Sediment Traps [Philippines]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Catch basin, silt traps, cascading canals, trenches, ditches
technologies_1712 - Philippines
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
Spécialiste GDT:
Manubag Jerry
Mt. Kitanglad Agri- Development Corporation
Philippines
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Mt. Kitanglad and Agri Development Corporation (MKADC) - Philippines1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)

Integrated Soil and Water Conservation Approach in Improving … [Philippines]
Integration of soil and water conservation technologies primarily aim to protect the area from loss of biodiversity and land degradation.
- Compilateur : Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
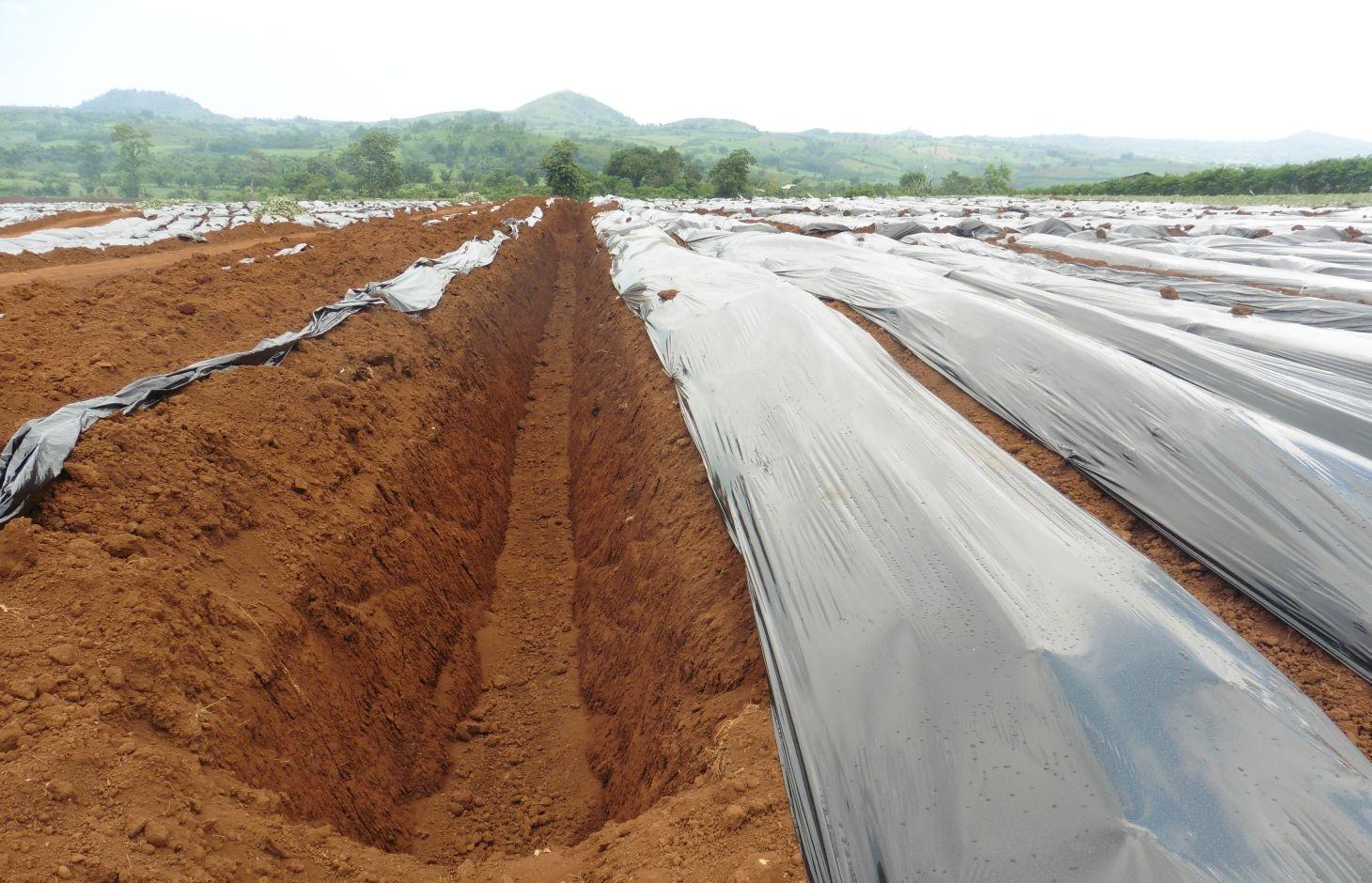
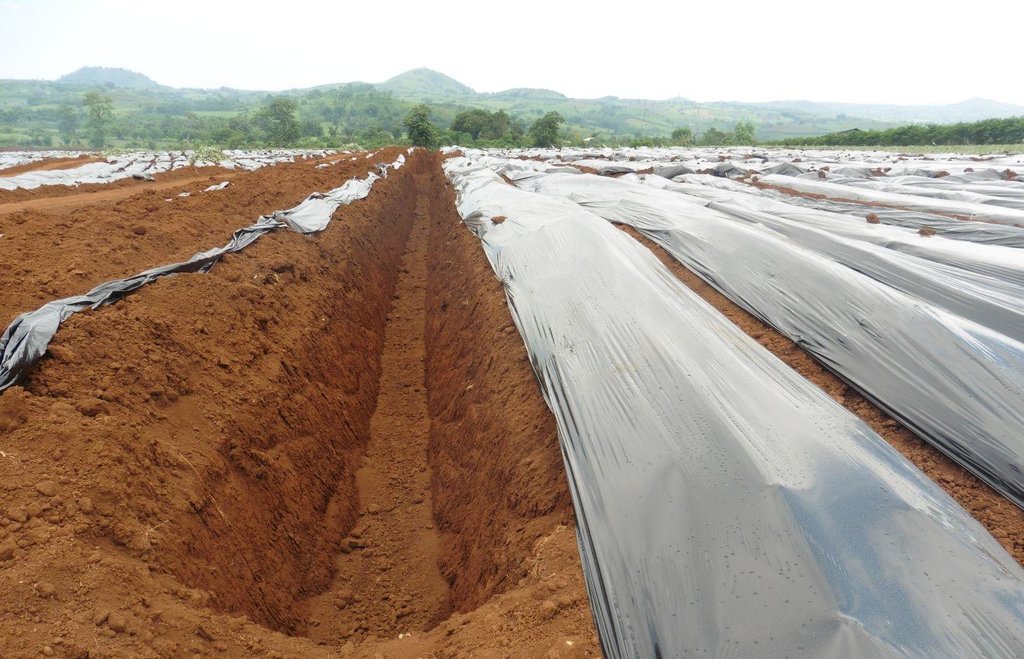
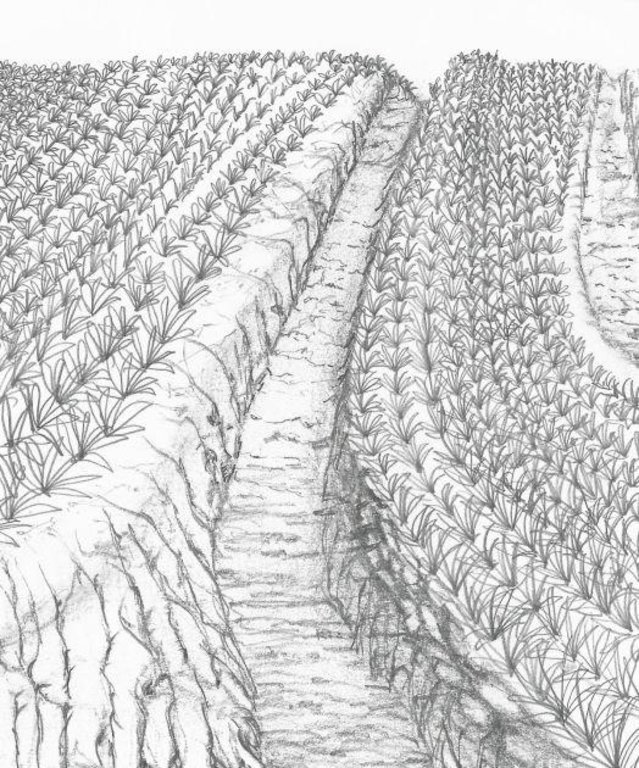
Sediment traps are structures built in the area which includes cascading catchment canal, silt traps and catch basin along perimeter, between pineapple fields and along diversion ditches to collect runoff during rains, preventing and minimizing the eroded soils cascading into natural bodies of water.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
Strategic construction of water catchment in and around existing pineapple fields to collect runoff during rains, aim to minimize eroded soil cascading into natural bodies of water. Sediment trap structures are earth canals designed to reduce soil erosion. The cascading catchment canal length depends on the slope, a length of five meters or longer is excavated when the slope of the area is less than 2%. The higher the slope percentage, the shorter the length of the canal. Silt traps are built along diversion ditches by stacking bamboo pegs or planting pineapple. Catch basin are bigger canals than the cascading canals which trap sediments that are not trapped in the silt traps and cascading canals. Weeds in this structures are not uprooted to further trap eroded soils or silts.
Purpose of the Technology: The technology aims to: (1) control of dispersed runoff; (2) serves as water harvesting facility; and (3) serves as sediment retention / trapping.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: In the establishment of sediment trap structures, the following activities are undertaken in the area: (1) Depending on the slope, sediment trap structure locations are identified; (2) Excavation of catch basin and cascading canals using back hoe; (3) Establishment of raised beds which are used for pineapple production; and (4) Construction of trenches with silt traps using bamboo pegs and pineapple plants. Cascading canals, trenches and diversion ditches are re-established every cropping season.
Natural / human environment: The area is under humid agro-climate condition with a topography ranging from 1-10% slope. It receives an average annual rainfall of approximately 3072 mm/year. The elevation ranges from 370-890 meter above sea level.
Mt. Kitanglad and Agri Development Corporation (MKADC) operates the area where the technology are being practiced. Farmers living within the area are the laborers of the company.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Philippines
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Valencia City
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Bukidnon
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, précisez la superficie couverte (en km2):
2,6066
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- 1-10 km2
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 2.6066 km2.
Around 20% of the area is devoted for sediment traps. The gross area of the company is 1,303.28 has which includes all other structures/ or conservation technology.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- au cours d'expérimentations / de recherches
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Establishment of sediment traps is a trial and error method,established canals are not permanent, design of canals are change the next cropping season when they observe that the current design is not effective.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses) - Précisez les cultures:
- ananas
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion/ or siltation
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Other: Ow: Waterways, drainage lines, ponds, dams
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Oui (Veuillez remplir les questions ci-après au regard de l’utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie)
Commentaires:
Cropland: Cp: Perennial (non-woody) cropping
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- récupération/ collecte de l'eau
- gestion de l'irrigation (incl. l'approvisionnement en eau, le drainage)
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S11: Autres
Commentaires:
Main measures: structural measures
Specification of other structural measures: Cascading canals, silt traps, catch basin
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wo: effets hors-site de la dégradation
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects
Main causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts)
Secondary causes of degradation: droughts
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Sediment traps are established to collect silts.
Location: Barangay Lurogan. Valencia City, Bukidnon
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, water harvesting / increase water supply
Structural measure: Cascading canal
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1m
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1m
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 5m
Structural measure: Catch basin
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5 m
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1m
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1m
Structural measure: Silt traps
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3m
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.75m
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5m
Auteur:
Mr. Patricio A. Yambot, Bureau of Soils and Water Management
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Philippine Peso
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
46,0
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Excavation of canal using back hoe | Before land preparation |
| 2. | Construction of bed | Once, before planting |
| 3. | Construction of trenches |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Equipements | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 100,0 |
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Desilting | Once in three months, but depends on the needs |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 100,0 |
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- humide
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- moyen (limoneux)
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth: moderately deep to deep (26 inches, 66.04cm of root penetration)
Soil fertility is medium ( With the incorporation of pineapple trash in the soil, there is now a build-up of OM content in the soil and based on soil analysis, essential elements in the soil are on adequate level for pineapple. )
Topsoil organic matter is medium (Soil organic matter ranges from 1.73% to 5.52% with highest in Perla Chan area and lowest OM in Gamboa area. Long term plan to reach 5% OM content in soil as effect of incorporating pineapple trash.)
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium (External and internal drainage of Ad luyon clay is good )
Soil water storage is high (ue to high clay content of the soil, it enables to store more water. )
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- employé (entreprise, gouvernement)
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
Off-farm income specification: The technology is more on trapping sediments, and is irrelevant with respect to additional income for the farmers
Level of mechanization: mechanised (Construction of sediment traps ad catch basin require machines i. e. back hoe)
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- grande dimension
Commentaires:
An average of 1.5 hectare per household
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, sans titre de propriété
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- loué
Commentaires:
Usually leased from individual land users 10 to 15 years upon the return of the area the company assured they will return back to the soil to its original form.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
surface de production
gestion des terres
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
disponibilité de l'eau d'irrigation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
little (5-20%)
Impacts socioculturels
apaisement des conflits
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
récolte/ collecte de l'eau
ruissellement de surface
nappes phréatiques/ aquifères
Sols
perte en sol
Autres impacts écologiques
Has the Technology contributed to improve livelihoods and human well-being (eg education, health)?
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
yes, little
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
inondations en aval
envasement en aval
pollution des rivières/ nappes phréatiques
dommages sur les champs voisins
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | pas bien |
| tempête de vent locale | pas connu |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | pas connu |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 91-100%
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Mt. Kitanglad and Agri Development Corporation (MKADC) operates the area where the technology are being practiced. The technology has been introduced through experiments and adoption from neighboring farms.
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Other land users in the area do not adopt the technology due to the opportunity cost that will be incurred. This opportunity cost pertains to the reduction of their production area since part of it will be allotted/converted in the establishment of sediment structures.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Land user's view agree with experts opinion. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Sediment traps are effective in minimizing soil erosion and preserving the top soil. |
| Negative off-site effects are lessened i.e siltation of natural water bodies |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Land user's view agree with experts opinion. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Established sediment traps are not permanent, designs are changed per cropping season, this activity disturb soil biological and physical properties which might cause soil fertility decline and on-site erosion. Further, altering or modifying canal designs per cropping would entail more cost just for the establishment of sediment traps. | Design location of other sediment traps that could be used for more than one cropping to minimize cost. A research must be done to address this issue. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Integrated Soil and Water Conservation Approach in Improving … [Philippines]
Integration of soil and water conservation technologies primarily aim to protect the area from loss of biodiversity and land degradation.
- Compilateur : Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
Modules
Aucun module trouvé