Dugout Sunken Pond with Catchment Treatment [Inde]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Unknown User
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Fabian Ottiger
Bandha/ Pokhari (Oriya)
technologies_1475 - Inde
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
Spécialiste GDT:
Patnaik Kishore Chandra
Inde
Spécialiste GDT:
Pradhan Gandhi
Inde
Spécialiste GDT:
Tripathy Dasarathi
MALKANGIRI (ORISSA) INDIA
Inde
Spécialiste GDT:
Panda R.K
Central Soil & Water Conservation Research & Training Institute
Semiliguda, Koraput, Orissa, India
Inde
Spécialiste GDT:
Mohanty K.C
Sahid Laxman Naik Development Society
Malkangiri Orissa India
Inde
Spécialiste GDT:
Mishra BIJAYALAXMI
IDCWDP
Koraput
Inde
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Central Soil & Water Conservation Research & Training Institute - IndeNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Sahid Laxman Naik Development Society - IndeNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
IDCWDP (IDCWDP) - Inde1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
20/08/2004
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Approches de GDT
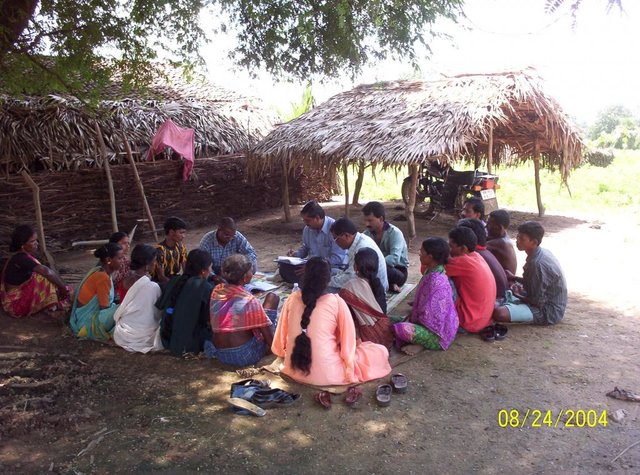

PARTICIPATORY APPROACH IN IDCWDP, DANIDA [Inde]
Participatory approach for holistic and intigrated development of the defined area on watershed basis involving all level of stake holders.
- Compilateur : Srikanta Kumar Parida
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
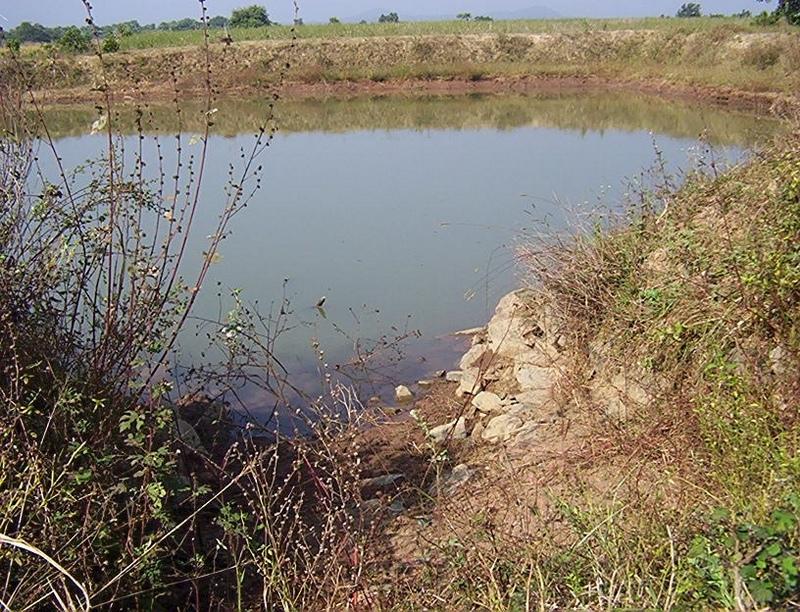
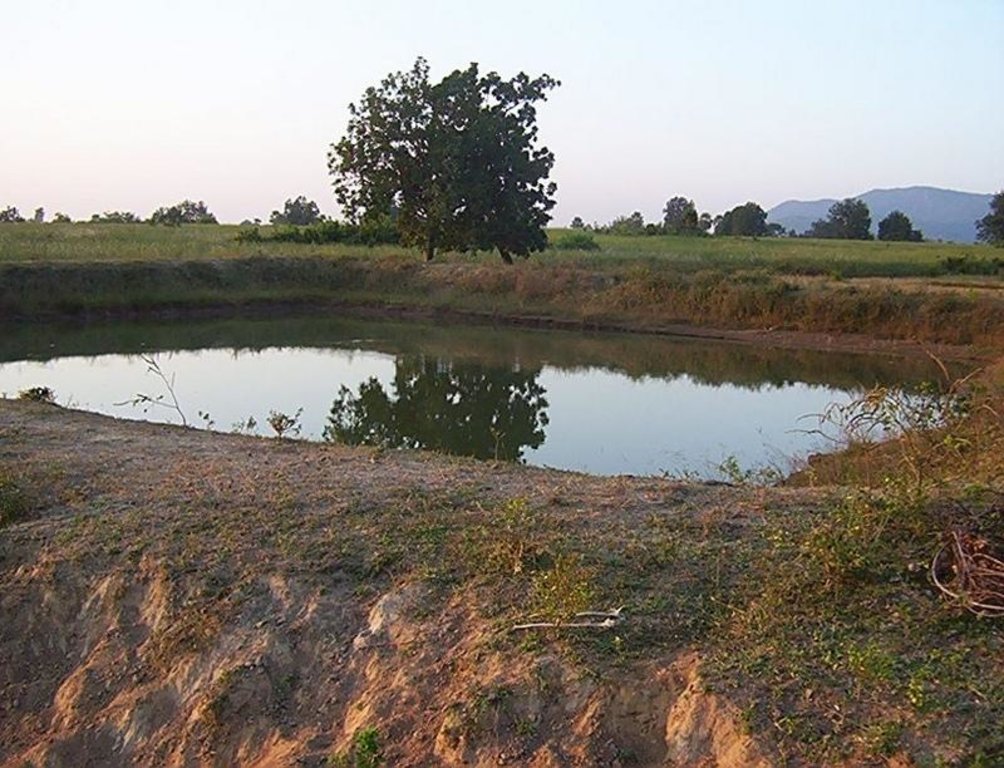
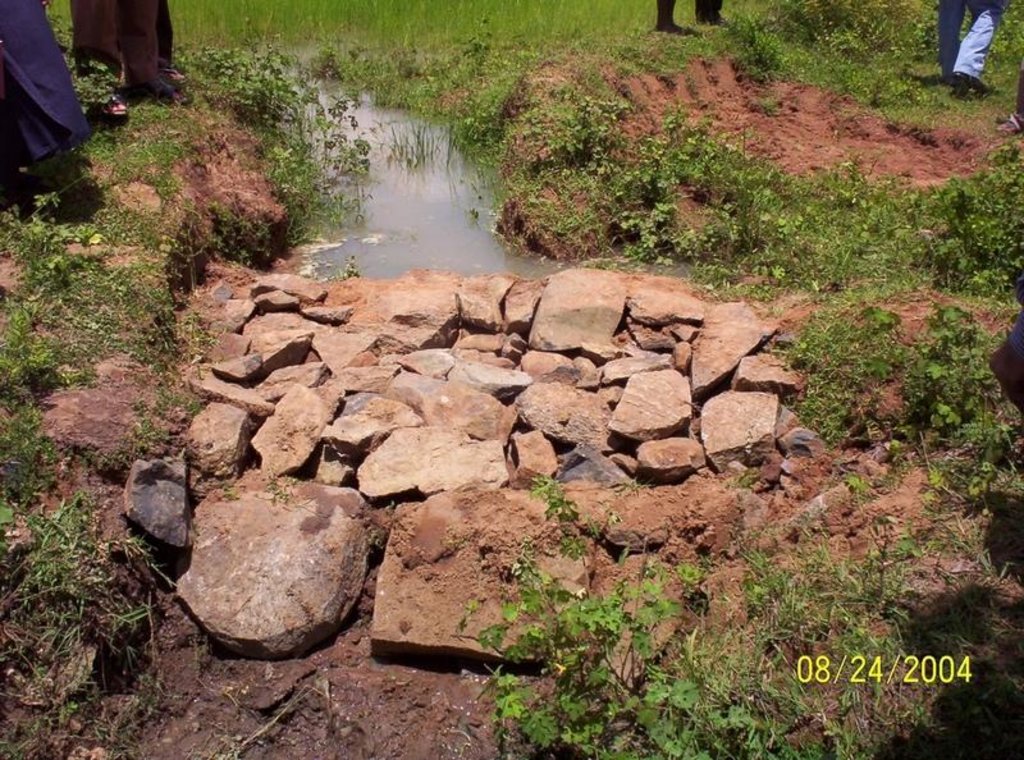
Dugout sunken pond with catchment treatment.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
(1) Total size of the project area = 4.75 Ha.
(2) Different structures taken up in the project area are
(i) Brushwood check dam- 6 Nos.
(ii) Drop structure- 8 Nos.
(iii) Dugout sunken pond - 1 No.
(3) All the above structures were positioned to ridge to valley treatment
(Ref.QT-6/2.1.2/a)
Purpose of the Technology: 1) Storage of runoff for cattle and human use.
2) Construction of structures to check soil erosion and sand casting.
3) Pisciculture.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment :-
1) SWC specialist selected sites for dugout sunken pond, layout the design.
2) SWC specialist also selected sites for drop structures, brushwood check
dams in gullied portion of project area with reference to vertical interval
of slope gradient and space between structures.
3) The execution of work were done by concerned villagers on payment basis.
4) During execution, 20% of the total cost of the dugout sunken pond was
contributed by the villagers in shape of labour.
5) Training on technical know how imparted to the villagrs during execution
of pond, bund, drop structure and brush wood check dam.
Maintenance:-
1) The dugout sunken pond requires (a) Desiltation once in two years (b)
Repair of earthern bund around inlet and outlet every year.
2) The drop structure & brushwood check dams requires little maintenance when
ever requires.
3) One management group has formed in the same village & funds has been
raised by doing pisciculture in the pond.
4) The management group is taking major reponsibility for its maintenance.
Natural / human environment: (1) Drainage line stablilized (2) Adjuscant area cultivated (3) Users group
formed and pisciculture taken up for the Ist time in the village.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Inde
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Orissa
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Orissa/ Malkangiri
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
National Watershed Development Project for Rainfed Area (NWDPRA)
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Principales cultures (vivrières et commerciales):
Major food crop: Paddy

Pâturages
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion):
1) A fellow, undulating, gullied piece of land.
2) Acute sand casting at the down stream cropland.
3) About 40% of the project area were practicing local paddy which suffers from erratic rainfall.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): A piece of land which depends upon the mercy of the Rain God for annual production.
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Jul - Nov
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- récupération/ collecte de l'eau
- apiculture, aquaculture, élevage de volailles, de lapins, du ver à soie, etc.
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.0475 km2.
A fellow, understanding, gullied piece ofland selected for the technology which suffers from sand casting and uncertainity of rain.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes - Coordination of traditional method of agricultural practices like along the slope, use of long term local varieity of seeds etc.), poverty / wealth (lack of captial)
Secondary causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Erosion problem), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge), Common social practices
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
Aerial view of dugout sunken pond
Location: Siadimal, Korkonda. Malkangiri/Orissa/ India
Date: 15.3.2005
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, water harvesting / increase water supply, Control of sand casting
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.15
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.45
Vegetative measure: In earthern bund slope
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): Compact
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 3.7
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Grass species: Vertivera and local grass slods
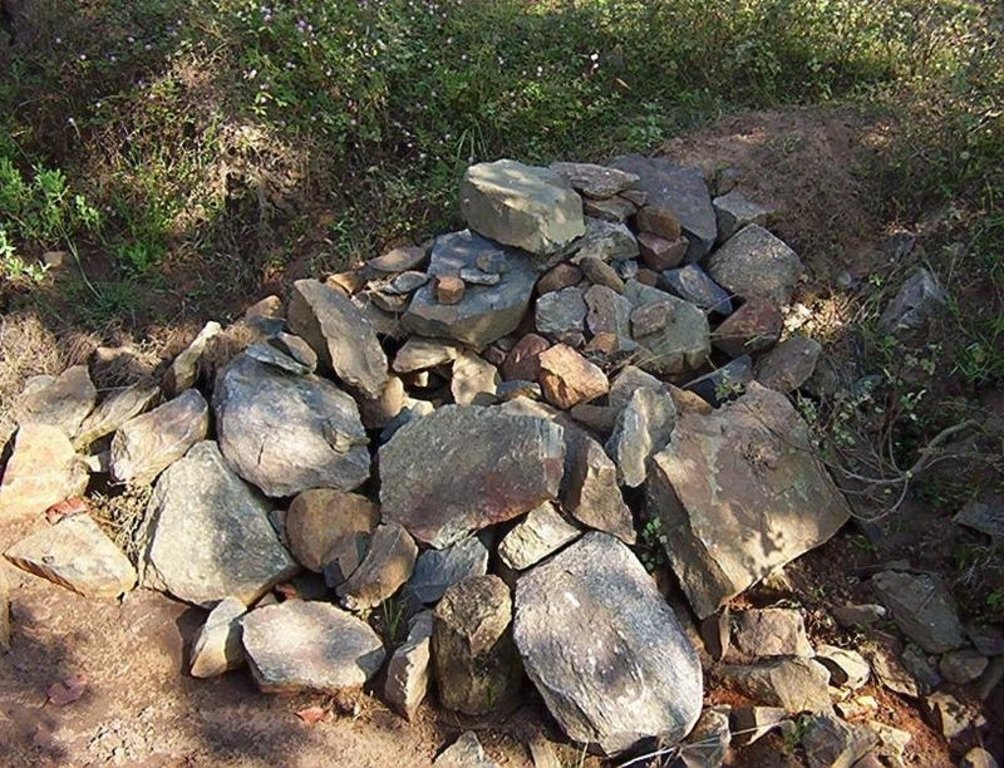
Structural measure: Sediment/Sand/Trap/brushwood check dam
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0.6
Spacing between structures (m): 10
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Structural measure: Sediment/Sand/Trap/ drop structure
Vertical interval between structures (m): 9
Spacing between structures (m): 15
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.05
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 5.3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Structural measure: Dam/Pan/Dugout sunken pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 28/26/24/22
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 28/26/24/22
Structural measure: Bund/Trapizoidal
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.85
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.50+8.9/2
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 157
Construction material (earth): Soil excavated from pond is used to built bund around pond.
Construction material (stone): Inlet and outlet of pond and drop structure are made up of stone
Construction material (wood): Brush wood check dams are made up of wooden poles and bush wood.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 8%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 3%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:41
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Rupee
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
45,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
0.89
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collection grass sods and vertivera slips | Végétale | beginning of rainy season |
| 2. | Transporting grass sods on established banks | Végétale | beginning of rainy season |
| 3. | Watering | Végétale | When dry in Ist. Season |
| 4. | Dugout sunken pond-Surveying | Structurel | Summer season |
| 5. | Dugout sunken pond- soil excavated from pondage area used in trapizodical bund around leaving inlet & outlet portion. | Structurel | Summer season |
| 6. | Dugout sunken pond- Collection and transporting stone to inlet & outlet site | Structurel | Summer season |
| 7. | Dugout sunken pond- construction of inlet & outlet with stone | Structurel | Summer season |
| 8. | Dugout sunken pond- collection of local grass sods & vertiver slops | Structurel | Onset of rain |
| 9. | Dugout sunken pond- turfing the bund slopes and planting of vertiver slips in rows at up stream and down steam side of inlet and outlet | Structurel | On set of rain |
| 10. | Brushwood check dam- surveying | Structurel | Summer season |
| 11. | Brushwood check dam- collection of wooden poles and brush wood | Structurel | Summer season |
| 12. | Brushwood check dam- collection of picked up stones | Structurel | Summer season |
| 13. | Brushwood check dam- fixing of wooden pole, weiving with brush wood, filling up the gaps with picked up stones | Structurel | Summer season |
| 14. | Brushwood check dam- collection of vertiver slips and planting in upstream and downstream of each structure | Structurel | On set of rain |
| 15. | Drop structure- surveying | Structurel | Summer season |
| 16. | Drop structure- collection & transportation of stones to work spot | Structurel | Summer season |
| 17. | Drop structure- construction of drop structure with stones | Structurel | Summer season |
| 18. | Drop structure- collection of vertiver slips and planting at up stream and down stream of structure | Structurel | On set of rain |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 225,0 | 225,0 | 14,0 |
| Equipements | Animal traction | ha | 1,0 | 49,0 | 49,0 | |
| Equipements | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | |
| Autre | Royalty charges for stones | ha | 1,0 | 6,0 | 6,0 | |
| Autre | Fishery and feed | ha | 1,0 | 9,0 | 9,0 | |
| Autre | Field bunding | ha | 1,0 | 73,0 | 73,0 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Water way | ha | 1,0 | 6,0 | 6,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 372,0 | |||||
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collecting vertiver slips & grass sods for gap filling | Végétale | Onset of rain /annual |
| 2. | Collection of grass sods and gap fillling to bund layers | Structurel | On set of rain/Annualy |
| 3. | Desiltation | Structurel | Before on set of rain/Biannualy |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 18,0 | 18,0 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Field bunding | ha | 1,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Water way | ha | 1,0 | 1,0 | 1,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 21,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
The above calculation is based on the total establishment/ recurring cost both born by the project and land users is devided by the total project area i.e 4.75 ha. To get average hect. cost.
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Availability of stone affects the cost from implementing SWC
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
1760,00
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
South Eastern Ghat Agro Climatic Zone
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitudinal zone: 101-500 m a.s.l. (423 m a.s.l.)
Landforms: Plateau/plains (2-7% slope)
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility: Medium
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
Soil water storage capacity: Medium
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- traction animale
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
30% of the land users are average wealthy and own 60% of the land.
70% of the land users are poor and own 40% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Land users from SWC technology area proctise contour plough, line sowing and using HYV paddy have increased their income significantly.
Level of mechanization: Manual labour and aniaml traction (bullock plough, both ranked 1)
Market orientation of production system: Pisciculture (Selling at village level)
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- communauté/ village
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- accès libre (non organisé)
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
diversité des produits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Fish add to their income
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Closure of land by pondage area
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
disponibilité de l'eau pour l'élevage
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Pisciculture support to live stock, dirnking water for cattle
Impacts socioculturels
institutions communautaires
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Management group formed and strengthened due to continurous income from pisciculture.
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Training conducted
Linkage with other institutions
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to different activities in the pond linkage to other institution has increased like Horticulture, Fishery etc.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Quantité avant la GDT:
90
Quantité après la GDT:
40
drainage de l'excès d'eau
Sols
humidité du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to water storage
perte en sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
87
Quantité après la GDT:
45
Autres impacts écologiques
Biodiversity
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
envasement en aval
Soil moisture regime
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
neutre / équilibrée
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 90-100%
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
19 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: If the community find the technology is low cost to teke up and gets eye catching benefits, then the treand of adoption is good.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Water problem for human and cattle solved How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular maintenance of pond needed |
|
Damage of crops reduced by construction of series of structures How can they be sustained / enhanced? More field bunding, vegetative cover should be imparted. |
|
Users group brings villagers closure How can they be sustained / enhanced? Manageent group to be reorganised annuly |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Water scarcity of the area partly solved How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular desilting shound be done. |
|
Heavy sand casting and soil loss controled How can they be sustained / enhanced? More vegetative cover required for catchement area |
|
Crop production increased in the project area How can they be sustained / enhanced? Should be replicated by the people. |
|
Pisciculture added extra income to the villagers How can they be sustained / enhanced? Hybrid fingerlings to be adopted |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Sand casting could not be checked fully | By full vegetative cover and more structural measures it can be checked. |
| Sediment deposit in down stream area decreased | The loss can be over come by increasing crop yield. |
7. Références et liens
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Watershed Survey Report
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Director of Soil Conservation, Orissa, Bhubaneswar
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Plan and Estimate
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
-do-
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

PARTICIPATORY APPROACH IN IDCWDP, DANIDA [Inde]
Participatory approach for holistic and intigrated development of the defined area on watershed basis involving all level of stake holders.
- Compilateur : Srikanta Kumar Parida
Modules
Aucun module trouvé