Check dam for land [Chine]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Fei WANG
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : David Streiff
淤地坝,谷坊
technologies_1455 - Chine
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Mu Xingming
xmmu@ms.iswc.ac.cn
Institute of Soil and Water Conservation, CAS and MWR
Chine
Spécialiste GDT:
Wen Zhongmin
zmwen@ms.iswc.ac.cn
Institute of Soil and Water Conservation, CAS and MWR
Chine
Spécialiste GDT:
Spécialiste GDT:
Chen Yun-ming
ymchen@ms.iswc.ac.cn
Institute of Soil and Water Conservation, CAS and MWR
Chine
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Northwest A&F University (NWAFU) - Chine1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
20/12/2008
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Approches de GDT

Project of check-dam for land [Chine]
Approach of check dam for land is a kind of soil and water conservation activity to reduce the sediment discharge and improve the agricultural condition through building a dam across the valley in order to silt the sediment from upstream untill it convert to land with few soil erosion and …
- Compilateur : Fei WANG
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Check dam for land is a structural SLM practice that is constructed in the valley of a watershed in order to slow down the runoff and increase sedimentation. After this, the land quality of the controlling area will increase because soil and water conditions in this place are imporved.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
The check dam is a small dam designed to reduce flow velocity, control soil erosion, and allow to settle on the bed of the valley. The whole system includes main body of dam, spillway, overflow and supporting measures. The check dam for land is a small dam mainly for land after it is filled up by the sediment from upstream area, from several years to 20 years in common, it could be flat land in the valley, not mainly for water collection (different from reservior).
Purpose of the Technology: Check dams in the Loess Plateau are very common. There are many advantages. The check dam could not only reduce the erosion of the gullies, furthermore it retain the sediment in the flow and this decreases the sediment of the Yellow River. The check dam is good quality land for the soils because of the sedimentation of organic matter and other nutrients from topsoil . In this region soils are deep and very fertile because most soil is from the top soil upstream. The soil moisture of check dam is also much better than in any other places in the watershed because the flood should go away from its surface and the water inflitration is great in raining seasons.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The establishment needs enough money because it has to be safe enough, and the maintenance cost is not so high. The catchment with great soil erosion is better when we considered the formation time of land.
Natural / human environment: The controlling area of check dam for land varies greatly from 30 square km or more. Since the "Grain for Green" Project of China in 1999, the soil erosion on the slope decreased. The time from reservoir to land need more time because there is less and less sediment from upstream and the sedimentation changed slowly.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Chine
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Shaanxi Province
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Yanhe River Basin
Commentaires:
Boundary points of the Technology area: Only one check-dam for land is listed here.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a entre 10-50 ans
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- au cours d'expérimentations / de recherches
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
It is an old methodology in the Loess Plateau. Since 2003, the check dam had been determined as "Highlight Project " of the Ministry of Water Resources in order to expand in the whole area of the Yellow River Basin.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Mixte (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres), incluant l'agroforesterie
- Sylvo-pastoralisme
Principaux produits/ services:
major cash crop: beans, sunflower, apple, Chinese date, alfalfa
major food crop: Potato, millets, maize, buckwheat
other crop: vegetable

Voies d'eau, plans d'eau, zones humides
- Etangs, barrages, retenues d'eau
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Normally, the bed of valley is V-shaped and is covered by grass and trees. For the seasonal torrent or flash, it is very difficult to plant crops. The gully also cuts down by runoff and extends because of erosion's gravity .
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): It can not be used as agricultural purpose, especially to get more food.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
Si l'utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie, indiquez l'utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie:
Mixed: Ms: Silvo-pastoralism
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 300Longest growing period from month to month: March to NovemberSecond longest growing period in days: 200Second longest growing period from month to month: April to October
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- mesures en travers de la pente
- gestion des eaux de surface (sources, rivières, lacs, mers)
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 19.4 m2.
The total area with different measures is almost 2000 km2 . Yanhe River is a first class branch of Yellow River, China. The average channel slope is 3.26‰, and the area of whole basin is 7,687 km2. It is situated in the semi-arid North Temperate Zone with an average annual precipitation varying from 500 to 550 mm, and an average annual air temperature ranging from 8.5 to 11.4℃. It is in hilly gully area of the Loess Plateau covered by loess. The landform is broken seriously. The gully density (the length of channel in one km2) is amount to 2.1 to 4.6 km•km-2. The soil loss is severe all along.
