Water Spreading Weirs [Ethiopie]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : GERBA LETA
- Rédacteurs : Torben Helbig, Noel Templer
- Examinateurs : William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Biye Baahiwe
technologies_6715 - Ethiopie
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
Spécialiste GDT:
Mohamed Badal
Natural Resource Development Protection and Utilization Department of Somali Region Bureau of Agriculture.
Ethiopie
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - Kenya1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
Commentaires:
It is soil and water conservation and degraded land rehabilitation technology. Furthermore, the water harvested can be used for spate irrigation and growing food crops and livestock feed.
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Water Spreading Weirs are designed to protect the degradation of agricultural fields and rangelands. They contribute to soil and water conservation and enhance the productive use of dry valleys for food crops and livestock fodder production via the harvest and spread of runoff water and fertile soils.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
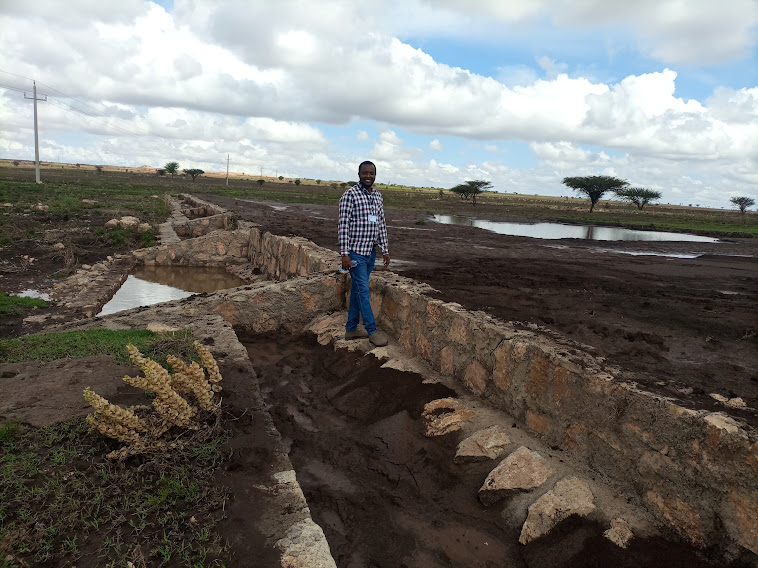
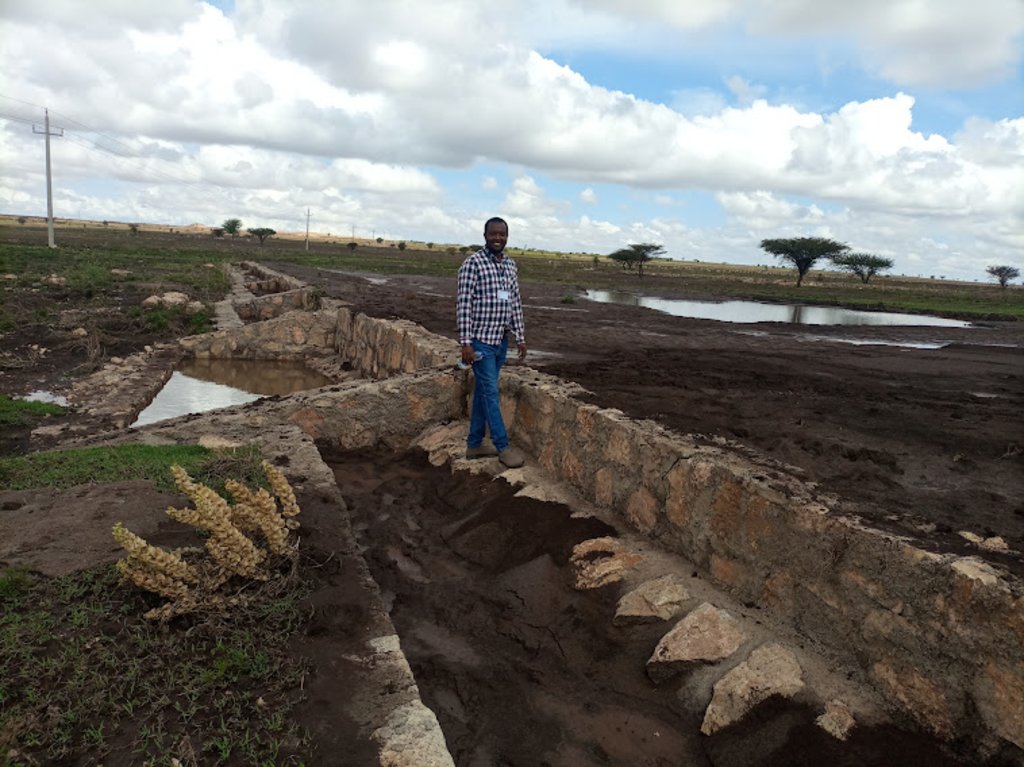
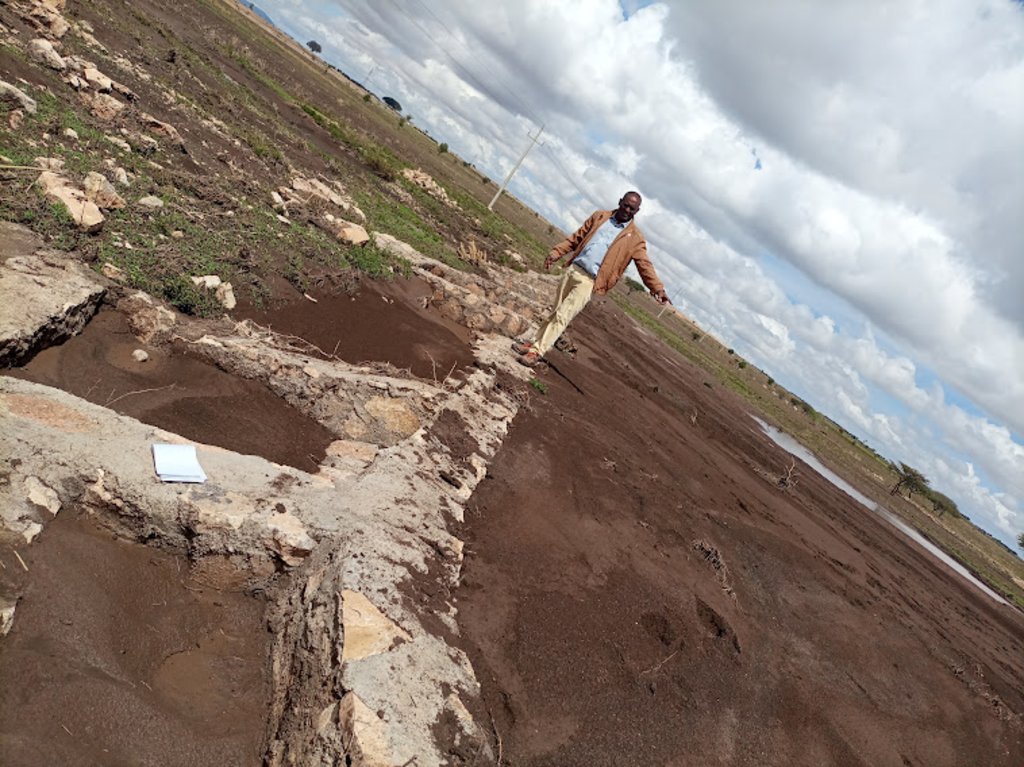
Water Spreading Weirs (WSWs) spread runoff water to the tips of the structure's wings, slowing down the speed of runoff and arresting the sediment pouring downstream. WSWs are applicable both on farmland and rangelands to improve the productive use of the land’s resources. They protect soil erosion and control gully development as well as increasing surface and sub-surface water availability. Activities such as mobilization of the community through awareness creation are among the numerous tasks implemented to put the technology in place. The community participates in site selection and participatory planning. Other stakeholders assist in area delineation, profiling the implementation area, and design. Labour and inputs such as surveying and construction materials, notably stone, sand, water, and cement, and equipment such as line levels, theodolites, spades, hoes, forks, string and measuring tapes etc. are required. On top of these, implementing the technology is supported by satellite images and ground validation exercises.
The main purpose of the technology is to reduce land degradation, harvest and use runoff water for spate irrigation and household uses, improve environmental resilience to the risks of drought, increase the depth and fertility of land behind the structure by capturing sediment washed away, allow infiltration of water and increase overall production of food and fodder crops. Also, the contribution to groundwater recharge is immense. Furthermore, it allows the agropastoral community to grow both cash and food crops which helps to ensure food security. Above all, the water harvested means people can remain in the area and that their livestock have access to drinking water for about three months after interception of rainfall. However, the agropastoralists may be discouraged by the size of the WSWs which can be from one hundred to over two hundred meters across. Care also must be taken that the structures do not cross livestock migration routes.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
Remarques générales concernant les photos:
The photo is trying to portray the water and soil harvested/stopped from running downstream. The detachment and removal of the topsoil without cover and fragile soil types are easily removed and transported to a long distance beyond the regional territory. The trends denied the productive use of land resources. In contradiction, the structure mitigates the loss of water and soil.
2.4 Vidéos de la Technologie
Commentaire, brève description:
Video for this technology was not captured.
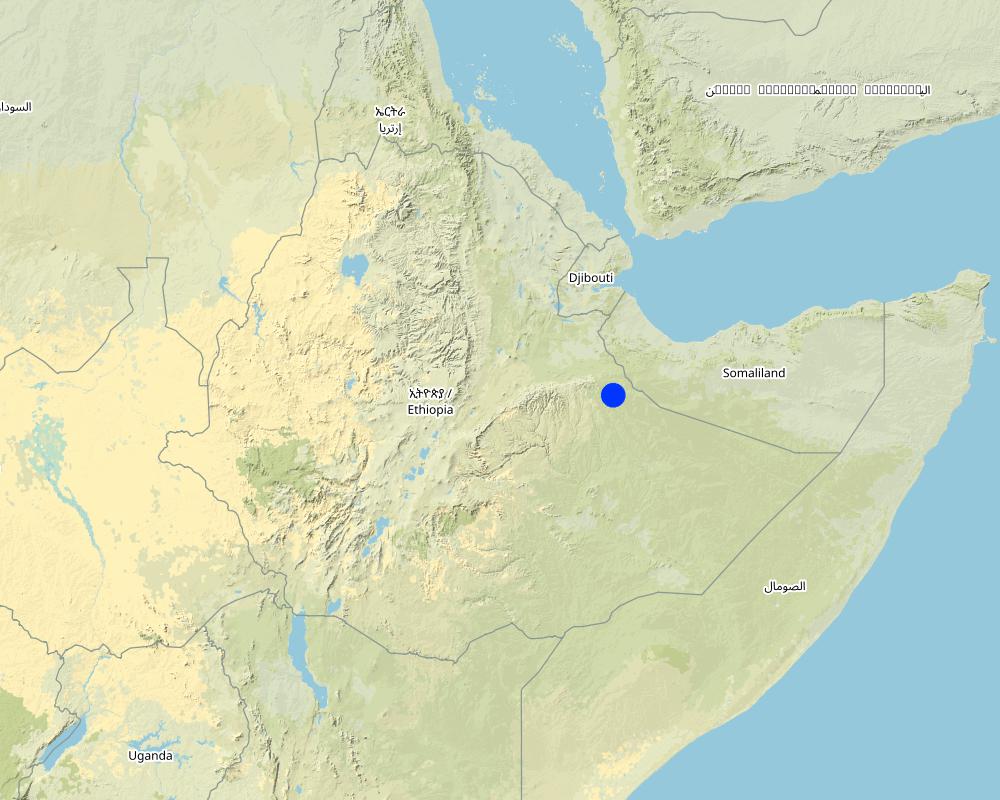
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Ethiopie
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Somali
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Amadle kebele, South Jijiga district
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- appliquée en des points spécifiques ou concentrée sur une petite surface
Est-ce que les sites dans lesquels la Technologie est appliquée sont situés dans des zones protégées en permanence?
Non
Commentaires:
It is located on the farmland used by the extended family and beyond.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
2022
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The technology was put in place in partnership with the government bureau of agriculture and line office with the Capacity Development and Strengthening Drought Resilience (CDSDR) Project of the GIZ in the Somali Region.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- protéger un bassin versant/ des zones situées en aval - en combinaison avec d'autres technologies
- réduire les risques de catastrophes
- créer un impact économique positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agropastoralisme (y compris les systèmes culture-élevage intégrés)

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - maïs
- céréales - sorgho
- légumineuses et légumes secs - soja
- légumes - autres
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
The legume crop is chickpea. Whereas, the vegetables are tomato and onion.
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Oui
Si oui, précisez quelles cultures sont produites en culture intercalaire:
Maize is intercropped with chickpeas.
Est-ce que la rotation des cultures est appliquée?
Oui
Si oui, veuillez préciser:
Cereal crop sorghum rotates with maize and chickpeas. Essentially, crop production suffers from a lack of adequate rainfall. For example, during the last two to three years the area experienced drought. Mainly livestock supports the livelihoods of the inhabitants.

Pâturages
- Agro-pastoralist
Type d'animal:
- chameaux
- cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
- caprine
- ovins
Est-ce que la gestion intégrée cultures-élevage est pratiquée?
Oui
Si oui, veuillez préciser:
Essentially, the farming operation is practiced by oxen-plow in which case the animals provide traction force whereas crop residue supply feed to the animals.
Produits et services:
- manure as fertilizer/ energy production
- viande
- lait
- transports/ traction
Commentaires:
Agro-pastoralism is the common practices in Amadle kebele of south Jijiga district.
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Non (Passez à la question 3.4)
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Commentaires:
The rainfall distribution is erratic with violent erosive feature flooding the plain with severe damage when flowing downstream.
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion intégrée cultures-élevage
- mesures en travers de la pente
- gestion de l'irrigation (incl. l'approvisionnement en eau, le drainage)
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S6: Murs, barrières, palissades, clôtures
Commentaires:
The technology is Water Spreading Weirs, stop the run-off and distribute the water across the farmland.
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines
- Wm: mouvements de masse/ glissements de terrain

érosion éolienne des sols
- Et: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)
- Ed: déflation et déposition
- Eo: effets hors site de la dégradation

dégradation physique des sols
- Pi: imperméabilisation des sols

dégradation hydrique
- Ha: aridification
- Hs: changement de la quantité d’eau de surface
- Hg: changement du niveau des nappes phréatiques (eaux souterraines) et des aquifères
- Hp: baisse de la qualité des eaux de surface
- Hq: baisse de la qualité des eaux souterraines
Commentaires:
The technology/structure contributes strongly to soil and water management. The tremendous loss of both resources is immensely reduced by the application of water spreading weirs.
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
Commentaires:
The technology reduces the speed of runoff, stores the sediments, and distributes the water across the structure which creates an opportunity for spate irrigation and the use of residual moisture as supplemental sources of irrigation for growing early maturing crops.
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
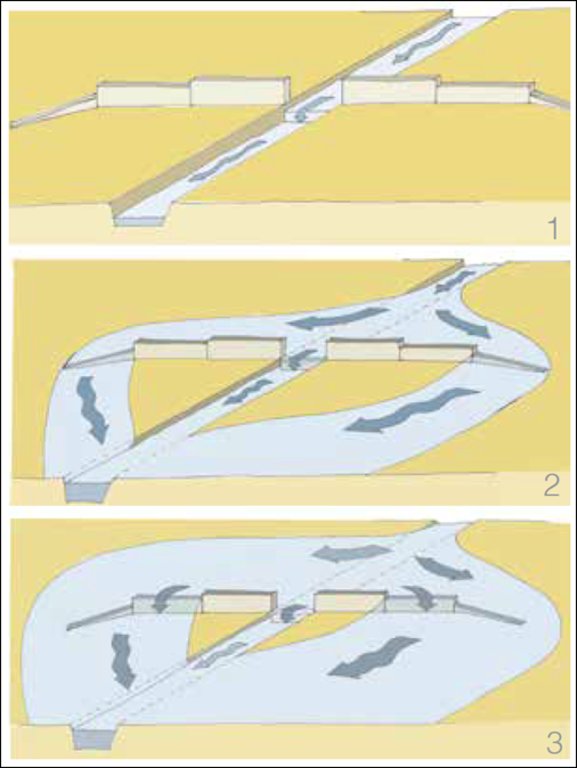
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Spate schemes depending on the increase supply flow:
Part i: The flow of small flood rested channel in the river bed
Part ii: A small or medium flood and overflows pours on the lower wings, &
Part iii: A large flood also pours on high wings.
Auteur:
Anonymous consultant
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par entité de la Technologie
Précisez l'unité:
1 WSW
Précisez les dimensions de l'unité de terrain (le cas échéant):
Variable ( could be from 100m to over 200m depending on the steepness and width of the farmland.
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars américains
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
8.414 USD
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Assessing the field (observation) | |
| 2. | Consult the local community along with agricultural partners at different levels | |
| 3. | Surveying and profile data collection | |
| 4. | Develop design and get approval | |
| 5. | Outsource the engineering/masonry works | |
| 6. | Train the masonry workers | |
| 7. | Supply materials | |
| 8. | Implement (execute the excavation and the masonry work) | |
| 9. | Monitor the development (construction supervision) |
Commentaires:
Note: 1 USD = 53.481 Ethiopian birr (ETB) when this data is collected.
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
Si vous n'êtes pas en mesure de décomposer les coûts dans le tableau précédent, donnez une estimation du coût total de la mise en place de la Technologie:
27490,0
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
So far, the project entirely cover the investment and maintenance costs.
Commentaires:
According to the project and regional bureau of agriculture experts, a single structure costs 27, 490 USD. However, in one cascade (dry valley treatment unit) about 8-10 structures are necessary to successfully address the objective of the technology (Soil and Water Management) and ensure productive use of the land from soil arrest and residue of moisture captured in the area. It also enables the use of runoff for spate irrigation.
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Assess and identify the damage | During the off-season for ease of access to the sites |
| 2. | Estimate the level and cost of damage | During the off-season |
| 3. | Supply materials | |
| 4. | Employ the masonry worker | |
| 5. | Construct /maintain the damaged parts | Before the short/long rainy season. |
Commentaires:
Maintenance costs are largely associated with the degree of damage and cost of materials and masonry worker or labor costs that consistently changing in current Ethiopia.
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Si vous n'êtes pas en mesure de décomposer les coûts dans le tableau précédent, donnez une estimation du coût total de l'entretien de la Technologie:
12154,0
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
The cost is borne by the project.
Commentaires:
The technical experts give only an estimate of both initial investment and maintenance costs. Variations in materials and labor costs are frequent beyond the imagination. However, maintenance depends on the degree of damage. It seems that maintenance cost estimation takes the highest sides which may dishearten the adoption of the technology in the absence of projects.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Economic crisis and frequently escalating material costs along with rising financial inflation.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
750,00
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Rainfall is erratic and erosive. The project site receives rainfall twice a year (Belg- short rain from March to April and Meher- long rain from June to September). However, the number of days on which rain is intercepted is fewer than the ranges stated over here.
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
Jijiga Meteorology station
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
South Jigjiga district is characterized by hot weather.
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- situations concaves
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
The topography where WSW technology/structures are put in place is mostly on gentle slopes across the dry valley drainage line.
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
The soil ranges from black silty loam to brown silty and fragile soils that are highly vulnerable to flood. It easily detached and moved away with runoff.
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
> 50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
faible/ absente
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
faiblement potable (traitement nécessaire)
La qualité de l'eau fait référence à:
eaux souterraines
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Oui
Précisez:
As the weather of the area is often too hot salinity is not uncommon in the aquifer.
La zone est-elle inondée?
Oui
Régularité:
épisodiquement
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Rainfall is characterized by erratic and erosive nature. Therefore, flooding is common when heavy rain is intercepted.
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
Diversité des habitats:
- faible
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
Less biodiversity of plant species. Acacias are the common trees, and opuntia and euphorbia species are also common plants in the area. A wild species that may be considered invasive is common in the area. The lower growing weed (wild species) locally known as Weylowed is suggested introduced from Yemen to the Somali part with onion.
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Semi-nomade
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- traction animale
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
It is the community who are benefiting from the technology. Furthermore, this respondent is a regional SLM specialist. Therefore, specific information on age and gender is not given here though the community was also consulted.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
Extended family groups of four households are using the land where the WSW is put in place.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- communauté/ village
- individu, sans titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- communautaire (organisé)
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
- individuel
Est-ce que les droits d'utilisation des terres sont fondés sur un système juridique traditionnel?
Oui
Précisez:
Land use right is based on clan and extended family.
Commentaires:
The land is also owned by individuals. However, there is no land measurement and certification in this region.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
It is the expert's conviction that crop production in the area increased with water harvest and spread over the farm for use as spate or supplementary irrigation to the seasonal rainfall.
qualité des cultures
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
As the moisture harvested by the structure is believed to add grain filling period, the crop quality is also expected to increase.
production fourragère
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Fodder production also increases with the availability of good soil and moisture conserved in the farm behind the structure.
qualité des fourrages
production animale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increases with increasing availability of feed or fodder from either crop residue, natural grass or browse.
production de bois
risque d'échec de la production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
It rather improves crop resilience because of improved soil moisture.
diversité des produits
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Opportunities can be created to increase the size of land under farming with increasing availability of moisture and fertile soils.
gestion des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Moisture availability eases the management operation.
production d'énergie
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
disponibilité de l'eau potable
qualité de l'eau potable
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Basically, quality is not a priority issue for agro pastoralists in dry valley areas.
disponibilité de l'eau pour l'élevage
qualité de l'eau pour l'élevage
disponibilité de l'eau d'irrigation
qualité de l'eau d'irrigation
demande pour l'eau d'irrigation
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
As the structure reduces the degree of degradation, expense on agricultural inputs is believed to be reduced.
revenus agricoles
diversité des sources de revenus
charge de travail
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
situation sanitaire
droits d'utilisation des terres/ de l'eau
opportunités culturelles
possibilités de loisirs
institutions communautaires
institutions nationales
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
It promotes land users' understanding of SLM through training and exposure to the actual structure and soil and water harvested behind the structure.
apaisement des conflits
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
They may manage to access water for livestock drink and/or household consumption.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
quantité d'eau
qualité de l'eau
récolte/ collecte de l'eau
ruissellement de surface
drainage de l'excès d'eau
nappes phréatiques/ aquifères
évaporation
Sols
humidité du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The structure harvests soil moisture on the farm. It reduces the speed of runoff, stops, and spread over the farm.
couverture du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increased through production of more biomass.
perte en sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The physical barriers stops the soil and water loss.
accumulation de sol
encroûtement/ battance du sol
compaction du sol
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
salinité
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
It is related to a warm climate that triggers evaporation and salinity development in the long run.
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
acidité
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
Couverture végétale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
diversité végétale
espèces étrangères envahissantes
diversité animale
espèces bénéfiques
diversité des habitats
contrôle des animaux nuisibles/ maladies
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
impacts des inondations
glissements de terrains/coulées de débris
impacts de la sécheresse
impacts des cyclones, pluies torrentielles
émissions de carbone et de gaz à effet de serre
vitesse du vent
microclimat
Précisez l'évaluation des impacts sur site (sous forme de mesures):
As the intervention is in its early phase, it is difficult to give an assumption before and after the application of SLM (technology or physical structure). However, a 40 years old woman known as Run Muhamed gave us her insight into the productivity of the land by comparing the hindsight vs the current harvest under highly erratic and erosive rainfall distribution. Accordingly, over the years the harvest per hectare diminished from 0.75 ton/ha to 0.1 ton/ha. This signals the effect of climate change/climate variability and land degradation on crop production. Her household is one of the owners of the land among the other four members of the extended family where the WSW was put in place.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
disponibilité de l'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
As the structure is recently constructed, it is dire to envisage the off-site impacts of the technology at this juncture. However, it has a positive contribution to the availability of groundwater in the adjacent farms.
flux des cours d'eau fiables et stables en saison sèche
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Streams are less common in the dry valley.
inondations en aval
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
It reduces the speed and volume of downstream flooding.
envasement en aval
pollution des rivières/ nappes phréatiques
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Need an investigation of its impact on the groundwater.
capacité tampon/de filtration
sédiments (indésirables) transportés par le vent
dommages sur les champs voisins
dommages sur les infrastructures publiques/ privées
impact des gaz à effet de serre
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Believed to reduce it in the long run.
Précisez l'évaluation des impacts extérieurs (sous forme de mesures):
The intervention believed to improve the existing negative consequences of degradation through promoting soil and water management and reducing risks of crop failure.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | modérément | |
| précipitations annuelles | décroît | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | modérément |
| tempête de sable/ de poussière locale | pas bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | modérément |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| crue éclair | modérément |
Commentaires:
After an extended dry year, like this season, the technology is overloaded with a flash flood. The soil was frequently exposed to the sun and the prevailing heat waves in the area were easily detached by torrential rain. Then the soil and water were partly arrested whereas an immense amount washed away. It seldom could topple the structure if not the cascade comprises eight to ten structures with relatively short intervals to support one another. Furthermore, the dry valley soil is very fragile let alone exposed to a long-term drought that is associated with a heavy shower at the beginning of a short season like this season.
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- cas isolés/ expérimentaux
Commentaires:
It is a technology implemented at the community or extended family level. It is too early to evaluate the adoption trend at this particular time.
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Non
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| The technology/structure reduce soil and water erosion. |
| Harvest water and make the people and livestock beneficiaries from the still water for crop production, drinking, and household uses. |
| Increase soil moisture and risks of crop failure because of shortage of rainfall. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Rehabilitate both degraded agricultural and grazing lands. |
| Improve agropastoralist access to livestock feed and benefit from the positive impact caused by the technology. |
| Eventually, contributes to the improvement of ecology and overall ecosystem functioning. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| High initial investment cost. | Enhance the in-kind contribution of the land users, and increase matching funds from the government as cost-sharing with other projects. |
| Agropastoralist complains about the space it occupies in their farmland regardless of the benefit they accrue over a long period. | Increase the awareness of the community on the productive uses of the degrading land based on the evidence. |
| The structure may fall over the livestock migration/travel routes that are not acknowledged by some members of the community. | During masonry work, precaution is essential to calm down the possible complaints that could emerge because of the raised structure by leveling the crossover roads/paths. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| An inadequate number of structures in a cascade subjected to ineffective soil and water management and distribution of rainwater to support as supplementary sources of moisture for crop production. | Increase the number of structures per conceptual statement and standardize the intervals between the structures. |
| Excessive land users' desire that is unassociated with a tangible contribution to the development of the technology from their side. | Further building land users understanding of SLM technologies and their benefits so that they can build a sense of ownership and accountability to contribute and complement the external efforts. |
| Land users give emphasis mainly on the immediate benefits of the technology (harvesting water for livestock drinking and household use) than the objectives of rehabilitating the dry valley for productive use of it such as crop and livestock feed production. | Acknowledging the immediate benefits, and the mainstreaming work regarding the pillar objectives of the project intervention. |
| The initial investment, as well as maintenance costs, are either expensive or overestimated by local actors. Such a higher cost may discourage land users in the absence of projects or SLM funds. | It would be good to be pragmatic in cost estimation. Furthermore, adapting the technology using local materials may promote the adoption and sustainability of the structure for widespread use. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
Three individuals.
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
One person.
- interviews/ entretiens avec les spécialistes/ experts de GDT
Four individuals.
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
23/03/2023
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Mekdaschi & Linger, 2013. Freie Universitat Berlin
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
https://www.geo.fu-berlin.de/en/v/iwrm/Introduction/Principles/index.html
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes en ligne
Titre/ description:
Water-spreading weirs
URL:
https://www.unccd.int/best-practice/water-spreading-weirs
Titre/ description:
Water Spreading Weir - NATURAL RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
URL:
https://nrmdblog.wordpress.com/2016/12/12/water-spreading-weir/
7.4 Observations d'ordre général
The questionnaire is inclusive and more relevant to evaluate such physical structures as a technology. However, successive drought seasons experienced in the area subject the fragile soil to be easily detached and immensely moved by the early rains past the structure. This may affect the valuation of the efficiency of the technology since dry areas are also characterized by a flash flood that could certainly mask the benefits of such a good technology.
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé