Multilayer Farming Systems For Ensuring Food Diversity And Increasing Resilience [Inde]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Santosh Gupta
- Rédacteurs : Noel Templer, Stephanie Katsir
- Examinateur : Udo Höggel
Mishrit kheti
technologies_6724 - Inde
- Résumé complet en PDF
- Résumé complet en PDF pour impression
- Résumé complet dans le navigateur
- Résumé complet (non formaté)
- Multilayer Farming Systems For Ensuring Food Diversity And Increasing Resilience: 5 octobre 2023 (inactive)
- Multilayer Farming Systems For Ensuring Food Diversity And Increasing Resilience: 20 novembre 2023 (inactive)
- Systèmes agricoles multicouches pour garantir la diversité alimentaire et accroître la résilience: 17 avril 2024 (public)
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - KenyaNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Ecociate Consultants (Ecociate Consultants) - Inde1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
Commentaires:
Multilayer farming is a farming practice that involves cultivating a mix of vegetables and fruits on a small piece of land. Additionally, by growing a variety of crops together, multilayer farming can increase yields and provide a more diverse range of foods for households.
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Multilayer farming, also known as multi-tier farming, is a technique of intercropping crops of different heights, root and shoot patterns, and maturation times in small plots of land. This technique is cost-effective, easily adaptive, and participatory, providing a large number of food groups to farmers to improve their nutritional levels, providing insurance against crop failure, reducing pest and disease incidence, and improving soil properties and soil fertility conditions. Multilayer farming minimizes crop-weed competition, and soil erosion, and optimizes resource utilization resulting in higher returns and better nutritional value. It promotes sustainable agriculture, maintains a balanced diet, increases income per unit area, and reduces the risk of crop failure.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
Multilayer farming is an agricultural model that aims at achieving maximum production per unit area by utilizing water, manure, and land resources to their full potential. This method is based on the synergies between the different crops and plants planted on a given piece of land. This method is cost-effective and yields more benefits than other farming systems. By cultivating four to five crops with the same amount of fertilizer and water required for a single crop, farmers can increase their income, and multiple crops can be harvested yearly using the same piece of land.
Multilayer farming is based on scientific, ecological, and economic principles, promoting crop diversification, maximizing productivity, utilizing resources more efficiently, and promoting intensive input use. Moreover, it ensures the sustainability of farm resources and the environment in the long term.
The multilayer farming system mainly consists of an overstory of trees or shrubs with an understory of economic or forage crops. By incorporating these principles, farmers can achieve greater yields and financial success while promoting environmental sustainability.
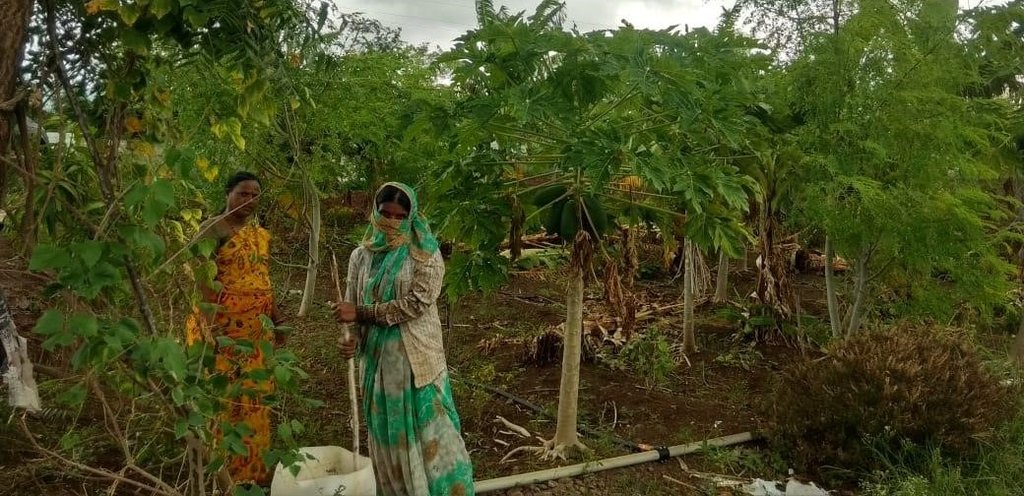
As a part of the program's approach, WOTR (Watershed Organisation Trust, the project implementing partner trained women change-makers) to spread awareness among villagers about the importance of nutrition and a healthy diet. Since 2018, the active promotion of multilayer farming to address food and nutrition insecurity in Maharashtra is undertaken. As a result, 1124 plots across 150 villages in Maharashtra have adopted this unique farming method to enhance food and nutrition security.
The multilayer farming system involves several steps to ensure maximum productivity from the available resources.
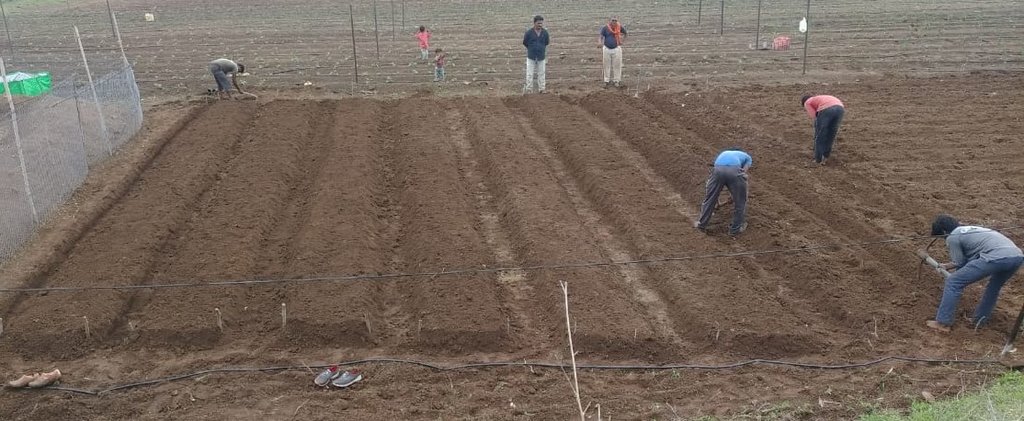
1.The first step is land preparation, which involves applying 300 kg of cow dung or vermicompost along with one kg of Trichoderma powder per 36 x 36 feet plot. Trichoderma is a bio-fungicide that helps to prevent fungal infections in plants and roots.
2.Next, eight beds of 3 x 36 feet are prepared with 1.5 to 2 feet of space left in between. These beds need to be arranged in the North-South direction to ensure that plants receive adequate sunlight.
3.After preparing the bed, 1-foot deep channels are dug to drain excess water so ensuring that the crops are not waterlogged.
4.Finally, in the middle of each bed, vegetable and fruit crops are planted according to a crop planning chart. By planting a variety of crops in the same plot, the multilayer farming system ensures the effective utilization of resources and provides an even distribution of income and employment throughout the year by producing several off-season crops.
The multilayer farming system has numerous benefits that make it an effective and sustainable farming method. It makes effective use of soil, water, and other resources, reducing waste and increasing productivity. Additionally the system reduces climate-specific damage and enhances soil health, helping to maintain an ecological balance in the environment. The soil covered minimizes water loss due to soil evaporation, generating a higher income per unit area with an even distribution of income and employment throughout the year. The multilayer farming system generates jobs and allows for better utilization of labor while reducing the impacts of climate-specific hazards such as high-intensity rainfall, soil erosion, and landslides. Multilayer farming also utilizes soil moisture at different depths and solar energy at different heights, improving soil characteristics and adding organic matter to the soil. It reduces pests and disease infestation and provides micro-climate conditions which ensure better productivity of crops underneath. Overall, multilayer farming is a sustainable and efficient farming method that not only maximizes productivity but also enhances soil and environmental health while promoting economic and social well-being.
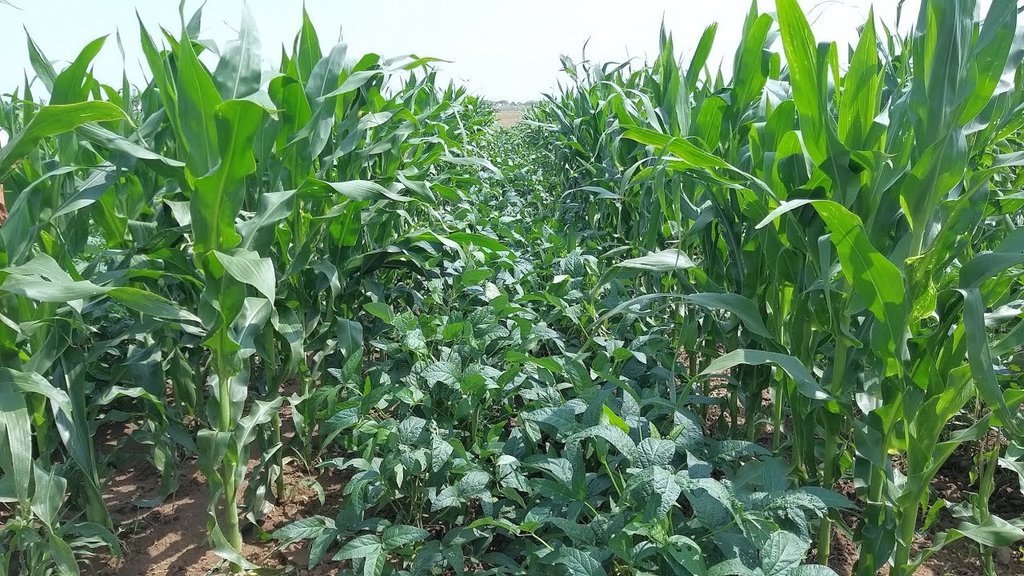
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
Remarques générales concernant les photos:
The images provide a visual representation of the essential steps followed by farmers to establish a successful multilayer farming system. These steps include land preparation, bed preparation, and planting a variety of crops in the same plot. The dates mentioned here are the dates of collection of these photos from the project implementing team as the photos were taken by different team members at different times.
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Inde
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Maharashtra
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Ahmednagar
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- appliquée en des points spécifiques ou concentrée sur une petite surface
Est-ce que les sites dans lesquels la Technologie est appliquée sont situés dans des zones protégées en permanence?
Non
Commentaires:
In Maharastra State, there are different districts where multilayer farming plots are established such as Ahmednagar, Satara, and Dhule
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
2018
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- au cours d'expérimentations / de recherches
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The intervention is a result of experiments and research by WOTR and other agencies at different project locations
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- s'adapter au changement et aux extrêmes climatiques et à leurs impacts
- créer un impact économique positif
- créer un impact social positif
- Ensure nutritional security
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Non

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - sorgho
- céréales - blé d'hiver
- Sugarcane, Horticulture crops like Pomegranate, Guava, Mango etc, Onion, pulses
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
In places where irrigation source is availbe the growing seasons vary between 2 to 3
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Oui
Est-ce que la rotation des cultures est appliquée?
Oui
Si oui, veuillez préciser:
In places where irrigation is available, farmers grow Kharif crops (summer crops) followed by Rabi crops (winter crops).
Commentaires:
The majority of farmers in various regions tend to practice mono-cropping due to rainfall variability and less rainfall in the region. However, in places where an irrigation source is available, farmers tend to grow second crops in the Rabi season or go for horticulture crops such as fruits and vegetables.
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Oui (Veuillez remplir les questions ci-après au regard de l’utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie)
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agroforesterie

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
- Horticulture Crops
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- cultures florales
- légumes - autres
- drumstick, marigold, radish, dolichos beans, coriander, spinach, fenugreek, dill, okra, brinjal, tomato, red pumpkin, maize, cowpea, castor, ridge gourd
Plantations d'arbres et d'arbustes - Précisez les cultures:
- manguier, mangostane, goyave
- papaye
- Sapota
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Oui
Si oui, précisez quelles cultures sont produites en culture intercalaire:
In multi-cropping systems, fruits and vegetables are planted in a systematically planned manner using crop planning charts. This approach ensures that the growth of plants complements each other, providing adequate nutrition for the family throughout the year.
Est-ce que la rotation des cultures est appliquée?
Oui
Si oui, veuillez préciser:
The combination of vegetables is selected based on the suitability to climate conditions as tomatoes are grown during the winter season, beans during the summer seasons etc.
Commentaires:
The land was mostly converted from mono-cropping systems to a multi-cropping system
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
Commentaires:
Multi-cropping systems involve covering the soil with crops throughout the year, which helps to reduce evaporation losses. In addition, irrigation is provided using drip or sprinkler systems to minimize water losses. This approach not only conserves water but also helps to maintain soil moisture levels, leading to higher yields and improved plant health. By adopting these practices, farmers can improve the sustainability and resilience of their agricultural systems.
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- Amélioration de la couverture végétale/ du sol
- gestion de l'irrigation (incl. l'approvisionnement en eau, le drainage)
- Jardins/ potagers familiaux
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A1: Couverture végétale/ du sol
- A2: Matière organique/ fertilité du sol
- A5: Gestion des semences, amélioration des variétés

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes

modes de gestion
- M1: Changement du type d’utilisation des terres
- M4: Changement majeur dans le calendrier des activités
Commentaires:
1. Effective utilization of natural resources
2. Reduces climate-specific damage & enhances soil health and reduces water loss due to evaporation from the soil
3. The income per unit area increases substantially with this system and multilayer farming ensures the yield of some crops throughout the year
4. Utilizes the soil moisture well at different depths of soil and effectively utilizes solar energy at different heights
5. Improve the soil characteristics and adds organic matter to the soil
6. Provides a partial guarantee against the market glut of a single commodity and the efficient cultivation of a range of products is possible
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation physique des sols
- Ps: affaissement des sols organiques, tassement des sols

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
- Bq: baisse de la quantité/ biomasse
- Bs: baisse de la qualité et de la composition/ diversité des espèces
- Bp: augmentation des insectes nuisibles (ravageurs)/ maladies, baisse des prédateurs
Commentaires:
Multilayer farming covers the soil throughout the year with crops, fruits, and vegetables. The micro-climate enables diversified crops to grow together and provide nutrition to the family through out the year. The year around soil cover reduces soil erosion by wind and flood.
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Multilayer farming improves soil fertility by improving the microbial activities in the soil as the ecosystem of different root zones, plants and organic matter coupled with organic inputs creates a healthy plant environment
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par superficie de la Technologie
Indiquez la taille et l'unité de surface:
1
Si vous utilisez une unité de superficie locale, indiquez le facteur de conversion vers un hectare (p.ex. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha = :
ha
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
INR
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
80,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
200
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land Preperation | June |
| 2. | Preperation of beds for seed sowing | June |
| 3. | Sowing of seeds for fruits | Early June |
| 4. | Fencing of the field | Before the sowing |
Commentaires:
Farmers can use local resources such as Bamboo or other crop residues for fencing purposes as well. Land needs to be prepared before the onset of monsoon (during the summer season). Once a multilayer plot is established there is no need to prepare the land as well.
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Land preparation | person days | 2,0 | 200,0 | 400,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Preperation of beds for sowing | Person days | 3,0 | 200,0 | 600,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Fencing material | Lumpsum | 1,0 | 5000,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds for fruit trees (seeds and planting material) | Plant | 100,0 | 50,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Fram yard manure | Tons | 10,0 | 600,0 | 6000,0 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Miscellaneous | 1,0 | 2000,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 19000,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 237,5 | |||||
Commentaires:
Costs towards labour, farm yard manure and sometimes seeds are internally arranged by the land users thus there may not be any cost to pay.
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Sowing of seeds | June-July/October-November/April/March/April |
| 2. | Application of organic manures | Across the year at critical growth stages |
| 3. | Irrigation | Across the year at critical growth stages |
| 4. | Bio-inputs | Based on the plant needs |
| 5. | Harvesting of leafy vegetables, fruits, fodder and other produces | Multiple plucking during the year |
| 6. | Sales of farm produces | Multiple times during the year |
Commentaires:
Maintenance activities vary farmers to farmers depending upon the kind of fruits and vegetables planted, availability of resources and land area under cultivation
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Sowing of seeds | Person days | 8,0 | 200,0 | 1600,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Application of FYM and other inputs | Person days | 5,0 | 200,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Maintenance and monitoring of the field | Person days | 50,0 | 100,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Harvesting | Person days | 20,0 | 200,0 | 4000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds and planting material | Kg | 0,25 | 1000,0 | 250,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Farm yard manure and other inputs | Tons | 5,0 | 750,0 | 3750,0 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Other cost | Lumpsum | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 16600,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 207,5 | |||||
Commentaires:
These farms are mostly managed by the farmers themselves without hiring any additional labour. Thus, labour cost is not something farmers need to pay for.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
1. Availability of family labour to manage the field operations
2. Availability of dairy animals at the household level to meet the FYM needs
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
561,00
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Deccan Plateau, Hot Semi-Arid Eco-Region as per the ICAR classification of Ecological Zone
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
https://krishi.icar.gov.in/jspui/bitstream/123456789/30264/1/MH14.pdf
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Length of growing period: less than 90 days
Rainy days: 44
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Physiographically the district can be broadly divided in four major characteristic landforms viz., hill and ghat section (7.6% area); foothill zone (19.4% area); plateau (3.71% area) and plains (occupy 69.30% area). The intervention has been implemented in different villages of the district.
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
The soil types of the district are broadly divided into four categories namely coarse shallow soil; medium black soil; deep black soil and reddish soil occupying about 38, 41, 13 and 8 percent of the cultivated area respectively. In the first two categories, soil moisture is the predominant limiting factor affecting productivity of crops particularly under rainfed condition. (source-http://www.kvk.pravara.com/pages/District%20Profile/District%20Profile.htm)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
> 50 m
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
La qualité de l'eau fait référence à:
à la fois les eaux souterraines et de surface
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Non
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
On an average 26.3 per cent of the cultivated area is under irrigation, out of which 71.5 per cent is under well irrigation (including lift irrigation) and remaining area is under canal irrigation. (http://www.kvk.pravara.com/pages/District%20Profile/District%20Profile.htm)
The overall stage of ground water development for the district is quite high i.e., 79.8%. Further ground water development is not recommended without adhering to the precautionary measures i.e., artificial recharge to augment the ground water resources and adoption of ground water management practices. Ground water quality in the wells
monitored by the concerned authorities in the district is affected because of high NO3 concentrations. (http://cgwb.gov.in/District_Profile/Maharashtra/Ahmadnagar.pdf)
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
Diversité des habitats:
- faible
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
The majority of the area is under farming. Mono cropping is the generally practiced by farmers.
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
- groupe/ communauté
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- jeunes
- personnes d'âge moyen
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Most land users covered during the project are small and marginal farmers with land up to 2 ha. The focus has been on women farmers to ensure the self-consumption of diverse food groups harvested from the multi-layer plots. The land users belong to a heterogeneous group of individuals coming from different social backgrounds and caste segments.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
Nearly 61% of farmers fall into the category of landholding less than 1 hectare. (https://mahades.maharashtra.gov.in/files/publication/dsa_ahmednagar_2014.pdf)
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- accès libre (non organisé)
Est-ce que les droits d'utilisation des terres sont fondés sur un système juridique traditionnel?
Non
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
Commentaires:
The district is one among the progressive districts of Maharashtra and is well connected with a good network of roads and railways.
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Round the year farm, produce of vegetables and fruits is available from multilayer fields. The data is based on the observation of land users, there has not been any study to assess possible qualitative improvements
diversité des produits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Farmers grow multilayer crops in smaller land sizes thus increasing the diversity of the products and the nutrition quality at the household level
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Efficient use of land by growing Multilayer Farming led to efficient utilization of the small farm plots
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
disponibilité de l'eau d'irrigation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The use of micro irrigation led to a more efficient use of the same quantity of water allowing for the irrigation of land for a longer duration
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Organic inputs such as cow dung, cow urine, etc were used. This reduced the cost of the inputs.
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Income from farms increased as farm yields increased. Excess produce of vegetables and fruits is sold in the market.
diversité des sources de revenus
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
As the farmers shift from mono-crop to multilayer cropping. This reduces the risk of crop failure faced by mono-crop farmers.
Autres impacts socio-économiques
Intake of Nutritional Food
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Intake of nutritional food increased as the availability of fruits and vegetables no longer depended exclusively on markets
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
situation sanitaire
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Nutritional food available for consumption
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
évaporation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Crop cover for a longer duration over the soil, reducing evaporation losses
Sols
humidité du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Use of organic practices and covering the soil with crop and dry crop litter for a longer duration increased the soil moisture retention capacity
couverture du sol
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Bio-inputs and dry crop litter added to the soil increased the soil organic matter
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
diversité végétale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Crop diversity: vegetables and fruit crops are grown
contrôle des animaux nuisibles/ maladies
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
As multiple crops are grown, pest and disease infestation is reduced
Précisez l'évaluation des impacts sur site (sous forme de mesures):
The impact areas indicated in the document are based on the experience and observations of the land users and field-level workers of implementing agencies. There has not been any scientific study to measure the quantitative impact of the intervention.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Commentaires:
The micro-climate of the multilayered farm is maintained, enabling the crops to grow well
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- 1-10%
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 91-100%
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Oui
Si oui, indiquez à quel changement la Technologie s'est adaptée:
- évolution des marchés
Spécifiez l'adaptation de la Technologie (conception, matériaux/ espèces, etc.):
The Vegetable and fruits crops are modified based on the Household requirement
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Diversified vegetables and fruits available for household consumption |
| Increase in household income, as the excess produce is sold in the market and also reduced dependency on markets to purchase fruits and vegetables |
| Small farm plot (1300 sq. ft) is utilized under multilayer farming, remaining farmland is available for cereal, etc |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Water use efficiency because of the use of micro irrigation and reduction of evaporation as the crops and dry matter cover the soil |
| A good micro-climate of the multilayer farm plot is maintained |
| Availability of a good range of food groups to farmers may lead to improvement in nutritional parameters especially for women and children |
| Improved soil health due to mixed cropping system and enhancement soil microbial activities |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Labor engagement throughout the year | Mechanization suitable for small farm plots |
| Availability of farm yard manure to ensure cultivation following natural farming practices | Promotion of animal husbandry (dairy) in convergence with the government departments |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The produce from multilayer farming is diversified and comes in small quantities. Therefore the selling of these small quantities of produce is done in the local market. | Creation of farmers' collectives for selling larger amounts of produce in the market |
| Availability of irrigation is important to ensure the sustainability of intervention | Some water based enterprises can be developed to support the farmers not have irrigation facilities |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
5
- compilation à partir de rapports et d'autres documents existants
4
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
09/04/2023
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes en ligne
Titre/ description:
How is multilayer farming done?
URL:
https://wotr.org/2020/07/18/how-multilayer-farming-is-done/
Titre/ description:
Enhancing Household Food and Nutrition Security With Multilayer Farming
URL:
https://www.csrmandate.org/enhancing-household-food-and-nutrition-security-with-multilayer-farming/
Titre/ description:
Kitchen Garden, Multilayer Farming Boost Food Security in Maharashtra
URL:
https://wotr.org/2020/05/07/kitchen-garden-multilayer-farming-boost-food-security-in-maharashtra-2/
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé