Integrated runoff water management [Ouganda]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Alex Lwakuba
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1749 - Ouganda
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Erabu John
MMAIF, DEPT of Agriculture
Orungo subcounty, Amuria county, Katakwi District
Ouganda
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Ministry of agriculture, animal industry and fisheries (MAAIF) - Ouganda1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
18/04/2000
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
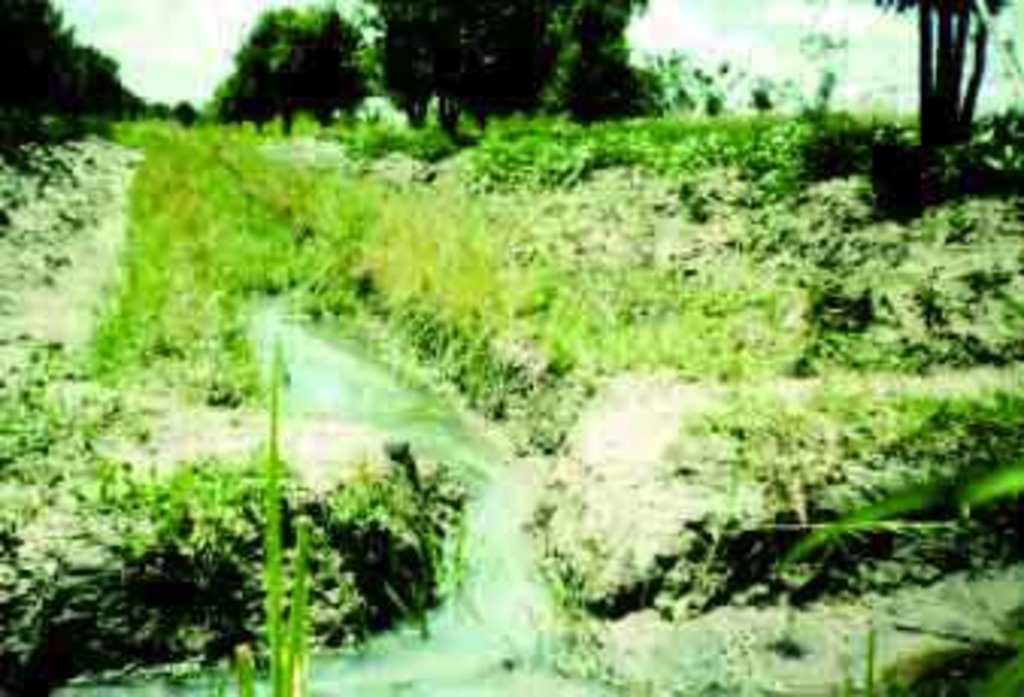
This is a system of integrated runoff water and drainage management that allows cultivation in a swampy valley bottom.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
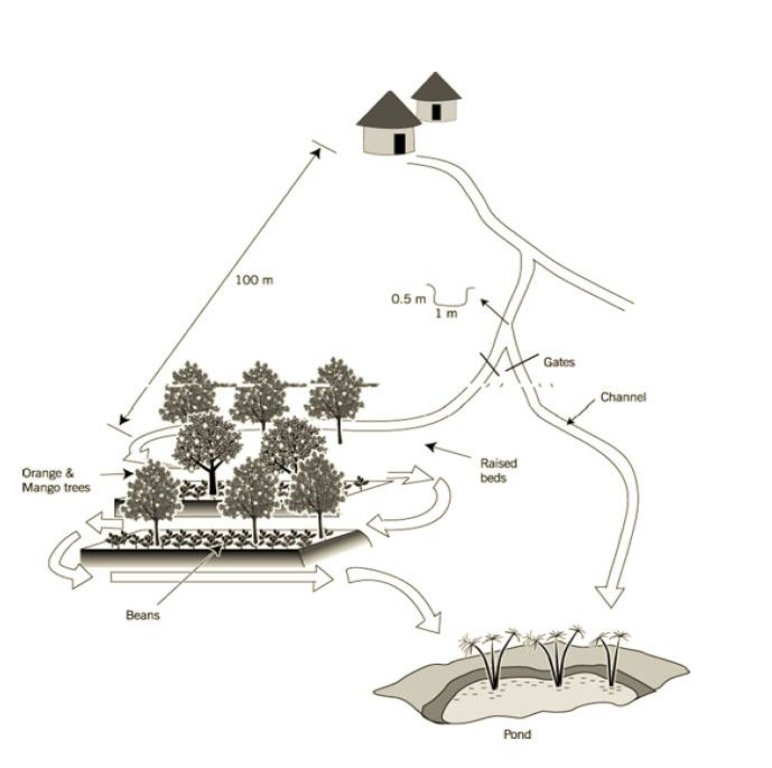
Setting up the infrastructure involves dividing the land in the valley into raised beds of ±10 m x 20 m which are separated by furrows, acting as drainage channels. Below the furrows is a pond. These furrows, however, can also fulfil the opposite role – distributing runoff water from upslope in the valley bottom if required. A diversion channel has been constructed to guide runoff from a track towards the valley. The channel is 0.5 m deep, 1 m wide, over 100 m in length and with a gradient of 0.5% - 1.0%. It is estimated that the ratio of catchment to cultivated area is 10:1. The channel is left open to divert runoff in times of shortage (though, naturally, as with any rainwater harvesting system, there has to be rain locally before it can be harvested). This water then can be held by the furrows whose outlet can be blocked. Citrus fruits (oranges) and mangoes are planted on the beds, and intercropped with annuals.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose is production of cash crops, based on reclamation of land and control of concentrated runoff. The impact is achieved through a flexible method
of drainage/water harvesting, which helps ensure suitable moisture conditions for growth.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The main maintenance aspect is clearing inlets, channels and removing vegetation, using common household hand tools such as spades and hoes.
Natural / human environment: The technology is situated in a valley near a swamp. It consists of growing both annual and perennial crops throught the year. The farm is located in a semi-arid area. The soil is sandy loam and shallow.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Ouganda
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Katakwi
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Katakwi
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
an adoption from another district by the landuser but with a lot of modifications and technology
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- s'adapter au changement et aux extrêmes climatiques et à leurs impacts
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
Principales cultures (vivrières et commerciales):
Major cash crop annual cropping: Rice
Major food crop annual cropping: Casava, sorghum
Major other crop annual cropping: Carrots

Mixte (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres), incluant l'agroforesterie
- Agroforesterie
Principaux produits/ services:
Major cash crop: Eucalyptus
Major food crop: Citrus
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): the major land use problem in the area are cutting down of trees, burning of bushes lack of crop roatation and water and soil conservation methods.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): continous cultivation leading to low yields lack of soil and water conservation methods eg ploughing across the slope
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion de l'irrigation (incl. l'approvisionnement en eau, le drainage)
- dérivation et drainage de l'eau
- gestion des eaux de surface (sources, rivières, lacs, mers)
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- 1-10 km2
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 5 m2.
the area under the technology reported covers farmers in one parish which approximates 5 km2
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
Commentaires:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
Sketch of the runoff harvesting system
Uganda
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, water harvesting
Structural measure: diversion ditch/cut-off drain
Spacing between structures (m): 10
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.45
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 140
Construction material (earth): soil dug out to make channel and ditches
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 2.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 1.00%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 1.00%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:10.00
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Uganda shillings
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
1000,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
1.00
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | ploughing, 2nd plough, diving the blocks, digging | Structurel | dry season |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 270,0 | 270,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 42,0 | 42,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 23,0 | 23,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Compost manure | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 345,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 60 month(s)
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | cleaning inlets | Structurel | during rains/each cropping season |
| 2. | cleaning channels | Structurel | during rains/each cropping season |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 340,0 | 340,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 315,0 | 315,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 71,0 | 71,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 726,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
structures; channels 140mts long, W 1m depth 0.45m
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
labour intensive and time consuming in the digging of channels
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility: Low
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- riche
- très riche
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- traction animale
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 30% of the land (with over 10 cows).
10% of the land users are rich and own 25% of the land (with 5 - 10 cows).
20% of the land users are average wealthy and own 20% of the land (with 3-5 cows).
25% of the land users are poor and own 15% of the land (with 1-3).
40% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land (without cows).
Off-farm income specification: majority of farmers are poor have no access to loans
Level of mechanization: Manual labour (cleaning, weeding and harvest) and animal traction (both ranked 1)
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Commentaires:
Land ownership: group, individual, not titled, individual, titled
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
gestion des terres
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
charge de travail
Autres impacts socio-économiques
Input constraints
Impacts socioculturels
institutions communautaires
institutions nationales
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
apaisement des conflits
Impacts écologiques
Sols
humidité du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Negative: Can lead to waterlogging
perte en sol
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
diversité végétale
diversité animale
diversité des habitats
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
vitesse du vent
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
inondations en aval
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Commentaires:
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
500 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Only one close neighbour has shown interest in copying him. ‘A few’ others from further away, also have. One constraint to adoption is the large amount of labour involved in setting up the system.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| increased incomes |
|
increased soil moisture content How can they be sustained / enhanced? adopt mulching |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
water runoff can be managed easily How can they be sustained / enhanced? constantly maintain the structure |
|
increased yields How can they be sustained / enhanced? adopt composting |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| need skills for the adopters | adopter need training |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| labour intensive | encourage group work |
| costly to construct | encourage household savings |
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé