Sediment Traps [菲律宾]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Catch basin, silt traps, cascading canals, trenches, ditches
technologies_1712 - 菲律宾
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Manubag Jerry
Mt. Kitanglad Agri- Development Corporation
菲律宾
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Mt. Kitanglad and Agri Development Corporation (MKADC) - 菲律宾1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Integrated Soil and Water Conservation Approach in Improving … [菲律宾]
Integration of soil and water conservation technologies primarily aim to protect the area from loss of biodiversity and land degradation.
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
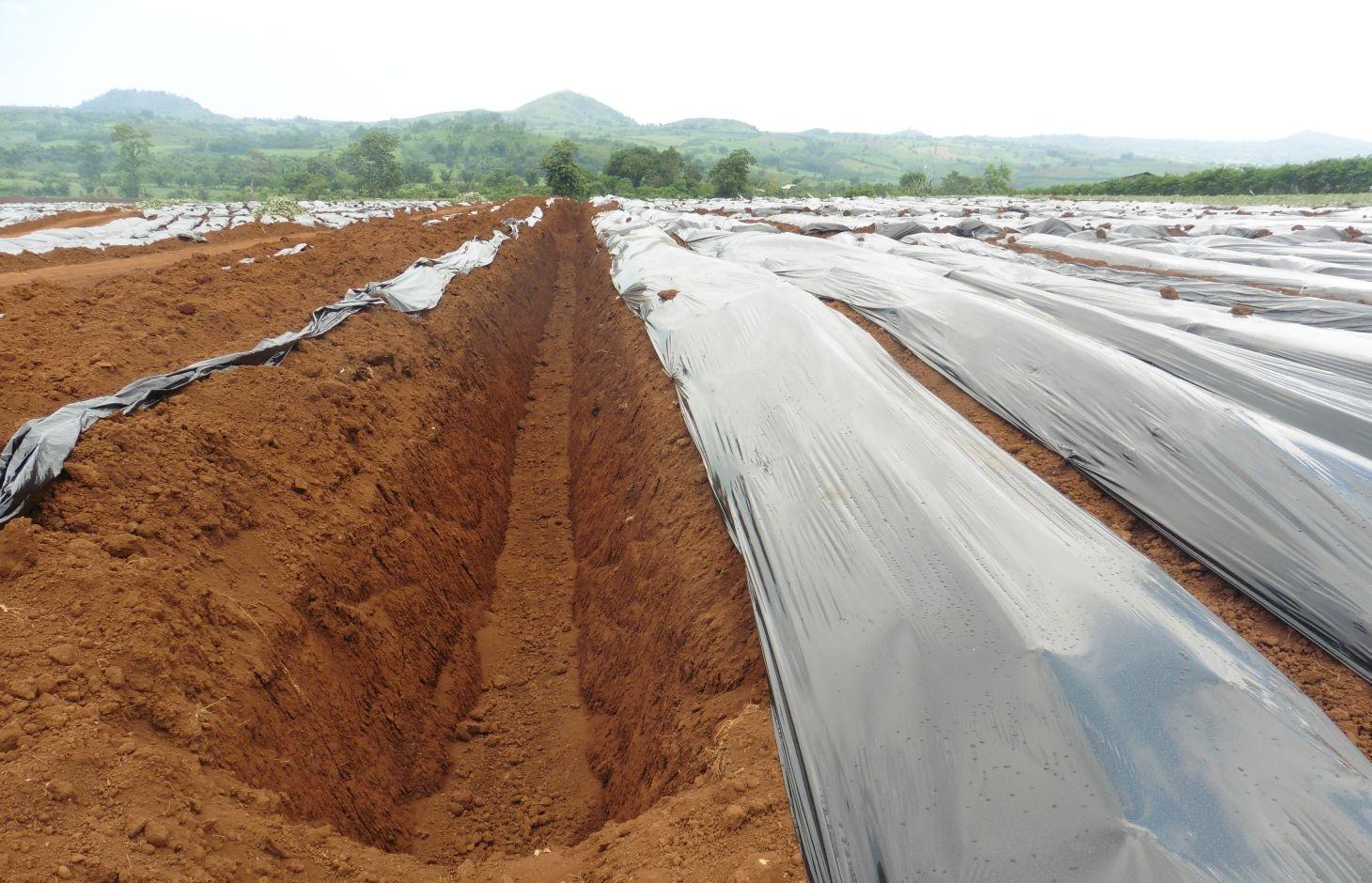
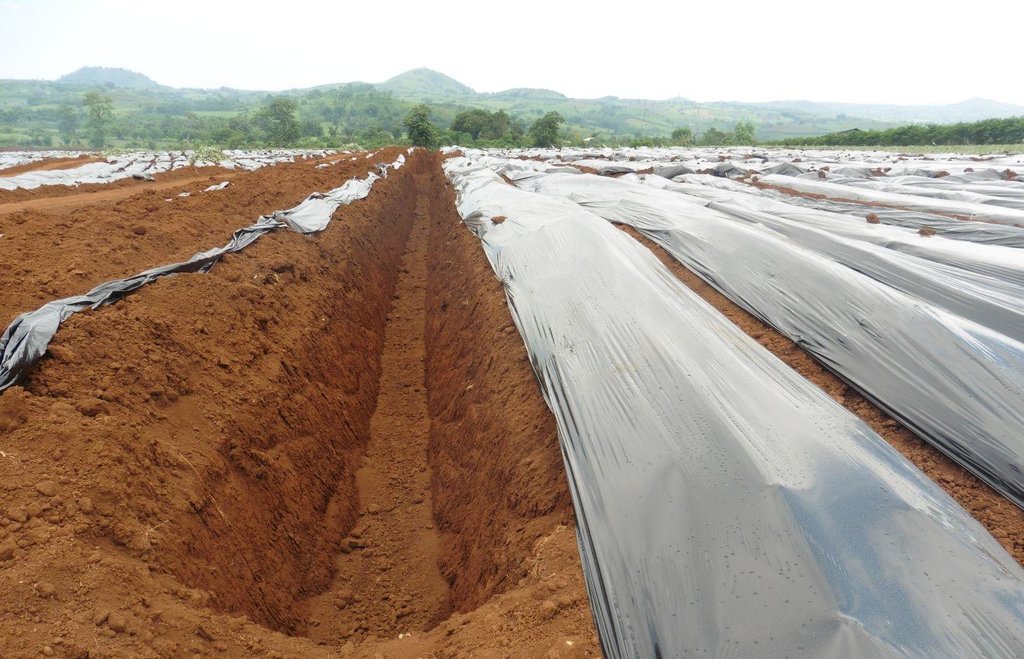
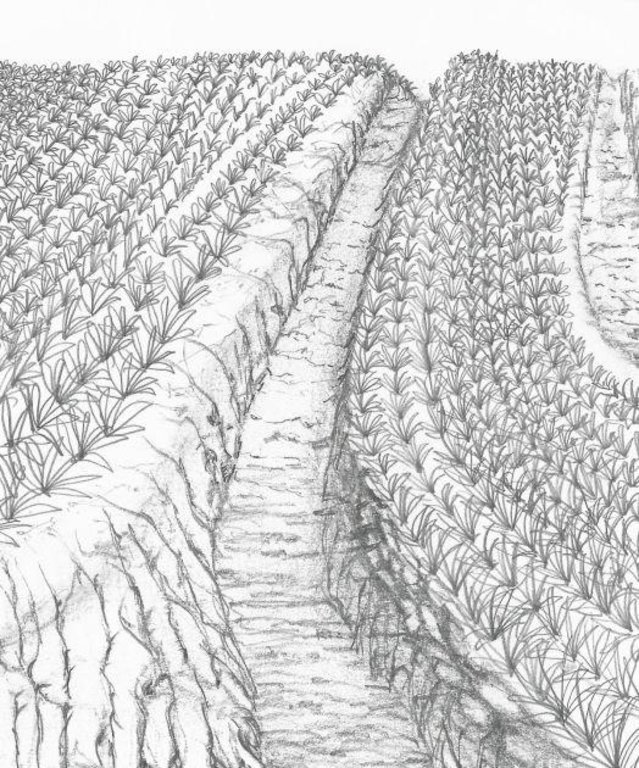
Sediment traps are structures built in the area which includes cascading catchment canal, silt traps and catch basin along perimeter, between pineapple fields and along diversion ditches to collect runoff during rains, preventing and minimizing the eroded soils cascading into natural bodies of water.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
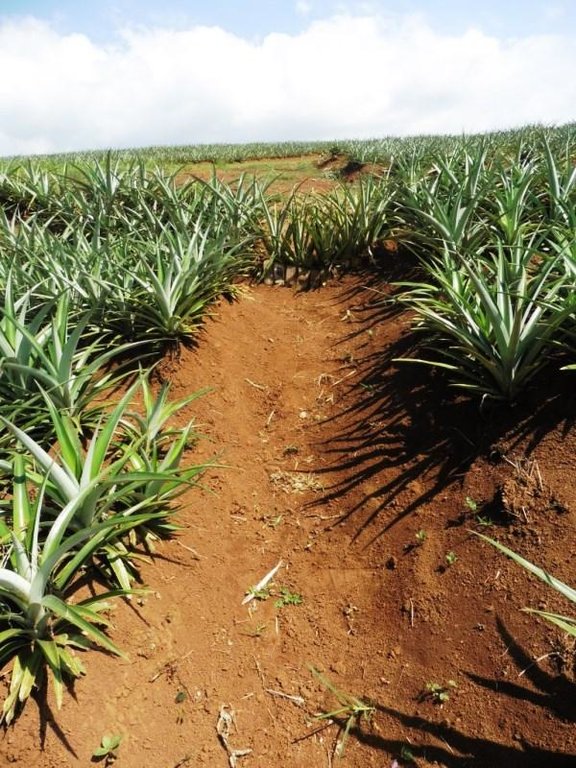
Strategic construction of water catchment in and around existing pineapple fields to collect runoff during rains, aim to minimize eroded soil cascading into natural bodies of water. Sediment trap structures are earth canals designed to reduce soil erosion. The cascading catchment canal length depends on the slope, a length of five meters or longer is excavated when the slope of the area is less than 2%. The higher the slope percentage, the shorter the length of the canal. Silt traps are built along diversion ditches by stacking bamboo pegs or planting pineapple. Catch basin are bigger canals than the cascading canals which trap sediments that are not trapped in the silt traps and cascading canals. Weeds in this structures are not uprooted to further trap eroded soils or silts.
Purpose of the Technology: The technology aims to: (1) control of dispersed runoff; (2) serves as water harvesting facility; and (3) serves as sediment retention / trapping.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: In the establishment of sediment trap structures, the following activities are undertaken in the area: (1) Depending on the slope, sediment trap structure locations are identified; (2) Excavation of catch basin and cascading canals using back hoe; (3) Establishment of raised beds which are used for pineapple production; and (4) Construction of trenches with silt traps using bamboo pegs and pineapple plants. Cascading canals, trenches and diversion ditches are re-established every cropping season.
Natural / human environment: The area is under humid agro-climate condition with a topography ranging from 1-10% slope. It receives an average annual rainfall of approximately 3072 mm/year. The elevation ranges from 370-890 meter above sea level.
Mt. Kitanglad and Agri Development Corporation (MKADC) operates the area where the technology are being practiced. Farmers living within the area are the laborers of the company.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
菲律宾
区域/州/省:
Valencia City
有关地点的进一步说明:
Bukidnon
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
2.6066
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 1-10 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 2.6066 km2.
Around 20% of the area is devoted for sediment traps. The gross area of the company is 1,303.28 has which includes all other structures/ or conservation technology.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
注释(项目类型等):
Establishment of sediment traps is a trial and error method,established canals are not permanent, design of canals are change the next cropping season when they observe that the current design is not effective.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 多年一作(非木材)
多年生(非木质)作物 - 指定作物:
- 菠萝
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion/ or siltation
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Other: Ow: Waterways, drainage lines, ponds, dams
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)
注释:
Cropland: Cp: Perennial (non-woody) cropping
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 集水
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S11:其它
注释:
Main measures: structural measures
Specification of other structural measures: Cascading canals, silt traps, catch basin
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects
Main causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts)
Secondary causes of degradation: droughts
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Sediment traps are established to collect silts.
Location: Barangay Lurogan. Valencia City, Bukidnon
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, water harvesting / increase water supply
Structural measure: Cascading canal
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1m
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1m
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 5m
Structural measure: Catch basin
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5 m
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1m
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1m
Structural measure: Silt traps
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3m
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.75m
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5m
作者:
Mr. Patricio A. Yambot, Bureau of Soils and Water Management
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Philippine Peso
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
46.0
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Excavation of canal using back hoe | Before land preparation |
| 2. | Construction of bed | Once, before planting |
| 3. | Construction of trenches |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | ||
| 设备 | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 |
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Desilting | Once in three months, but depends on the needs |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 |
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth: moderately deep to deep (26 inches, 66.04cm of root penetration)
Soil fertility is medium ( With the incorporation of pineapple trash in the soil, there is now a build-up of OM content in the soil and based on soil analysis, essential elements in the soil are on adequate level for pineapple. )
Topsoil organic matter is medium (Soil organic matter ranges from 1.73% to 5.52% with highest in Perla Chan area and lowest OM in Gamboa area. Long term plan to reach 5% OM content in soil as effect of incorporating pineapple trash.)
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium (External and internal drainage of Ad luyon clay is good )
Soil water storage is high (ue to high clay content of the soil, it enables to store more water. )
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 员工(公司、政府)
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
Off-farm income specification: The technology is more on trapping sediments, and is irrelevant with respect to additional income for the farmers
Level of mechanization: mechanised (Construction of sediment traps ad catch basin require machines i. e. back hoe)
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 大规模的
注释:
An average of 1.5 hectare per household
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
注释:
Usually leased from individual land users 10 to 15 years upon the return of the area the company assured they will return back to the soil to its original form.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
生产区域
土地管理
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
little (5-20%)
社会文化影响
冲突缓解
生态影响
水循环/径流
水的回收/收集
地表径流
地下水位/含水层
土壤
土壤流失
其它生态影响
Has the Technology contributed to improve livelihoods and human well-being (eg education, health)?
注释/具体说明:
yes, little
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
对邻近农田的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
| 局地风暴 | 未知 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Mt. Kitanglad and Agri Development Corporation (MKADC) operates the area where the technology are being practiced. The technology has been introduced through experiments and adoption from neighboring farms.
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Other land users in the area do not adopt the technology due to the opportunity cost that will be incurred. This opportunity cost pertains to the reduction of their production area since part of it will be allotted/converted in the establishment of sediment structures.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Land user's view agree with experts opinion. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Sediment traps are effective in minimizing soil erosion and preserving the top soil. |
| Negative off-site effects are lessened i.e siltation of natural water bodies |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Land user's view agree with experts opinion. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Established sediment traps are not permanent, designs are changed per cropping season, this activity disturb soil biological and physical properties which might cause soil fertility decline and on-site erosion. Further, altering or modifying canal designs per cropping would entail more cost just for the establishment of sediment traps. | Design location of other sediment traps that could be used for more than one cropping to minimize cost. A research must be done to address this issue. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Integrated Soil and Water Conservation Approach in Improving … [菲律宾]
Integration of soil and water conservation technologies primarily aim to protect the area from loss of biodiversity and land degradation.
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
模块
无模块