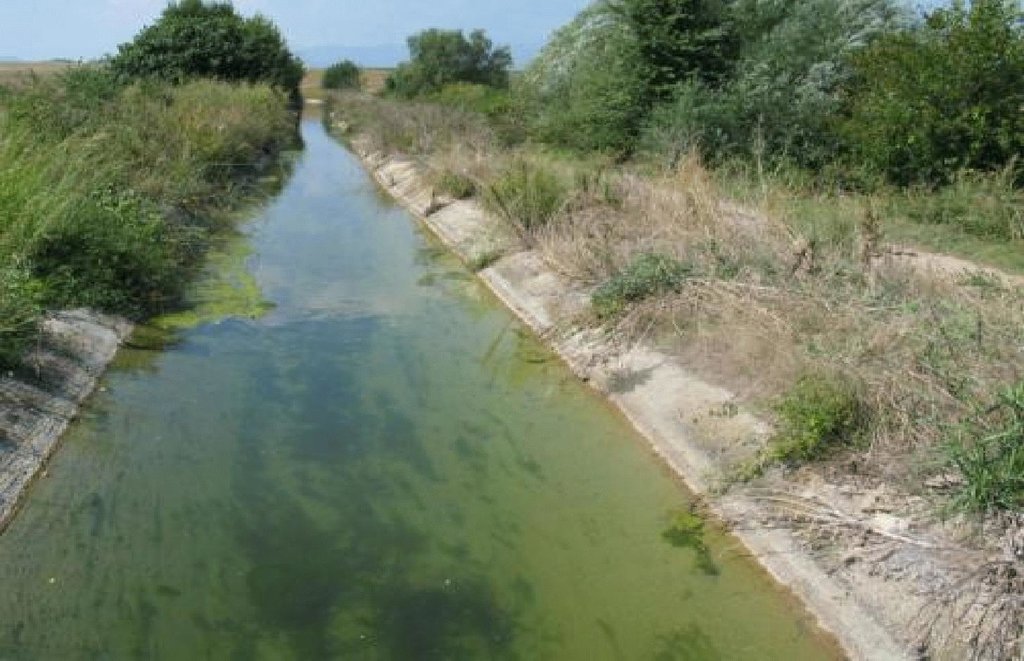
Freshwater transport from local streams for irrigation purposes, in order to replace the traditional form of irrigation (by pumping saline groundwater from wells).
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
In low-lying regions suffering from overuse of the ground water for irrigation and seawater intrusion, pumping groundwater is detrimental and results in soil degradation (salinization) and reduced plant growth.
Purpose of the Technology: For this reason, freshwater is transported over distances of up to 500 m (or more) from surface streams, for irrigation using water of better quality. In this way, overexploitation of the aquifer is being reduced.
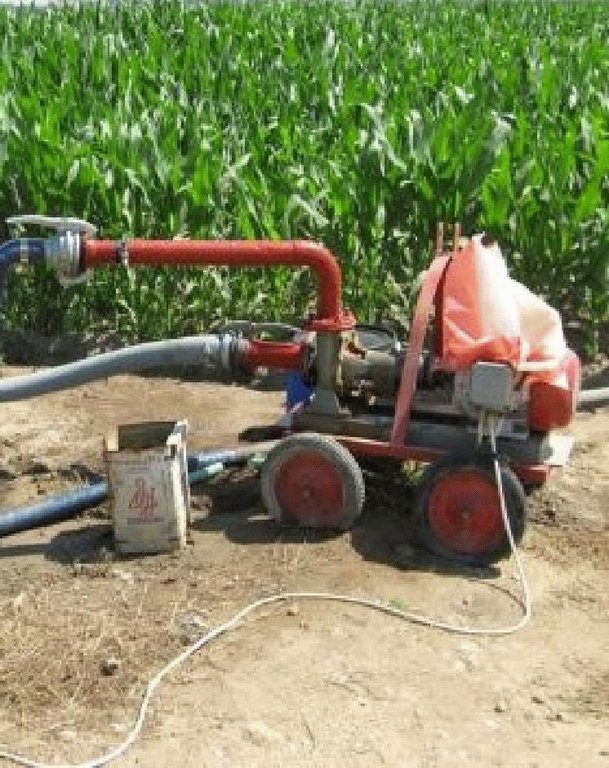
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The pumps transfer water from canals or streams for irrigation purposes. A pumping station (10HP), pipes (PP-R, Ø 1100mm) for water transport and diesel or electricity for pump operation are the major items needed to replace groundwater with freshwater irrigation. However, annual maintenance of the pump and network is necessary.
Natural / human environment: The majority of families living in the research area make their living mostly from agricultural activities but also from livestock. Croplands are dominantly irrigated by wells (groundwater) and only those which are close to streams are irrigated with freshwater. Owing to over-pumping of the aquifer in order to irrigate the crop fields, there has been seawater intrusion over the past years. As a result, irrigation with groundwater led to saline soils. The group affected by this process comprises farmers who are now beginning to understand the extent of the desertification problem in the area. The degradation process significantly affects the quality of life of the local people. Saline soils lead to low productivity and thus to lower incomes (causing poverty) and thus an increase in social unrest. Although the farmers are totally aware of the on-going degradation problem that affects their fields and their livelihoods, they seem to be unwilling to change the way they irrigate their fields (with groundwater) as long as they do not have an alternative source of irrigation such as freshwater from local streams. The lack of information about how the salt-affected fields can be restored also makes the farmers believe that this situation is permanent and will extend over a wider area.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Grèce
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Prefecture of Xanthi
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Eastern Macedonia and Thrace
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- au cours d'expérimentations / de recherches
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Principales cultures (vivrières et commerciales):
Major cash crop annual cropping: Maize, cotton, wheat
Major food crop annual cropping: Maize, wheat
Major cash crop perennial (non-woody) cropping: Clover
Other crops perennial (non-woody) cropping: Clover
Major cash crop tree/shrub cropping: Olive trees
Major food crop tree/shrub cropping: Olives
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil salinization and sodification.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil salinization.
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Commentaires:
Water supply: mixed rainfed - irrigated, full irrigation
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 100Longest growing period from month to month: April to August
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion de l'irrigation (incl. l'approvisionnement en eau, le drainage)
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 9.59 m2.
Areas adjacent to freshwater surface streams.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

modes de gestion
- M7: Autres
Commentaires:
Main measures: management measures
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cs: salinisation/ alcalinisation
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cs: salinisation / alkalinisation
Main causes of degradation: disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (overexploitation of groundwater), over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.) (overexploitation of groundwater), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers of the area, poor soil drainage), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (lack of freshwater supply network), increased pressure on groundwater for irrigation
Secondary causes of degradation: change in temperature (higher temperature), change of seasonal rainfall (reduced rainfall), droughts (climate change)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Commentaires:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
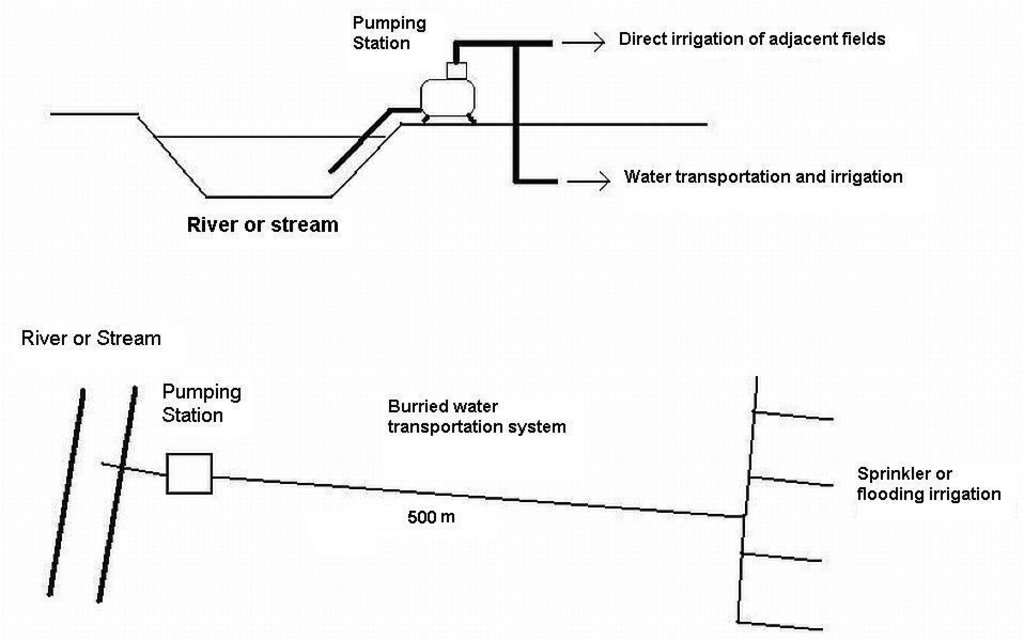
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
Scheme showing the SLM technology application
Location: Eastern Nestos Delta River Basin. Prefecture of Xanthi
Date: 14/03/2010
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: water spreading, replacing saline groundwater with surface freshwater, reduce pressure/overexploitation on aquifer
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase of infiltration, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater
Agronomic measure: soil desalinization
Material/ species: freshwater
Remarks: salinity leaching
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
euro
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
0,7
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | construction of irrigation network | Agronomique |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | Irrigation network | 1,0 | 969,0 | 969,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | hire of an ecavator | Irrigation network | 1,0 | 1107,0 | 1107,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Pumping station | Irrigation network | 1,0 | 3460,0 | 3460,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Water transport pipes | Irrigation network | 1,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Autre | Diesel fuel (1 Lt) | Liter | 1,0 | 1,4 | 1,4 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Electricity (1 Kw) | Liter | 1,0 | 0,4 | 0,4 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 5537,8 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
Life span of the irrigation network: Lifetime
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Network maintenance | Agronomique | annualy |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | Irrigation network | 1,0 | 138,0 | 138,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Hire of an ecavator | Irrigation network | 1,0 | 275,0 | 275,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Pumpiong station | Irrigation network | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | 100,0 |
| Autre | diesl fuel or erlectricity | Irrigation network | 1,0 | 1512,0 | 1512,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 2125,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
The above costs are calculated on May, 2011.
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Diesel or electricity price affects the final cost.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Thermal climate class: temperate. Mediterranean type climatic conditions
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitudinal zone: 0-100 m a.s.l. (Below 10m (plain costal region))
Landforms: Plateau/plains (Plain costal region)
Slopes on average: Flat (Plain region)
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility is low-medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is poor/none (hard-pan formation, crusting and water repellency)
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
bonne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
uniquement pour usage agricole (irrigation)
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Ground water table: on surface (near the coastline or/and adjucent to Nestos river), < 5 m (the rest of Nestos river basin)
Water quality (untreated) is for agricultural use only (irrigation) (Occassionaly wastewater discharges from upstrem factories)
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- élevé
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
Coastal wetlands with high biodiversity
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- commercial/ de marché
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- groupe/ communauté
Niveau de mécanisation:
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
70% of the land users are average wealthy and own 80% of the land.
20% of the land users are poor.
10% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Animal breeders or/and factories workers.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: 1-2 ha, 2-5 ha, 5-15 ha (very few individuals)
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- loué
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- accès libre (non organisé)
- communautaire (organisé)
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Quantité avant la GDT:
3.4t/ha
Quantité après la GDT:
4.2t/ha
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increased, but: Sodic soils may first require gypsoum application
risque d'échec de la production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Less salinity risk
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
disponibilité de l'eau d'irrigation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to increased demand for freshwater
qualité de l'eau d'irrigation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to increased demand for freshwater
demande pour l'eau d'irrigation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Freshwater for irrigation from streams/river
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Requires funding for implementation
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Better crop quality
Autres impacts socio-économiques
Demand for groundwater
Impacts socioculturels
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Income increase and thus well-being.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
qualité de l'eau
drainage de l'excès d'eau
nappes phréatiques/ aquifères
évaporation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
For sodic soils
Sols
encroûtement/ battance du sol
salinité
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
flux des cours d'eau fiables et stables en saison sèche
inondations en aval
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to water abstraction from streams/river for irrigation
pollution des rivières/ nappes phréatiques
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to reduced groundwater exploitation
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Type de changements/ extrêmes climatiques | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | pas bien |
| tempête de vent locale | pas connu |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | pas bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | pas connu |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Commentaires:
The benefits are obvious from the first year of application of the SLM technology and the maintenance cost is logical.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
50
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 90-100%
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
50 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The remaining area (50 %) is irrigated with groundwater.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Better yield How can they be sustained / enhanced? Application of fertilizers |
|
More income due to improved crop quality How can they be sustained / enhanced? Selection of crop type |
|
Better future perspective for the area How can they be sustained / enhanced? Financial motives |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Increased irrigation water quality which result in better soil quality How can they be sustained / enhanced? Construction of more irrigation canals |
|
Remediation of soils How can they be sustained / enhanced? Better drainage systems |
|
Groundwater recharge How can they be sustained / enhanced? Construction of more irrigation canals |
|
Improved quality/quantity of yield How can they be sustained / enhanced? Selection of the most suitable crop type |
|
Improved livelihood of the locals How can they be sustained / enhanced? Better local products promotion |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Bureaucratic problems | Promotion of fast track financial programs |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Installation cost | Financial aid from government/EU |
| Applicable only for fields adjacent or very close to a fresh water source | Construction of canals |
7. Références et liens
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Gkiougkis I. et. al. (2010) Proceedings of the 12th International Congress, Geological Society of Greece, Patras, May, 2010
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Combating Soil Salinization [Grèce]
Use of freshwater to combat soil salinization.
- Compilateur : John Gkiougkis
Modules
Aucun module trouvé