Check dam ponds [Ethiopie]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Eyasu Yazew
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Fabian Ottiger
May me'ekori ketri
technologies_1547 - Ethiopie
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Spécialiste GDT:
Kifle Weldearegay
+251 90 233 5495
Mekelle University
P.O.Box 231, Mek'ele, Ethiopia
Ethiopie
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Mekelle University (Mekelle University) - Ethiopie1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
11/11/2012
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
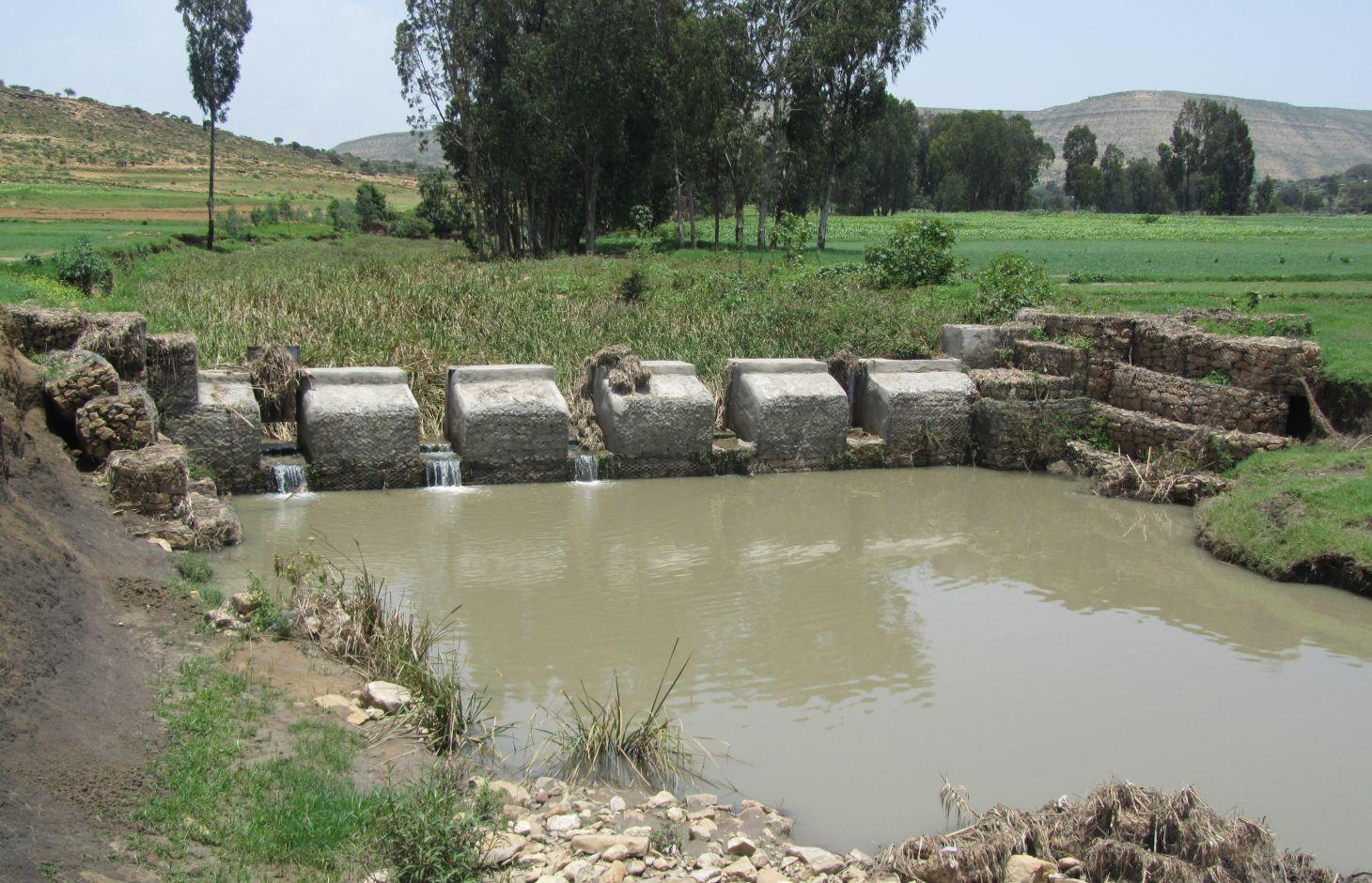
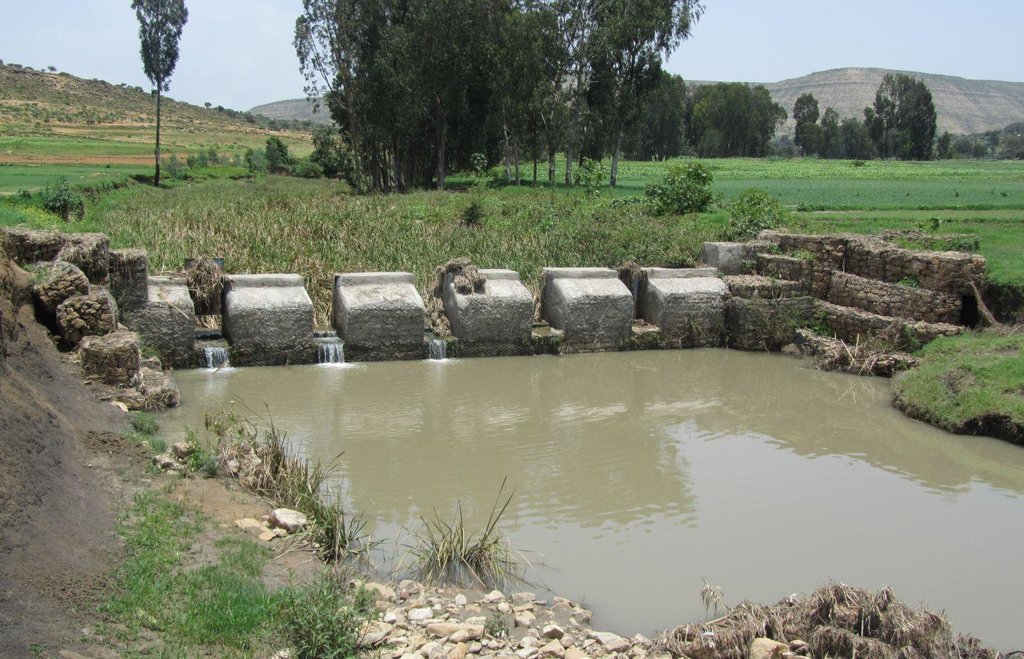
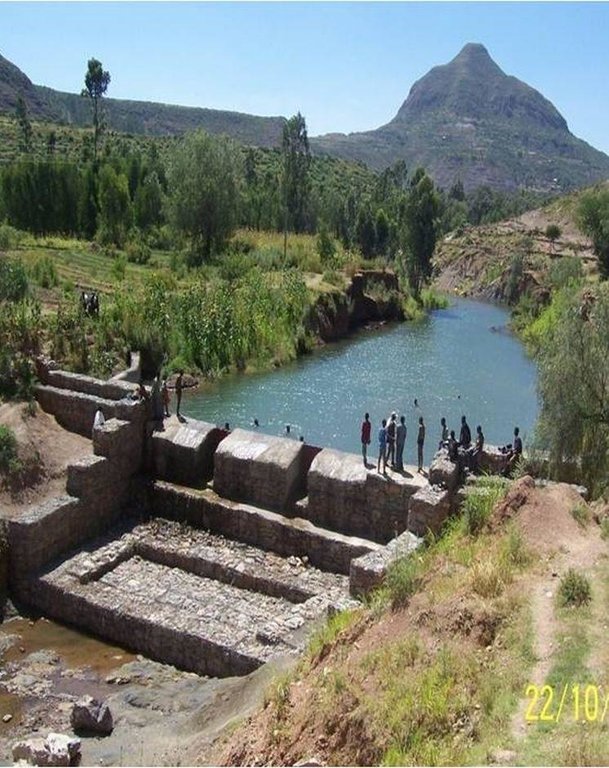
It is a raised wall constructed across a stream/gully using stone, concrete and/or gabion for dual purpose, namely, to pond/store the stream flow behind it for irrigation purpose while at the same time reducing the runoff velocity and enhancing gully rehabilitation.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
A check dam pond is a raised wall constructed across a gully from stone, concrete and/or gabion to store water behind it for irrigation purpose using either gravity or lifting mechanism. The structure generally consists of construction of foundation, apron, retaining wall and the checkdam. The width of the checkdam ranges between 1 - 2 m while the height varies between 1 - 2 m depending up on the gully depth. The length of the checkdam depends on the gully width. The spacing between adjacent checkdams is determined based on two factors, namely, the gradient of the river bed and the availability of potential land that can be irrigated. It is also provided with a number of sluice gates which will be removed during the main rainy season to minimize siltation.
