Staggered Contour Trench [Afghanistan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Aqila Haidery
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : David Streiff
Jerma (Dari)
technologies_1715 - Afghanistan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Spécialiste GDT:
Spécialiste GDT:
Spécialiste GDT:
Spécialiste GDT:
Sirat Aliaver
AKF
Afghanistan
Spécialiste GDT:
Altaf Jalil
altaf.jalil@akdn.org
AKF
Afghanistan
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Sustainable Land Management Project, Bhutan (SLMP)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Aga Khan Foundation (AKF) - SuisseNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Sustainable Land Management Institute Organistatio (Sustainable Land Management Institute Organistatio) - Afghanistan1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
01/10/2015
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Earthen trenches with soil bunds built along contours in staggered design
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
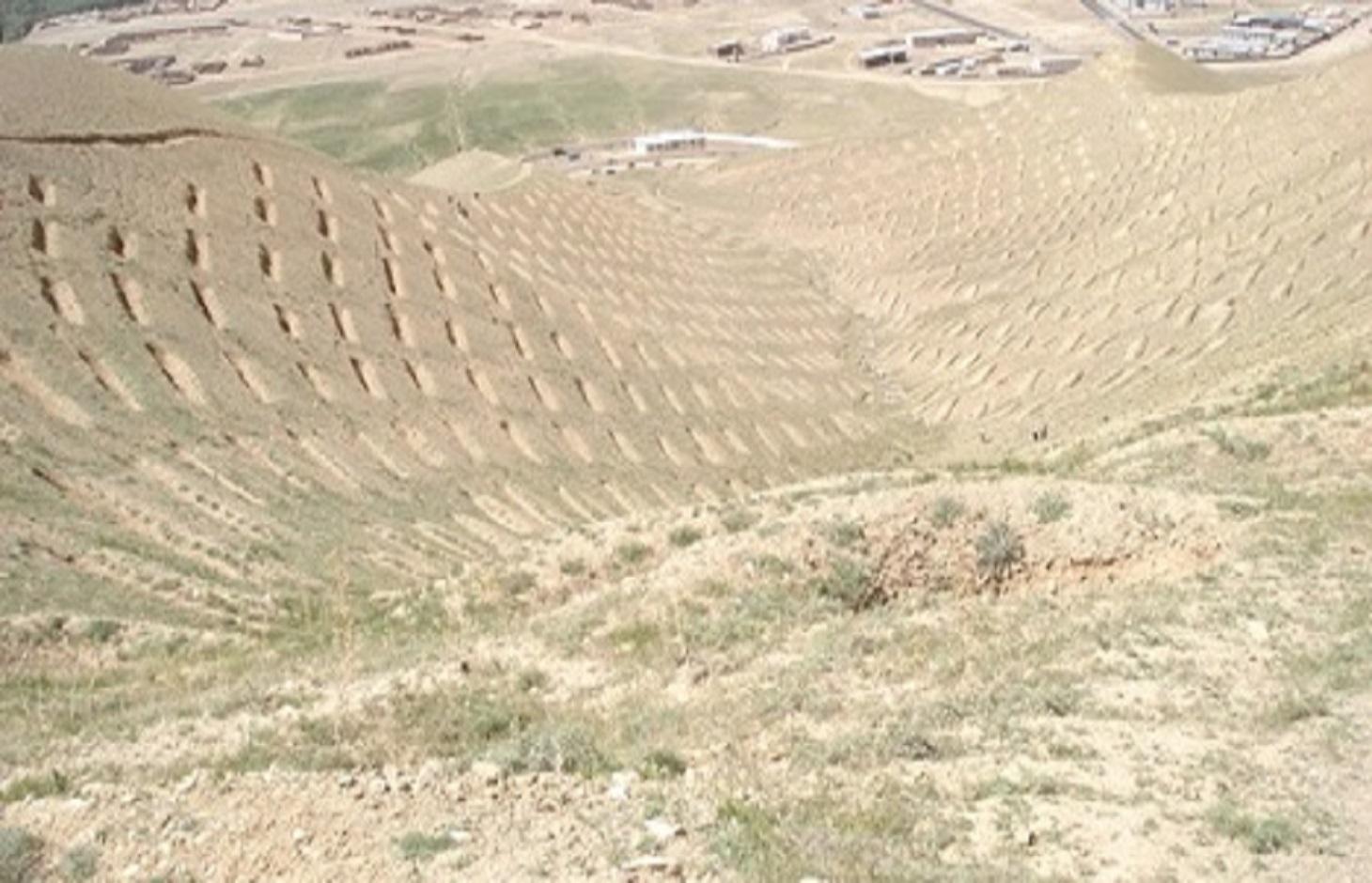
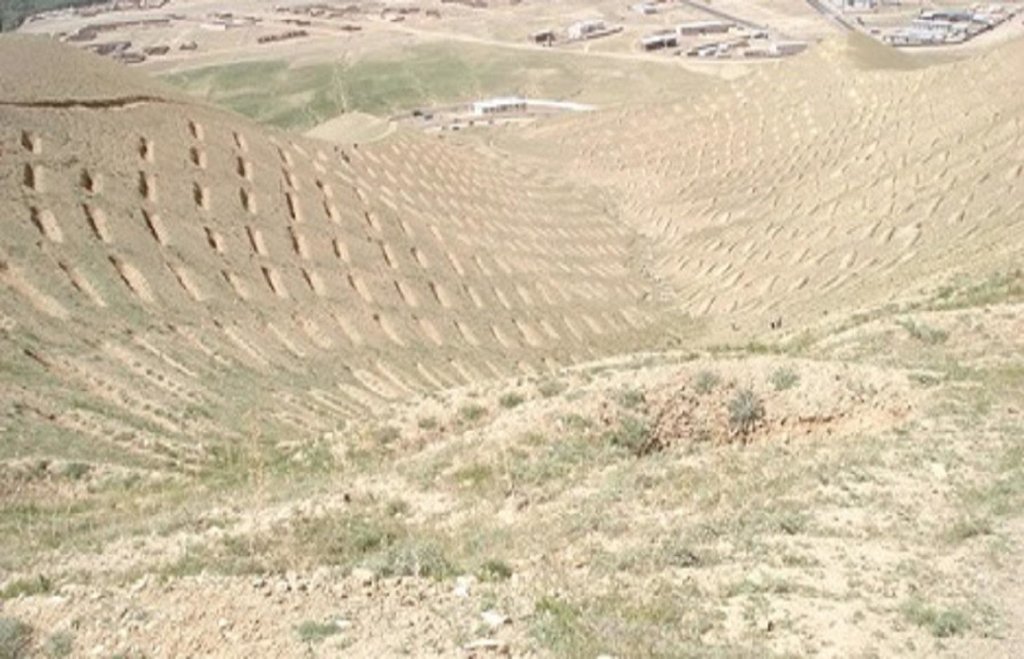
The SCTs technology is documented by Sustainable Land Management Project/HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation which is funded by Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC), with close support and cooperation of the Agha Khan Foundation (AKF). The staggered Contour Trenches (SCTs) were constructed at a degraded site in Bamyan center (Bamyan province) by Agha Khan Foundation (AKF) project with financial support of the Canadian International Development Agency (CIDA).
Totally 1470 contour trenches were constructed at the site, which has an area of 24 hectares.
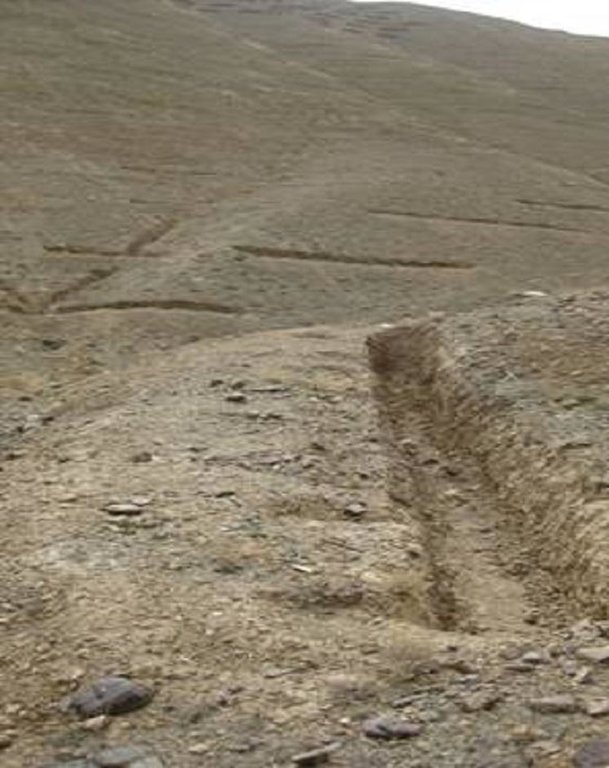
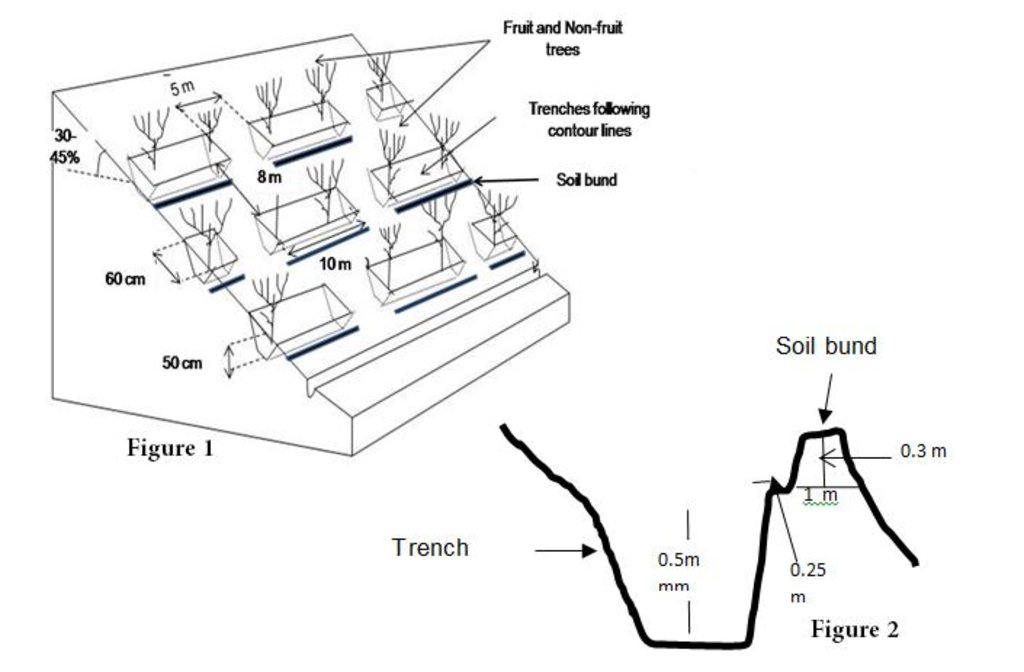
The size of each trench measured 10 m in length, 0.6 m in width and 0.5 m in depth. The trenches had soil bunds on the lower side having a width of 1 m and height of 0.3 m. Contour lines were prepared using an A-frame and lime and the spacing between two contour lines was 8 m considering the slope. All the trenches were dug out manually. Local people were employed for construction works. Along with the SCTs, other measures were applied such as plantation of fodder grass, shrub and non-fruit trees, gully plugs, water harvesting tanks and brushwood plugs. The area is excluded from grazing and shrub cutting.
The land was extensive grazing land before the project implementation and got extremely degraded due to a lack of management by the land users. There was rampant exploitation of natural vegetation for meeting domestic energy needs and for grazing. Droughts, which frequently occur in the region, contributed to the slow degradation of the vegetation.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose of the technology is to reduce flash flood risks and improve land productivity (both upstream and downstream) so that more fodder, fuel wood and fruits could be produced and farmers affected by flash floods could grow more crops. The technology, which is part of a watershed technology system, helps in retaining runoff and sediment and improves soil moisture content. It also helps in water infiltration which eventually contributes to improved ground water recharge.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: SCTs were established in a step-wise manner; as follows: (1) Site surveying, (2) Site mapping, (3) Planning, (4) Marking contour lines with the help of an A-frame, and (5) Trench excavation and bund construction.
The establishment cost for staggered contour trenches, was about 15,500 USD or 645 USD/ha. Most of the money was spent on labour. There have been no expenses in maintenance of SCTs since their establishment in 2008.
Natural / human environment: The technology is applied in semi-arid condition as the area receives annual rainfall of about 400 mm to address land degradation. The site formally belonged to the state but the local communities have use rights. AKF is still maintaining the site and using it for training and demonstration purpose. Several exposure visits for SLM specialist, land users, students and teachers have been also organized at the site.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Afghanistan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Zai Mahmood village, Bamyan center, Afghanistan
2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire les risques de catastrophes
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Pâturages
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Flash floods, gully/rill/sheet erosion, loss of natural vegetation and low productivity of the land due to degradation compounded by climatic factors.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Declining productivity of land resulting in shortages of fodder and fuel wood and loss of fertile land in the downstream areas due to flash floods.
Grazingland comments: The area is closed for livestock.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Forests / woodlands: Fp: Plantations, afforestations
Type of grazing system comments: The area is closed for livestock.
Si l'utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie, indiquez l'utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 180; Longest growing period from month to month: April to September
Densité d'élevage/ chargement (si pertinent):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- fermeture de zones (arrêt de tout usage, appui à la réhabilitation)
- mesures en travers de la pente
- gestion des eaux souterraines
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- 0,1-1 km2
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.24 km2.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S4: Fossés isohypses, trous
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale

dégradation hydrique
- Hs: changement de la quantité d’eau de surface
Commentaires:
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
A detailed staggered contour trenches layout and its specifications (Fig. 1), and the cross section of soil bunds (Fig. 2)
Location: Bamyan. Bamyan center/Bamyan province
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Technical knowledge required for SLM specialist: high
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase of infiltration, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase / maintain water stored in soil, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Spacing between structures (m): 8
Bund/ bank: level
Spacing between structures (m): 8
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par superficie de la Technologie
Indiquez la taille et l'unité de surface:
1 ha
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars US
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging of the contour trenches and construction of the soil bunds | Structurel | |
| 2. | Marking contour lines (A frame and lime) | Structurel |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Digging of the contour trenches and construction of the soil bunds | persons/day/ha | 100,0 | 6,43 | 643,0 | |
| Equipements | A frame and lime | ha | 1,0 | 1,8 | 1,8 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 644,8 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 4 month(s)
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | No maintenance activities have been implemented for staggered contour trenches and soil bunds up to now. | Structurel |
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Despite the application of the structural measure of the SCTs AKF is still continuing its financial support for the plantation of the area. Thus irrigation which is a costly activity is still continued by AKF's support. The planted saplings of fruit and non-fruit trees are irrigated for six months/year, i.e. from April to September. Water is carried to the site by tankers. Each month, 75 tankers are used and the cost of one tanker is 12 USD or 600 Afghani. In addition, 16 persons are employed for one time irrigation.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Bamyan receives heavy snow falls and rain falls in winter season
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility is very low - low
Soil drainage / infiltration is oor due to sealing
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
> 50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
faible/ absente
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
uniquement pour usage agricole (irrigation)
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
- mixte (de subsistance/ commercial)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- employé (entreprise, gouvernement)
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Mainly men were involved in the activities due to cultural reasons.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
100% of the land users are average wealthy.
Off-farm income specification: This is more applicable for poor small landholders or landless families.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- accès libre (non organisé)
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- accès libre (non organisé)
Commentaires:
Formally, state owned. The site is now protected from open grazing and shrub cutting with support from the local communities.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production fourragère
qualité des fourrages
production animale
risque d'échec de la production
diversité des produits
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Decreased production area
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
disponibilité de l'eau pour l'élevage
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
situation sanitaire
opportunités culturelles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
As the site is greener now
possibilités de loisirs
institutions nationales
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Especially of DAIL (Department of Agriculture, Irrigation and Livestock) and the persons who visit the site
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
livelihood and human well-being
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
récolte/ collecte de l'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Runoff, dew, snow, etc.
ruissellement de surface
nappes phréatiques/ aquifères
Sols
couverture du sol
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
diversité végétale
diversité animale
contrôle des animaux nuisibles/ maladies
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
risques d'incendies
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
inondations en aval
envasement en aval
sédiments (indésirables) transportés par le vent
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to better vegetation cover
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Type de changements/ extrêmes climatiques | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| tempête de vent locale | bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | bien |
Commentaires:
SCT must be combined with vegetation and management measures
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
The benefits stated are the combined impacts of all measures-structural, vegetative and management. SCTs have helped in the establishment of vegetative measures by contributing to increased soil moisture, reduced runoff and soil loss.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 90-100%
Commentaires:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The whole project activities were implemented by external supports
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: As the implementation of a watershed project requires high costs and investments which can not be affordable for the individual land users.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| The land users views were not considered. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Helps in reducing flash flood risks due to less runoff How can they be sustained / enhanced? Proper institutional mechanisms, involving the government, non-government and community institutions should be developed for sustaining project activities. Department of Agriculture, Irrigation and Livestock DAIL; (Bamyan) should take lead |
|
Conserves soil and enhances soil cover and fertility leading to more on-site production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Vegetative measures should be strengthened |
| Complements re-greening efforts by reducing erosion and conserving moisture |
| The quality of contour trenches and soil bunds are very good and maintenance costs negligible |
| The site is used for demonstration, training and exposure visits |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Establishment costs are very high | Voluntary community contributions, if they have an active stake in the project, would reduce the costs, otherwise, there has to be external support at least for the establishment phase |
| Loss of land for production | Planting suitable plants inside the trenches and along soil bunds |
| Requires high level of technical knowledge for establishment | Practical training for the target groups |
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé