Dugout Pond [Inde]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Mulchand Kag
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Talawadi
technologies_1472 - Inde
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)

Comprehensive watershed development [Inde]
Participatory approach that includes a package of measures leading to empowerment of communities to implement and sustain watershed development.
- Compilateur : David Gandhi
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
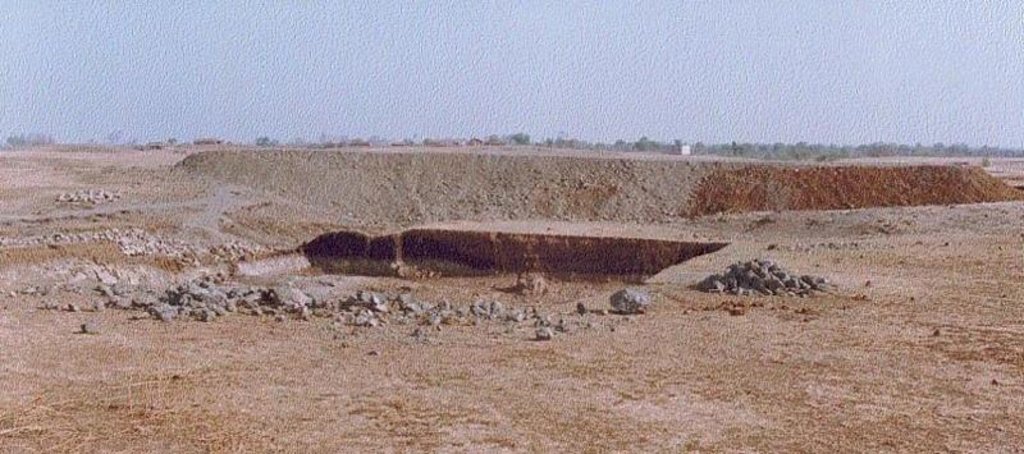
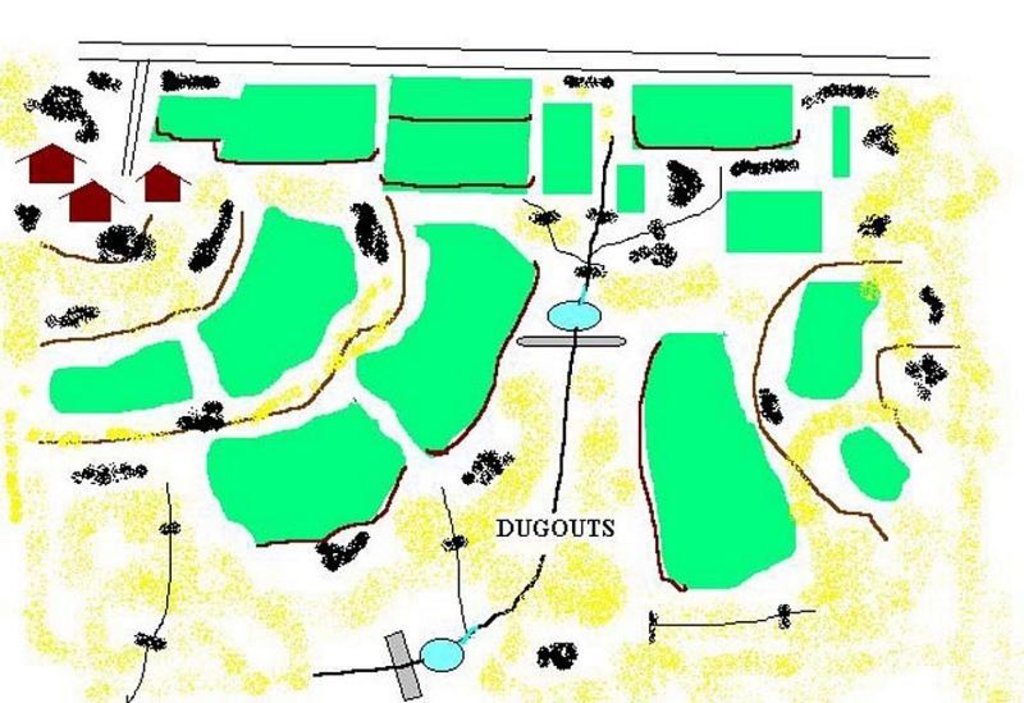
Dugout pond is a sunken water harvesting structure constructed along the rills in upper catchment for the purpose of storage of runoff and recharge of ground water.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
Dugout pond is a rectangular shape subsurface pond with the excavated material forming an embankment down stream. It is constructed in the upper catchment of the watershed, along the rill/shallow gully. The site for the pond should be where there is a depression. The size may vary from small to large depending on the size of catchment, needs of the farmers, availability of finance, bed rock strata.
Purpose of the Technology: 1- Storage of runoff. 2- Increase in water levels of shallow wells 'odees' through increased percolation. 3- Flood control through series of such structures. 4- Low cost, low risk alternative for poor community. 5- Benefits to community living in upper catchment.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: 1- Site selection with community. 2- Design and preparation of estimate by the project staff. 3- Descussion with VWDC and community, identification of users, descussion regarding contribution, agreement, work plan. 4- Layout and construction under VWDC supervision with technical support from the project. 5- Treatment of catchment.
Natural / human environment: Responsibility of user group.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Inde
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Madhya Pradesh
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, précisez la superficie couverte (en km2):
48,0
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- 10-100 km2
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 48 km2.
The area comprises 36 villages with 1632 household mainly tribal. Villages comprise a larger settlement along with a number of hamlets. The topography is rolling and gently undulating. The area forms the catchment of the Larki stream, which forms the upper catchment of the river Mahi.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The technology has been developed by the project as modification/improvement to Dugout pond constructed under NWDPRA (National Watershed Development Program for Rainfed Areas).
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- s'adapter au changement et aux extrêmes climatiques et à leurs impacts
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agropastoralisme (y compris les systèmes culture-élevage intégrés)

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - maïs
- céréales - blé d'hiver
- cultures de plantes à fibres - coton
- légumineuses et légumes secs - fèves
- légumineuses et légumes secs - autres
- légumineuses et légumes secs - soja
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Mar Second longest growing period in days: 135 Second longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Sep

Pâturages
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): 1. Utilisation of slopy and stony (class VI) land for agriculture. 2. Agriculture practices along the slope, use of erosion permitting crop eg. Cotton, Maize. 3. Excessive grazing of grass land.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): shallow soils, low soil moisture , low yields , non-availability of grazing land.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Monsoon - Cotton + Maize + Blackgram /Soyabean. Winter (with irrigation) - Wheat + Gram (excluding Cotton fields).
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Commentaires:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- récupération/ collecte de l'eau
- gestion de l'irrigation (incl. l'approvisionnement en eau, le drainage)
- gestion des eaux souterraines
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines

dégradation hydrique
- Ha: aridification
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Ha: aridification
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (Social causes - Lack of awareness and mobilisation amongst the communities.), Top down approach (Macro planning rather than micro (village level) planning.)
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
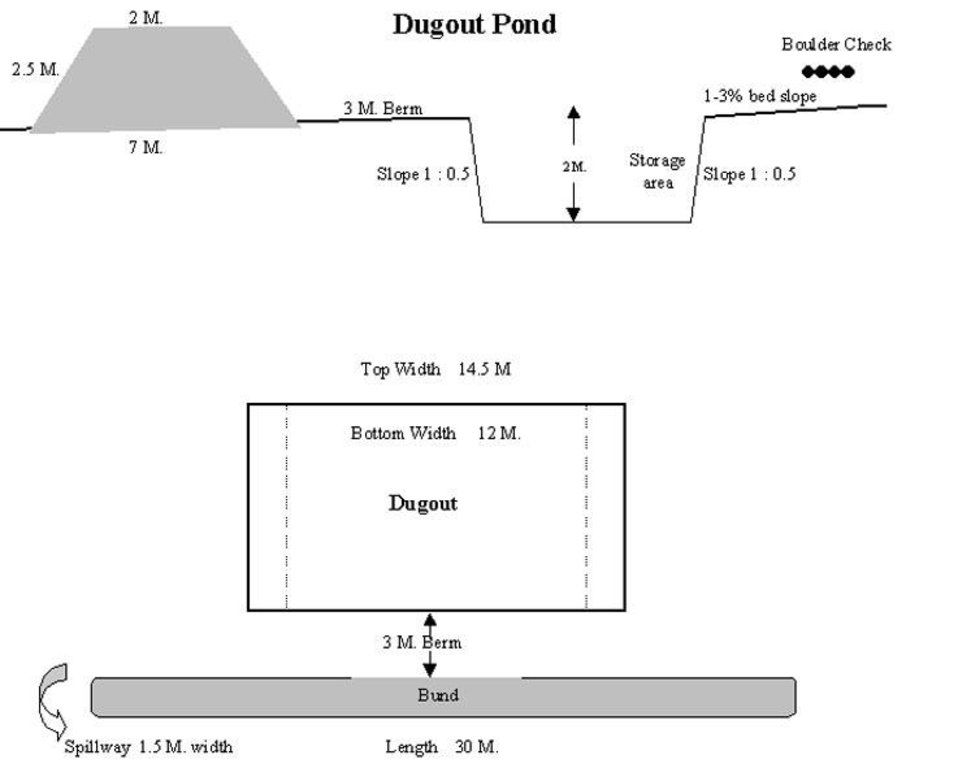
Technical Drawing of Dugout Pond
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase of infiltration
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, water harvesting / increase water supply
Construction material (earth): Excavated material used for embankment.
Construction material (stone): Excavated stones used for pitching.
Auteur:
Rajesh Parihar, India
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Rupees
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
48,85
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
1.00
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Discussion in VWDC meeting | March-April |
| 2. | Site selection | March-April |
| 3. | Identification of beneficiaries, users group formation | March-April |
| 4. | Design & estimate | March-April |
| 5. | Agreement with VWDC | March-April |
| 6. | Treatment of catchment area | April-May |
| 7. | Construction of dugout pond | April-May |
| 8. | Seeding of embankment | June-July |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Monitoring by users group | Year around/Regular |
| 2. | Report of damage, breakage in VWDC | Rainy season/After heavy shower |
| 3. | Decision regarding repair by VWDC/UG | Rainy season/After heavy shower |
| 4. | Necessary repaires carried out | Rainy season/After heavy shower |
| 5. | Desilting | Dry season/annual |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Commentaires:
The size of dugout described in 2.7.1 is :- Excavated area - 13m long X 12m wide X 2.5m Bund - 30m long X2.5m height X 2m top width X 7m bottom width
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
1- Cost of excavation increases with hardness of strata. 2- Non availability of stones locally for pitching.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
800,00
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
However for the past 4 years the area has received below average rainfall.
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
90 - 120 days LGP - monsoon
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Landforms: Ridges (ranked 1, gradually undulating topography) and hill slopes (ranked 2)
Slopes on average: Moderate (ranked 1, fields in upper catchment) and gentle (ranked 2, fields in valley portion)
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average: Shallow (ranked 1, fields on ridge/slopes), very shallow (ranked 2, ridge portion) and moderately deep (ranked 3, fields in valley)
Soil fertility: Medium (ranked 1) and low (ranked 2, fields on ridge/slopes, grass land)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (ranked 1, sloping land, shallow soils) and medium (ranked 2, fields in valley)
Soil water storage capacity: Low (ranked 1, shallow soils) and medium (ranked 2, deep soils)
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: > 4%
33% of the land users are average wealthy and own 33% of the land (Few farmers with wells, fields in valley.).
50% of the land users are poor and own 57% of the land (Majority of farmers.).
17% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land (Very small holding.).
Off-farm income specification: While main income is from rainfed agriculture, significant income is obtained during migration, which increases during drought periods.
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (ranked 1, land preparation), manual labour (ranked 2, land preparation, weeding, harvesting) and mechanised (ranked 3, threshing)
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- communauté/ village
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- accès libre (non organisé)
- individuel
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
1672
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
1632 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
40 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The community is very poor and hence requires some financial support to offset loss of wages.
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Comprehensive watershed development [Inde]
Participatory approach that includes a package of measures leading to empowerment of communities to implement and sustain watershed development.
- Compilateur : David Gandhi
Modules
Aucun module trouvé