Purpose of the Technology: In addition to storing water for irrigation, check dam ponds decrease slope length, slope angle, runoff velocity and minimize soil erosion.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment of a check dam pond starts with collection and transportation of stone and sand. The construction is started by setting out the dimensions from the design on the selected site and excavating the foundation for the different parts, namely, key trench, apron and retaining wall. The check dam is then constructed using gabions filled with stones and tightly tied together with wire. Finally the superstructure is plastered using mortar to prevent the passage of water through the body. Gates of about 1 m wide are finally constructed at about 1 m interval and fitted with sluice gates. Maintenance usually involves fixing damaged gates and reinforcing gabions.
Natural / human environment: Check dam pond is implemented in gentle (2 - 5%) and moderate (5 - 8%) slopes and in medium and light soil types of at least 1 m depth. It increases water availability for irrigation and livestock consumption purposes. It also reduces runoff velocity thereby decreasing soil erosion and enhancing gully rehabilitation.
It requires skilled labour and high construction cost. As a result, it is constructed through external support. However, the number of communities seeking for external support and willing to contribute their share is at the rise. The technology minimizes greatly the risk of crop failure and improves the livelihood of the land users.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Ethiopie
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Tigray
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Kilite Awlaelo
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Principales cultures (vivrières et commerciales):
Major cash crop: Vegetables such as tomato and onion
Major food crop: heat, barley, teff, maize
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Deforestation and overgrazing, high erosion risk, gully formation and land loss, decline in productivity.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Population pressure, deforestation, flood, soil erosion, reduced productivity.
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 150Longest growing period from month to month: June - NovemberSecond longest growing period in days: 105Second longest growing period from month to month: January - April
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- récupération/ collecte de l'eau
- gestion de l'irrigation (incl. l'approvisionnement en eau, le drainage)
- gestion des eaux de surface (sources, rivières, lacs, mers)
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- 1-10 km2
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S6: Murs, barrières, palissades, clôtures
Commentaires:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines
- Wm: mouvements de masse/ glissements de terrain
- Wo: effets hors-site de la dégradation
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wm: mass movements / landslides, Wo: offsite degradation effects
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Steep topography that increases amount and velocity of flood), population pressure
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing, floods, land tenure, poverty / wealth, education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
Commentaires:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
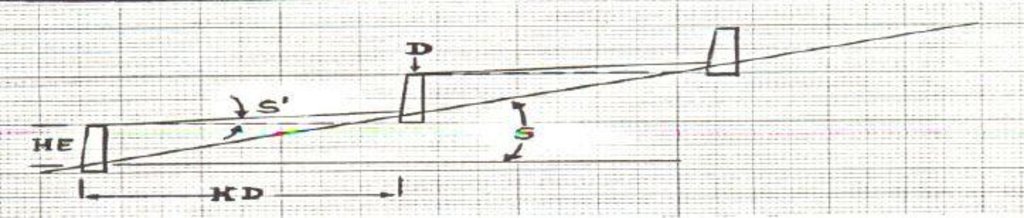
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
Check dam ponds are raised walls constructed across a stream/gully using stone, concrete and/or gabion for dual purpose, namely, to pond/store the stream flow behind it for irrigation purpose while at the same time reducing the runoff velocity and enhancing gully rehabilitation.
Location: Tigray. Kilte Awlaelo
Date: 10/10/2014
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Technical knowledge required for Engineer/designer: high
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope length
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, increase of infiltration, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Wall/ barrier
Vertical interval between structures (m): n/a
Spacing between structures (m): n/a
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1 - 2
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1 - 2
Construction material (stone): Stones are usually shaped in order to piece together very well.
Construction material (concrete): The chekdam is usually plastered by concrete on the upstream side to prevent the passage of water th
Construction material (other): Gabion, Sheet metal and Angle iron.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 2 - 8%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Birr
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
18,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
2.50
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site clearance and excavation of foundation | Structurel | Dry season |
| 2. | Stone collection and transportation | Structurel | Dry season |
| 3. | Sand collection and transportation | Structurel | Dry season |
| 4. | Gabion masonry work | Structurel | Dry season |
| 5. | Plastering | Structurel | Dry season |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 4678,0 | 4678,0 | 25,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Cement | ha | 1,0 | 953,0 | 953,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Gabion | ha | 1,0 | 6268,0 | 6268,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Sheet metal | ha | 1,0 | 44,0 | 44,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Angle iron | ha | 1,0 | 56,0 | 56,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 11999,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 6 month(s)
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Fixing damaged gates and reinforcing gabions | Structurel | Dry season |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: Digging hoe, shovel, hammer, crow bar
Since the check dam ponds generally vary in depth, width and most importantly in length depending up on the gully profile, calculation of cost per meter length will not be a reliable presentation. As a result, one typical check dam pond was selected and the total volume of the structure and the corresponding total cost of construction calculated. Then, the cost per cubic meter of the check dam was determined by dividing the total construction cost to the total volume of the structure.
The calculation includes the cost for the purchase of industrial materials (cement, gabion, sheet metal and angle iron) and cost of labour used for the construction including site clearance and excavation of foundation, stone and sand collection and transportation, gabion masonry work and plastering.
The price of the industrial materials and the labour wage used in the cost calculation apply to 2012. The daily labour wage for plastering is 180 Birr while it is 50 Birr for all other works.
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Labour, availability of construction material, depth and width of gully.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Average rainfall of 450-550 mm, Main rainy season from Mid-June to August.
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility is low (medium soils, ranked 1) and very low (light soils, ranked 2)
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium (ranked 1) and good (ranked 2)
Soil water storage capacity is medium (ranked 1) and low (ranked 2)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
bonne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
uniquement pour usage agricole (irrigation)
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Availability of surface water is good (September - January). Also medium (February-June)
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- groupe/ communauté
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- traction animale
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
10% of the land users are rich and own 10% of the land.
60% of the land users are average wealthy and own 55% of the land (35 Birr/day/person).
30% of the land users are poor and own 35% of the land.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
Average land holding is 0.6 ha per household.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- communautaire (organisé)
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
Mobile communication:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
risque d'échec de la production
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
disponibilité de l'eau pour l'élevage
qualité de l'eau pour l'élevage
disponibilité de l'eau d'irrigation
qualité de l'eau d'irrigation
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
revenus agricoles
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Also: Requires skilled labour
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
situation sanitaire
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increased investment in health care as a result of increased income.
institutions communautaires
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
apaisement des conflits
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
quantité d'eau
récolte/ collecte de l'eau
nappes phréatiques/ aquifères
évaporation
Sols
perte en sol
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
diversité végétale
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
disponibilité de l'eau
inondations en aval
envasement en aval
dommages sur les infrastructures publiques/ privées
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
500 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is no trend for spontaneous adoption due to high costs. However, communities are increasingly seeking external support to implement this technology.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Increased water availability for irrigation and livestock consumption How can they be sustained / enhanced? Watershed management |
|
Reduced soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Construction of retaining walls |
|
Increased employment opportunity and income from irrigation How can they be sustained / enhanced? Cultivation of high value crops |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Increased water availability for irrigation as well as livestock consumption How can they be sustained / enhanced? Integrated watershed management |
|
Reduce slope length, angle and erosion risk and enhance gully rehabilitation How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular maintenance of the structure |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| High cost of construction | Selecting a site that has good availability of construction material and that can irrigate as large area as possible. |
| Require skilled labour | Training of land users |
| Labour intensive | Mass mobilization |
7. Références et liens
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Staff members of the Kilte Awlaelo Wereda Office of Agriculture and Rural Development and Office of Water Resources Development
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé