Banana manure pits and mulching [Rwanda]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Desire Kagabo
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Gusasira no gutera urutoki mu myobo irimo ifumbire mborera
technologies_1160 - Rwanda
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Spécialiste GDT:
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Rwanda Agriculture Board (Rwanda Agriculture Board) - RwandaNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - Italie1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
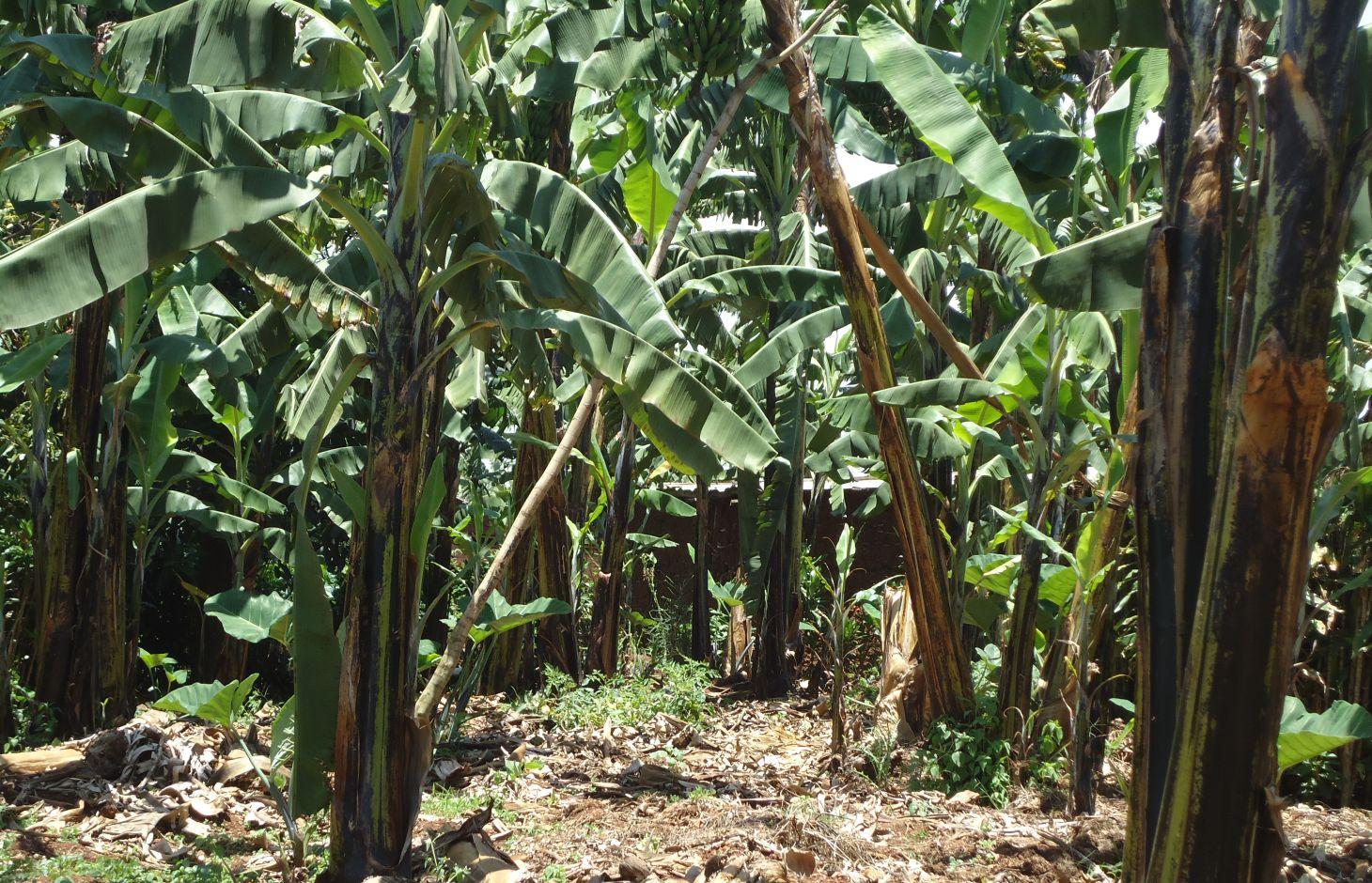
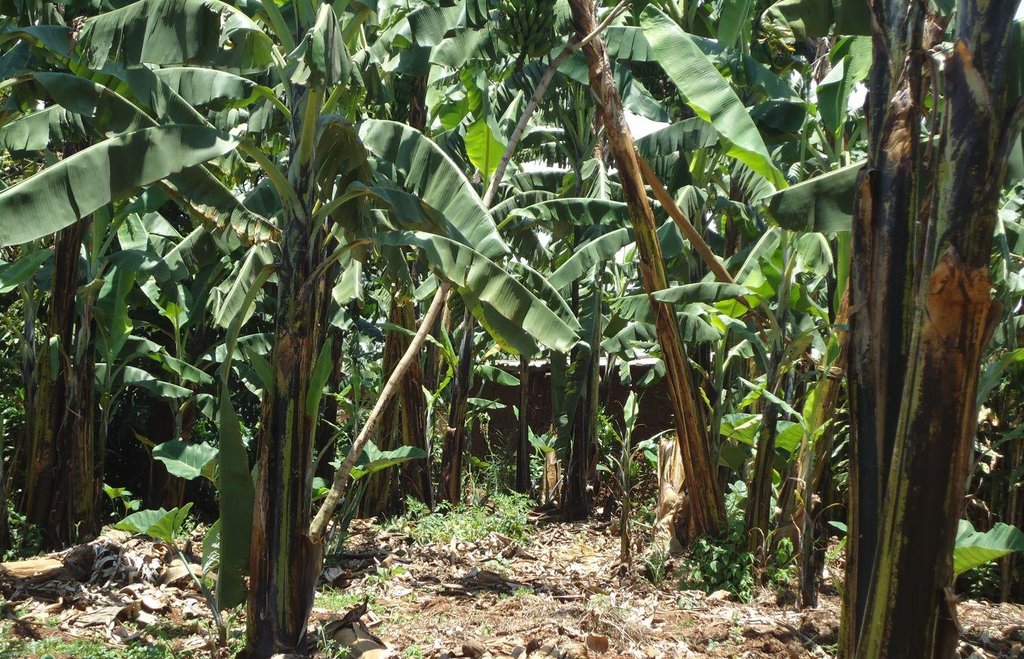
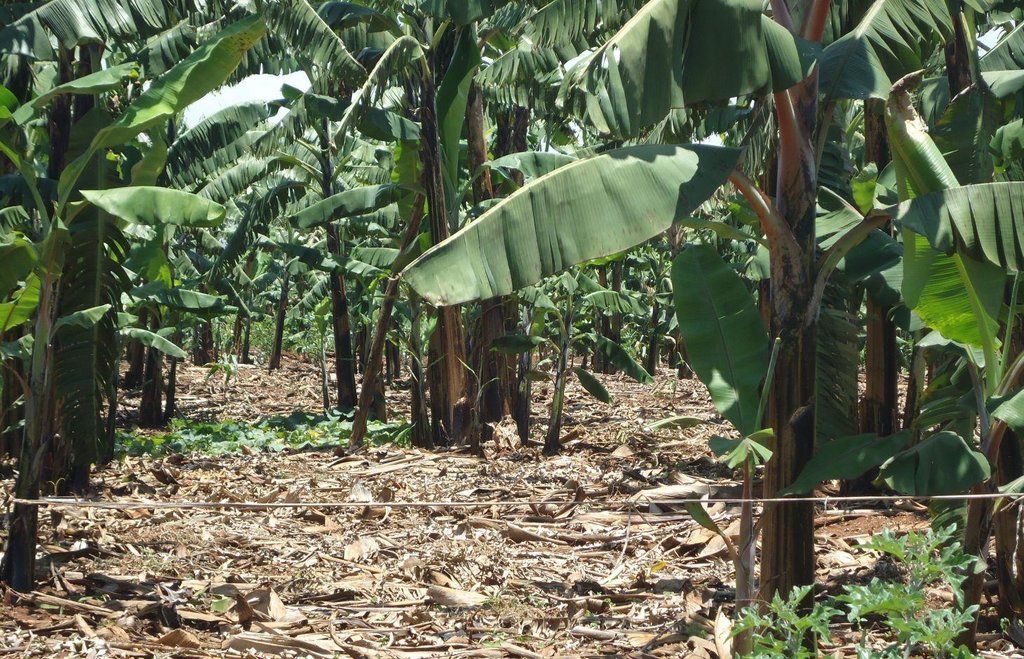
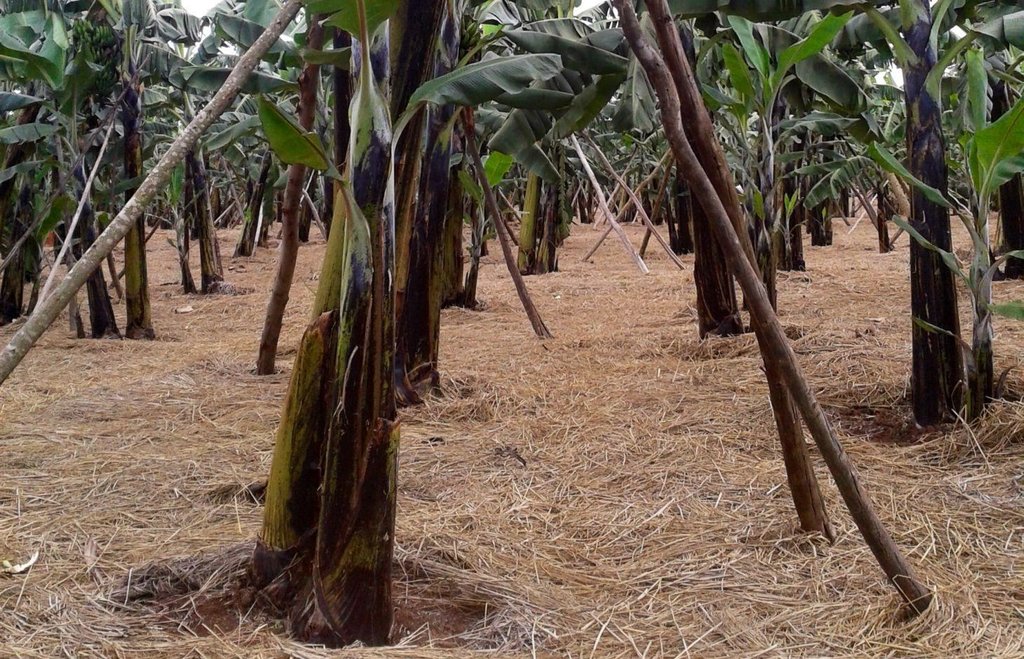
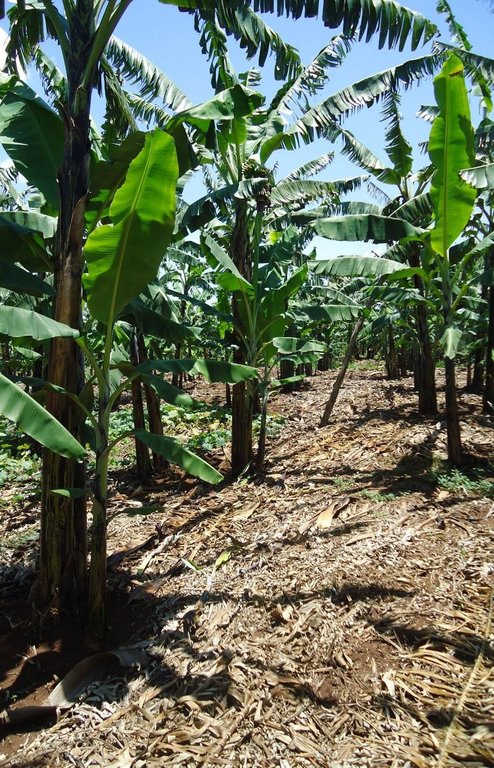
Banana planted in a regularly spaced manured pits and in combination with grass and banana mulch application to enhance soil fertility and moisture and improve crop production.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
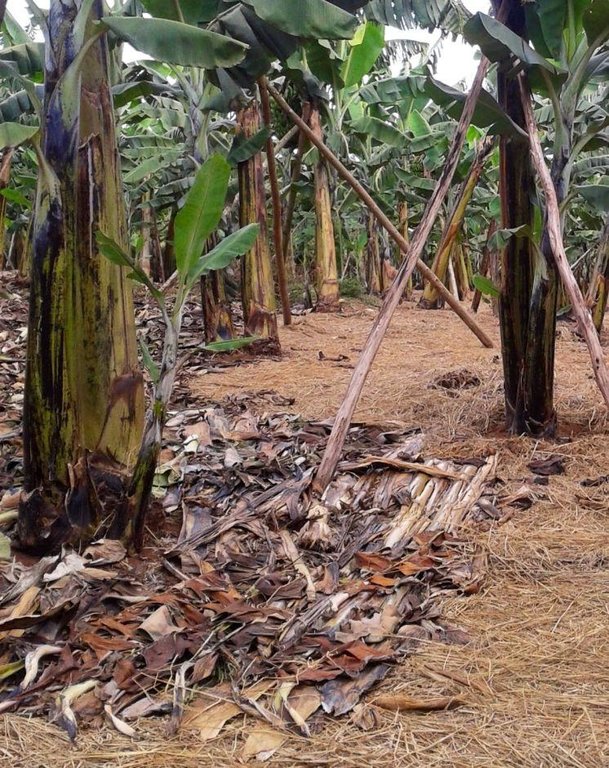
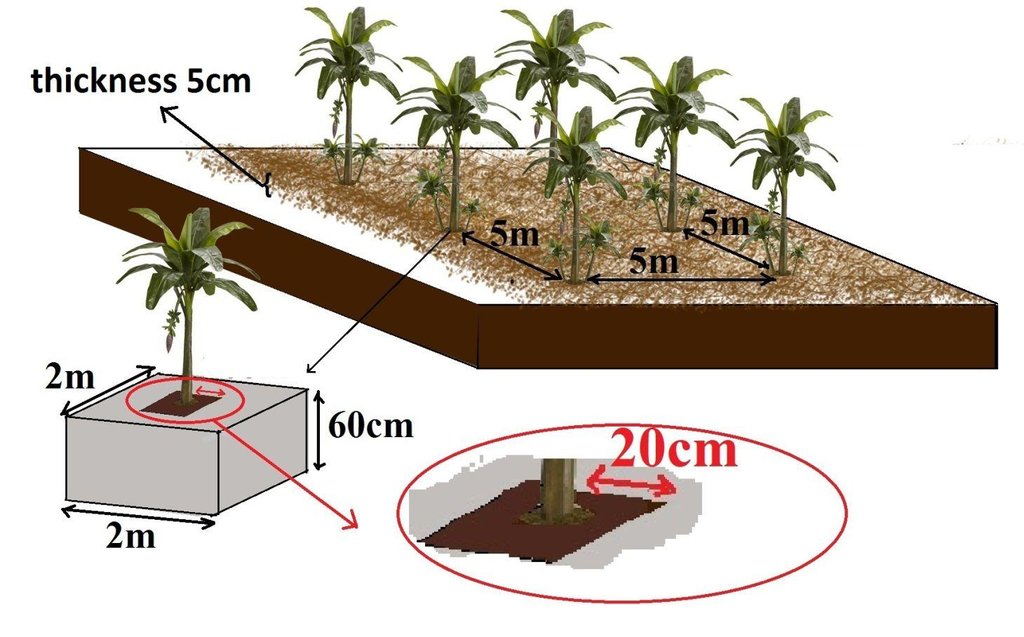
Banana is planted in a manure pit and the soil surface is carefully covered by banana or grass mulch. The manured pit is 0.6m deep and 2.0-2.0m wide. During establishment activities pits are filled with a mixture of soil and organic manure. Attention should be made when adding the mixed soil to the pits as a radius of 20 cm starting from the center of the pit where the banana is planted must not be filled with the mixture but filled merely with soil.This will assure that banana roots grow deeper in search for the nutrients. Recommended parallel and perpendicular spacing between the banana planting pits is 5m.
Purpose of the Technology: Banana manured pits and mulch application is a combination of an agronomic and structural technique. This method allows nutrients to be concentrated around the roots zone and keeps longer the available soil water content and controls the soil erosion.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The banana manure pits and mulching provides easy crop management options. The high demand of water and nutrients by banana can be easily met to maximize the fruiting potential. To achieve this potential, farmers are required to maintain a minimum of 3 plants per pit, one mature (grand) banana plant fruiting, a second half grown (mother), and one sucker (child) growing in the same pit. Every four months a farmer is expected to harvest a bunch of banana of around 80 kg per pit.
Natural / human environment: The constituted layer of mulch prevents rainwater from eroding the top soil, improves soil organic carbon, provides shade to plant roots, and most importantly keeps longer soil moisture in dry seasons.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Rwanda
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Rwanda
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Kirehe District (Eastern province)
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- 10-100 km2
Commentaires:
The area covered by this technology has been estimated
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a entre 10-50 ans
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- grâce à l'innovation d'exploitants des terres
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses) - Précisez les cultures:
- bananier/plantain/abaca
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 180; Longest growing period from month to month: Sept to mid Febr; Second longest growing period in days: 150; Second longest growing period from month to month: mid March to mid Jun
Commentaires:
Major cash crop and major food crop: Banana
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Banana plantation is sensitive to dry season where evapotranspiration is high, and high erosion impact in rainy season.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Surface runoff
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Cp: Perennial (non-woody) cropping
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Oui (Veuillez remplir les questions ci-après au regard de l’utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie)

Pâturages
- Extensive grazing
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- Amélioration de la couverture végétale/ du sol
- gestion intégrée de la fertilité des sols
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A1: Couverture végétale/ du sol

structures physiques
- S4: Fossés isohypses, trous
Commentaires:
Main measures: agronomic measures, structural measures
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, manure / compost / residues, pits
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)
Commentaires:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Lack of knowledge in soil conservation practices.), droughts (it tend to happen due to the unpredictable rainfed changes), population pressure (as the population increases the soil exploitation increases as well)
Secondary causes of degradation: poverty / wealth
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
This technology consists of a pit of 0.6x2x2m respectively, for depth, length and width. Banana is planted in center of each pit in which organic manure from different sources is added and mixed with the soil. The spacing along the row and between rows is 5 m. The top soil is taken back and only 15-30 kg of organic manure are added and mixed with soil. Attention should be made when adding the mixed soil to the pits as a radius of 20 cm starting from the center of the pit where the banana is planted must not be filled with the mixture but filled merely with soil.
Location: Kayonza. Kayonza/South/Rwanda
Date: 2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, increase of biomass (quantity)
Mulching
Material/ species: grasses, crop residues and strow of banana
Quantity/ density: 50,000 m3
Remarks: in bananas field the thickness of mulch is about 5 cm, which including a total quantity of 50,000 m3
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: farmyard manure
Quantity/ density: 12t/ha
Remarks: According to the spacing only 400 banana can be grown per ha and a pits may receive 30 kg of FYM
Pits
Material/ species: A pit have a distance of 2m x 2m with 60cm deep
Quantity/ density: 400pitsha
Remarks: The distance between two pits is 1 m which means 5m between 2 consecutive banana
Auteur:
Kagabo Desire and Ngenzi Guy, RAB, 5016 Kigali
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars américains
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
1.70
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Establishment of pits | |
| 2. | Seedling plantation | |
| 3. | Seedling transportation |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Land preparation, planting, thinning weeding | persons/day/ha | 221,7647 | 1,7 | 377,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 30,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Acquisition of suckers | ha | 1,0 | 937,5 | 937,5 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Compost manure | ha | 1,0 | 650,0 | 650,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 1994,5 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 1994,5 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Thinning banana field | dry season |
| 2. | Weeding | rainy season |
| 3. | Planting seedlings | rainy season |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 42,0 | 42,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Thinning and weeding | ha | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 67,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 67,0 | |||||
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The labor affects most the cost of this technology. However, suckers or planting materials could increase the cost if not readily available at farm gate or in the neighborhood.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- situations concaves
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium - low
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
faible/ absente
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
faiblement potable (traitement nécessaire)
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
The mulched land become a suitable niche of many kind of lizard and rat
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
20% of the land users are average wealthy and own 70% of the land.
78% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
2% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- moyenne dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- accès libre (non organisé)
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Quantité avant la GDT:
50 tons
Quantité après la GDT:
190 tons
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Because of the new technology the yield is 4 fold
risque d'échec de la production
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
revenus agricoles
Quantité avant la GDT:
1233
Quantité après la GDT:
4687
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The net family income has improved by 4 fold
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Quantité avant la GDT:
125
Quantité après la GDT:
258
situation sanitaire
Quantité avant la GDT:
70%
Quantité après la GDT:
90%
livelihood and human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The technology increases banana production and the net farm income
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
évaporation
Sols
humidité du sol
couverture du sol
perte en sol
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
pollution des rivières/ nappes phréatiques
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | pas bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- > 50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
43000 housheolds covering 80 percent of stated area
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 91-100%
Commentaires:
43000 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Increase production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular maintenance |
|
Reduce surface runoff by enhancing the retention soil moisture How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular maintenance |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Increased food security and income of land users How can they be sustained / enhanced? Scaling up the technology |
|
Increased water holding capacity How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good maintenance by regularly replacing mulch |
|
Increased soil moisture How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good maintenance by adding very often organic manure |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| This technology maybe expensive at establishment phase, maybe not affordable by every smallholder farmer | Allow farmers to access credits through farmer saving schemes or cooperatives |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé