Diversion construction with gates and distribution channels [Yémen]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : ahmed algalal
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
الحواجز (الرزم) والبوابات والسواقي
technologies_1562 - Yémen
- Résumé complet en PDF
- Résumé complet en PDF pour impression
- Résumé complet dans le navigateur
- Résumé complet (non formaté)
- Diversion construction with gates and distribution channels: 24 juin 2017 (inactive)
- Diversion construction with gates and distribution channels: 24 juin 2017 (inactive)
- Diversion construction with gates and distribution channels: 13 août 2019 (inactive)
- Diversion construction with gates and distribution channels: 25 novembre 2022 (public)
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
AL Hadrami Yahya
General Directorate of Irrigation
Yémen
Spécialiste GDT:
Sallam Ahmed
Agricultural Research and Extension Authority
Yémen
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Agricultural Research and Extension Authority (AREA) - YémenNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
General Directorate of Irrigation - Yémen1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)
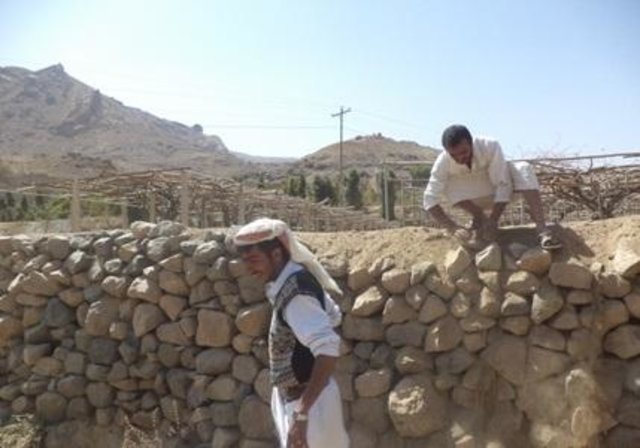

Rehabilitation of terraces and diversion construction with gates … [Yémen]
The rehabilitation of walls and outlets of the terraces and diversion construction with accessories from channels and gates are carried out by the local community in a regular way
- Compilateur : ahmed algalal
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
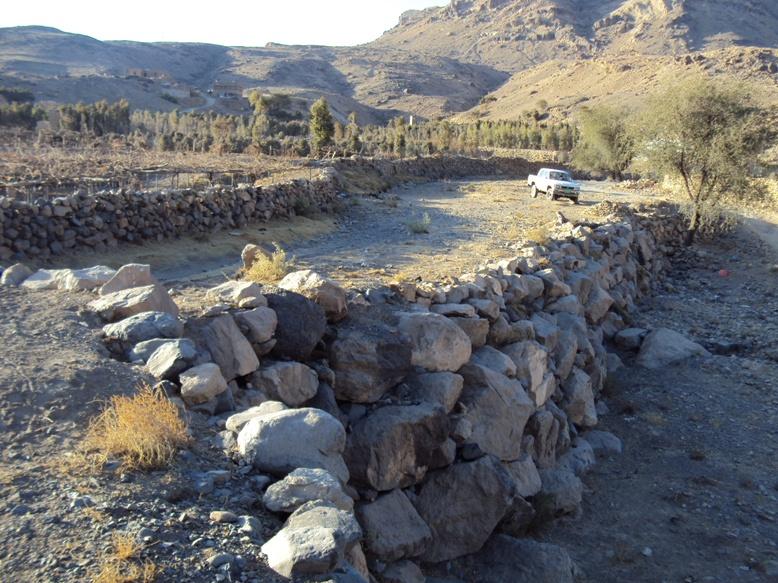
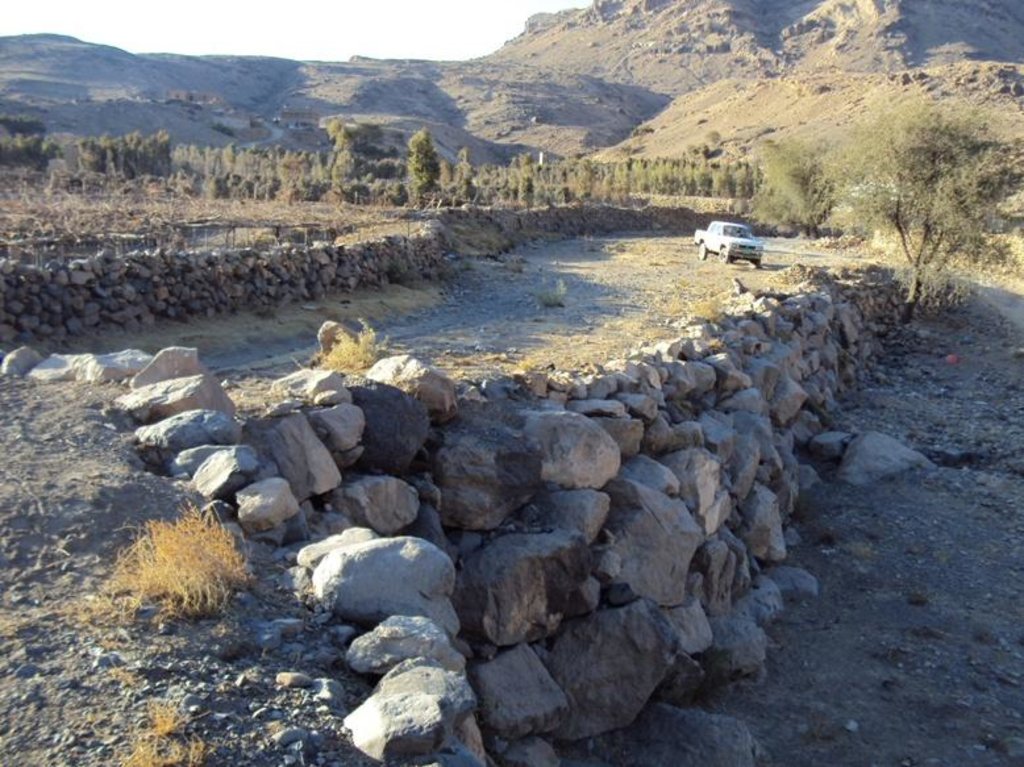
The stone existed in the region are used for building diversion constructions to raise the level of wadi bed to the level of the inlet of the cultivated land that need to be irrigated from water harvesting in addition to distribution channels in the fields
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
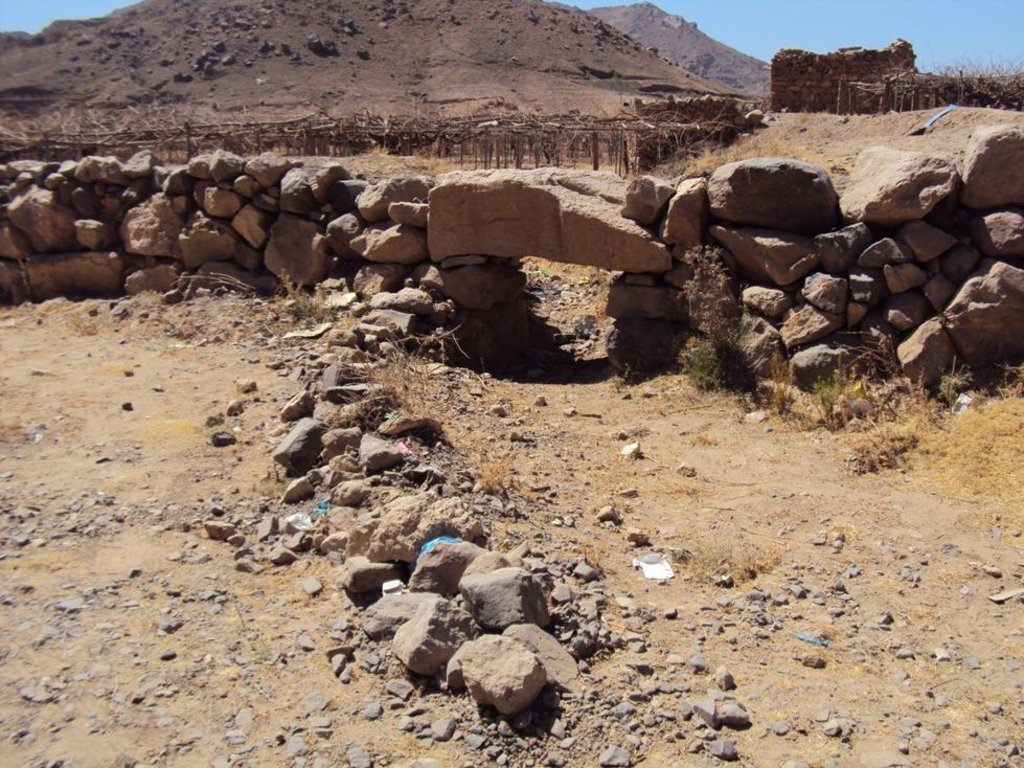
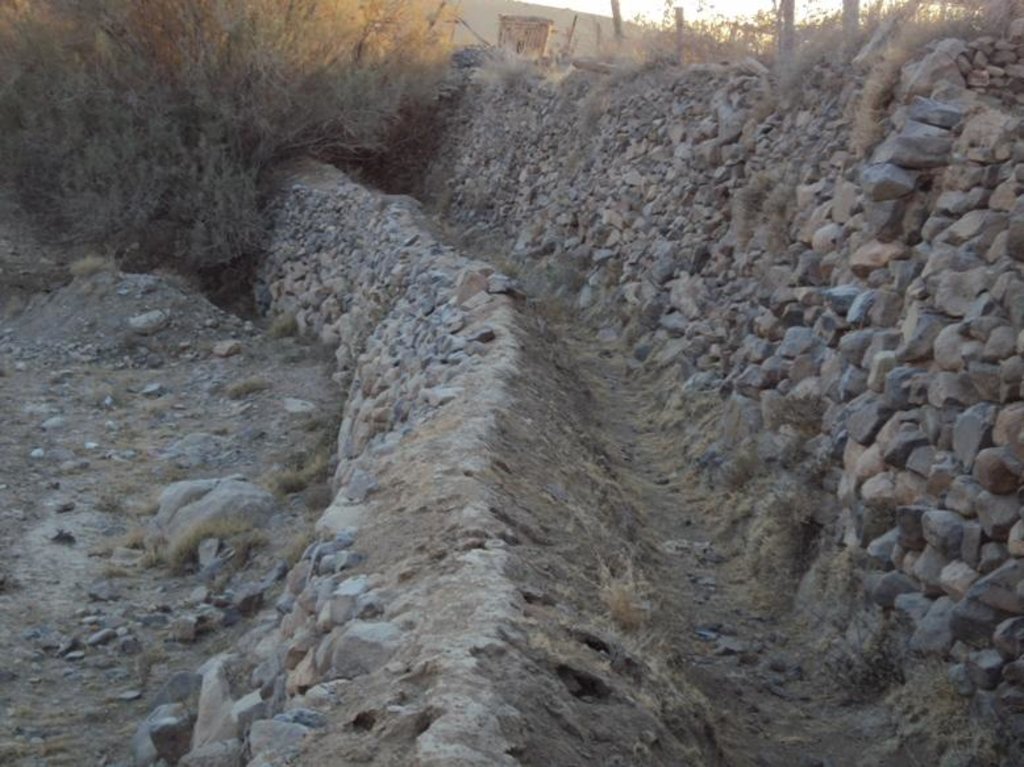
Diversion construction (DC) technology is one the structural solutions using stones with slope and tan 30 to slow the water flow and to deposits the carried materials with water to allow water to pass throw the inlet (gate) to the fields that need to be irrigated without damaged mainly vines and qat crops. The site of DC must be built in direction of water flow to direct it to pass to the fields need to be irrigated to get a benefit from this water harvested the height of the DC should be equalled to the height of the cultivated land which ranges between 2-4 meter and the width is 1.5 meter and the length is ranged between 40-60 meter based on the width of wadi bed. The DC should not built totally in one time but should be gradually and by the time as a result of deposit be come at the same level of fields need to irrigated. Finally when the height of DC become equally to level of the field need to irrigated the gate should be determined according to water requirement of cultivated crops. After that distribution channels should built at 1-2 wide, 0.5- 0.8 height and 10-100 length. Such as this type of technology is considered a long term process in the past due to lack of equipments and implements. However now it can be done in short time if all requirement provided especially funds and equipments.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Yémen
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Sana
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Bani Hushaish district
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 20.6 km2.
Alrawanah Bani Hushaish, which is located on the eastern side of the capital Sanaa, and is about 16 km away
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a plus de 50 ans (technologie traditionnelle)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- dans le cadre d'un système traditionnel (> 50 ans)
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
It is a very ancient technology but was rehabilitated in 1956 by the community
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Plantations d'arbres et d'arbustes - Précisez les cultures:
- raisins
- Qat
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 90
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Low productivity due to a lack of water (drought)
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): drought
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?

Terres cultivées
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Commentaires:
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Commentaires:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated and post-flooding
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- mesures en travers de la pente
- dérivation et drainage de l'eau
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S11: Autres
Commentaires:
Specification of other structural measures: Diversion construction with gates and distribution channels
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)

dégradation hydrique
- Ha: aridification
Commentaires:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: floods, droughts, poverty / wealth (poverty)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (up takes of major elements of fertility without subsistent)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
Commentaires:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Barrier cuts waterway with gates and distribution channels
Location: Alrawanah Uzlat. Bani Hushaish district
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (Construction process requires skills and experiences)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Has sufficient expertise)
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading
Secondary technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, Reduce runoff
Structural measure: Diversion construction
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 2 - 4
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1– 1.5
Structural measure: Gates
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5 -1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.7–1.2
Structural measure: Channels
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5–0.8
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1 - 2
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 10-100
Construction material (stone): The diversion construction and the gates are constructed by stones existing in the region
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5%
Auteur:
AL-Galal
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars américains
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
7.00
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collecting stones and building barriers with gates | Before the rainy season |
| 2. | Building channels | Before the rainy season |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Collecting stones and building barriers with gates | persons/day/barrier | 225,0 | 7,0 | 1575,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Building channels | persons/day/barrier | 7,0 | 7,0 | 49,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Animal traction | barrier | 1,0 | 46,5 | 46,5 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Tools | barrier | 1,0 | 46,5 | 46,5 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Animal traction for channel building | barrier | 1,0 | 16,3 | 16,3 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 1733,3 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 1733,3 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 3 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repair diversion construction and gates | annually after the rainy season |
| 2. | Clean channels | annually after the rainy season |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Repair diversion construction and gates | persons/day/unit | 13,0 | 7,0 | 91,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Clean channels | persons/day/unit | 2,0 | 7,0 | 14,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 105,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 105,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: big hammers, shovel, soil leveller
Costs were calculated according to the current situation, for the barrier with a gate length of 60 meters and a height of 2 meters, and for the channels with an average length of 50 meters and a width of 1 meter.
With regard to maintenance has been developed a lump sum annually where maintenance was done at the current time using modern equipment and as a result of no collapse charges barriers and accessories in most years has been estimated annual sum for the purpose of maintenance in the event of any damage
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
- Transportation and gradient
- difficult roads
- cutting stones
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitudinal zone: 2400 m a.s.l.
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil texture: Flood deposits
Topsoil organic matter: After falling vines leaves and grasses
Soil fertility is low - medium (output of the flood deposits)
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium - good
Soil water storage capacity is medium - high
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
> 50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
faible/ absente
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
faiblement potable (traitement nécessaire)
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Ground water table: 400 m
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- groupe/ communauté
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- traction animale
Genre:
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Women could not do the hard work, therefore, men work on the farm and women do the house works.
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
70% of the land users are average wealthy and own 90% of the land (moderate income).
30% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Level of mechanization: Also small tractors are used
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- moyenne dimension
Commentaires:
0.45 - 0.9 ha fragmentation of tenure is the cause of the small ownership per household
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
Commentaires:
There are three types of land ownership owned, Waqf, and a share at 70%, 20%, 10% respectively.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
risque d'échec de la production
gestion des terres
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
disponibilité de l'eau potable
demande pour l'eau d'irrigation
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
diversité des sources de revenus
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
opportunités culturelles
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
livelihood and human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
As a result of improving income and reducing the work load, the access to education is enhanced
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
quantité d'eau
récolte/ collecte de l'eau
ruissellement de surface
nappes phréatiques/ aquifères
Sols
humidité du sol
perte en sol
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
diversité des habitats
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
impacts des inondations
Autres impacts écologiques
surface crusting
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
disponibilité de l'eau
inondations en aval
envasement en aval
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- > 50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
537 households covering 100 percent of the stated area
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 91-100%
Commentaires:
537 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The technology is applied in the whole region, but the lack of capital is an obstacle for continuing conservation operations
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Harvesting flood waters How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continue maintenance operations |
|
Reduction of the runoff speed How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continue maintenance operations or introduce cement materials in the construction process to increase the ability to withstand various conditions |
|
Distribution of water on a regular basis How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintenance of channels to ensure sustainability |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| buried sediment distribution channels | lining channels for easy cleaning process |
| Construction costs and labour requirements are high | use modern equipment in the construction and maintenance processes |
| you need time for implementation | Use of modern equipment |
| Severe floodings can demolish barriers and gates | Use of cement materials |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Report of traditional knowledge and customs (sallam, et al, 2008)General Census of Population, Housing and Establishment (Census, 2004). Guide of agricultural climate in Yemen (Al Khorasani, 2005).
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Agricultural Research and Extension Authority, AREACentral Bureau of StatisticsAgricultural Research and Extension Authority, AREA
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Rehabilitation of terraces and diversion construction with gates … [Yémen]
The rehabilitation of walls and outlets of the terraces and diversion construction with accessories from channels and gates are carried out by the local community in a regular way
- Compilateur : ahmed algalal
Modules
Aucun module trouvé