level bund with double stone walls [Ethiopie]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Sabina Erny
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
cab
technologies_1061 - Ethiopie
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Department of Geography, University of Basel (Department of Geography, University of Basel) - Suisse1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)
food-for-work programm [Ethiopie]
food-for-work programm with distribution of grains and oil
- Compilateur : Sabina Erny
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
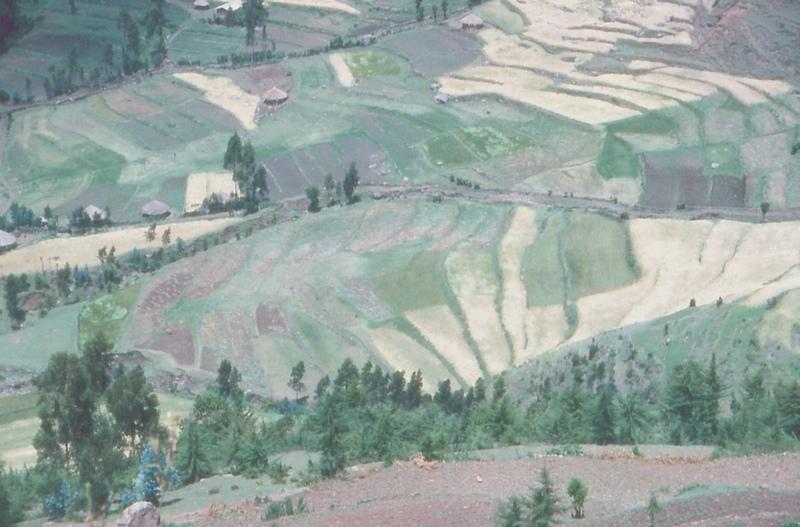
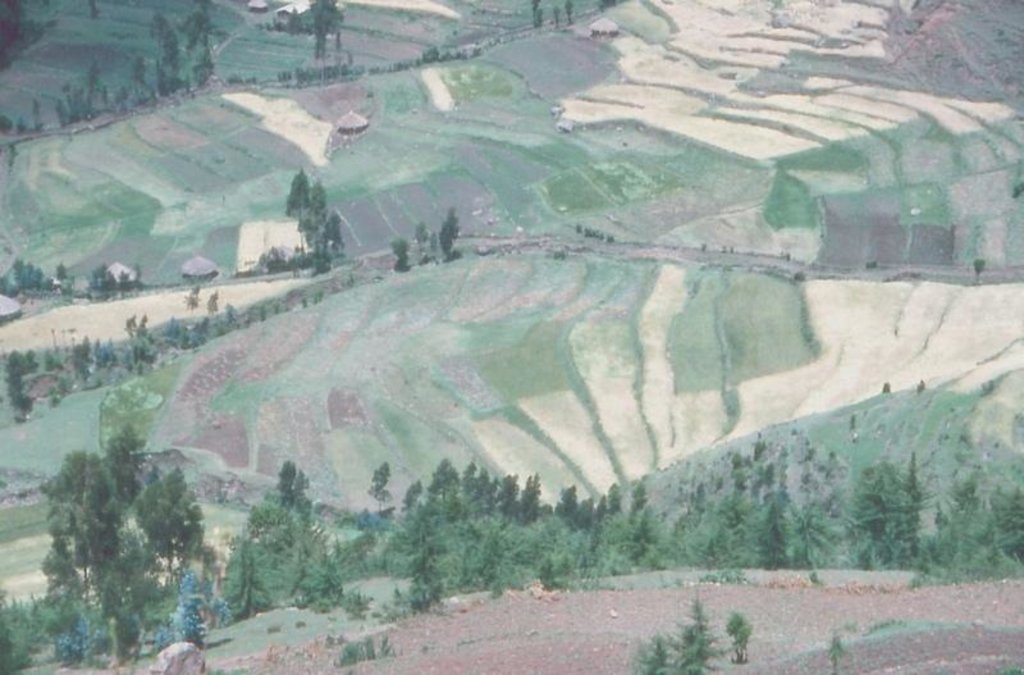
level bund with double stone walls with soil and grass to stabilize the structure
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
Two level rows of stones are piled up and the space between them is filled up with soil. Grass is growing on it so it can stabilize the bund. The soil can accumulate behind the bund. The land and the bunds slowly develop into terraces. It is combined with contour ploughing.
Purpose of the Technology: control runoff and soil erosion
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: through food-for-work program. Maintenance is up to the farmers, some maintain it regularly, throughout the year, others don't.
Natural / human environment: on gentle and steep slopes
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Ethiopie
Région/ Etat/ Province:
South Wello
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- 0,1-1 km2
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
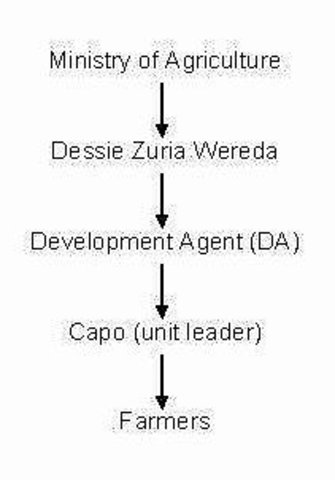
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
it was implemented by the government
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

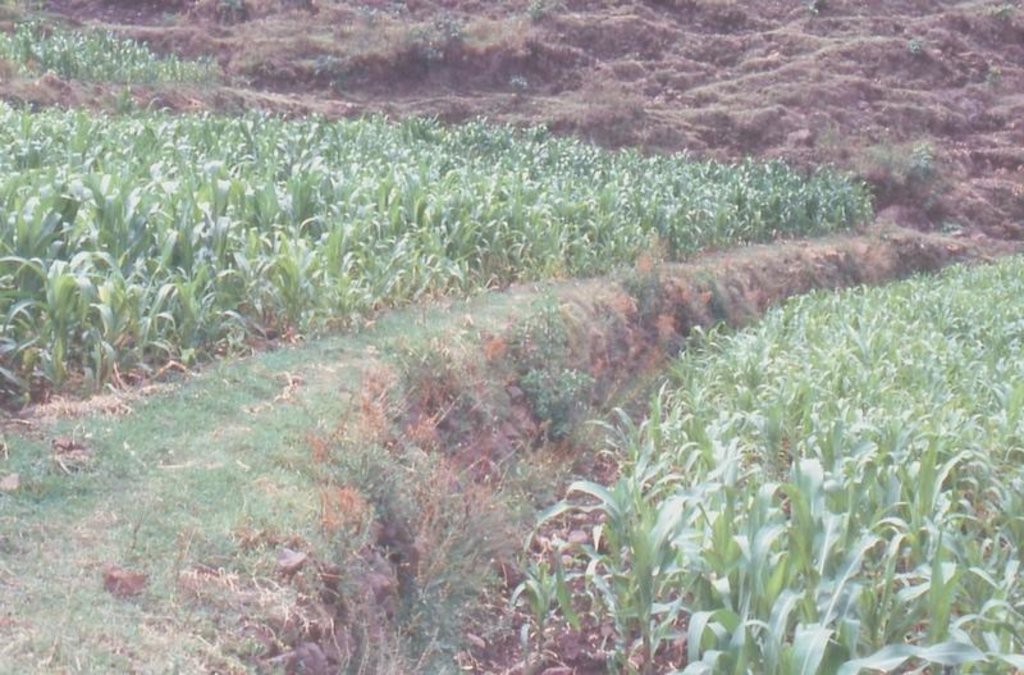
Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - orge
- céréales - maïs
- légumineuses et légumes secs - fèves
- wheat, emmer wheat, teff
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Jul - Nov Second longest growing period in days: 150 Second longest growing period from month to month: Feb - Jun

Pâturages
Type d'animal:
- bétail - laitier
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): erosion, decline of soil fertility and yield decline other major SWC specialist: shortage of grazing land and of forage
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): erosion, runoff, drought, climate
Grazingland comments: area closure: only during July-October some areas are closed, otherwise no area closure any more. Make hay for the cattle to feed them in the dry season.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: barley/wheat/emmer wheat - beans or teff - maize - barley/wheat/emmer wheat - beans or teff - maize
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- Amélioration de la couverture végétale/ du sol
- mesures en travers de la pente
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A3: Traitement de la couche superficielle du sol

pratiques végétales

structures physiques
- S2: Diguettes, digues
Commentaires:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures
Type of agronomic measures: contour tillage
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wo: effets hors-site de la dégradation
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
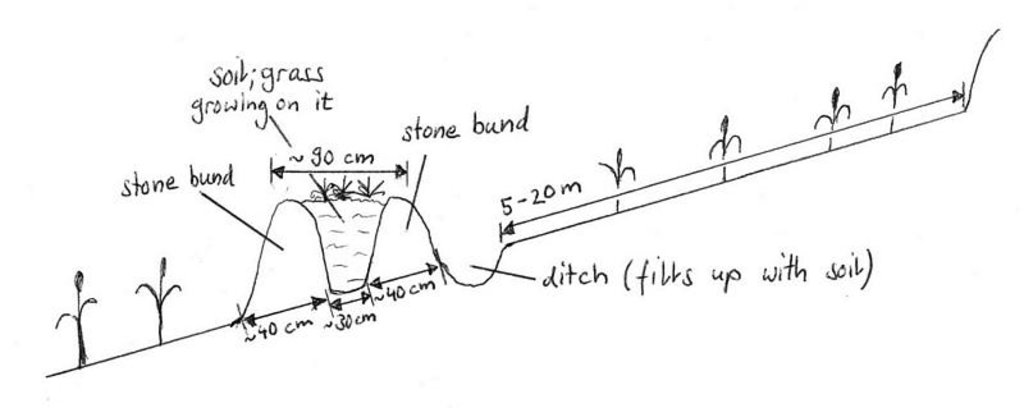
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Drawing showing a level bund with double stone walls, Maybar, Ethiopia
Location: Maybar. Wello
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length
Secondary technical functions: improvement of soil structure, increase in soil fertility
Contour tillage
Remarks: because of the design of the terraces
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 10.00%
Construction material (earth): earth from the ditch just behind the structure on the upper side
Construction material (stone): normal, big stones from the field
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 10%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Auteur:
Sabina Erny, Basel, Switzerland
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
birr
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
8,8
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
0.50
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | it has grown itself on the bund | |
| 2. | measurement of fields, to know where to build the bunds | |
| 3. | constructing the stonewalls | December - January |
| 4. | filling the bunds in between with soils from the ditch behind the structure, on the upper side | December - January, sometimes in November and June |
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | contour ploughing | dry season and rainseason / several times |
| 2. | none, cattle are grazing on it | |
| 3. | observation | December-January/every year after harvesting |
| 4. | rebuilding the structure | December-January/every 1-3 years |
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
the slope: the steeper, the more bunds are needed; labour is a problem if there is no food-for-work any more
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
1067,00
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
Moist dega
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Landforms: Hill slopes (ranked1, mainly steep hills), footslopes and ridges (both ranked 2)
Slopes on average: Hilly (ranked 1), rolling (ranked 2, more than 80% of the land has a slope degree from over 13%) and steep (ranked 3)
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- abondant (>3%)
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average: Very shallow (about 40% of the area) and moderately deep (both ranked 1), shallow and deep (both ranked 2)
Soil texture: Fine/heavy (of the major soil type)
Soil fertility: Medium
Topsoil organic matter: High (ranked 1, in the major soil type) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium (ranked 1) and poor (ranked 2, somtimes there is waterlogging)
Soil water storage capacity: Low (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- riche
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- traction animale
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
10% of the land users are rich and own 38% of the land (only rough estimates).
58% of the land users are average wealthy and own 36% of the land (only rough estimates).
32% of the land users are poor and own 26% of the land (only rough estimates).
Off-farm income specification: farmers employ others for ploughing, so they can go to the market
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (ranked 1, ploughing with oxen) and manual work (ranked 2, hacking)
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
200
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 0-10%
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
200 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: some farmers are building level bund with double stone wallss without any incentives
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Biological soil conservation techniques for Maybar area, Ethiopia. Kassaye Goshu. 1997.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
CDE, Bern
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Classification of the Environment Conditions. H.-J. Krüger. 2003.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
CDE, Bern
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Area of Maybar, Wello, Ethiopia: Long-term Monitoring of the Agricultural Environment 1981-1994
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
CDE, Bern
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
The Use, Maintenance and Development of Soil and Water Conservation Measures by Small-Scale Farming Householfs in Different Agro-Climatic Zones of Northern Shewa and Southern Wello, Ethiopia.Yohannes Gebre Michael. 1999.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
CDE, Bern
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

food-for-work programm [Ethiopie]
food-for-work programm with distribution of grains and oil
- Compilateur : Sabina Erny
Modules
Aucun module trouvé