Sorghum Terrace of Diredawa (STD) [Ethiopie]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Daniel Danano
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Daga (Oromifa)
technologies_1067 - Ethiopie
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Aberra Wondwosen
Dire Dawa Agricultural and Rural Development Office
Ethiopie
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - ItalieNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development of Ethiopia (Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development) - Ethiopie1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
It is a structural measure constructed across the slope to control erosion and increase soil moisture.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
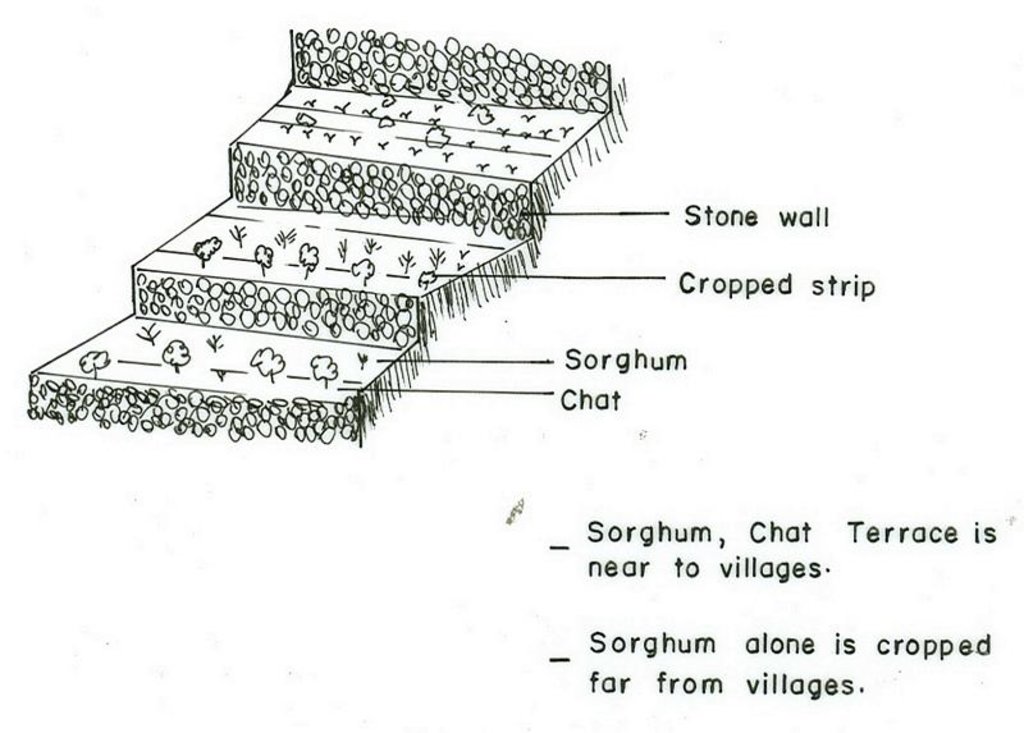
Sorghum terrace of Diredawa locally called as Daga is constructed by placing stone walls across a slope following contour lines. The development of Sorghum terrace involves activities of creating an embankment at a given spacing, which depends on slope. Cultivation in the terrace is done by the use of Dengora (local name for spade like hand tool) if the land is sloping and by oxen if land slope is gentle (<8%). The purpose of developing Sorghum Terrace of Diredawa (STD) is to collect as much rainwater as possible for growing sorghum, which is planted by broad casting. Sorghum is the staple food in the area. Since rainfall is erratic, the STD allows more water to be stored in the soil. STD is maintained every year and also upgraded while performing different farm activities (Ploughing, Weeding, etc.,). Every time maintenance is made breaks in the terrace are repaired and additional height given to the terrace until it forms bench. STD is very suitable to areas with erratic rainfalls, sloping cultivated fields and land having abandant stones for construction. It is suitable to areas with semi-arid to arid climatic conditions and soils ranging from shallow depth to moderately deep.
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Ethiopie
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Dire Dawa
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Dire Dawa
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- 100-1 000 km2
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a plus de 50 ans (technologie traditionnelle)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agro-sylvo-pastoralisme

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - sorgho
- légumineuses et légumes secs - fèves
- plantes à racines et à tubercules - pommes de terre
- chat
Plantations d'arbres et d'arbustes - Précisez les cultures:
- manguier, mangostane, goyave
- papaye
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 180 Longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Oct
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Oui
Si oui, précisez quelles cultures sont produites en culture intercalaire:
Sorghum + Potato

Pâturages
Pâturage extensif:
- Pastoralisme de type semi-nomade
Pâturage intensif/ production fourragère :
- Affouragement en vert/ zéro-pâturage
Type d'animal:
- caprine
Espèces:
caprine
Nombre:
2

Forêts/ bois
Produits et services:
- Bois d'œuvre (de construction)
- Bois de chauffage
- Pâturage/ broutage
- fodder
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The major land use problems in the areas with out SWC are overgrazing/overbrowsing by livestock specially by the small stock. Goats over browse shrubs in hill slope letting it to be bare and hence enhance erosion. Cutting of trees/shrub for fire wood denudes hillsides.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Declining status of the vegetative cover led to lack of wood for construction and fire wood.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Yes
Grazingland comments: A substantial area has been closed around the technology area. Livestock owners are given the opportunity to cut grass from enclosures and carry it home to stall feed the animals. Most farmers like to stallfeed their animals. Number of livestock in the area is small and is limited to 1 or 2 of large stock and 2-3 of small stocks.
Problems / comments regarding forest use: Individual households plant agroforestry trees (fruits, shade trees, hedgerows) in the homestreads and on field boundaries. Trees naturally grown are maintained in scattered manner in crop fields. These are primarily used as shelter for animals that are tethered and also used as fodder and fuelwood.
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, grazing / browsing
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Sorghum-beans
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Oui (Veuillez remplir les questions ci-après au regard de l’utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie)
Commentaires:
from grazing to cultivated land
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Commentaires:
Water supply: Also post-flooding
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- Amélioration de la couverture végétale/ du sol
- mesures en travers de la pente
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A2: Matière organique/ fertilité du sol
- A3: Traitement de la couche superficielle du sol
Commentaires:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures
Type of agronomic measures: early planting, mixed cropping / intercropping, contour planting / strip cropping, mulching, green manure, manure / compost / residues, contour tillage
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
Commentaires:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
DireDawa
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: reduction of slope angle, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Early planting
Material/ species: Sorghum + Chat
Quantity/ density: 17500 +400
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Sorghum + Potato
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: Sorghum + Chat
Mulching
Material/ species: Sorghu Stalk/residue
Green manure
Material/ species: Sorghum/Chat-beans
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Sorghum/Chat
Contour tillage
Remarks: Ploughing along the contour
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: O : other
Number of plants per (ha): 17500-2000
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.2
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.2-0.3
Perennial crops species: Chat
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 10.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 3.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.00%
Terrace: backward sloping
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1-2
Spacing between structures (m): 4-6
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5-2
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50-300
Bund/ bank: level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1-2
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3-0.5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50-300
Construction material (earth): earth is placed upslope of the stone wall to provide reinforcement
Construction material (stone): stone is used for the embankment
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 12%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 4%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: from grazing to cultivated land
Control / change of species composition: from mono-cropping to mixed cropping
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Birr
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
8,6
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
0.71
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Chat planting by cutting | early rains |
| 2. | Sorghum planting | early rains |
| 3. | Sowing | with rains & withdrawal of rains |
| 4. | Contour marking & layout | dry period/after harvest |
| 5. | Digging foundation | after light rains/moist soil |
| 6. | Stone collection | dry season |
| 7. | Stone wall placement | after light rains/moist soil |
| 8. | Earth support upslope | after light rains/moist soil |
| 9. | Clear vegetation | dry period |
| 10. | Construct Daga | dry season |
| 11. | Land preparation | after the 1st rains |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 272,0 | 272,0 | 50,0 |
| Equipements | Animal traction | ha | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Compost manure | ha | 1,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 301,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 35,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tillage | dry season / 2-3 |
| 2. | Sowing | dry season / each cropping season |
| 3. | Cultivation | early rains, after sawing, before flowering / each cropping season |
| 4. | Weeding | after flowrinf / each cropping season |
| 5. | Harvest | dry season, after crop matures / each cropping season |
| 6. | Cultivation | during rains /2 |
| 7. | Weeding | withdrawal of rains /1 |
| 8. | Stone collection | dry season/1 |
| 9. | Repairing breaks | before planting/1 |
| 10. | Add stone wall height/upgrading | before planting/1 |
| 11. | Plant stablizing/ trees/shrubs | after rains/1 |
| 12. | Planting of useful trees & fruit trees | after rains / annual |
| 13. | Cultivation and weeding | during rains / 2 |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 40,7 | 40,7 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 40,7 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 4,73 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: hand tools for digging earth and breaking stone
The cost is mainly for construction and maintenance of the structural measures and cost of production.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Slope:- As the slope increases cost of construction increases, Soil depth:- when the soil depth is shallow digging the foundation becomes more costly.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
600,00
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Landforms: Also hill slopes (ranked 2) and valley floors (ranked 3)
Slopes on average: Also hilly (ranked 2) and moderate as well as gentle (both ranked 3)
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility is low (ranked 1), medium (ranked 2) and very low (ranked 3)
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is low (ranked 1), medium (ranked 2) and very low (ranked 3)
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- traction animale
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
40% of the land users are average wealthy and own 60% of the land.
60% of the land users are poor and own 40% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Land users who have SWC on their land spend more time in agricultural activities compared to those who have not applied SWC measures.
Level of mechanization: Manual work (ranked 1, on steeper slopes where terraces are closer manual labour is used) and animal traction (ranked 2, on gentle slopes animal traction is used for tillage and cultivation)
Market orientation of cropland production system: Subsistence ( They do not produce enough for their own consumption in case of sorghum/cereal crops but chat is produced more for market, ranked 1) and mixed (ranked 2)
Market orientation of forest production system: Subsistence (Chat is planted for consumption as well as market, ranked 1) and mixed (Farmers sell part of the grain they have produced)
Market orientation of production system: mixed (subsistence and commercial) (Farmers sell part of the grain they have produced.)
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Commentaires:
Most of the open access grazing land and degraded hills where animal graze is communal land.
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Because of high moisture in the soil
production fourragère
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
multipurpose tree species with good production potential are planted.
qualité des fourrages
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
multipurpose tree species with good production potential are planted.
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
due to structures occupying land
gestion des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
due to structural obstraction
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Impacts socioculturels
institutions communautaires
institutions nationales
apaisement des conflits
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Quantité avant la GDT:
50
Quantité après la GDT:
0
Sols
humidité du sol
perte en sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
100
Quantité après la GDT:
5
Autres impacts écologiques
Soil fertility
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
inondations en aval
envasement en aval
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
légèrement positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 11-50%
Commentaires:
30% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Production increased How can they be sustained / enhanced? external support with incentives such as tools, material for constructing structures for flood and runoff diversion. |
|
more soil moisture How can they be sustained / enhanced? integration of measures that reduces evapotranspiration |
|
Soil erosion controlled How can they be sustained / enhanced? exercise effective maintenance |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
have higher efficiency for retaining water in the soil How can they be sustained / enhanced? Strengthening maintenance, avoid livestock,exercise stall feeding, enhancing runoff and flood farming |
| mantenance is simple because material is available |
| Forms bench terrace easily |
| Soil loss is remarkably reduced |
| Production doubled and even increased by 150-200% |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| hindering movement | provide path way for humans and oxen during farm operation |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé