Improved Kibanja cropping system [Tanzanie]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Jasson Rwazo
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : David Streiff
Ekibanja ekiine emikolele emirungi (Haya/Nyambo)
technologies_1183 - Tanzanie
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Government:
Spécialiste GDT:
Government:
Makung'uto Iddi
Missenyi District Council
Tanzanie
Government:
Kagaruki Anna Grace
Missenyi District Council
Tanzanie
Government:
Subira John
Missenyi District Council
Tanzanie
Spécialiste GDT:
Kaihura Fidelis
+255 754273849
Fidelis.kaihura@fao.org
Kagera TAMP
P.O.Box 127 Bukoba
Tanzanie
Government:
Kitundu Elizabeth
Missenyi District Council
P.O.BOX 38 Missenyi
Tanzanie
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - ItalieNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - Tanzanie1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
11/07/2012
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Approches de GDT

Integrated farm knowledge adoption [Tanzanie]
The way and means through which a performing farmers adopt and use a combination of indigenous and scientific to maximaze production.
- Compilateur : Jasson Rwazo
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
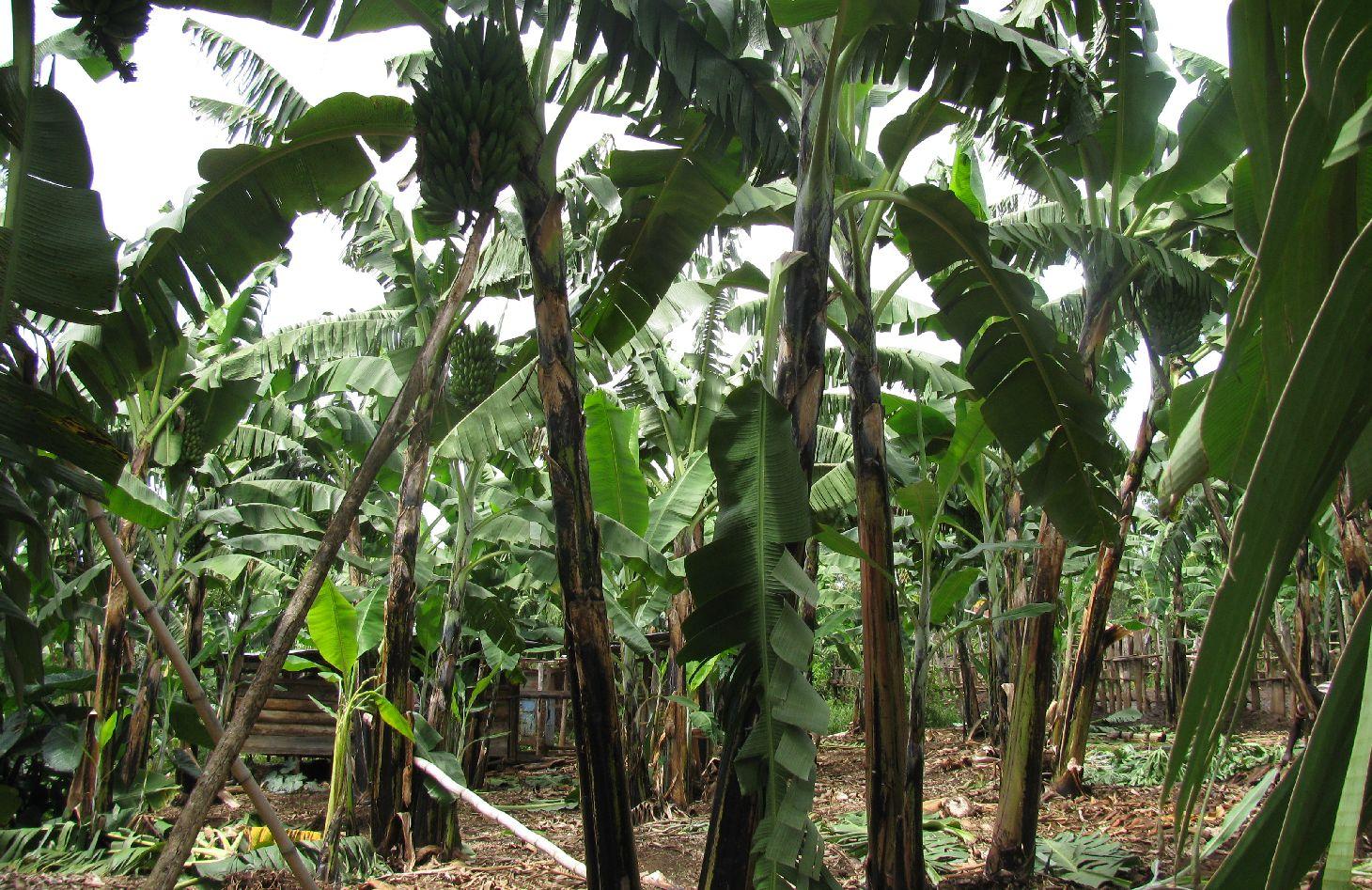
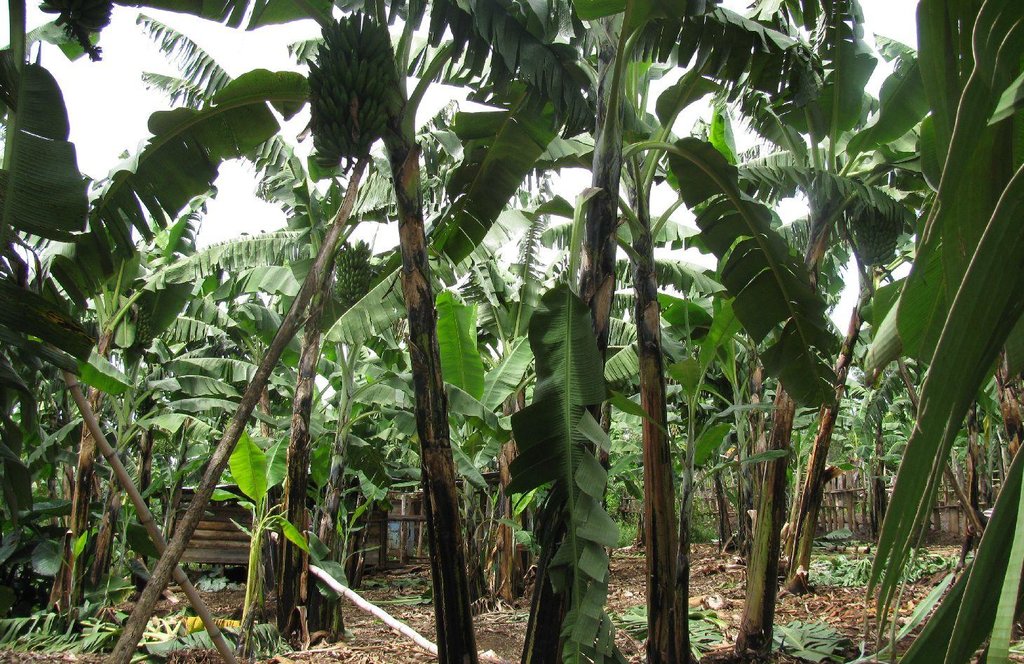
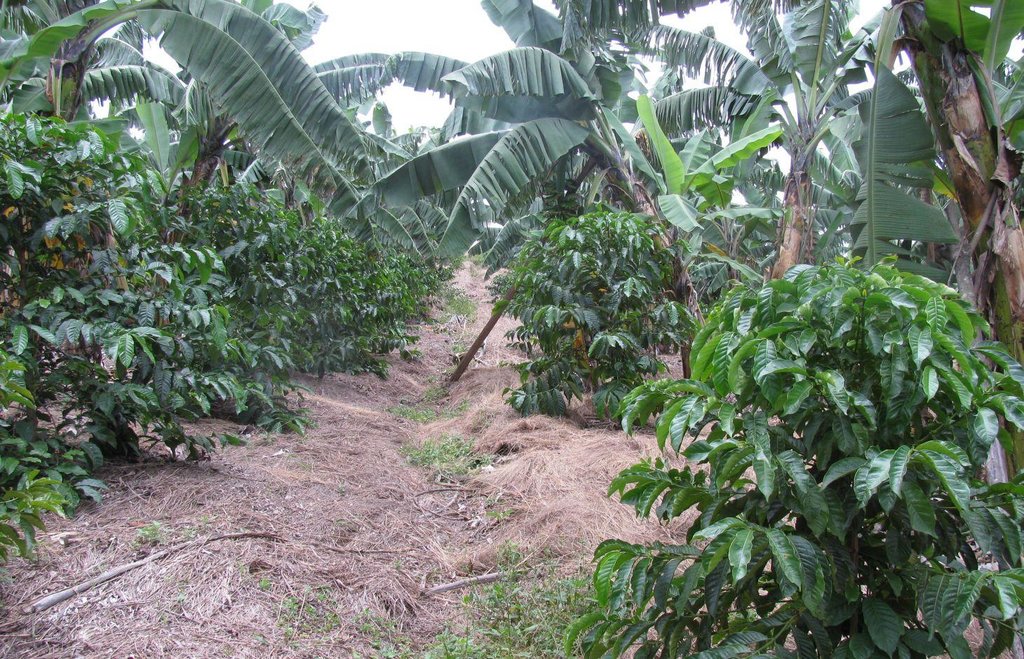
This is a traditional banana and coffee complex cropping system interplanted with annual crops, trees,shrubs, vegetables and other diverse plants of social economic importance.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
Improved traditional multi-cropping system that combines banana and coffee as main crops planted in a specific spacing to optimize plant stands. Banana and coffee are intercropped with; 1. annuals crops: Maize, beans, yams, coco-yams;2. Vegetables: Lycoperscum esculentum, Amaranthus spp, Cucumis communis and Solanum aethopium ;3. Shrubs of social economic value. Trees (e.g Maesopsis eminii, Makhcamia lutea, Ricinus comunis, Ficus thorninghii) and shrubs (Dracaena usambarensis) are planted on the farm edge. These serve as live fence, wind breaker, source of timber, fuel wood, medicine and protect the field against erosion. To optimize farm production, application of 15cm thick mulch ( grass mulch and banana prunnings), farmyard or compost manure and interplanting with soil fertility and/or soil moisture improvement trees are ensured. With problems of climate change, water harvesting ditches and trenches are constructed. Water harvesting ditches are constructed to collect water from micro catchments like roads or homestead. Sustainability of the Improved Kibanja system has always been assured through crop/livestock integration approaches.The cropping system is typical in high rainfall areas along foot slopes, valley bottoms or hilltops preferably on fertile and deep soils.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose is improve soil fertility,moisture, controlling soil erosion (wind and water) and suppressing weeds in order to improve the production banana, coffee and other inter planted crops.
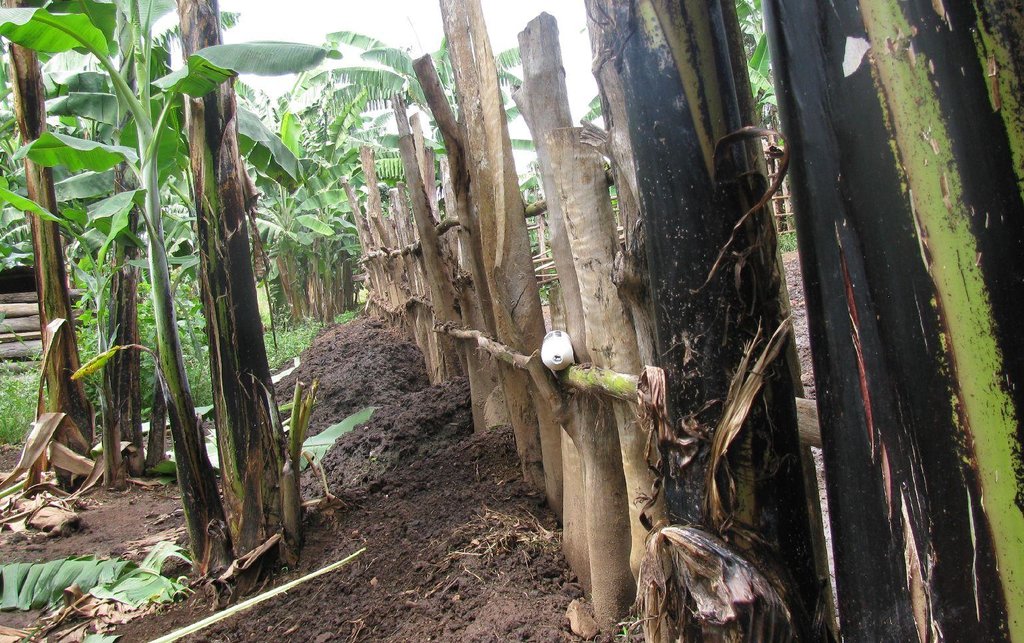
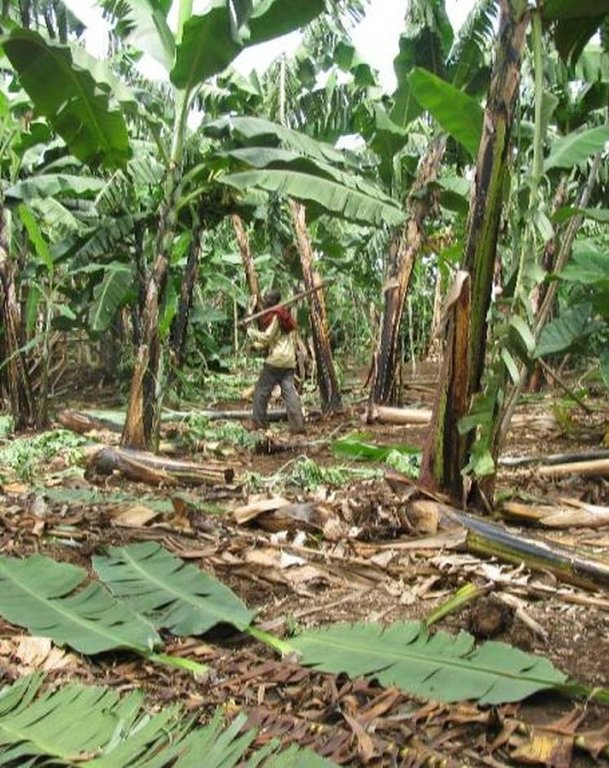
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment activities: 1. Land clearing and preparation: Slashing, uprooting tree stumps, ploughing and pitting 60cm x 90cm banana hole and 60cm x 60cm coffee (Mid June to August) using simple farm implements; 2.Farm Yard Manure application: 60 Kg per banana holes and 36 Kg per coffee hole (August to early September); 2. Planting: 308 banana suckers at 3.6m x 8m spacing, 830 coffee seedlings at 3m x 8m spacing in alternating row, edge row trees seedling at 10m spacing and 15cm spacing for shrubs e.g. Dracaena usambarensis (September to November);4. Excavation of water retention structure ( after planting mainly in Novermber). Full establishment of Improved Kibanja cropping system can be attained in three years.
Maintenance activities:1. Weeding:Done two times per year (mid January to February / July to augost) before planting annual crops; 2.FYM enrichment: Every after 3 years; iii. banana dethrashing and desuckering ,topping mulch, coffee pruning and harvesting (Immediately after weeding); 4. Other maintenence activities: Disease control (nematode, banana weevils, Banana Xanthamonas Wilt) and Propping (using pole to support banana plant with heavy bunches against wind); 5.Inputs: Labour, farmyard manure, propping poles, mulch; 6. Simple farm implements:Hand hoe,machete and wheel barrow.
Natural / human environment: The technology is implemented in mixed land use type under sub humid condition receiving 1000-1500mm of rains per year. A combination of soil and water improvement measures (FYM application, Mulching, water retention ditches and live fencing) complement each other to minimize risk of crop failure and hence improve production. The slope is gentle to moderate , soil depth is moderate and soil texture loam. Simple hand tools are traditional used,Land ownership is individual not titled. Application of this technology determined by high establishment and maintenence cost.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Tanzanie
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Tanzania
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Missenyi District, Kyazi Village
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Improved traditional land use system: The use of combination of measures in Improved Kibanja Cropping system in Kagera has been existing for more than 100 year ago.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- improve soil fertility
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Mixte (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres), incluant l'agroforesterie
- Agro-sylvo-pastoralisme
Principaux produits/ services:
Ficus thoninji,Markhamia lutea,Maesopesis eminii
major cash crop: Beans, banana and avocado
major food crop: Beans and banana
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil nutrient loss, decline of soil moisture and soil erosion by wind and fast water runoff.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Reduced crop production, loss of indigenous medicinal plants, reduced water water quatity in natural water sources.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Due to mixed farming and agroforestry there is high nutrient cycling resulting in high productivity
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: Short rains (September to December); Second longest growing period in days: 65; Second longest growing period from month to month: Long rains (March to June)
Densité d'élevage/ chargement (si pertinent):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- agroforesterie
- brise-vent/ plantations abris
- récupération/ collecte de l'eau
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.062 km2.
2ha approximately
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A2: Matière organique/ fertilité du sol

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes
- V2: Herbes et plantes herbacées pérennes

structures physiques
- S4: Fossés isohypses, trous

modes de gestion
- M3: Disposition/plan en fonction de l'environnement naturel et humain
Commentaires:
Secondary measures: management measures
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, retaining more vegetation cover, mulching, manure / compost / residues, minimum tillage, pits
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -against wind, aligned: -along boundary, aligned: -linear
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
Commentaires:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Cultivation along the slope and overcultivation), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Cultivation of season crop without reprenishing of soil nutrients), change of seasonal rainfall (Fractuation in rain season), droughts, population pressure, education, access to knowledge and support services
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), land tenure, poverty / wealth, inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Auteur:
Jasson Rwazo, P.O.BOX 38 Misseny Tanzania, rjrwazo@gmail.com
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
Location: Kyazi Village. Missenyi District, Kagera Region, Tanzania
Date: 2012.08.28
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (The technology requires moderate technical knowledge for adoption)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (The technology requires moderate technical knowledge for adoption)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter
Secondary technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply, reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity)
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Banana
Quantity/ density: 304
Remarks: 3.6 m by 8m
Retaining more vegetation cover
Material/ species: Beans
Remarks: Random
Mulching
Material/ species: Grass mulch, banana(Prooning) trashes mulch
Quantity/ density: 10000
Remarks: Spreading the mulch
Material/ species: Coffee
Quantity/ density: 830
Remarks: 3m by 8m
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Farmyard manure, farm residure,
Quantity/ density: 40 tone
Remarks: Spreading on the pit
Minimum tillage
Material/ species: Hand hoe,matechette
Pits
Material/ species: Hand hoe,matechette
Aligned: -against wind
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 277
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): Random
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): Random
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): Random
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 100000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.01
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.01
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 100000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.01
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.01
Trees/ shrubs species: Maeesopsis Eminii, Dracaena usambalensis,Erythrina abysinica
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Pawpaw, Orange, Avocado
Perennial crops species: Banana, Coffee, Vanilla
Other species: Carisa edulis (shrubs)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 6.3%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 6.3%
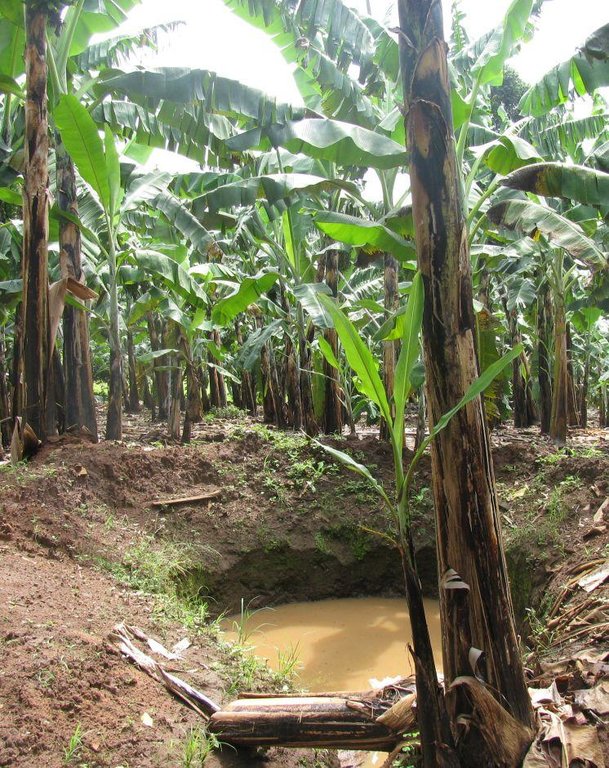
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0.4
Spacing between structures (m): 6
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.15
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.15
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Waterway
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0.4
Spacing between structures (m): 6
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.75
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.4
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 5
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0.4
Spacing between structures (m): 6
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.75
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.4
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 5
Construction material (earth): 2.25 m3 of earth material used per ditch
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 6%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 8%
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 10m3
Catchment area: 1.6Ham2
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:3.5
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars US
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
1
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land clearing and preparation:Slashing,uprooting tree stumps, ploughing and pitting | June to August | |
| 2. | Availing and applying 54 tone Farm Yard | August to early September | |
| 3. | Planting: 308 banana suckers 830 coffee and tree edge low tree seedlings | From September | |
| 4. | Construction of water harvesting ditches | Structurel | Once year |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Land clearing | persons/day | 202,0 | 1,18316 | 239,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Construction of water harvesting ditches | persons/day | 4,0 | 0,937 | 3,75 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 61,56 | 61,56 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seedlings | pieces | 1138,0 | 0,0468 | 53,26 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Manure | tons | 54,0 | 34,7222 | 1875,0 | |
| Autre | Cuttings | ha | 1,0 | 2234,6 | 2234,6 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 4467,17 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 36 month(s)
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Topping grass mulch | Agronomique | 3 times per year |
| 2. | Farm yard manure enrichment | Agronomique | 2 times per year |
| 3. | Removal of sediments and debris in water retention ditches. | Agronomique | Every year |
| 4. | To replacement propping Poles | Agronomique | Every 1.5 year |
| 5. | To corve transportation cost | Agronomique | Manure |
| 6. | Replacement of propping pole and live hedges | Végétale | Every 1.5 year |
| 7. | Removal of sediments and debris in water retention ditches | Structurel | Once per year |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Topping grass mulch | persons/day | 10,0 | 4,101 | 41,01 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Applying FYM | persons/day | 10,0 | 3,906 | 39,06 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Removal of sediments | persons/day | 4,0 | 0,9375 | 3,75 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | To replacement propping Poles | persons/day/ha | 10,0 | 3,906 | 39,06 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Tools | per ha | 4,0 | 1,875 | 7,5 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Farm yard manure | tons | 20,833 | 46,8 | 974,98 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Wood | pieces/ha | 600,0 | 0,625 | 375,0 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Mulching material | bundle | 300,0 | 1,875 | 562,5 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Transportation | trips | 19,0 | 61,673 | 1171,79 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 3214,65 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: Machetes, Mattocks, Hand hoe, spade, wheel barrow, Machete,Hand hoes, spade, Hand hoe,Machete, Spade
Cost assesment completed in June 2012
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Manure is most determinate factor high transportation cost especially during establishment
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Avarage rainfall 1200mm, Bimode rainfall, 5 month dry season
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
Thermal climate class: tropics. Annual temperature 23C
Length of growing period 120 -300 days
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- situations concaves
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitudinal zonation: 1270m a.s.l
Slopes on average: Movement of soil due to erosion, exposure of parent rock on some part of the farm
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average: Shallow on the hill slope and moderately deep on the valley bottom, also deep sometimes
Soil texture (topsoil): Sandy loam
Topsoil organic matter: Due to the high use of organic manure (farm yard manure) and mulch
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium due to the high use of organic manure (farm yard manure), mulch, good aeration
Soil water storage capacity is medium due to the high use of organic manure (farm yard manure) and mulch
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
> 50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
faiblement potable (traitement nécessaire)
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
Different species of soil micro organisms and plant species
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- mixte (de subsistance/ commercial)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: The land inheritance is mainly dominated by male, women mostly use the land for production of understory crops such as beans; banana and coffee production is dominated by men
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%; 3%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 30% of the land (Own 2.5-5 acre land, car, 10-20 catlle,brick wall house).
15% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land (Own 1-2.5 acre of land,2-5 cattle, brick wall house).
60% of the land users are average wealthy and own 35% of the land (Own 0.5-1 acre of land,2-3 goats,mud wall house with corrugarated iron roof).
15% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land (Own 0-0.5 acre of land, no livestock, mud house withgrass roofing).
5% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land (Does not own land or own less than 0.5 acre of land, work as casual labour).
Off-farm income specification: 90% of land users income depends on on- income
Market orientation of production system: Mainly for substence for commecial
Level of mechanization: Using hand tools
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, sans titre de propriété
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Quantité avant la GDT:
50
Quantité après la GDT:
300
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Bunch of banana with 70 kg each
risque d'échec de la production
diversité des produits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Depend mainly on banana sell
gestion des terres
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Quantité avant la GDT:
1875 $
Quantité après la GDT:
1406 $
revenus agricoles
Quantité avant la GDT:
6250
Quantité après la GDT:
25000
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Annual income in dollar
diversité des sources de revenus
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Solery depend on farm
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Reduced weeding, but technology is labour intensive.
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Quantité avant la GDT:
1000
Quantité après la GDT:
4000
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increase in bunch of banana produde annually
situation sanitaire
Quantité avant la GDT:
5
Quantité après la GDT:
2
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Frequency of attedndence to hospital due to edequate food supply
possibilités de loisirs
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Adoption by neighbouring farmers
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
récolte/ collecte de l'eau
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
10
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to water harvesting dithchers along the foot path in the farm
ruissellement de surface
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to the use of mulch and corver crops
évaporation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to corver crop and mulch
Sols
humidité du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Use of banana trash mulch and other corver crops
couverture du sol
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
émissions de carbone et de gaz à effet de serre
risques d'incendies
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to mulching material
vitesse du vent
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
disponibilité de l'eau
dommages sur les champs voisins
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Type de changements/ extrêmes climatiques | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | bien |
| tempête de vent locale | bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | bien |
Commentaires:
Use drainage trenches
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
Depending on regular application of manure and mulch plus good management of the farm
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- plus de 50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
317 households (70 percent of all land users in the area)
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 90-100%
Commentaires:
317 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Limited with high labour and input cost (Manure)
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Increased house hold food security and income How can they be sustained / enhanced? Schedule regular maintenance activities |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Soil moisture conservation How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintenance of water harvesting ditches and replacement of mulching materials |
|
Soil fertility improvement How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular application of manure and mulch |
|
Improvement of soil structure and aeration How can they be sustained / enhanced? Manure and mulch application |
|
Control of soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintenance of plant cover and water retention ditches, manure and mulch application |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| High labour and capital demand | Phase in implementation and regular maintenance of the technology |
| High risk of fire | Use of fire breaks |
7. Références et liens
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Improving Productivity of Field Crops and Post Harvest Management in North west Tanzania,United Republic of Tanzania Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Cooperatives,2008
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes disponibles en ligne
Titre/ description:
Kagera TAMP project website
URL:
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Integrated farm knowledge adoption [Tanzanie]
The way and means through which a performing farmers adopt and use a combination of indigenous and scientific to maximaze production.
- Compilateur : Jasson Rwazo
Modules
Aucun module trouvé