Orchard-based Agroforestry (intercropping) [Tadjikistan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Erik Bühlmann
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1002 - Tadjikistan
- Résumé complet en PDF
- Résumé complet en PDF pour impression
- Résumé complet dans le navigateur
- Résumé complet (non formaté)
- Orchard-based Agroforestry (intercropping): 2 novembre 2021 (public)
- Orchard-based Agroforestry (intercropping): 20 août 2019 (inactive)
- Orchard-based Agroforestry (intercropping): 19 juillet 2017 (inactive)
- Orchard-based Agroforestry (intercropping): 17 juillet 2017 (inactive)
- Orchard-based Agroforestry (intercropping): 10 mars 2017 (inactive)
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - SuisseNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - Kirghizistan1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
15/07/2005
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
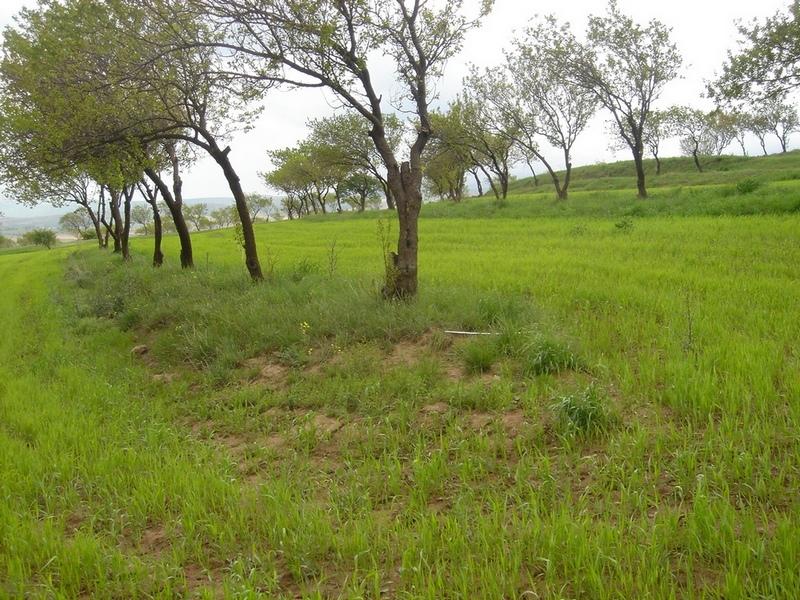
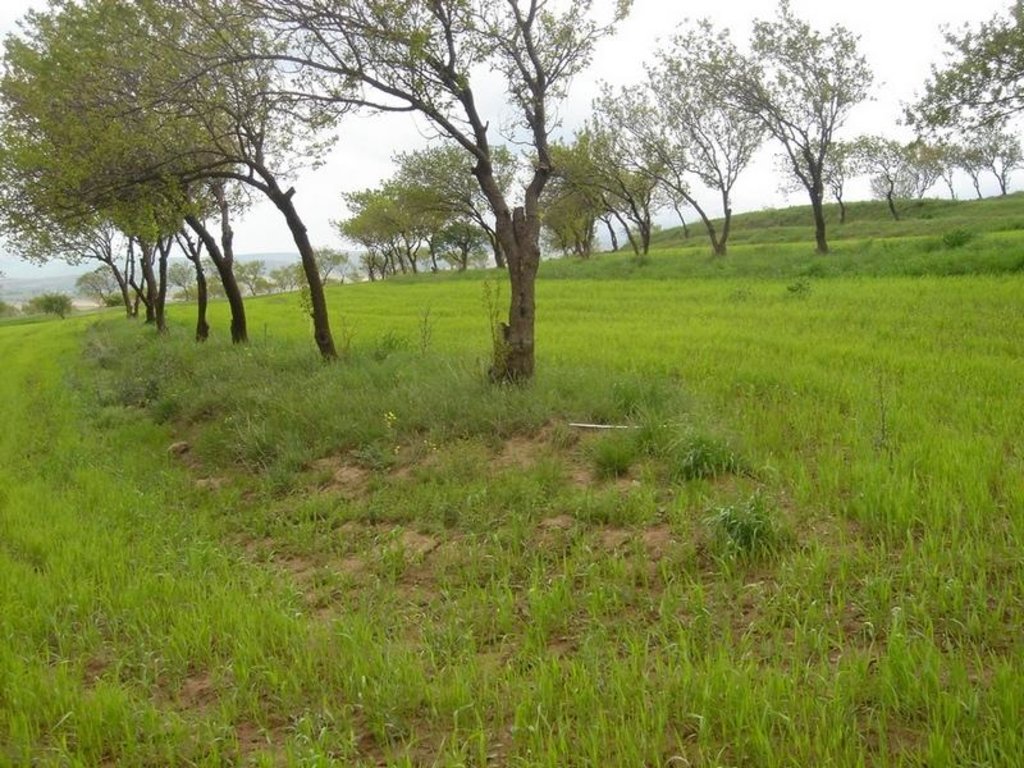
Intercropping of wheat in an existing orchard that was established during the Soviet period.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
The technology involves intercropping wheat in an existing apricot orchard, that was established during soviet times to increase farm production, by integrating different resources in an environment protected from soil erosion. The intercropped area is ploughed by tractor. In general, farmers do not practice crop rotation since they usually allocate cereal production to the most fertile field plots of their farm.
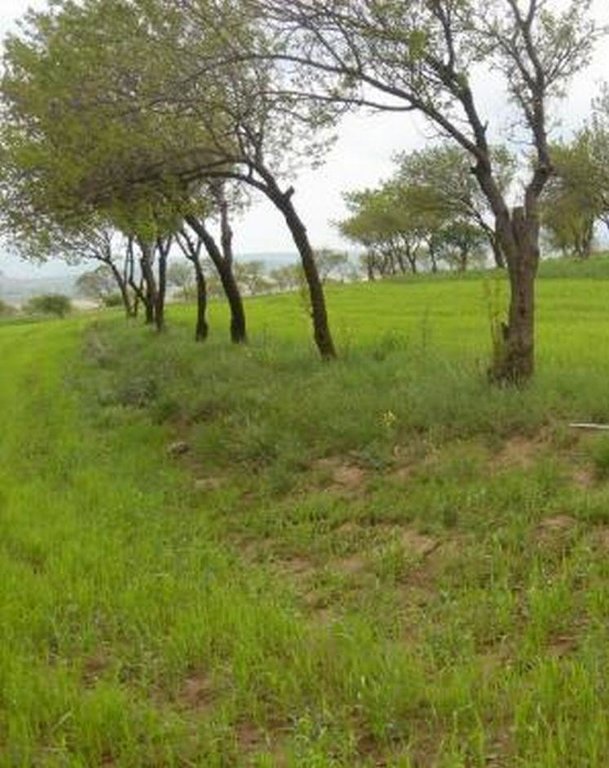
Along the trees aligned on contour, a three metre wide grass strip is left uncultivated to control runoff, and to protect the ground from splash erosion. Spacing between rows is 13 metres, which allows unhindered farm operations.
Most orchards in Faizabad Rayon were established during Soviet times. Tree rows were planted close together in order to obtain maximum yields from the orchard monoculture systems. Some of the tree rows were removed, allowing more space for intercropping.
Purpose of the Technology: The technology is applied in existing orchards which generally range between 10-25% in gradient. In existing orchards, intercropping alone is relatively cost intensive. Harvesting two crops at a time increases overall farm production and improves food security since harvests of intercropped food crops are found to be more reliable than those on exposed annual cropland. However, many orchards are still owned by state farms which usually do not practice intercropping. Since management of fruit trees require considerable labour and material inputs (e.g. chemicals for pest/disease control as well as fertilisers) which often cannot be met by farmers, yields of fruit trees have declined after the privatisation of these areas. Furthermore, farmers often lack knowledge of appropriate orchard management techniques and miss opportunities to gradually replace old trees by new seedlings.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Tadjikistan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Tajikistan
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Faizabad Rayon
Map
×3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles

Mixte (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres), incluant l'agroforesterie
- Agroforesterie
Principaux produits/ services:
major cash crop: fruits
major food crop: wheat
other: chickpeas, flax, perennial herbaceous fodder plant
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): severe water erosion (rills and gullies) and subsequent fertility decline on cropland and overgrazed pastures
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): fertility decline, soil erosion and washing downslope of seeds before they can sprout
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Intercropped winter wheat and sometimes chickpeas are sown in autumn; flax, alfa alfa, esparzet, and also chickpeas are sown in early spring
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- agroforesterie
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- 1-10 km2
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A6: Autres

pratiques végétales
- V5: Autres

modes de gestion
- M1: Changement du type d’utilisation des terres
Commentaires:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, contour tillage
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
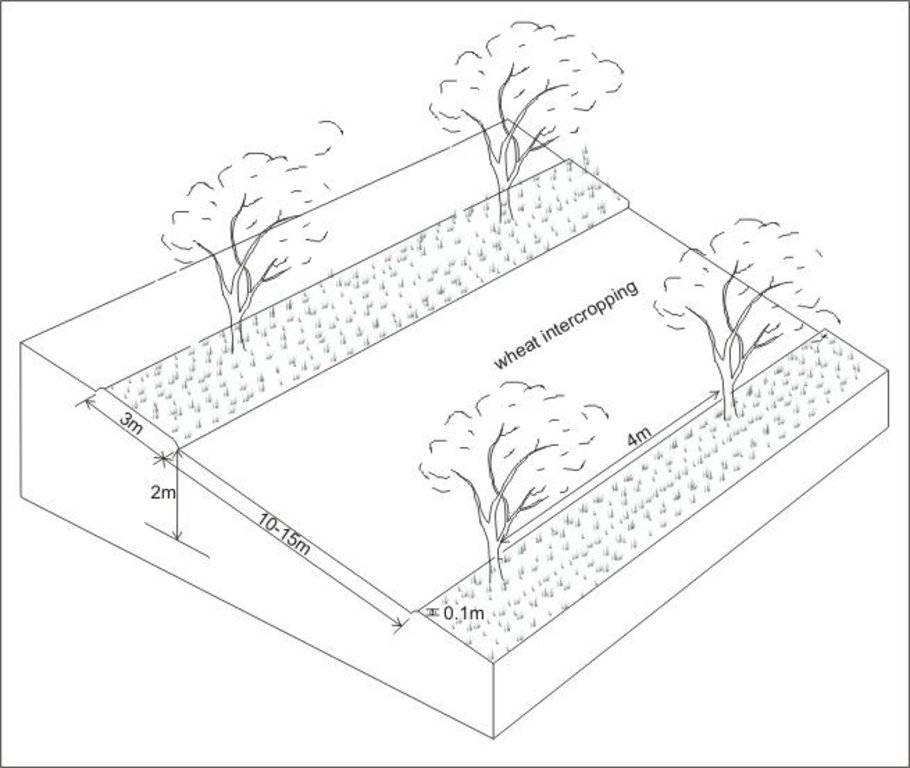
Intercropping of wheat between apricot trees aligned on contour
Location: Chinoro. Faizabad Rayon, RRS
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope length
Secondary technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, reduction in wind speed, increase in soil fertility
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: winter wheat
Quantity/ density: 150kg/ha
Remarks: intercropping between tree rows
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: superphosphate, silitra
Quantity/ density: 200kg
Remarks: only for intercropped wheat
Contour tillage
Remarks: between tree rows
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 200
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 13
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Vegetative measure: aligned: contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 10
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Fruit trees / shrubs species: apricot trees
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 18.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.00%
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars US
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
3.00
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | establishment of apricot orchard by state enterprise | Végétale | established in 1989 |
| 2. | acquiring land use rights for existing orchard lands from local authorities | Végétale | |
| 3. | thinning and clearing of tree rows | Végétale |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | thinning and clearing of tree rows | ha | 1,0 | 6,0 | 6,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | tools | ha | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 31,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 0 month(s)
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | disc ploughing (area for intercropping) | Agronomique | before sowing / annual |
| 2. | sowing (winter wheat) | Agronomique | |
| 3. | applying of fertiliser | Agronomique | early spring / each cropping season |
| 4. | harvesting | Agronomique | summer / each cropping season |
| 5. | pruning of fruit trees | Végétale | autumn/winter /annual |
| 6. | cutting of grass strip | Végétale | summer /annual |
| 7. | applying manure for fruit trees | Végétale | winter/early spring /annual |
| 8. | removal of twiggs affected by insects/deseases | Végétale | spring /weekly |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | sowing and weeding | ha | 1,0 | 18,0 | 18,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | pruning of fruit trees | ha | 1,0 | 45,0 | 45,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | cutting of twiggs affe | ha | 1,0 | 15,0 | 15,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | machine use | ha | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | seeds | ha | 1,0 | 30,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 40,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 218,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: tools: saw, sickle, pruning shears, fork, bucket
per hectare (with the described spacing of trees and tree rows)
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The number of trees influences costs considerably, since orchard management is labour and input intensive
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
- semi-aride
growing period between 180-210 days
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Landforms: Also valley floors
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility: low-high
Soil drainage / infiltration: medium - good
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
- mixte (de subsistance/ commercial)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- > 50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
- riche
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
5% of the land users are rich and own 15% of the land.
75% of the land users are average wealthy and own 70% of the land (local authorities sometimes need to be bribed in order to acquire land use rights for orchard land).
Off-farm income specification: In general, all farmers (including those applying SWC technologies) are highly dependent on off-farm income, which in most cases is earned in Russia either by themselves or by their relatives.
Market orientation of production system subsistence (self-supply): Only surpluses are sold or exchanged for other goods
Level of mechanization: Ploughing is carried out using a tractor whenever possible, but animal traction also existent.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Commentaires:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology also 0.5-1 ha
Households with 1-2 ha are depending on available working force, labour is limiting factor
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- loué
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
gestion des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
due to intercropping, management of trees gets more difficult
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
intercropped wheat requires additional inputs to an already input intensive orchard system
revenus agricoles
Autres impacts socio-économiques
fruit production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
due to lack of fertilisers and pesticides
fruit yields
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
due to inappropriate pruning
Impacts socioculturels
apaisement des conflits
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
NA
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 90-100%
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: In general, there is a growing demand for orchard land for intercropping. However, a considerable amount of orchards are still managed by state farms which usually do not maintain intercropping systems.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
two harvests at a time How can they be sustained / enhanced? increase in farm production |
| good wheat harvests in intercropping systems |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| low costs for establishment (intercropping only) |
| wheat production with very little soil erosion |
| intercropping can improve food security of low income families |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| yield of fruit trees insufficient because required inputs are not affordable | gradually replace old trees by new seedlings |
| Insufficient yields of intercropped plants because of shadow of old/large fruit trees | |
| orchard systems vulnerable to pests, late frost and strong winds |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| productive orchard systems require considerable amounts of recurrent inputs (e.g. chemicals for pest/disease control, fertiliser) which locals often cannot afford | avoiding intercropping of sparsely growing crops in vulnerable intercropping systems; improving ground cover by mulching |
| in comparison to orchards with an intact grass cover, intercropping of sparcely growing plant species increases the risk of soil erosion | |
| intercropped wheat hinders maintenance activities of fruit trees |
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé