Disability inclusive, flood resilient cluster village [Bangladesh]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Subir Saha
- Rédacteurs : Subir Saha, Manuel Rothe
- Examinateurs : Alexandra Gavilano, Joana Eichenberger
"Protibandhita Bandhob Bonna Sohisnu Gucca Gram"
technologies_2005 - Bangladesh
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Book project: where people and their land are safer - A Compendium of Good Practices in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) (where people and their land are safer)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Christoffel Blindenmission (CBM) - Suisse1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
Commentaires:
Not problematic with regard land degradation. It provides efficient and sustainable use of available land resources.
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)

Disability inclusive Disaster Risk Reduction [Bangladesh]
The disability inclusive approach is centered around the meaningful contribution and leadership of persons with disabilties during the entire project management cycle, from the planning stage to the evaluation of the impact of a project. It contributes to empowering them to overcome social exclusion and recognizes their needs and priorities …
- Compilateur : Subir Saha
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
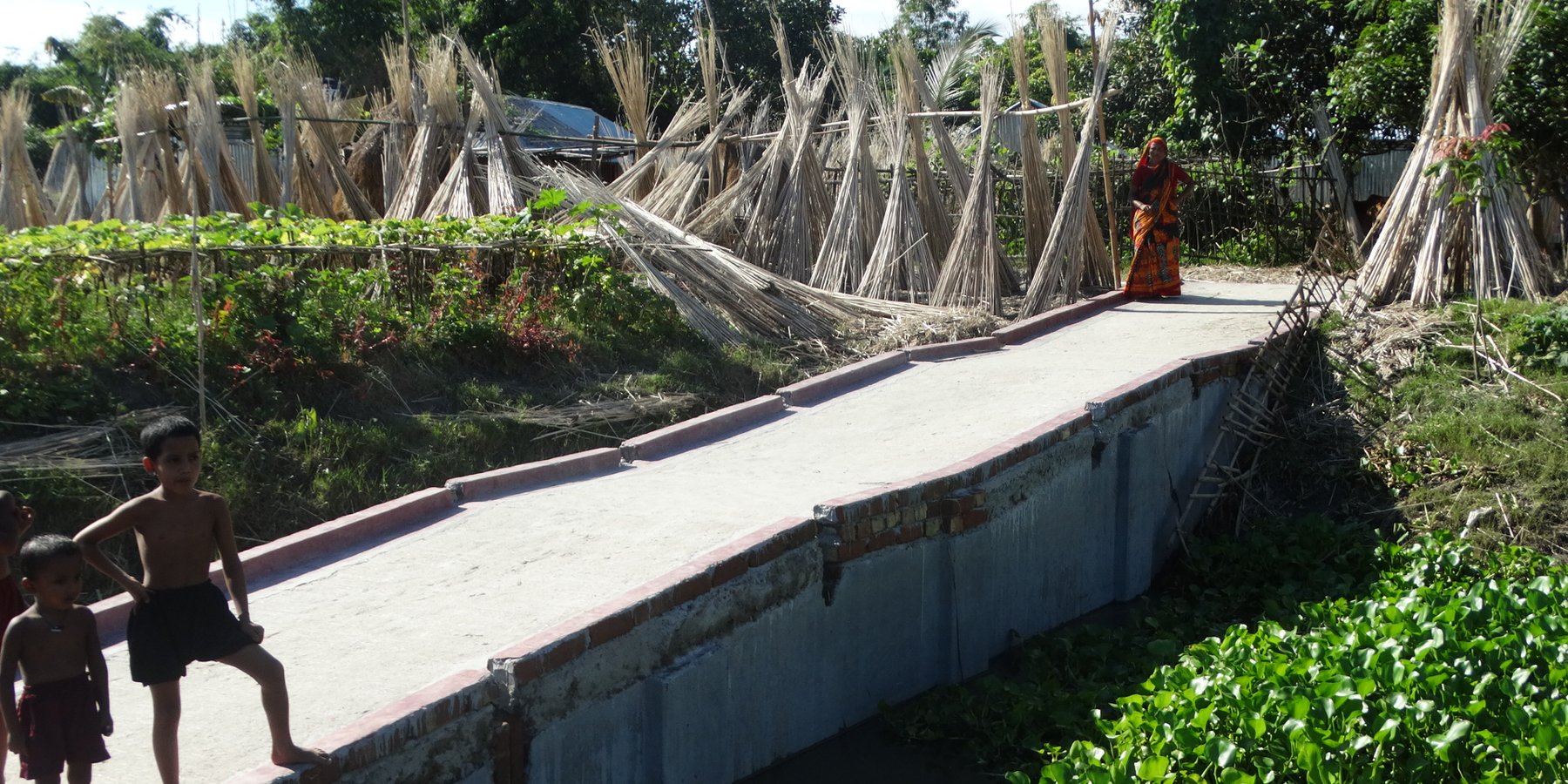
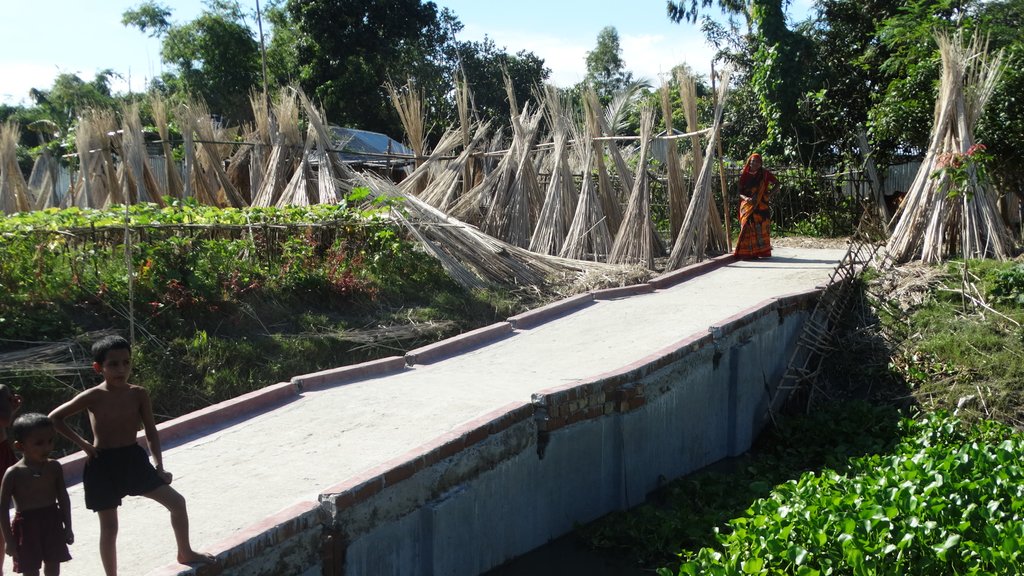
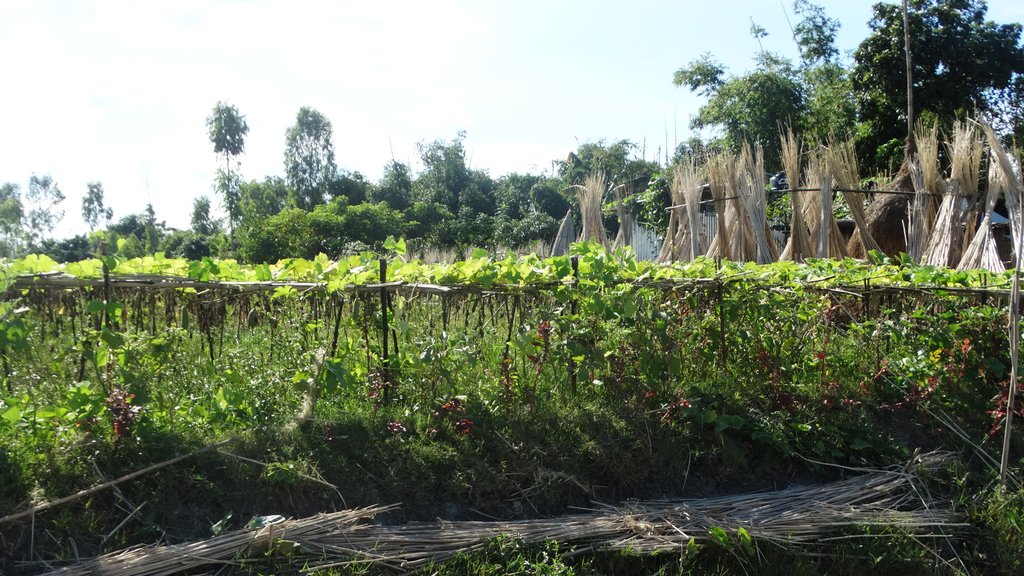
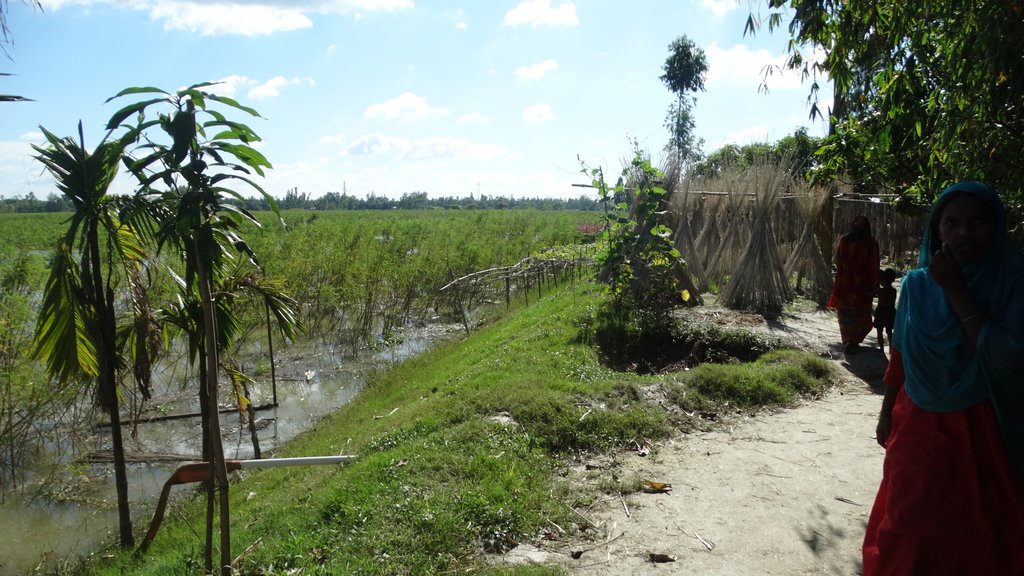
The inclusive, flood-resilient cluster village provides safe housing, food security and income generation for multiple families, including persons with disabilities, in a highly flood prone area of Gaibandha District in northern Bangladesh. The land was raised above flood level and is protected by deep rooted fruit trees to prevent soil erosion and provide income for the land users.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
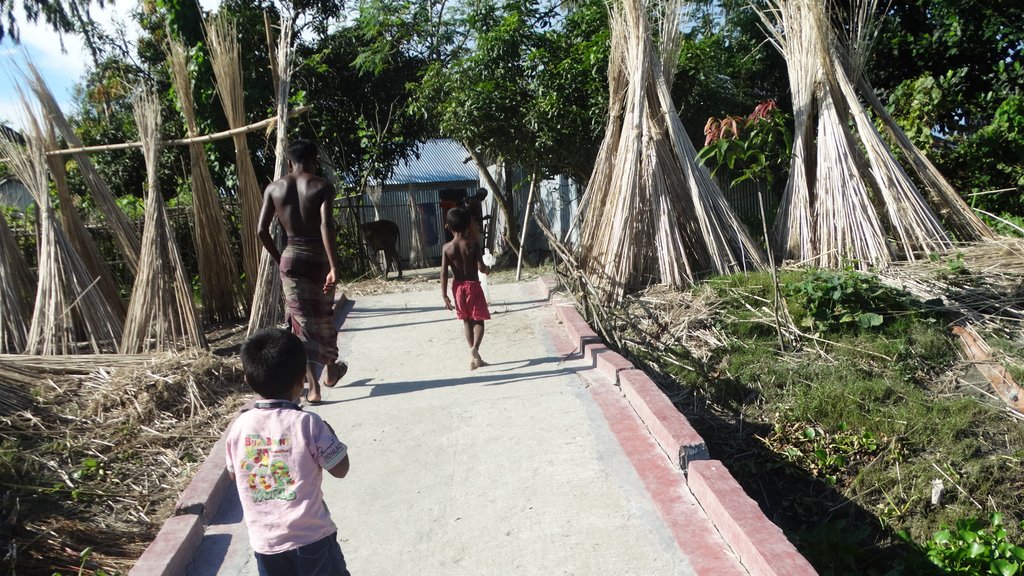
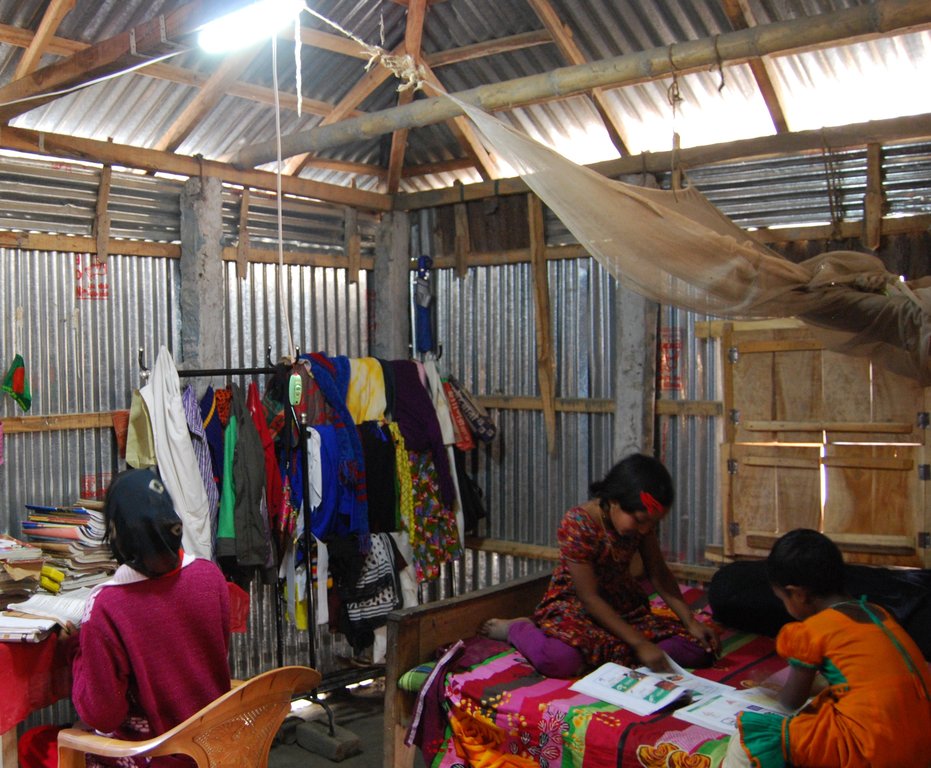
The inclusive, flood-resilient cluster village was introduced in a rural area with a high risk of recurring monsoon floods. The purpose of the technology is to provide safe housing, safe shelter for livestock, food security and income generation for ten families, including persons with disabilities.
The main components of the technology are:
1) The raising of a piece of land by seven feet (213cm), to three feet (91cm) above expected highest flood levels. Solid soil was banked up to encircle a 30'000 square feet (roughly 50x57m) piece of land and then the space within was filled up with sand collected from a nearby river bank. A one-foot layer of solid soil was added to cover the entire area.
2) The protection of the raised land from soil erosion during floods by planting a combination of deep-rooted fruit- and medicine trees around the border of the raised land. The trees include a number of different types of deep-rooted and light-rooted fruit trees and one type of medicine tree, Azadirachta Indica, locally known as "Neem". In addition, the slope of the border area was covered by grass turf to protect the soil from being washed out by rain. Two types of deep-rooted and flood resistant grasses were used. A drainage system was installed to facilitate water runoff.
3) The planting of a 150 square feet (14m2) commonly used homestead vegetable garden at the center of the cluster village. The cultivated vegetables include red spinach, jute leaf, basella leaf, spinach, radish, cabbage, okra, bottle-guts, cucumber and beans, allowing for a summer and a winter harvest. Together with the fruit trees, the vegetable garden provides food security during prolonged flooding. They also provide improved nutrition and income generating opportunities through selling of a part of the harvest in the market.
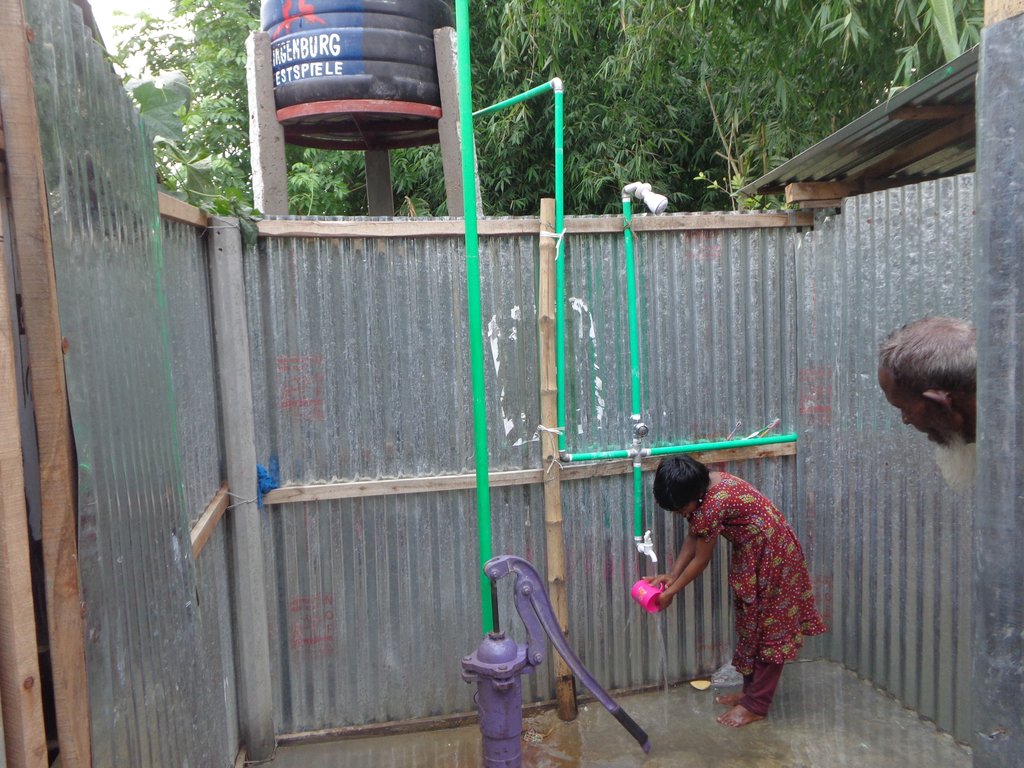
4) Making the village accessible for persons with disabilities through different accessibility measures, including the construction of a ramp, connecting the cluster village entrance with the road, and of accessible common Water-, Sanitation- and Hygiene (WASH) facilities, including a latrine, deep bore hole water source and water storage tank.
5) Installation of a solar panel to ensure uninterrupted, flood-resilient power supply. The level of power supply is sufficient to ensure coverage of electricity needs during flood season, when regular supply is around 15% below annual average.
The Cluster village was constructed as part of a disaster risk reduction project by CDD (Center for Disability in Development) from Bangladesh, with the support of CBM (Christoffel Blindenmission), an international development organization and funded by a donor from Germany. The main cost for inputs were provided to the land users by the project, including rent of construction machinery, paid labor, soil and construction material for the ramp and WASH facilities. The land users contributed labor and seedlings for the planning of the border trees and the homestead vegetable garden.
The main benefits of the technology from the perspective of land users are the protection it provides for houses and livestock, which would otherwise be in danger of loss during floods. The availability of food, water and electricity allows land users to remain in their homes during floods and avoid evacuation and the risk associated with it, including for example protection risks or the risk of theft. The flood protected vegetable gardens and fruit trees provide a year-round, sustainable source of food and income, providing food security and improved nutrition. The Neem tree provides medical and hygiene uses of the branches and leaves.
The cluster village is used as a safe space for the land users and other members of the community and their livestock during floods. Land users who are persons with disabilities or elderly benefit from the accessible infrastructure. With multiple families sharing land, the cluster villages provides optimal utilization of land resources. An additional benefit mentioned by land users is that the joint use by multiple families led to a more progressive social culture.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Bangladesh
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Gaibandha District
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Horipur Union, Sundargonj Sub district,
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- appliquée en des points spécifiques ou concentrée sur une petite surface
Commentaires:
Kani Charitabari, Horipur Union, Sundargonj sub district, Gaibandha District.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
2016
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The technology was introduced as part of a disaster risk reduction project, implemented the Center for Disability in Development (CDD) with the support of Christoffel Blindemission (CBM) and with participation and leadership of the local community. The project was financially supported a group of donors from Germany.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire les risques de catastrophes
- s'adapter au changement et aux extrêmes climatiques et à leurs impacts
- créer un impact économique positif
- créer un impact social positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Implantations, infrastructures
- Habitats, buildings
Commentaires:
Number of growing seasons per year: 2 (Summer and winter)
Livestock density : Livestock are available in every household.
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- Amélioration de la couverture végétale/ du sol
- mesures en travers de la pente
- Jardins/ potagers familiaux
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes
- V2: Herbes et plantes herbacées pérennes

structures physiques
- S7: Collecte de l'eau/ approvisionnent en eau/ équipement d'irrigation
- S8: Structures d'assainissement/ de gestion des eaux usées
- S9: Abris pour plantes et animaux
- S10: Mesures d'économie d'énergie

modes de gestion
- M1: Changement du type d’utilisation des terres
- M2: Changement du niveau de gestion / d'intensification
- M6: Gestion des déchets (recyclage, réutilisation ou réduction)
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wr: érosion des berges
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
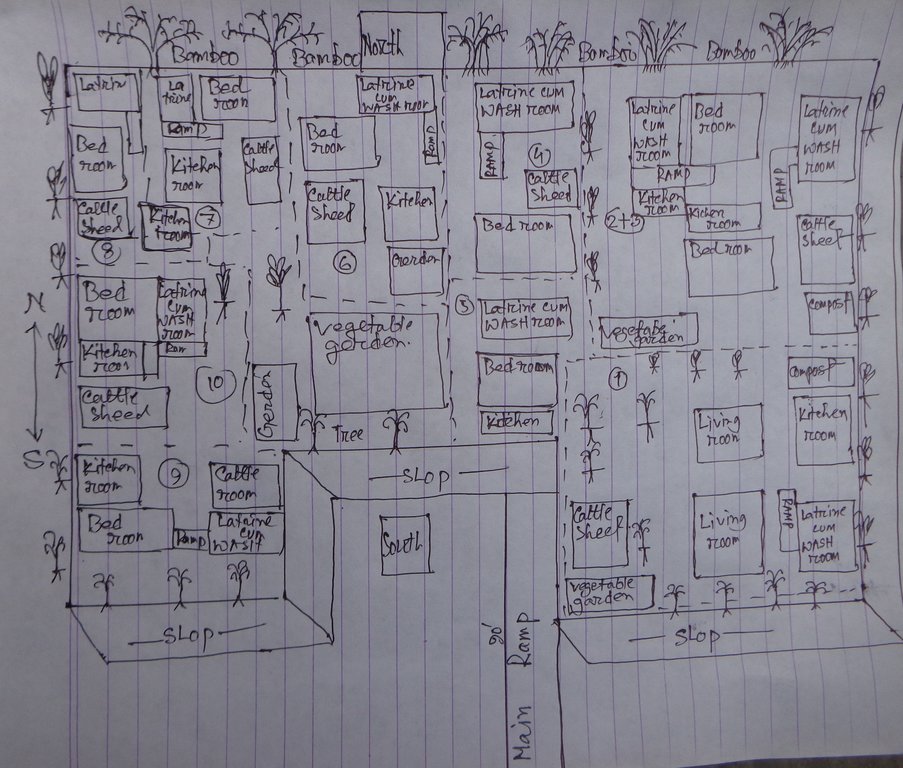
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
The drawing shows the layout of the disability inclusive, flood resilient Cluster village. The components of the technology are:
Raised land/plinth: 1) Purchase of land of a total area of 18'000 square feet (ca. 40x40m). Land ownership transferred to joint ownership of 10 families. 2) Collect 15'000 cubic feet (425m3) of solid soil from different pieces of land in the community. The soil was donated by members of the community, who were either related to the land users of the cluster village or donated in support of the construction of a safe space which can be used by the community during floods. 3) Banking up of 3 feet (91cm) of solid soil along the borders of the land. 4) Filling of area with 140'000 cubic feet (3965m3) of sand, extracted from a nearby riverbank with a rented sand extraction machine, raising the land to 6 feet (183cm). 5) Covering the entire area with one additional foot of solid soil, rasing the land to 7 feet (213cm), which means 3 feet (91cm) above the maximum expected flood levels.
Soil protected through deep-rooted trees: 1) Planting of deep-rooted and light-rooted fruit trees, surrounding the entire border of the raised land. The trees include deep rooted fruit trees like mango, black berry, jack-fruit, guava, coconut and areca nut, light-rooted fruit trees like banana and Papaya, a deep-rooted medicine tree, locally called "Neem" and the light-rooted Dhol Kalmi tree (pink morning glory). The number of deep-rooted threes was 100, with a spacing of around 5 feet in between each. They were planted to cover the entire perimeter of the raised land. In between the deep-rooted trees, 60 light-rooted trees were planted. In front of the deep-rooted trees, 60 bamboo bushes were planted to provide additional protection from wind and rain. 2) Turfing of the entire slope surrounding the cluster village with two flood resistant grasses: Durva (Cynodon dactylon) and Catkin grass. 3) Installation of a central drainage system with 15 plastic pipes ensuring water runoff from the wastewater pond.
Road access through ramp: The connecting ramp of the cluster village is 90 feet length, 6 feet width. There are five landing point of this ramp with smooth slopping. The construction material includes class one brick, brick stone, cement, sand, polythene and red oxide color for color contrast, which is appropriate for low vision and visually impaired persons. There is a 5 inch border on both sides of the ramp for safe movement of a wheel chair user.
Accessible household water and sanitation facilities: Latrine and wash-room are constructed for every house in the cluster village, following universal design standards. Latrines are connected to the wash room and the main house through ramps. There is a railing on both sides of the latrine and the entrance is wider for access of a wheel chair users. Water system for the latrine and wash room is provided from a water tank on three pillars behind the latrine, which is also connected to the main house for provision of drinking water. The tank is filled by hand pump ('magic pump') which functions with minimal hand pressure. The WASH facilities are accessible and usable by everyone including persons with disabilities, pregnant women or aged persons.
Home vegetable gardens: Every household has an individual homestead vegetable gardens where land users cultivate seasonal vegetables year-round. Gardens vary in size between averaging about 1.5 decimal (60m2) in size and are surrounded by bamboo fencing. The land owners are using organic fertilizer/compost for the vegetable production of their choice. By using cow's manure and wastage they are producing the compost in the behind of their houses in a ditch.
Solar system: A mini solar system is installed on the roof for each house by using a small panel with a 12-volt battery . Each system has the capacity of providing power for light for 8 hours. An introduction to system maintenance was given to the land users by the provider of the solar system.
Auteur:
Shahidul Islam
Date:
09/11/2016
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par entité de la Technologie
Précisez l'unité:
Cluster village
Précisez les dimensions de l'unité de terrain (le cas échéant):
18'000 square feet piece of land
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Bangladeshi Taka
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
80,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
300
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selecting the place for cluster village construction | During rainy season in 2015 |
| 2. | Establish collaboration with 10 families who will become land users | December 2015 |
| 3. | Land Raising & Ramp construction | December 2015 to March 2016 |
| 4. | Reconstruction the existing houses of the land users on the raised land | April 2016, before onset of rainy season 2016 |
| 5. | Planting of deep- and light-rooted fruits trees, bamboo bushes and grass turfing along the boundery | February 2016 to March 2016 |
| 6. | Install accessible water & sanitation system | April-June 2016 |
| 7. | Establish home garden in front of each house | June-July 2016 |
| 8. | Install mini solar system for each house | Aug-sep 2016 |
| 9. | Prepare livestock shed for each house | October 2016 |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Land raising, tree planting and turfing on slope | person days | 290,0 | 300,0 | 87000,0 | 10,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Ramp construction | person days | 115,0 | 350,0 | 40250,0 | 10,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | House reconstruction and WASH facilities | person days | 200,0 | 400,0 | 80000,0 | 10,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Solar system installation | person days | 10,0 | 300,0 | 3000,0 | 10,0 |
| Equipements | WASH equipment (latrine, magic pump, water tank, pipes, switch, pillars and other) | pieces | 10,0 | 46658,0 | 466580,0 | |
| Equipements | Solar system | pieces | 10,0 | 6300,0 | 63000,0 | |
| Matériel végétal | Deep rooted trees | pieces | 100,0 | 40,0 | 4000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seed for vegetable | KG | 5,0 | 1000,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Sapling purchase | pieces | 100,0 | 50,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Light rooted tree | pieces | 60,0 | 30,0 | 1800,0 | |
| Engrais et biocides | Organic fertilizer (compost) | KG | 600,0 | 10,0 | 6000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Rent for shallow machine for sand extraction | Daily rent | 10,0 | 28800,0 | 288000,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Grass turfing | square feet | 15000,0 | 10,0 | 150000,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Allowance for house reconstruction material | House | 10,0 | 2000,0 | 20000,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Ramp construction | Piece | 1,0 | 125750,0 | 125750,0 | |
| Autre | Project management (monitoring and support) | persons-days | 180,0 | 2400,0 | 432000,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 1777380,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 22217,25 | |||||
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
The project, human resource supported by CBM, CDD and a funded by private donor.
Commentaires:
Labor for tree plantation, home stead gardening & house reconstruction was contributed by the land users.
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Turfing: Repair leakages, replace grass etc. | before onset of rains |
| 2. | Tree maintenance: Cutting branches, manure of roots etc. | Rainy season |
| 3. | Vegetable gardening | Summer & Winter season |
| 4. | Housing repairs | After harvesting season/ once in a year |
| 5. | Water and Sanitation system servicing and repairs | After harvesting season/once in a year |
| 6. | Solar system maintenance | Winter season/once in ayear |
| 7. | Village group meeting for decision making and conflict resolution | Once in a month |
| 8. | Organic composting/fertilizer production | Continuous |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | House repairs | person days | 10,0 | 300,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Ramp repairs | person days | 10,0 | 300,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Plingth raising and plantation | person days | 30,0 | 300,0 | 9000,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Solar system servicing by technical experts | piece | 10,0 | 500,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seed for vegetable gardening | KG | 5,0 | 1000,0 | 5000,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Soil for slope maintenance | square feet | 5000,0 | 10,0 | 50000,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Sand for slope maintenance | KG | 5000,0 | 2,0 | 10000,0 | |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 85000,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 1062,5 | |||||
Commentaires:
Land users are agreed to contribute 100% maintenance cost
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Market fluctuation and scarcity of goods in the flood season.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Heavy rainfalls are one of the causes for flooding
Zone agro-climatique
- humide
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- abondant (>3%)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
> 50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Oui
Régularité:
fréquemment
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
Diversité des habitats:
- faible
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- > 50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
- groupe/ communauté
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- traction animale
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- jeunes
- personnes d'âge moyen
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Age of land users includes children, youth, middle-aged as well as elderly.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
Land users jointly own the land of the cluster village. They do not own any additional agricultural land and work as daily laborers and sharecropers.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- groupe
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- individuel
Commentaires:
Land users own the land of the cluster village jointly, including a proportional share of land- and water use rights.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Fruit and vegetable production increased after introduction of the cluster village. Because of decreased loss of home and property during floods, labor is freed for crop production which increased overall crop production in the wider area.
qualité des cultures
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Fruit and vegetable quality is improved because of availability of Irrigation.
production animale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Livestock mortality rate is reduced because of safe space in Cluster village.
risque d'échec de la production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Homestead vegetable garden and fruit tree plantation above flood level has a significantly reduced risk of production failure.
diversité des produits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The flood-protected homestead vegetable garden allows for higher product diversity.
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increased availabilty of flood protected land for vegetable gardening.
production d'énergie
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Energy supply was not available before installation of solar panel.
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
disponibilité de l'eau potable
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Installation of deep tube well water source.
qualité de l'eau potable
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Significantly higher water quality during flood, because of flood protected water source in cluster village.
disponibilité de l'eau pour l'élevage
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Installation of deep tube well water source.
qualité de l'eau pour l'élevage
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Significantly higher water quality during flood, because of flood protected water source in cluster village.
disponibilité de l'eau d'irrigation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Irrigation available to land users after installation of deep tube well.
demande pour l'eau d'irrigation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Demand for irrigation water increased because of vegetable garden.
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increase of farm income through selling of fruit and vegetables.
diversité des sources de revenus
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Additional income source through selling of fruit and vegetables.
disparités économiques
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Decreased income disparities between the land users of the cluster village due to fruit and vegetable production available to all land users, Decrease income disparities between land users of the cluster village and other members of the communty because of the reduction of loss from flood damage.
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Somewhat increased workload for maintenance of technology but decreased because of avoidance of damaged from floods.
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increased food security through flood prodected homestead garden and tree plantation.
situation sanitaire
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Higher attendance of health workers because the cluster village offer suitable group meeting rooms and accomodation. Cluster village was constructed in vicinity of community clinic. Better hygiene through WASH facilities.
opportunités culturelles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The cluster village is a suitable meeting point for the entire community, for social gatherings or festivals.
possibilités de loisirs
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Cluster village offers common space for children and other land users for Joint recreational activities.
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Much improved situation for persons with disabiltiies who are part of the land users. All persons with disabiltiies in the wider community use the cluster village as a safe space during floods. Improved situation for all land users who are from marginalized parts of society (daily laborers and share croppers).
Impacts écologiques
Sols
perte en sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Soil erosion during floods decreased because of deep- and light-rooted border tree plantation.
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
impacts des inondations
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Raised land as safe space above flood level.
impacts de la sécheresse
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Drought impact in summer season decreased because of Irrigation.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
available shelter and safe space
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Cluster village provides additional safe space/shelter for the wider community.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | très bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- 11-50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
Around 10-15% of households which equals roughly 70 households.
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 0-10%
Commentaires:
The technology is replicated by households who receive assistance from local government for families at risk of flood damage.
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Oui
Si oui, indiquez à quel changement la Technologie s'est adaptée:
- évolution des marchés
Spécifiez l'adaptation de la Technologie (conception, matériaux/ espèces, etc.):
Peoples of cluster villages are selling vegetables and fruits in the local market and some of them are carrying the fruits in the distance market. They are becoming more interested to plant more fruit trees in the cluster village. If it is continue in future it would be a fruits and vegetable market in the cluster village. At the same time they started selling cows milk in the local market and its demand is increasing day to day.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Ownership of the land user's are there. Its a community driven initiative & disability inclusive in all respect. They are happy to give shelter to the other villagers during flood season. There is an opportunity to create an example of a model village in this area. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Its an innovative program. Peoples participation and their contribution is the main asset. Universal accessibility of the cluster village communicating benefit to other villagers during rainy as well as flood season. This pilot program can be replicated to other riverine areas in Bangladesh. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The intensity of floods is difficult to predict. With average flood levels rising, land users still have to live with the risk of flood levels going beyond the level of their rised land. | More research on changing weather/climatic patterns and scientific measurement of expected flood levels. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Government and Non government organizations extension services are not available in this area. Livelihood of the cluster village peoples depending on seasonal agriculture. | Income raising multiple activity need to be introduces. A small scale disability inclusive comprehensive project could be implemented here. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
7
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
10
- interviews/ entretiens avec les spécialistes/ experts de GDT
1
- compilation à partir de rapports et d'autres documents existants
4
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
09/11/2016
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Disability inclusive Disaster Risk Reduction [Bangladesh]
The disability inclusive approach is centered around the meaningful contribution and leadership of persons with disabilties during the entire project management cycle, from the planning stage to the evaluation of the impact of a project. It contributes to empowering them to overcome social exclusion and recognizes their needs and priorities …
- Compilateur : Subir Saha
Modules
Aucun module trouvé