Rehabilitation of degraded lands [Ethiopie]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Unknown User
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Fabian Ottiger
Yetegoda Meret Magegem (Amharic)
technologies_1070 - Ethiopie
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
30/05/2011
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Approches de GDT

Incentive Based Local Level Participatory Planning Approach [Ethiopie]
The approach involves, the use of incentives to motivate particpation of communities in the planning and implementation of SWC activities which improve land productivity and income.
- Compilateur : Philippe Zahner
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Activities that help maintain the productive potentials of soils through prevention and reduction of erosion, enhancing of rehabilitation rate by practicing measures such as microbasins, trench, eyebrow terrace, terraces, pitting and plantation of trees.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
The SWC technology comprises a combination of measures, which include agronomic, vegetative, structural and management measures. This means that in implementing the SWC technology combination of measures such as contour cultivation, grass strips, soil and stone bunds, area closure and improved grazing are applied in integration to rehabilitate degraded lands and restore their productivity. The purpose is to improve food security by reducing erosion and enhance the productivity of land by planting useful trees and fodder species. Unproductive land is changed to productive land by the practicing of the technology. The SWC technology is continously maintained and improved to meet the standards and qulity such that erosion is minimized. The technology is suitable to degraded and unproductive lands which were abondoned as result of low productivity and were previously under cultivation or grazing land. Closure of the area is followed by vegetative and structural measures to speed up the recovery / regeneration rate.
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Ethiopie
Région/ Etat/ Province:
SNNPR
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Alaba special woreda
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a plus de 50 ans (technologie traditionnelle)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
It is introduced technology.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Principales cultures (vivrières et commerciales):
Major cash crop annual cropping: Pepper
Major food crop annual cropping: Maize, teff
Major other crop annual cropping: Sorghum
Major cash crop perennial (non-woody) cropping: Chat, coffee
Major cash crop tree/shrub cropping: eucalyptus

Mixte (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres), incluant l'agroforesterie
- Agro-sylvo-pastoralisme
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Improper landuse, defforestation, overgrazing, lack of action to control erosion.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): lack of awarness, traditional way of ploughing, lack of technolog on SWC
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: open grazing is practiced
Grazingland comments: Nowadays closing a small individual plots and practicing cut and carrying system is being popular among land users.
Plantation forestry: replacing natural forests
Problems / comments regarding forest use: Forest/woodlands are mainly communal, so, replanting forests is undertaken by the community. Individual forests/woodlands are very few and small in size since there is a shortage of land for forests and tree plantation.
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, fruits and nuts, nature conservation / protection
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Haricot bean is planted after maize is planted and has allowed some height.
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines)
Constraints of Stone excavation (quarrying has caused a lott of damage on land.)
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 180 Longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Sep Second longest growing period in days: 120 Second longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Sep
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- Amélioration de la couverture végétale/ du sol
- mesures en travers de la pente
- récupération/ collecte de l'eau
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 60 km2.
Some of the SWC technology areas are well rehabilitated and the remaining sites are partially treated, because these are being newly started sites.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
Commentaires:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
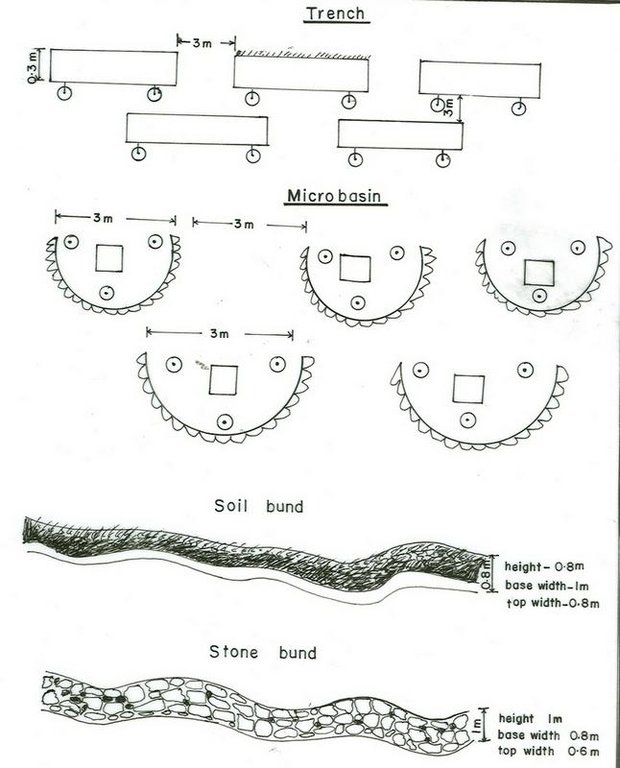
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
SNNPR
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, increase / maintain water stored in soil, reduction in wind speed, improvement of soil structure, increase in soil fertility
Better crop cover
Material/ species: teff, wheat
Quantity/ density: 10,000,000
Remarks: broad casting
Early planting
Material/ species: maize, sorghum
Quantity/ density: 60,000
Remarks: row planting and broad casting
Relay cropping
Material/ species: maize-haricot bean
Quantity/ density: maize-hari
Remarks: row planting
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: maize and haricot bean
Quantity/ density: 120,000
Remarks: row planting
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: maize, sorghum
Quantity/ density: 50,000
Remarks: strip cropping
Green manure
Material/ species: legumes
Quantity/ density: 100,000
Remarks: broad casting
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: leaves, cow dung
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: DAP, UreaTillag
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 10,000,000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.25
Aligned: -against wind
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 40000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 111
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
In blocks
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 40000
Trees/ shrubs species: sesbania, grevillea, acacia
Fruit trees / shrubs species: mango, avocado, orange
Perennial crops species: coffee, chat
Grass species: vetiver, elephant grass
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 8.00%
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 50
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.8
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 80
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.8
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 80
Terrace: forward sloping
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 50
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 10
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Terrace: backward sloping
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 50
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 10
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Bund/ bank: level
Spacing between structures (m): 40
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.8
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Bund/ bank: graded
Spacing between structures (m): 20
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.8
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 20%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 8%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: degraded land to forest land
Major change in timing of activities: structure in dry season, plantation in rainy season.
Other type of management: change of management / intensity level - protection of the closed area by site guards.
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Birr
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
8,6
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
0.70
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Seed collection (grass, trees) | Végétale | dry season |
| 2. | Seed bed preparation | Végétale | on set of rain |
| 3. | Sawing & Planting | Végétale | rainy season |
| 4. | Site selection | Structurel | dry season |
| 5. | participatory planning | Structurel | dry season |
| 6. | Area closing | Structurel | dry season |
| 7. | Trench, microbasin bund construction | Structurel | dry season |
| 8. | Plantation | Structurel | rain season |
| 9. | Site selection for closure area | Modes de gestion | dry period |
| 10. | Closing the degraded land | Modes de gestion | dry season |
| 11. | Construction of structural measures | Modes de gestion | onset of rains and dry seasons |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 387,0 | 387,0 | 26,0 |
| Equipements | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 85,0 | 85,0 | |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 33,0 | 33,0 | |
| Matériel végétal | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Stone | ha | 1,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 512,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 60 month(s)
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tillage/plough | Agronomique | dry season / annual |
| 2. | Compost making and application | Agronomique | before dry season / annual |
| 3. | Sawing and planting | Agronomique | / each cropping season |
| 4. | Plant protection | Agronomique | wet season / annual |
| 5. | Harvesting | Agronomique | dry season / each cropping season |
| 6. | Replanting | Végétale | rainy season /once a year |
| 7. | Weeding | Végétale | after rains /once a year |
| 8. | Cutting the matured trees | Végétale | dry season /once a year |
| 9. | Replanting | Structurel | rainy season/once a year |
| 10. | Reconstruction of structures | Structurel | dry season/once a year |
| 11. | Planting trees | Modes de gestion | rainy season / once a year |
| 12. | plant and harvest grass | Modes de gestion | / before and after rains |
| 13. | Replanting | Modes de gestion | / once a year |
| 14. | Terench and structural measures stablization with plantation | Modes de gestion | / once in a year |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 46,7 | 46,7 | 5,0 |
| Equipements | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 60,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 6,6 | 6,6 | |
| Matériel végétal | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 10,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Stone | ha | 1,0 | 41,4 | 41,4 | 2,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 101,3 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: hoe, shovel, wheel barrow, hammer
The cost is calculated for PD/person days on a hectar basis
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Tools and transport facilities (motorcycles), fuel and food grain.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
850-950 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
- semi-aride
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitudinal zone: 1501-2000 m a.s.l. (ranked 1) and 2001-2500 m a.s.l. (1700-2200m a.s.l., ranked 2)
Slopes on average: Gentle (ranked 1) and moderate (ranked 2, about 70% of the land is on a slope of 2-8%)
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil texture: Coarse/light (ranked1) and medium (ranked 2, sandy loam)
Soil fertility: High
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (well drained)
Soil water storage capacity: Very low (because it is sandy loam soil)
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
- mixte (de subsistance/ commercial)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- traction animale
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
10% of the land users are very rich.
25% of the land users are rich.
40% of the land users are average wealthy.
25% of the land users are poor.
5% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Land users who practice SWC measures get better production. Their incomes has increased compared to those who have not applied SWC.
Market orientation of cropland production system: subsistence (self-supply, part of the production is sold at local market), mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
Market orientation of grazing land production system: subsistence (self-supply, fodder plant for milk cow), mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
Market orientation of forest production system: subsistence (self-supply, tree plantation on individual plots ), mixed (subsistence/ commercial), commercial/market (plantation of a community forests)
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Commentaires:
Cropland: average cultivated land is about 1.5 ha/household
Grazing land: not more than 0.125 ha on average
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
production fourragère
qualité des fourrages
production de bois
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
decrease of grazing land
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Impacts socioculturels
institutions communautaires
institutions nationales
apaisement des conflits
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Quantité avant la GDT:
75
Quantité après la GDT:
25
Sols
humidité du sol
couverture du sol
perte en sol
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
contrôle des animaux nuisibles/ maladies
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
vitesse du vent
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
flux des cours d'eau fiables et stables en saison sèche
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
structural measures
inondations en aval
envasement en aval
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
52000
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 10-50%
Commentaires:
90% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
46800 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
5200 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Nowadays land users have better understanding on SWC technologies, so they protect their farm land from erosion with vegetation.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
SWC knoweldge is gained How can they be sustained / enhanced? through training and practical works |
|
additional income is created How can they be sustained / enhanced? diversification of SWC measures with in the same plot |
|
group work is encouraged/introduced How can they be sustained / enhanced? strengthening group formation |
|
food value has increased How can they be sustained / enhanced? from vegetables and fruits |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
degraded lands are rehabilitated and covered with plantation. How can they be sustained / enhanced? through increased participatory planning approach |
|
crop production has increased. How can they be sustained / enhanced? apply more combined technologies to enhance production |
|
wood production has increased How can they be sustained / enhanced? planting multipurpose plant species increased |
|
extensive grazing is changed to intensive grazing How can they be sustained / enhanced? to some extent number of animals are reduced |
|
the community is aware of the technilogy How can they be sustained / enhanced? land users construct SWC technologies on their farm land by their own |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| shortage of grazing land | use cut and carry system |
| destruction of crop by wild animals | making farmers group to protect them |
| shortage of incentives | practicing more community participation works. |
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Incentive Based Local Level Participatory Planning Approach [Ethiopie]
The approach involves, the use of incentives to motivate particpation of communities in the planning and implementation of SWC activities which improve land productivity and income.
- Compilateur : Philippe Zahner
Modules
Aucun module trouvé