The Ganguyi Hydrology Station (109°48′E, 36°42′N) located in the Ganguyi Town, Baota Country, Yan’an City, Shaanxi Province. The area up Ganguyi Hydrology Station is 5,891 km2, including of Jingbian County(256km2), Zhidan County(708km2), Ansai County(2,699km2) and Baota County(2,228km2). The average annual runoff is 0.22 billion m3, and the runoff modulus accounting for 4,776.36 m3•km-2•yr-1. The average annual sediment flow is 4.776 million tons, and the sediment flow modulus accounting for 8,100 t•km-2•yr-1. The coarse sediment (sediment particle diameter not less than 0.05 mm) flow modulus is 2,430 t•km-2•yr-1 on the Ganguyi Hydrology Station.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S5: Barrages/retenues, micro-bassins, étangs
- S11: Autres
Commentaires:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines
- Wo: effets hors-site de la dégradation
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (It is the reason of erosion that influence the valley.)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
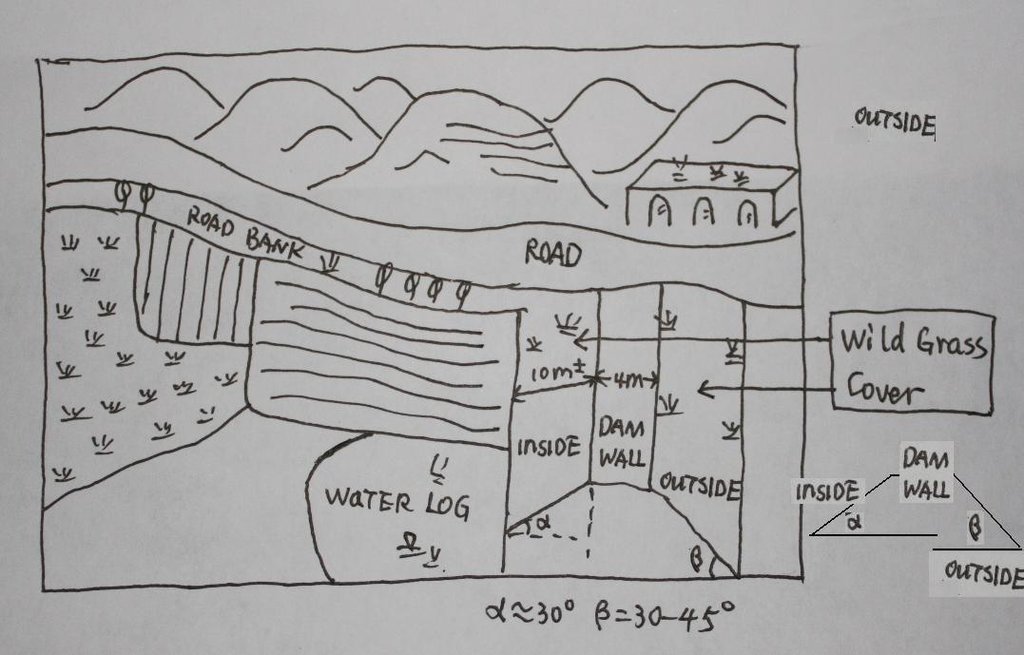
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
The check dam land.
Location: Mazhuang Watershed. Baota County, Yan'an City, Shaanxi China
Date: 2008-10-20
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (The design and construction need professional knowledge.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (it is easy to use, like alluvial land or wide terrace.)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap
Spillway
Vertical interval between structures (m): 3
Spacing between structures (m): 6
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 4
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 6
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 100
Dam/ pan/ pond
Vertical interval between structures (m): 10
Spacing between structures (m): 100
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 10
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 50-100
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 300-1000
Construction material (earth): The earth-bank dam is built in Yanhe River Basin.
Construction material (stone): to build the spillways
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 2-5%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 2%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 2%
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 180000m3
Catchment area: 58.3km2m2
Slope of dam wall inside: 30%;
Slope of dam wall outside: 60%
Dimensions of spillways: 3m
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars US
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
-2,17
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
8.80
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Field survey and location selection | Structurel | Before design |
| 2. | Design | Structurel | before construction |
| 3. | Build the dam wall | Structurel | |
| 4. | Check and accept | Structurel | After the construction |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Building the wall/ field survey and planning | Person/day | 180,0 | 8,8 | 1584,0 | 90,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Building the wall/ field survey | Machine/hrs | 75,0 | 43,8 | 3285,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Stone | m^3 | 40,0 | 26,35 | 1054,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 5923,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | check the dam wall | Structurel | annually |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | check annualy the dam wall | Person/day | 15,0 | 8,8 | 132,0 | |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 132,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: crawler type bulldozer, giant jet, tractor, traditional tools, ruler,
The grass on both sides of check wall is natural grass.
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The wide of dam wall affects the cost greatly, the wider, more expensive.The labour cost and the distance of rock quarry are also important.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
The mean annual rainfall in the basin is 515.2 mm in the duration from 1952 to 2000. The rainfall from May to Oct accounts for 446.8 mm, up to 86.7%; and that from Jun to Sep accounts for 367.6 mm, up
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Thermal climate class: temperate. The accumulating time that temperature above 0 ℃ about 3800 hours, and that above 10 ℃ is more than 3200 hours
It is based on the classification sysytem only based on the rainfall.
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- situations concaves
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitudinal zone: All check dam and check dam liand here is in such altitudinal zonation.
Slopes on average: Based on 1:100 thousand scale landform map
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average: The depth of Loess varies from nearly 30 m to more than 100 m in Yanhe River Basin. The depth of soil is less than this but it could be nearly 10 meters in commom.
Soil texture: There are more than 50% soil particle which are fine sand with size between 0.05 and 0.1 mm
Soil fertility very low: Lack of N, P and SOM
Topsoil organic matter: <0.5%
Soil drainage / infiltration good: The inflitration in Loess is very fast, but it prones to sealing when flashing
Soil water storage capacity low: Evaporation and drainage are easy
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
faiblement potable (traitement nécessaire)
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Availability of surface water also poor/ none and: Nearly all the branches of Yanhe are seasonal rivers
Availability of surface water medium: It is very stable in this region
Water quality (untreated): Good quality for there are few pollution sources
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
It is very stable in this region
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- mixte (de subsistance/ commercial)
- commercial/ de marché
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- groupe/ communauté
Niveau de mécanisation:
- traction animale
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Difference in the involvement of women and men: No clear difference
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
(The Check dam for land are build together in some villages for all the people funded by national sub).
Level of mechanization also manual work: The harvesting and other management are by hand
Level of mechanization animal traction: Tillage with animal power mostly
Level of mechanization mechanized/motorized: Tillage with machine in large area check-dam land.
Market orientation of production system mixed: Some production for themselves, but most of production is exchanged on the market.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
According to 0.054 ha per capita
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
- communauté/ village
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- accès libre (non organisé)
Commentaires:
Like other rural areas in China
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Quantité avant la GDT:
600
Quantité après la GDT:
6000
risque d'échec de la production
Quantité avant la GDT:
4500kg/ha
Quantité après la GDT:
2500kg/ha
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
In extreme year with great rainfall, low yield of check dam land
diversité des produits
surface de production
Quantité avant la GDT:
950
Quantité après la GDT:
59
Impacts socioculturels
institutions nationales
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
Quantité avant la GDT:
200 kg
Quantité après la GDT:
350 kg
Livelihoods and human well-being
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
drainage de l'excès d'eau
nappes phréatiques/ aquifères
Quantité avant la GDT:
8 m
Quantité après la GDT:
4-6m
Sols
humidité du sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
12-16%
Quantité après la GDT:
16-22%
perte en sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
60t/ha/yr
Quantité après la GDT:
5t/ha/yr
Autres impacts écologiques
long time period to form land
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Sediment from slope decelerate the process of building arable land. In other words the economic function can not appear soon.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
flux des cours d'eau fiables et stables en saison sèche
inondations en aval
Quantité avant la GDT:
2events/yr
Quantité après la GDT:
nearly no
pollution des rivières/ nappes phréatiques
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Type de changements/ extrêmes climatiques | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | bien |
| tempête de vent locale | bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | pas connu |
Commentaires:
The better condition of soil and water of check dam land improves the capacity of land tp cope with the changing climate.
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Commentaires:
In the first stage, there is no economic output but the check dam is going to fill up with sediments. Afterwards the check dam forms land and with it benefit which would keep up a long time.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- 10-50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
675 households in an area of 19.4 km^2 (11 percent of the area)
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 0-10%
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
675 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: All the lands (cropland on the slope or check dam land and forest et al, ) are shared evenly by people. Of course, the work like to build check dam should be finished by all the families.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: No single farmer or family can finish this work because the land right and great investment.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: More and more local farmers want to get more check dam land for its long-term benefits.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
The yield of check dam land is much higher than that on the slope land. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ask the local people to do more work without payment because they would get more benefits from this land as such. |
|
The yield is stable because the soil moisture is good even in dry year How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use the land efficient and mainten it. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
It could reduce the soil erosion originated from the gully. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The local people know this benefit that make them try to find chance to build check dam. |
|
The dam can retain the flow and sediment and reduces the sediment delivery of the downstream. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ask the people or government of the lower reaches to combat soil erosion through the building of check dams. |
|
The check dam land is fertile and productive How can they be sustained / enhanced? When we make the plan or design the construction, we should better take this into account. |
|
Land is fertile and productive How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improve the awareness of local people to use this technology. |
|
The ceck dam can be used as rural road. How can they be sustained / enhanced? When we make the plan or design the construction, we should better take this into account. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| It is too expensive to build the check dam. | Ask the government or other organization and person to invest in check dams.The local people can work together without payment. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The land in a check dam with less and less soil erosion on the slope, needs longer time to form | It is difficult to overcome this because the control of erosion on slope has higher priority. We can find how to use the water or the temporary wetland. |
| The input of check dam is quite high. | Ask the government or other organization and person to invest in check dams. The local people can work together without payment. |
7. Références et liens
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Soil and water conservation records of Shaanxi Province. 2000. Shaanxi People's Press, Xi'an City, China
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Library of ISWC, CAS
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Project of check-dam for land [Chine]
Approach of check dam for land is a kind of soil and water conservation activity to reduce the sediment discharge and improve the agricultural condition through building a dam across the valley in order to silt the sediment from upstream untill it convert to land with few soil erosion and …
- Compilateur : Fei WANG
Modules
Aucun module trouvé