Pepsee micro-irrigation system [Inde]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Shilp Verma
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Pepsee
technologies_1477 - Inde
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Sadagani Amitabha
International Development Enterprises
Inde
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
IWMI International Water Management Institute (IWMI) - IndeNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
International Development Enterprises - India (iDE-India) - Etats-Unis1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)

Market support and branding for input quality (Krishak … [Inde]
Market development and support through use of a brand name - Krishak Bandhu ('the farmer's friend') - to help ensure quality amongst manufacturers and suppliers of drip irrigation equipment.
- Compilateur : Shilp Verma
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
A grassroots innovation that offers most of the advantages of conventional micro-irrigation at a much lower establishment cost.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
The continued expansion of irrigation in India is causing increasing water shortages. This may be compounded by the potential effects of climate change. Drip irrigation - delivering small amounts of water directly to the plants through pipes - is a technology that could help farmers deal with water constraints. It is considerably more efficient in terms of water use than the usual open furrows or flood irrigation.
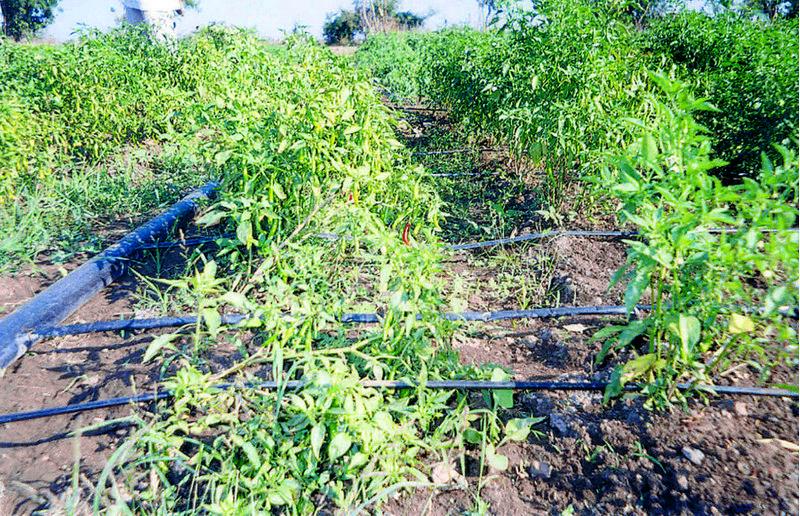
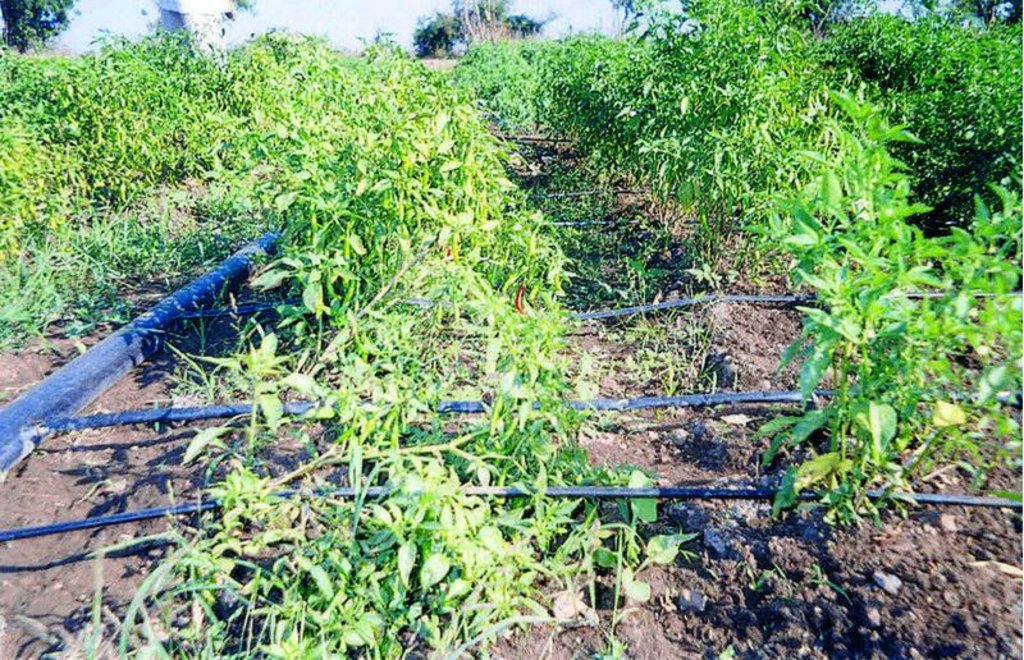
In West Nimar, Madhya Pradesh, droughts, diminishing groundwater, limited and erratic power supply coupled with poverty, compelled farmers to look for a technology that would enable them to irrigate their crops (mainly cotton) within these constraints. They tried out several cost-saving options such as using old bicycle tubes instead of the conventional drip irrigation pipes. But nothing caught on - until about five years ago - when a local farmer experimented with thin poly-tubing normally used for frozen fruit-flavoured ‘lollypops’ called pepsee. It spread to neighbouring cotton farmers, and its popularity has meant that today pepsee has become widespread in the region. Pepsee micro-irrigation systems slowly and regularly apply water directly to the root zone of plants through a network of economically designed plastic pipes and low-discharge emitters.
Technically speaking pepsee systems use low density polythene (65-130 microns) tubes which are locally assembled. Being a low pressure system the water source can be an overhead tank or a manually operated water pump to lift water from a shallow water table.
Such a system costs less than US$ 40 per hectare for establishment. But the tubes have a short life span of one (or two) year(s); an equivalent standard buried strip drip irrigation system amounts to between five and ten times the initial cost. The latter would, however, last for five to ten years. The critical factor is the low entry cost. Pepsee systems thus act as ‘stepping stones’ for poor farmers who are facing water stress but are short of capital and cannot afford to risk relatively large investment in a technology which is new to them, and whose returns are uncertain. The technology is today available in two variants: the original white pepsee and a recently introduced black pepsee which is of slightly better quality.
Recently, a more durable and standardised version of pepsee, given the brand name ‘Easy Drip’, has been developed and promoted by a local NGO, IDEI (see corresponding approach). Easy Drip is one product within a set of affordable micro-irrigation technologies (AMIT) promoted by IDEI.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Inde
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Madhya Pradesh
Autres spécifications du lieu:
West Nimar
Map
×2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- créer un impact économique positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- cultures de plantes à fibres - coton
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: May - Oct Second longest growing period in days: 120 Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Mar
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Acute groundwater stress associated with lowering of the groundwater table limits water for irrigation, coupled with poverty and reluctance to risk investing in relatively expensive- but efficient - drip irrigation systems.
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pleine irrigation
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion de l'irrigation (incl. l'approvisionnement en eau, le drainage)
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques

modes de gestion
Commentaires:
Main measures: structural measures, management measures
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation hydrique
- Hq: baisse de la qualité des eaux souterraines
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Hq: decline of groundwater quality
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing, droughts, land tenure (land subdivision), Land alienation
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
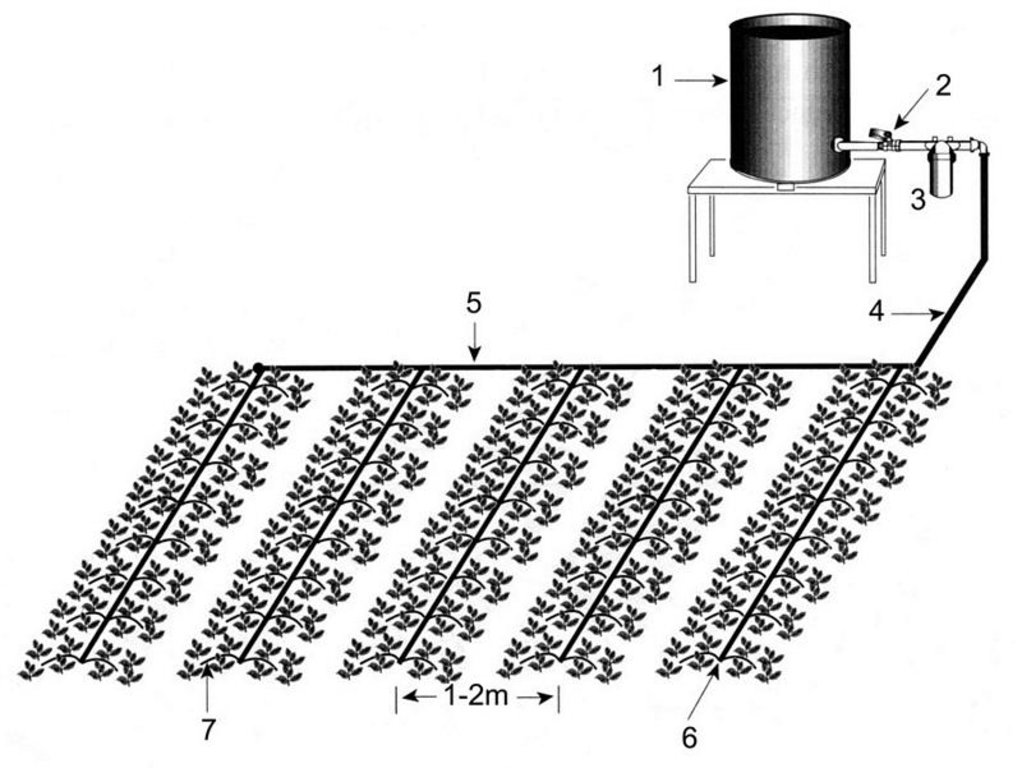
Components of pepsee/‘Easy Drip’ irrigation systems are described below.
1) Water source: For pepsee, commonly a water pump (in most cases electric) is used to lift water from a well and directly feed the irrigation system.
Alternatively, an overhead tank (minimum of 1 m above ground level) can be used for smaller systems up to 400 m2 area.
2) Control valve: valve made of plastic or metal to regulate pressure and flow of water into the system
3) Filter: Strainer filter to ensure that clean water enters into the system (optional in pepsee systems).
4) Mainline: 50 mm PVC (Polyvinyl chloride) or PE (Polyethylene) pipe to convey water from source to the sub-main.
5) Sub-main: PVC/PE pipe to supply water to the lateral pipes which are connected to the sub-main at regular intervals.
6) Lateral: PE pipes along the rows of the crops on which emitters are connected directly. Pipe size is 12–16 mm.
7) Emitters/micro-tubes: Device through which water is emitted at the root zone of the plant with required discharge. In pepsee farmers simply make pin holes in the plastic tube for water to pass. Easy Drip has inbuilt drippers/outlets along the lateral line which give a continuous wetting strip.
It is mainly used for row crops.
Pepsee uses cheap, recycled plastic tubes instead of the rubber pipes used in conventional drip irrigation kits. Space between emitters is variable, for cotton cultivation it is commonly 1.2 m (between plants, within and between rows). There is (usually) one emitter for each plant. Different sizes of valves, mainlines, etc, are available, depending on flow rate of water in the system. Additional components are joints (connectors) and pegs (used to hold the lateral and micro-pipes in place).
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: water supply, improved water-use efficiency (reduced loss, well directed, selective - and targeted irrigation
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, higher - germination and establishment rate
Structural measure: irrigation infrastructure
Construction material (other): poly-tubes - low density polythene (65-130 microns)
Change of land use practices / intensity level: from furrow to drip irrigation
Auteur:
Sijali IV 2001, Drip irrigation, RELMA, Nairobi
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Installation of water pump, control valve, filter (optional) and PVC piping(main/sub-main and lateral pipes). | dry season |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Lateral piping (Pepsee tube) | ha | 1,0 | 17,0 | 17,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Main/sub-main PVC piping | ha | 1,0 | 34,0 | 34,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Other parts (valves, joints et | ha | 1,0 | 40,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 95,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 95,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Re-installation of lateral pepsee tubes | dry season/ (every 1–2 years). |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Lateral piping (Pepsee tube) | ha | 1,0 | 17,0 | 17,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 21,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 21,0 | |||||
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil texture: Fine/heavy (black cotton soil; mostly vertisols, partly inceptisols and entisols)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Poor
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- commercial/ de marché
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
More land brought under irrigation. This is seen as a negative aspect
Revenus et coûts
charge de travail
Autres impacts socio-économiques
irrigated area
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Greater irrigated area with same amount of water
Impacts socioculturels
droits d'utilisation des terres/ de l'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
More farmers able to irrigate their land
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Poverty reduction
Social acceptance
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Drip irrigation confers the image of a progressive farmer
Impacts écologiques
Autres impacts écologiques
Water use efficiency
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 91-100%
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: No detailed information available regarding spread - though this is estimated to be several thousand farmers within West Nimar. All adoption has been spontaneous, without incentives, and the group which has adopted best comprises those who were previously using furrow irrigation. A large number of pepsee adopters are the resource poor farmers but rich farmers have also adopted pepsee.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Low initial investment and recurrent costs: risk in adopting new system limited How can they be sustained / enhanced? Keep costs of new variations of pepsee low. |
|
There are significant benefits in terms of reduced water use per unit of land, and in terms of yield per unit land area as well. |
| Few extra skills required to implement and operate the system. |
|
An eventual shift to conventional drip system is feasible: pepsee acts as a ’stepping stone’ How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote improved drip systems where pepsee has taken off. |
|
Higher yields, better quality, higher germination rate, lower incidence of pest attack; facilitates pre-monsoon sowing. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
|
Pepsee is based on drip pipes which have a limited life: delicate and cannot withstand high pressure |
Develop/use stronger piping materials such as ‘Easy Drip’. |
|
The increased water use efficiency has allowed an expansion in the area irrigated – which has used up the water ‘saved’. |
Develop/use stronger piping materials such as ‘Easy Drip’. |
|
Pepsee systems require replacement of lateral pipes each year and thus incur recurrent input and labour costs |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Verma S, Tsephal S. and Jose T: Pepsee Systems: grassroots innovation under groundwater stress. Water Policy, 6,pp. 303–318.. 2004.
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
http://www.iwaponline.com/wp/00604/wp006040303.htm
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Market support and branding for input quality (Krishak … [Inde]
Market development and support through use of a brand name - Krishak Bandhu ('the farmer's friend') - to help ensure quality amongst manufacturers and suppliers of drip irrigation equipment.
- Compilateur : Shilp Verma
Modules
Aucun module trouvé