Longan, Plum interplanting [Chine]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : zhangsheng LIU
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Development of Southward Fruit Trees
technologies_942 - Chine
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Water & Soil Conservation Office of Zhaoan County (Water & Soil Conservation Office of Zhaoan County) - Chine1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)

Interplanting fruit trees of Longan, Peach, Plum etc. [Chine]
Interplanting plum, peach and other fruit trees in longan orchard on level terraces in order to prevent soil and water loss and improve production of the fruit trees.
- Compilateur : zhangsheng LIU
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Interplanting plum, peach in the Longan orchard to conserve soil and water and improve soil fertility.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
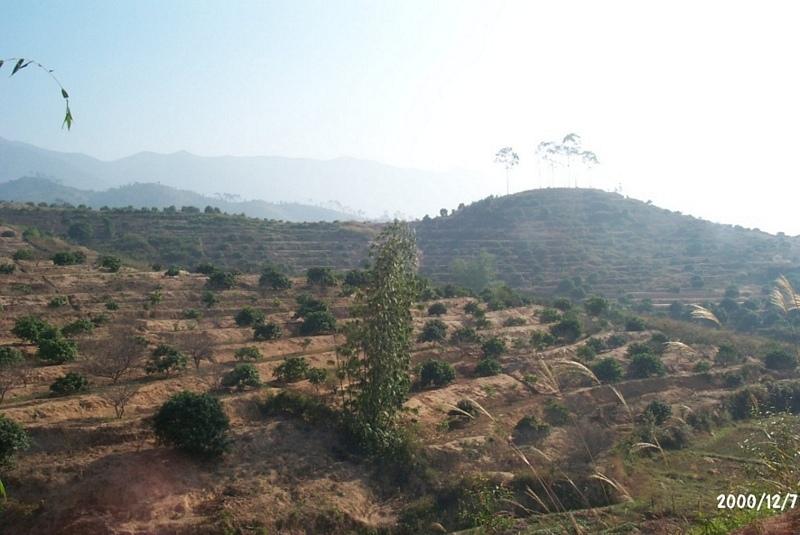
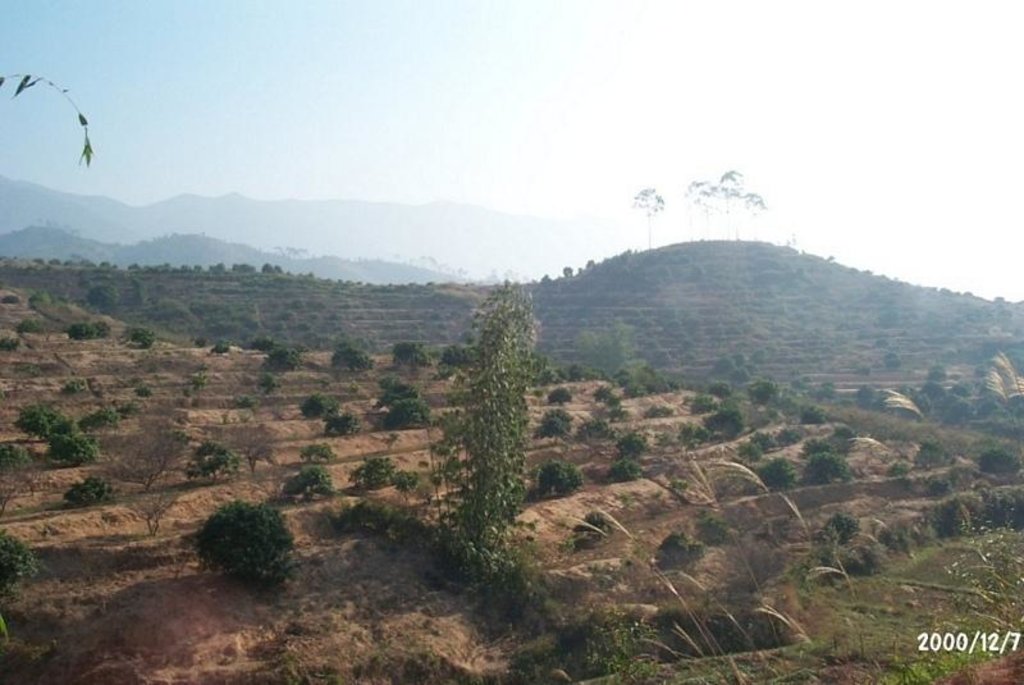
The technology is to interplant fruit trees in orchard so as to prevent water loss and soil erosion. To implement the project, local government gave financial support and SWC specialists gave technologically guide to local land users. The slope land in the hilly and mountain areas were constructed into terraces and plant trees in order to improve surface vegetation cover rate and reduce water and soil loss; the harvesting surplus rainfall in the raining season and irrigate the fruit trees in dry seasons.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Chine
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Fujian
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- 10-100 km2
Commentaires:
After the land users' arduously cultivating over many years, the former waste mountains have become a picture of vital force, the various growing fruit trees are very vital, water loss & soil erosion is controlled, and cultivated land can be used in a sustainable way.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a plus de 50 ans (technologie traditionnelle)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The technology originated from Institute of Water & Soil Conservation in Taiwan and improved by the national SWC specialists.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agroforesterie

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Plantations d'arbres et d'arbustes - Précisez les cultures:
- fruits à noyaux (pêche, abricot, cerise, prune)
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 240Longest growing period from month to month: Mar - OctSecond longest growing period in days: 120Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Oui
Si oui, précisez quelles cultures sont produites en culture intercalaire:
Interplanting plum, peach

Forêts/ bois
Produits et services:
- Bois d'œuvre (de construction)
- Bois de chauffage
- Fruits et noix
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The ground surface of the SWC application area did not plant grass and green manure. The soil in the mountaintop area is lean, where broadleaf forest could be planted.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Because the soil layer is thin and poor, the local farmers wouldn't like to invest in the area where water loss and soil erosion is serious.
Problems / comments regarding forest use: Commonly, supplementary planting of trees in the following Spring.
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- mesures en travers de la pente
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes
Commentaires:
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, contour ridging
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Causing land surface bare, ruderal cluster.), poverty / wealth (Lack of captial: hindering ulterior expanding of the water and soil conservation)
Secondary causes of degradation: Land subdivision (seperated land area can not be entirely developed)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
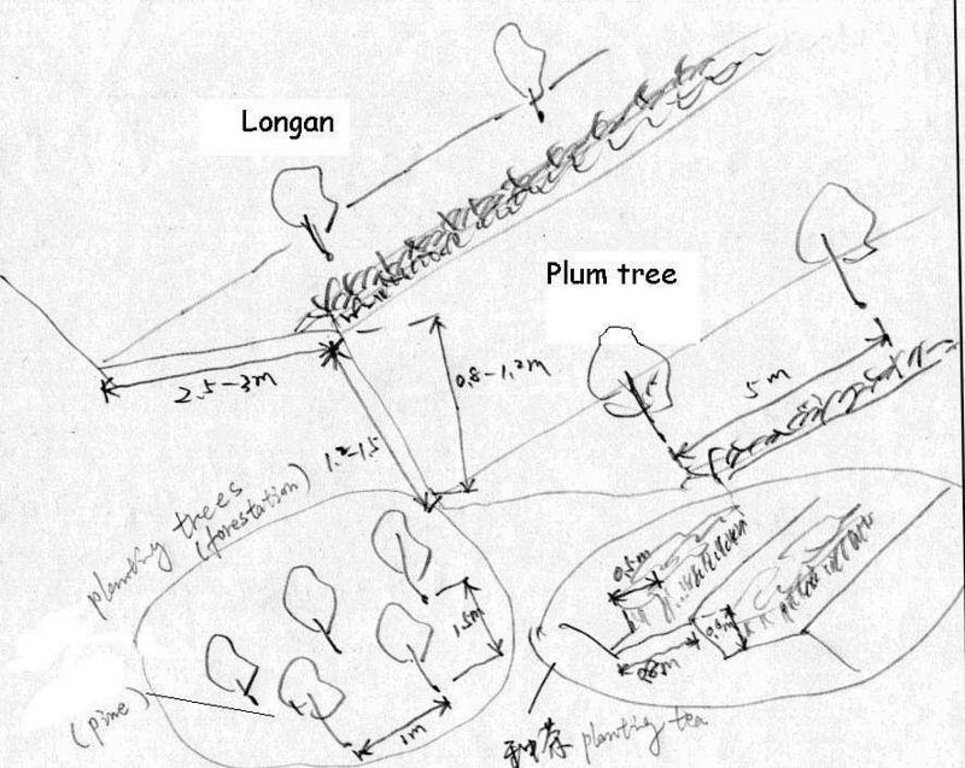
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Technical drawing of interplanting in orchard.
Location: Zhaoan county. Fujian
Date: 1997
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, improvement of ground cover, wind-break
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Plum trees
Quantity/ density: 238
Remarks: increasing ground cover
Contour ridging
Remarks: reasonable layout
Trees/ shrubs species: jequirity tree
Perennial crops species: Plum, peach lichi trees
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 15.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 60.00%
Construction material (earth): cheaper, local materials, good effect
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 28.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 13.00%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 26.00%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:2.00
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Forbidding disafforest in mountain areas for 3 years.
Auteur:
LIU Zhangsheng, Zhaoan, China
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars américains
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
8,3
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
2.40
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | plant trees | spring |
| 2. | Level off land | winter |
| 3. | weed | winter |
| 4. | digging ditch | spring |
| 5. | Level off land | Autumn |
| 6. | costruct bank of field | winter |
| 7. | Closure and forbidding disafforest | 3 years |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | digging ditch(interplant) | winter / Annually |
| 2. | irrigate | spring / Each cropping season |
| 3. | fertilization | Mar.Jun.Sep. /Annual |
| 4. | spew pesticide | Apl.Jul. /Annual |
| 5. | reinforce banks of level terrace | autumn/Annual |
| 6. | complementing seedling | spring / 1 |
| 7. | Fertilizing | Mar. Jun. / 2 |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Commentaires:
Slope angle degree, and earth volume being moved.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Main factor influencing the SWC cost is steeper slope. Since the slope steeper is, much more cost needed to level off terrace. In some places, the earth needs to be moved from one place to another which will spend a lot of labor forces.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- humide
- subhumide
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
slopes on average also moderate
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
- moyen (limoneux)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth als moderatly deep
Soil fertility very low - medium
Soil drainage / infiltration medium - good
Soil water storage capacity medium - high
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- riche
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- traction animale
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
12% of the land users are very rich and own 12% of the land.
44% of the land users are rich and own 44% of the land.
35% of the land users are average wealthy and own 35% of the land.
9% of the land users are poor and own 9% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Mainly in transport of goods and travelers, such as transport service. It needs much more idle labor forces.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
- individu, sans titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- loué
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- > 50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
1253 households
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 51-90%
Commentaires:
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
690 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
563 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The farmers have known that the SWC technology could produce benefits of improving agricultural production.
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Interplanting fruit trees of Longan, Peach, Plum etc. [Chine]
Interplanting plum, peach and other fruit trees in longan orchard on level terraces in order to prevent soil and water loss and improve production of the fruit trees.
- Compilateur : zhangsheng LIU
Modules
Aucun module trouvé