Terrace with Tree Barrier [Tadjikistan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Erik Bühlmann
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Alexandra Gavilano, David Streiff, Joana Eichenberger
technologies_1409 - Tadjikistan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - KirghizistanNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suisse1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)

Voluntary Labour Assistance [Tadjikistan]
Voluntary labour assistance for labour intensive activities whereby community members help each other in contributing labour on the basis of mutual understanding.
- Compilateur : Erik Bühlmann
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Forward sloping terraces stabilised with aligned poplar trees and adjacent grass strips
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
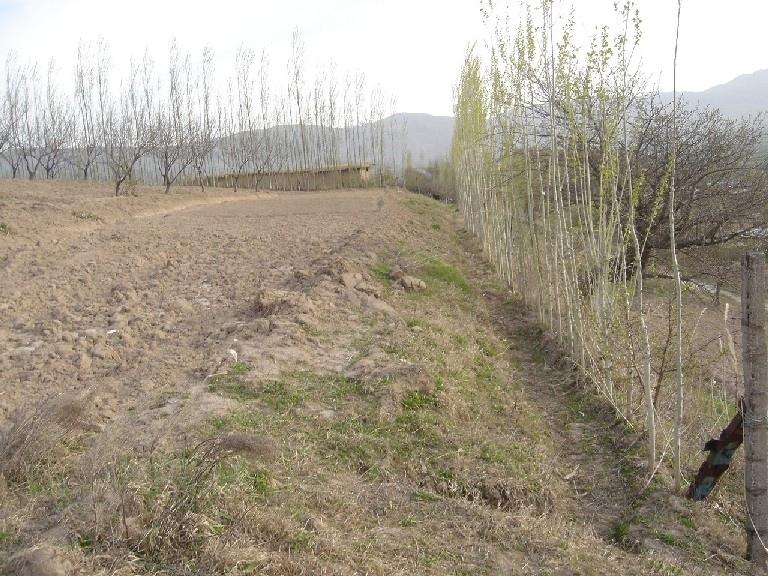
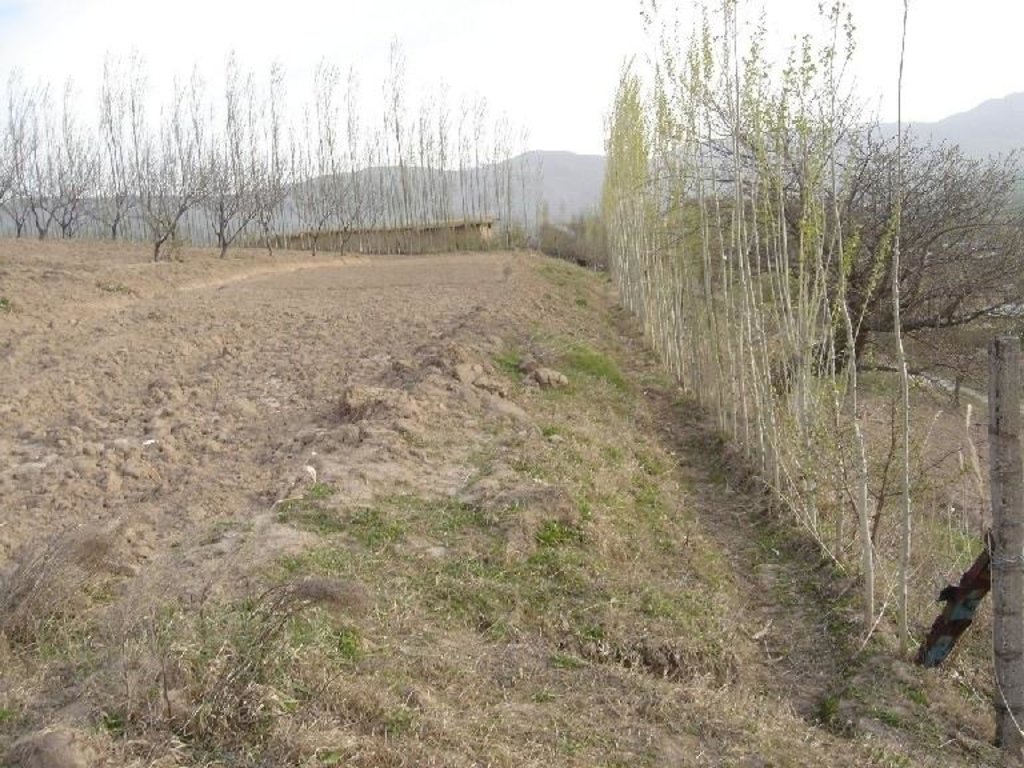
On steep and severely eroded cropland a forward sloping terrace (15% gradient) was established by moving available earth with a bulldozer. Below the terraced field, a cut-off drain diverts excessive rain and irrigation water to an existing gully. The terrace and the cut off drain are stabilised by an aligned tree barrier (poplar trees planted in 0.5 metre intervals), and by two parallel grass strips of 1-2 metres in width.
The terrace was built using a bulldozer. Digging the cut-off drain and planting the poplar cuttings was done by hand. For the initial establishment of the grass strip clods were transferred from a neighbouring pasture. The poplar trees are pruned in early spring; the cut off-drain needs to be cleared of washed in soil after heavy storm events. The described terrace is established on steep cropland prone to soil erosion. The technology is relatively simple to implement.
Purpose of the Technology: The terrace was established to reduce soil erosion and subsequent fertility decline through the reduction of the slope angle. The tree barrier is planted because of the usefulness of poplar trees for construction purposes and to mark field boundaries; its capability of acting as a stabilising terrace is a very useful extra side effect.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment costs and the rather low maintenance costs are offset by the benefits of the harvested wood produced. Poplar trees can be gradually felled and used for construction purposes 15 years after they are initially planted. Through reduction of the slope angle, the risk of soil erosion is lowered significantly. However, poplar trees can only be planted on land where sufficient water for irrigation is available, since they need to be watered on a weekly basis during the summer. Furthermore, the technology covers land which then cannot be used for cultivation of food crops.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Tadjikistan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
RRS
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Faizabad Rayon
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- 0,1-1 km2
Commentaires:
Общая площадь, на которой задействована технология, 0,5 квадратных метра.
Map
×2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- au cours d'expérimentations / de recherches
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agroforesterie

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - blé de printemps
- cultures de plantes à fibres - lin, chanvre, autres
- légumineuses et légumes secs - pois
Plantations d'arbres et d'arbustes - Précisez les cultures:
- fruits à pépins (pommes, poires, coings, etc.)
- fruits à noyaux (pêche, abricot, cerise, prune)
- fruits à coque (noix du Brésil, pistaches, noyers de bancoule, amandes)
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 210Longest growing period from month to month: March to August
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): severe water erosion (rills and gullies) and subsequent fertility decline on cropland and overgrazed pastures
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): soil erosion and fertility decline
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: If land is irrigated, then after the wheat harvest there can be immediate cultivation of vegetables
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- agroforesterie
- mesures en travers de la pente
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes

structures physiques
- S1: Terrasses
Commentaires:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour, aligned: -along boundary
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
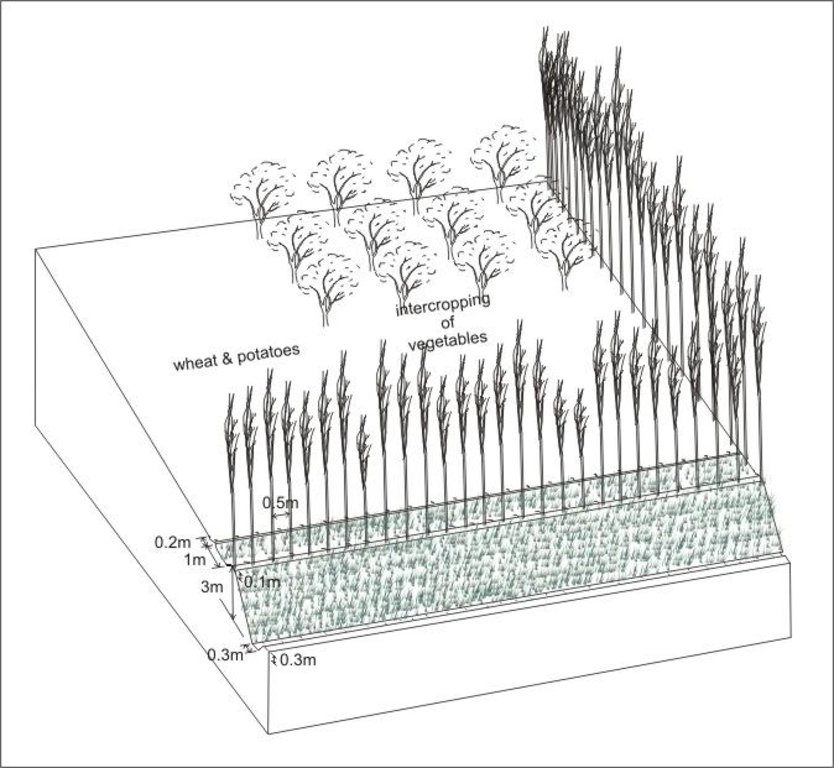
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Терраса с уклоном вперед, укрепленная полосой деревьев и травяными полосами, отводной канал используется для отвода излишков воды вниз по склону
Место расположения: Карсанг. Файзабадский район
Дата: 15.07.2005
Необходимые технические навыки для работников: средний
Необходимые технические навыки для землепользователей: средний
Основные технические функции: сокращение угла откоса, сокращение длины откоса
Вторичные технические функции: контроль рассеивающихся поверхностных стоков: запруда / замедление, контроль над концентрированными стоками: запруда / замедление, контроль над концентрированными стоками: дрена / отводка, улучшение земляного покрова, повышение / поддержание сохранения воды в почве, сокращение скорости ветра
Выравнивание: -контур
Растительный материал: Д: деревья / кустарники
Количество растений на гектар: 200
Вертикальная протяженность полос / рядов / блоков в м : 0.5
Выравнивание: -вдоль границы
Растительный материал: Д: деревья / кустарники
Количество растений на гектар: 200
Мероприятия, связанные с растительностью: выравнивание: контур
Растительный материал: Т: трава
Ширина полос / рядов / блоков (м): 3
Мероприятия, связанные с растительностью: Растительный материал: Т: трава
Мероприятия, связанные с растительностью: Растительный материал: Т: трава
Мероприятия, связанные с растительностью: Растительный материал: Т: трава
Виды деревьев/ кустарников: тополь
Инженерные мероприятия: отводной канал
Глубина канав/ям/дамб (м): 0.1
Ширина канав/ям/дамб (м): 0.2
Длина канав/ям/дамб (м): по всему участку
Строительный материал (земля): почва переносится с террасы
Если естественный склон был изменен в результате применения технологии, то текущее состояние склона: 15%
Уклон горизонтальной поверхности: 2%
Растительность используется для укрепления инженерных сооружений
Location: Karsang. Faizabad Rayon
Date: 15.07.2005
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, improvement of ground cover, increase / maintain water stored in soil, reduction in wind speed
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 200
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 200
Vegetative measure: aligned: contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Trees/ shrubs species: poplar trees
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 15.00%
Structural measure: cut-off drain
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.1
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.2
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): fielding
Construction material (earth): earth moved to form terrace
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 15%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 2%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Auteur:
Erik Bühlmann, Berne, Switzerland
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
3.00
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | digging of pits for tree planting | spring |
| 2. | planting of poplar cuttings | spring |
| 3. | transplanting of grass clods | spring |
| 4. | construction of terrace | autumn |
| 5. | digging of cut-off drain | autumn |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Building terrace | ha | 1,0 | 80,0 | 80,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Planting trees | ha | 1,0 | 75,0 | 75,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | tools | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 165,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 165,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | pruning of trees | eraly spring /annual |
| 2. | cutting of grass (grass strips) | summer /annual |
| 3. | irrigarion/watering of trees | summer /weekly |
| 4. | clearing cut-off drain from washed in soil | rainy season/after every rainfall event |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Prunning | ha | 1,0 | 12,0 | 12,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Cutting | ha | 1,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 15,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 15,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
costs per 100x100m plot, costs increase if longer field boundary is on contour
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
- semi-aride
growing period 180-210 days
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitudinal zone: Also 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility: low - high
Soil drainage / infiltration: medium - good
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- > 50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
- riche
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
5% of the land users are rich and own 15% of the land.
75% of the land users are average wealthy and own 70% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: In general, all farmers (including those applying SWC technologies) are highly dependent on off-farm income which in most cases is earned in Russia either by themselves or by their relatives.
Level of mechanization: whenever possible farmer rent tractors for tillage activities. All levels of mechanization are pre-existing.
Market orientation of production system subsistence (self-supply): only surpluses are sold
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Commentaires:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology also: 0.5-1 ha,
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- loué
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
due to increase in soil fertility
production de bois
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
poplar trees gradually harvested for construction purposes
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
area occupied by grass strips, barriers and ditches
gestion des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
tree barriers impede accessibility with machines
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Impacts socioculturels
institutions communautaires
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
drainage de l'excès d'eau
Sols
humidité du sol
perte en sol
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
vitesse du vent
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
inondations en aval
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
The terraces were established with the help of bulldozers which is costly, therefore short-term benefits are slightly negative.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
NA
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 91-100%
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| reduces soil erosion |
| slows fertility decline |
| 15 years after establishment poplar trees can be harvested, their wood is essential for construction and renovation of houses |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| reduces slope angle and, hence, decreases risk of soil erosion |
| relatively simple to implement |
| moderate establishment costs, low maintenance costs |
|
meets household needs for wood for construction How can they be sustained / enhanced? trees should be gradually harvested and replaced with new cuttings |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| loss of cropland due to structure, grass strips and trees | |
| cultivation using a tractor is impossible due to the type of terrain impeding access | |
| poplar trees require irrigation |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The poplar trees used to stabilise the structure require irrigation during summer | |
| farm operations hindered |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Voluntary Labour Assistance [Tadjikistan]
Voluntary labour assistance for labour intensive activities whereby community members help each other in contributing labour on the basis of mutual understanding.
- Compilateur : Erik Bühlmann
Modules
Aucun module trouvé