Rehabilitation of ancient terraces [Pérou]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Unknown User
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Andenes / Anchacas / Patapatas
technologies_1506 - Pérou
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
Spécialiste GDT:
Marquina Rodolfo
Centro de Estudios y Promoción del Desarrollo – DESCO
Pérou
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Centro de Estudios y Promoción del Desarrollo (DESCO) - Pérou1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)

Participatory catchment rehabilitation (Participación comunitaria para la rehabilitación … [Pérou]
Promoting the rehabilitation of ancient terrace systems based on a systematic watershed management approach.
- Compilateur : Philippe Zahner
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
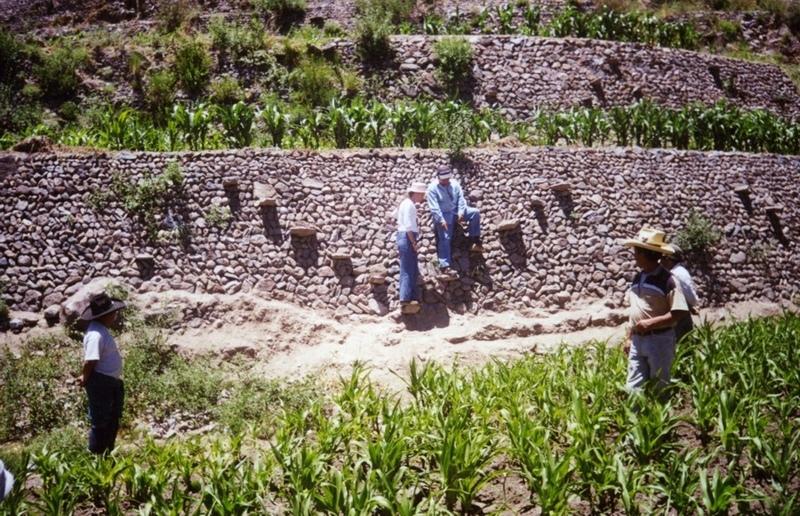
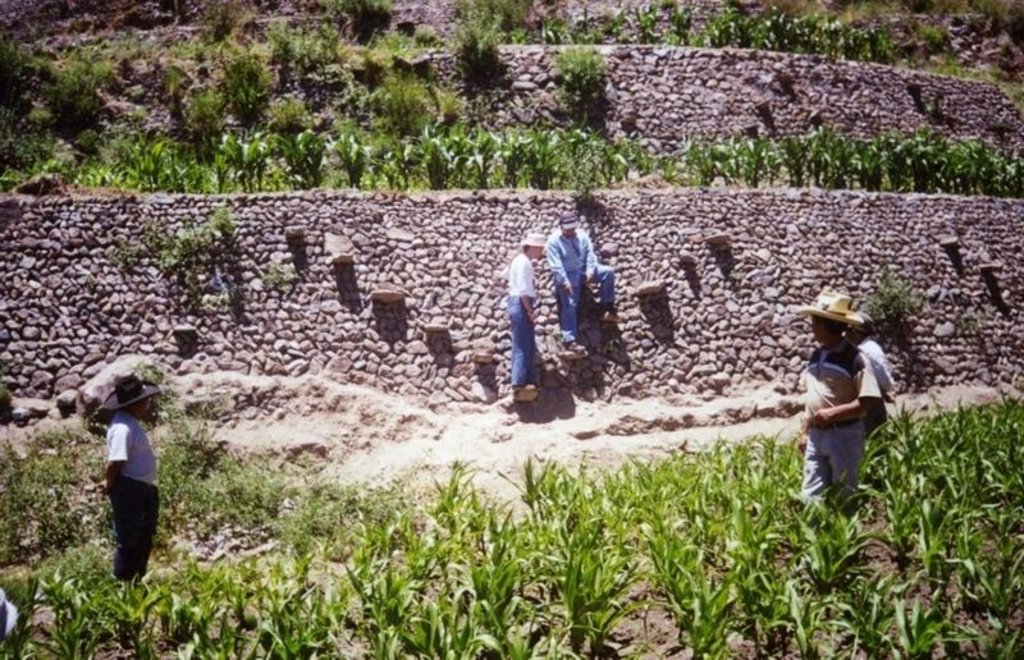
Repair of ancient stone wall bench terraces, and of an associated irrigation and drainage system.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
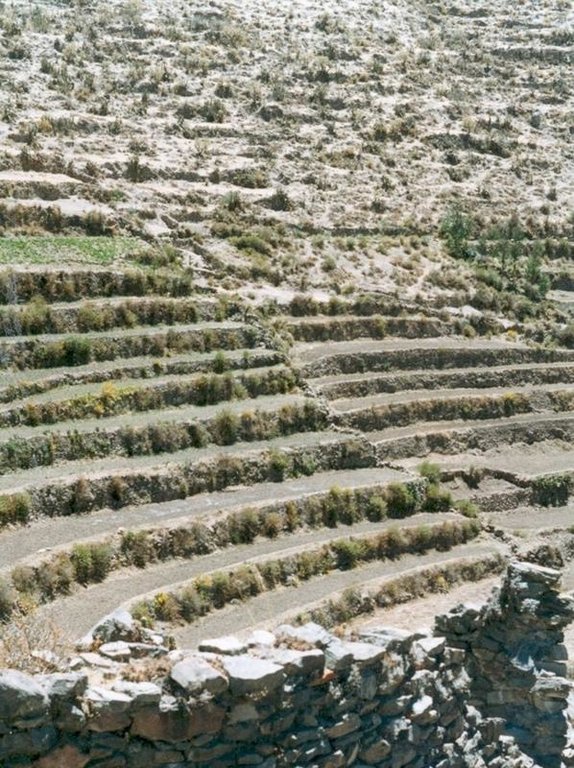
The level bench terrace system in the Colca valley of Peru dates back to 600 years AD. Since then the terraces have been continuously used for crop production, but due to lack of maintenance they have deteriorated, and the population has lost its traditional knowledge of repair.
The rehabilitation of the terraces recreates their original structural design. Broken sections are cleared and the various materials - stones, topsoil, subsoil and weeds - are removed and separated. The foundation is re-established, followed by construction of the stone wall (the ‘riser’). Backfilling with subsoil then takes place; this is consolidated and finally covered with topsoil. Simultaneously the complementary irrigation and drainage systems are reconstructed.
The rehabilitated terraces efficiently conserve soil and water on steep slopes, and they create a favourable microclimate for crops, reducing loss of stored heat at night by minimising air movement (preventing frosts) and mitigating dry conditions through moisture conservation. The main economic benefits are from increased yields and crop diversification.
Terraces are spaced and sized according to slope, eg on a 50% slope, terraces are 4 m wide with a 2 m high riser between terrace beds. Stones of ancient terraces had been widely used to build walls for boundary marking after privatisation of land, therefore a large amount of stone had to be provided by splitting rocks and transporting from other locations.
The area is characterised by steep slopes with loamy-sandy, moderately deep soils (on the terrace beds). Most of the annual precipitation (ca. 350 mm) falls within a period of 3 months, which makes irrigation necessary. The farmers in the area own, on average, 1.2 hectares of arable land, divided into around six plots in different agro-ecological zones. Production is mainly for subsistence. Important supportive technologies include agronomic measures such as improved fallow, early tillage, ridging, and intercropping. Tree and shrub planting at the base of terrace walls is an optional measure with the aim of stabilising the walls, diversifying production and again ensuring a good microclimate. On average 250 trees/ha are planted; these are mainly native species such as c’olle (Buddleia spp.), mutuy (Cassia sp.), molle (Schinus molle: the ‘pepper tree’) and various fruit trees including capulí (Prunus salicifolia).
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
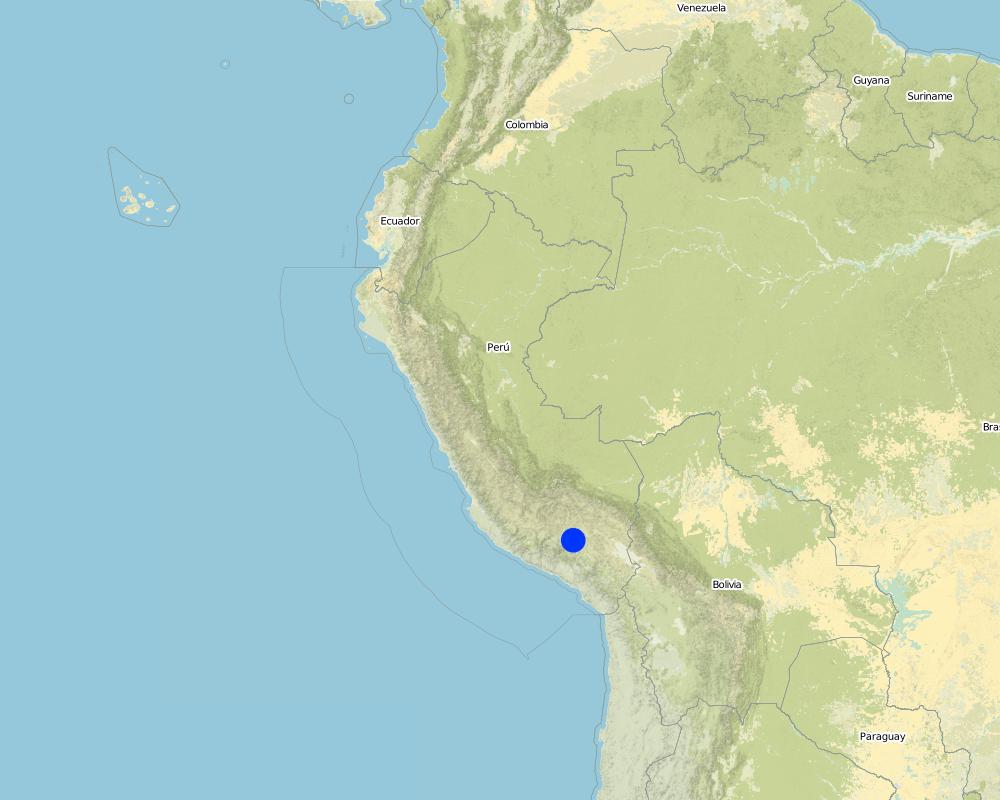
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Pérou
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Río Colca,Caylloma, Arequipa
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 100 km2.
Map
×2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- créer un impact économique positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - maïs
- cultures fourragères - luzerne
- légumineuses et légumes secs - fèves
- plantes à racines et à tubercules - pommes de terre
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: Dec - Apr

Pâturages
Pâturage intensif/ production fourragère :
- Affouragement en vert/ zéro-pâturage
Commentaires:
Main crops (cash and food crops): Major food crop: Potatoes, maize,beans, etc
Main animal species and products: Alfalfa (cut and carry)
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): - Loss of productive capacity: 30% of the agricultural land lost due to degraded terraces, severe deforestation (through
cutting for fuelwood), overgrazing and burning of grazing areas.
- Inefficient irrigation practices (flooding) due to poor maintenance of irrigation system (and drainage system in poor
condition), flood irrigation leads to deterioration of terraces.
- Loss of traditional knowledge of ancestral crop management practices (abandonment of appropriate rotation practices, lack of residue incorporation/recycling, unsystematic crop layout).
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Commentaires:
Water supply: mixed rainfed - irrigated and rainfed
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- mesures en travers de la pente
- gestion de l'irrigation (incl. l'approvisionnement en eau, le drainage)
- dérivation et drainage de l'eau
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S1: Terrasses
Commentaires:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)

dégradation hydrique
- Ha: aridification
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Ha: aridification
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
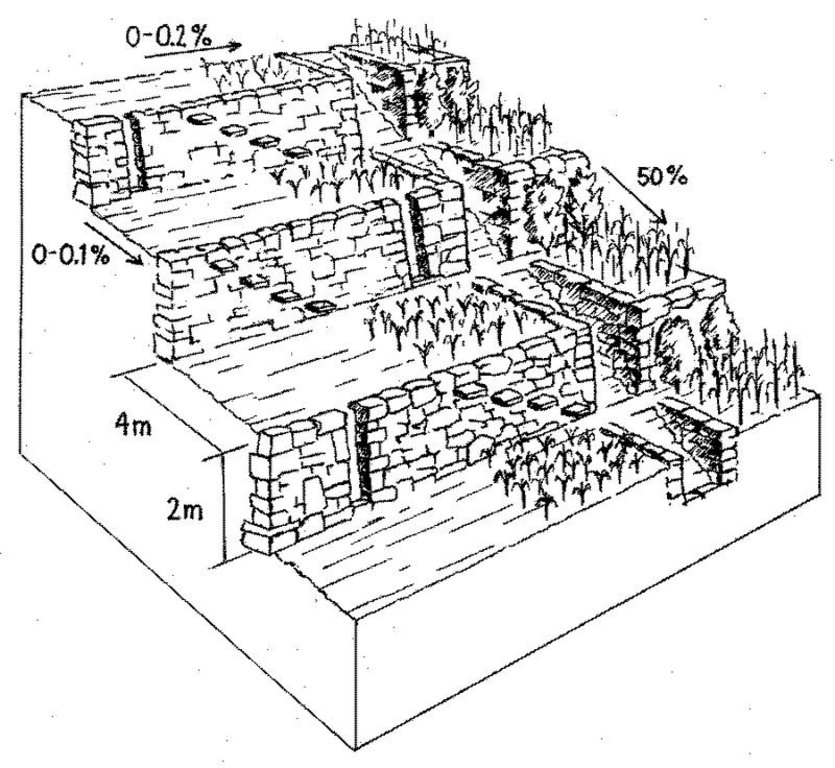
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Rehabilitated ancient terraces with high stone risers. Two options for irrigation and drainage of excess water are shown: outlets in the risers (left) and a broad water channel cutting perpendicularly through the terraces (right).
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply, improvement of microclimate
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, increase in organic matter, increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, improvement of soil structure
Auteur:
Mats Gurtner
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Separation of materials of collapsed wall: subsoil, topsoil, stone, weeds. | dry period. |
| 2. | Cleaning and re-establishment of the foundation according to originalstructure. | dry period. |
| 3. | Cutting stones from rocks (blasting and splitting); transporting. | dry period. |
| 4. | Reconstruction of the stone wall, building on the basis of remainingintact structures of ancient terraces; simultaneous reconstructionof irrigation channels and complementary structures. | dry period. |
| 5. | Backfilling with subsoil, moistening soil and consolidation with motor | dry period. |
| 6. | Covering with fertile topsoil. | dry period. |
| 7. | Levelling of terrace bed and completion of riser edge (lip). | dry period. |
| 8. | Planting of trees below terrace walls (optional). | dry period. |
| 9. | Improved fallow, early tillage, ridging, and intercropping (supportivemeasures). | dry period. |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 560,0 | 560,0 | 40,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Construction supervisor (days) | ha | 1,0 | 60,0 | 60,0 | |
| Equipements | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 180,0 | 180,0 | 40,0 |
| Equipements | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | 40,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Stone | ha | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | 40,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 1400,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 1400,0 | |||||
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Irrigation system cleaning. | |
| 2. | Clearing weeds from stone wall | (dry season)./ |
| 3. | Inspection of the stone walls’ stability | (before sowing)./ |
| 4. | Repair structures | (rainy season)./ |
| 5. | Tree and root pruning. |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 125,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 125,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: A-frame,tape measure,motor drill,wheelbarrow,shovel,pick,steel bar,sledgehammer,hoe,hand compressor.
Person days needed for rehabilitation of 1 ha of ancient terrace system depend on degree of deterioration, the dimensions of the wall, slope angle (the steeper the more terraces) and availability of stones. In the case of the project, under a typical situation, for physical rehabilitation of 1 ha with 6 terraces, each ca 600 m long, 3–4 m wide and 2 m high, with one third of the main structures in disrepair, 18 men and 7 women work for 5 days; shrub planting is extra. Land users bear 35% of the overall costs: they also provide food for the group during work. The programme pays the rest. 450 m3 of additional stones are required to repair the broken parts, the cost includes blasting/splitting rocks and transport to the construction site.
Supportive agronomic measures and agricultural inputs (seeds and manure) are not included. Maintenance costs vary considerably, depending on the specific situation: an average is taken here.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Landforms: Also hill slopes (ranked 2) and footslopes (ranked 3)
Slopes on average: Also hilly (ranked 2) and rolling (ranked 3)
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility: Medium (ranked 1, used for maize) and low (ranked 2)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (low recycling of organic matter)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Off-farm income specification: main source is wage labour in the valleys
Market orientation of grazing land production system: Subsistence (ranked 1) and mixed (ranked 2, 30% for market)
Market orientation of grazing land production system: Subsistence (ranked 1, complementary to crop production) and commercial/market (ranked 2, income generation to meet basic needs)
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Commentaires:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Also 2-5 ha (ranked 3)
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, sans titre de propriété
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- loué
- individuel
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Average 30%
gestion des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Careful management required (water and livestock)
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Easier crop management (level bench, alignment of crops). On the other hand increased labour constraints: heavy work, const. Maintenance. Heavy work by establishment
Autres impacts socio-économiques
Efficiency
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Efficient use of irrigation water and fertilizers
Input constraints
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Tools
Ccarcity of stones (in some places)
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
drainage de l'excès d'eau
Sols
humidité du sol
couverture du sol
perte en sol
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
diversité végétale
diversité animale
diversité des habitats
Autres impacts écologiques
Regular crop growth and development
Improved microclimate
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Reduced wind; conserving heat
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
flux des cours d'eau fiables et stables en saison sèche
inondations en aval
envasement en aval
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
240
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 11-50%
Commentaires:
90% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
2160 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
240 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption.
40% of terraces have been rehabilitated in 7 districts (8 micro-watersheds) of the Colca valley.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Facilitation of crop management activities (crop alignment, easier tillage with oxen plough, efficiency of pest control, etc) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Appropriate crop management (see measures mentioned in description). |
|
Improved microclimate facilitates crop growth and crop diversification How can they be sustained / enhanced? Complete with improved agronomic practices and agroforestry. |
|
Increased yields and food security How can they be sustained / enhanced? Conserve crop diversity and genetic variety. |
|
Cultural heritage How can they be sustained / enhanced? Conservation of traditional practices |
| Facilitation of crop management activities (crop alignment, easier tillage with oxen plough, efficiency of pest control, etc)-->Appropriate crop management (see measures mentioned in description). - Improved microclimate facilitates crop growth and crop diversification-->Complete with improved agronomic practices and agroforestry. - Increased yields and food security-->Conserve crop diversity and genetic variety Cultural heritage-->Conservation of traditional practices. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Traditional technology is of great value and adapted to local conditions How can they be sustained / enhanced? Awareness raising of the local population on maintenance of terraces. |
|
Successful implementation is product of evaluation, analysis and documentation of experiences How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further appraisal of the technology. |
|
Soil maintained on steep slopes, no soil loss due to water erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continuous maintenance and appropriate management through training. |
|
More efficient use of irrigation/rain water, longer storage of soil moisture How can they be sustained / enhanced? Permanent maintenance of structure. |
|
Maintenance of soil fertility How can they be sustained / enhanced? Recycling of organic matter. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Vulnerability of terraces to damage by grazing animals | Do not allow grazing on short terraces with high stone walls. |
| Land users are not skilled in repair of broken sections in the terrace system | More training on maintenance and conservation. |
| Vulnerability of terraces to damage by grazing animals-->Do not allow grazing on short terraces with high stone walls. - Land users are not skilled in repair of broken sections in the terrace system-->More training on maintenance and conservation. Editors’ comments: Terracing systems on hillsides date back to the beginning of agriculture. Often these feature walls (‘risers’) built of stone, and sometimes they are used for irrigation – as in this case from Peru. While many ancient systems have fallen into disrepair with out-migration of rural populations, this is an example of project-based rehabilitation. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
|
Specialised work, not easy to carry out – complex system of different structures |
Promote applied research and extension. |
|
High rehabilitation costs; increased by loss of traditional forms of reciprocal work, and a trend towards individualism |
Reactivate and strengthen traditional labour systems based on reciprocity and mutual help. |
| Limited availability of stones impedes the rehabilitation process |
Carry stones from adjacent or remote places, give training in rock splitting. |
| Not appropriate for use of agricultural machines | Awareness creation. |
| Private properties, but not titled |
Promote the legalisation of titles to facilitate the access to credit and technical assistance. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Mejia Marcacuzco AP Folleto de divulgación: Andenes, construcción y mantenimiento. (undated).
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Treacy, JM (undated) LasChacras de Coporaque: Andenes y riego en el valle del Colca. Instituto de Estudios Peruanos. DESCO
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Participatory catchment rehabilitation (Participación comunitaria para la rehabilitación … [Pérou]
Promoting the rehabilitation of ancient terrace systems based on a systematic watershed management approach.
- Compilateur : Philippe Zahner
Modules
Aucun module trouvé