Holistic demonstration [Inde]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Unknown User
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Fabian Ottiger
Samagra Jalanayan Abhivrudhi Pratyakshike (Kannada)
technologies_1084 - Inde
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
12/03/2004
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Holistic demonstration includes integrated cultivation of Agri-Horti-Silvi technologies. Along with the Soil & water Conservation structures suitable to the site.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
Holistic demonstration was taken in the upper reach, middle reach and lower reach (2 hectares each) in a village in the watershed. The demonstration units includes soil & water consercvation structures also. Crop demonstration with integrated pest management, seed treatment, pitcher irrigation practices, varietal trails were implemented to increase the overall per capita income of the farmer. However, the suitable SWC was according to the site of lower reach/ upper reach or middle reach. The plot was accommodated with suitable field crops, horticultural species either on the bunds or in the fiels itself and some fodder crops, some forestry species etc.
Purpose of the Technology: The demonstration units now serve as the units of awareness brining in understanding the holistic approach and also to encourage the other farmers to replicate the same in their fields.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: (1) site selection with concerned farmer, (2) design and preparation of estimates by the project staff, (3) discussion with the VWDC and community, (4) discussion regarding contribution with the farmer (5) layout and construction by the project staff with the contribution from the concerned farmers.
Natural / human environment: This technology was taken up in the semi arid condition and in the erratic rainfall conditin.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Inde
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Karnataka
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Chitapur taluk of Gulbarga district
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a plus de 50 ans (technologie traditionnelle)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Mainly from the SWC specialist
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Mixte (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres), incluant l'agroforesterie
- Agro-sylvo-pastoralisme
Principaux produits/ services:
Major cash crop annual cropping: Redgram
Major food crop annual cropping: Jowar
Major other crop annual cropping: Sesamum
Major cash crop perennial (non-woody cropping): Mango
Major food crop perennial (non-woody cropping): Drumstick, curryleaf
Major cash crop agroforestry: Bengalgram
Major food crop agroforestry: Mango, sapota
Major other crop agroforestry: Neem, teak
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, fruits and nuts, nature conservation / protection
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Crop land : Low yields due to erosion, less soil moisture, shallow to medium soils. Poor and erratic rainfall, water holding capacity is less.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Crop land - Uncertain rainfall, more soil loss and poor yields.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: the village cattle are let free for grazing on the common land for some time in the day and they go back and then I is again stall feeding.
Plantation forestry: Yes
Other type of forest: others (scattered)
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: During kharif (monsoon) season the main crop is redgram (Tur), in addition few cereals were taken, followed by jowar in the major rabi (post-monsoon) crop. No cultivation was o\bserved in summer, farmer are now cultivating vegetable and fruit crop,
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Commentaires:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated and post-flooding (both ranked 2)
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct Second longest growing period in days: 120 Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- perturbation minimale du sol
- lutte intégrée contre les ravageurs et les maladies (incluant l'agriculture biologique)
- gestion de l'irrigation (incl. l'approvisionnement en eau, le drainage)
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.12 km2.
The technology area comprises of 2 ha area each in upper reach, middle reach and lower reach in a village of the watershed. In this area cultivation of agri-horti-silvi practices, agronomic trials, in-situ conservation etc were taken with active involvement of the the farmers.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify, poverty / wealth (lack of captial)
Secondary causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (other (migration)), labour availability (lack of labour, cost of labour), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
Commentaires:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
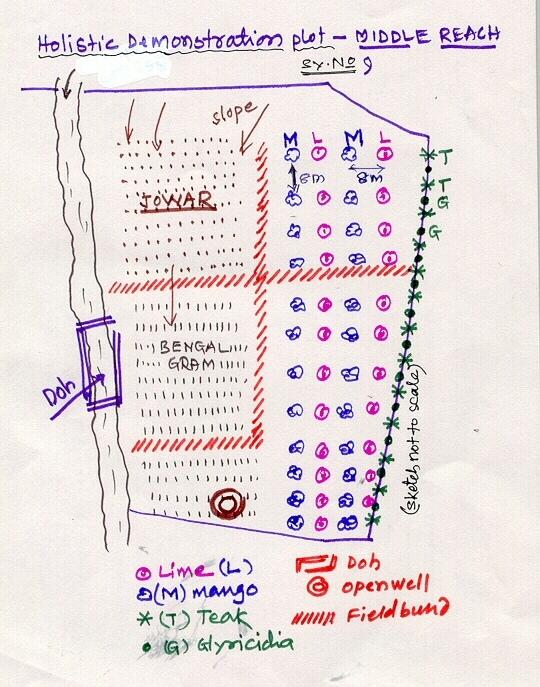
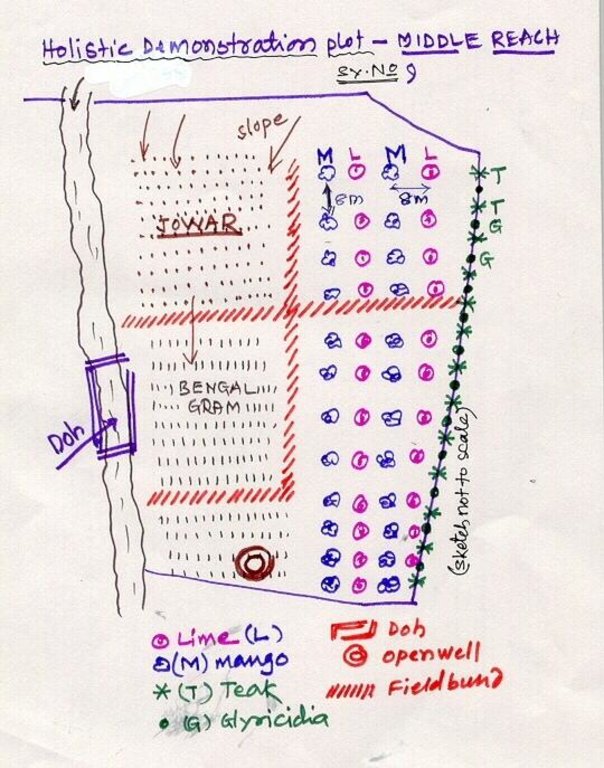
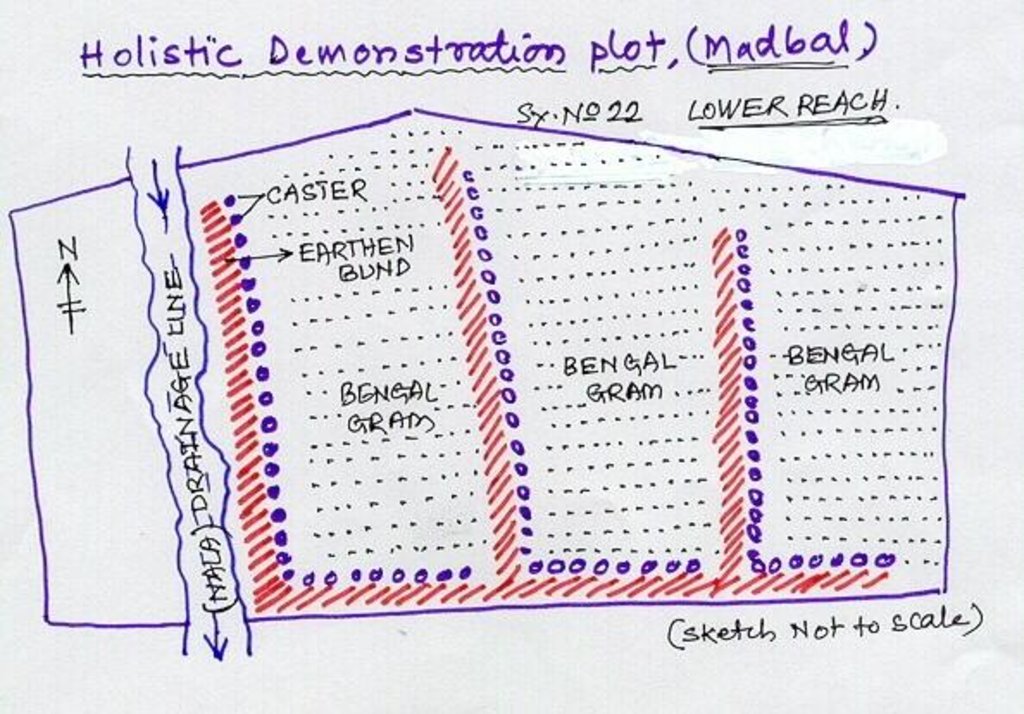
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
Lower Reach holistic demonstration plot showing various soil & moisture conservation structures, field crops and bund stabilization by vegetation.
Location: Bennur-B nala watershed Chitapur taluk. Chitapur taluk, Gulbarga District (Karnataka state
Date: 20.4.2004
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, water harvesting / increase water supply, increase in soil fertility
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: saplings
Quantity/ density: 100
Remarks: layout
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: sapplings
Quantity/ density: 360
Remarks: layout
Legume inter-planting
Quantity/ density: 200
Remarks: layout
Agronomic measure: others (vermicompost)
Material/ species: material
Minimum tillage
Remarks: material
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 100
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 500
Trees/ shrubs species: Neem, Glyricdia, Pongamia, Bamboo
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Mango. Tamarind, Lime, Sapota, Clustard apple
Grass species: Napiar
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 2.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 1.00%
Dam/ pan/ pond
Vertical interval between structures (m): 4
Spacing between structures (m): 50
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 12
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 12
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 12
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 12
Bund/ bank: semi-circular/V shaped trapezoidal
Vertical interval between structures (m): 4
Spacing between structures (m): 50
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 50
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.9
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50
Structural measure: pit, sediment sand / trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 30-40
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 6
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.9
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50
Structural measure: other (brushwood dam)
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 80
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 6
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.9
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 0
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 1%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 2%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 1%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:10
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: Multidimensional participatory holistic farming system, fallow to cultivable land
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Rupees
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
46,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
0.73
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging of pits | Végétale | Sumer |
| 2. | Procurement of seed/ seedlings | Végétale | Before rainy season |
| 3. | Sowing of grass, shrub seeds | Végétale | After first shower |
| 4. | Planting of sappling | Végétale | After first shower |
| 5. | Survey/ layout | Structurel | April |
| 6. | Excavation of ditches | Structurel | may |
| 7. | Transportation of stones to the site | Structurel | May |
| 8. | Construction of bunds, farm pond | Structurel | may |
| 9. | Construction of brushwood dam, doh | Structurel | June |
| 10. | Training, capacity building of the farmer | Modes de gestion | february - March |
| 11. | Establishment of sructural measures | Modes de gestion | April-June |
| 12. | establishment of vegetative measures | Modes de gestion | July-September |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 510,0 | 510,0 | 10,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 114,0 | 114,0 | 3,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 169,0 | 169,0 | 74,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 157,0 | 157,0 | |
| Engrais et biocides | Biocides | ha | 1,0 | 76,0 | 76,0 | |
| Engrais et biocides | Compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 15,0 | 15,0 | 10,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Stone | ha | 1,0 | 110,0 | 110,0 | 3,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Wood | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 3,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Earth | ha | 1,0 | 26,0 | 26,0 | 2,0 |
| Autre | Pitcher pots | ha | 1,0 | 72,0 | 72,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 1259,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 36 month(s)
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Mulching | Agronomique | Summer / each cropping season |
| 2. | Across slope ploughing | Agronomique | Summer / each cropping season |
| 3. | In-situ maisture conservation | Agronomique | before sowing / |
| 4. | Watering | Végétale | summer /once in 10 days |
| 5. | Weeding, mulching | Végétale | 2-3 months after planting /twice in a year |
| 6. | Re-seeding of grass/ shrub | Végétale | before first shower /up to 2 years |
| 7. | casualty replacement | Végétale | before first shower /1, 2, and 3rd years |
| 8. | fencing | Végétale | during sumer period /every summer season of 2nd, 3rd and 4th year |
| 9. | Repair of breaches in bund | Structurel | July to september/as required |
| 10. | Desilting of traps | Structurel | October-November/annual |
| 11. | Refresher interaction with farmer | Modes de gestion | / seasonally |
| 12. | Rgular meetings | Modes de gestion | / as and when required |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 51,0 | 51,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 11,1 | 11,1 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 16,9 | 16,9 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 15,7 | 15,7 | |
| Engrais et biocides | Biocides | ha | 1,0 | 7,6 | 7,6 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Stone | ha | 1,0 | 11,0 | 11,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Wood | ha | 1,0 | 1,0 | 1,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Earth | ha | 1,0 | 2,6 | 2,6 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Pitcher pots | ha | 1,0 | 7,2 | 7,2 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 124,1 | |||||
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Non availability of stones, boulders
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
750-800 mm
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitudinal zone: 101-500 m a.s.l. (422.8 m a.s.l.)
Landforms: Plateu/plains (3-4% slope, ranked 1), ridges (ranked 2)
Slopes on average: Gentle (3-4%)
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average: Moderately deep (60 cm, ranked 1) and deep (ranked 2)
Soil fertility: Medium (eroded soils)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (absence of vegetation)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Poor (high run-off from stony surface)
Soil water storage capacity: Very low
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
- mixte (de subsistance/ commercial)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- très pauvre
- pauvre
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
7% of the land users are average wealthy and own 26% of the land.
65% of the land users are poor and own 58% of the land.
28% of the land users are poor and own 16% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Off season employment
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Commentaires:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology:
Cropland: 0.5-1 ha: Joint farmers, land shared by brothers (ranked 1), 1-2 ha (ranked 2), 2-5 ha (ranked 3)
Grazing land: 0.5-1 ha: Not much grazing land is available in the village.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Drought from last 3 years
production fourragère
qualité des fourrages
production de bois
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
SWC takes small piece of cultivable land
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Impacts socioculturels
institutions communautaires
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Village watershed development committee, users groups etc.
institutions nationales
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
apaisement des conflits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Project support is expected by most of the farmers at a time.
Impacts écologiques
Sols
humidité du sol
couverture du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Area was previously barren
perte en sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Good vegetative cover
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Ground cover established with vegetative hedges.
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
vitesse du vent
Autres impacts écologiques
Soil fertility
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Introduction of legume species (glyricidia)
Biodiversity
Waterlogging
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Not a genereal problem. But only on this plot.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
flux des cours d'eau fiables et stables en saison sèche
inondations en aval
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
In-situ conservation
sédiments (indésirables) transportés par le vent
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Establishment of ground covers
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
452
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 0-10%
Commentaires:
60% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
417 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
5% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
35 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Overall returns fro\m the piece of land is increased owing to horticulture and agriculture crops. Biomass increases. This is seen by other farmers and they are motivated to go for its adaption.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Economic sustainability How can they be sustained / enhanced? vegetative and green manure vermicompost etc. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Effective SWC How can they be sustained / enhanced? maibntenance by the individual farmers |
|
water harvesting How can they be sustained / enhanced? Desilting structure |
|
Integrated approach How can they be sustained / enhanced? regular contact |
|
increased production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Integrated cultivation |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Production (benefits) adversly affected due to drought. | Due to longer dry spel in the area (last three years) |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Non-availability of agricultural improved seed material at local level | by linkage of VWDCs with the Agricultural Research Station and Krishi Vignyan Kendra. |
| conflicts | demands by more number of farmers could not be met by the project at a time. |
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé