Keeping natural riparian vegetation and stabilizing riparian with gabions at Naro Moru River [Kenya]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Manuel Fischer
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1570 - Kenya
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Cosmetic company:
Horsey John
Cinnabar Green Ltd.
Kenya
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - SuisseNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Cinnabar Green Ltd. (CG) - Kenya1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
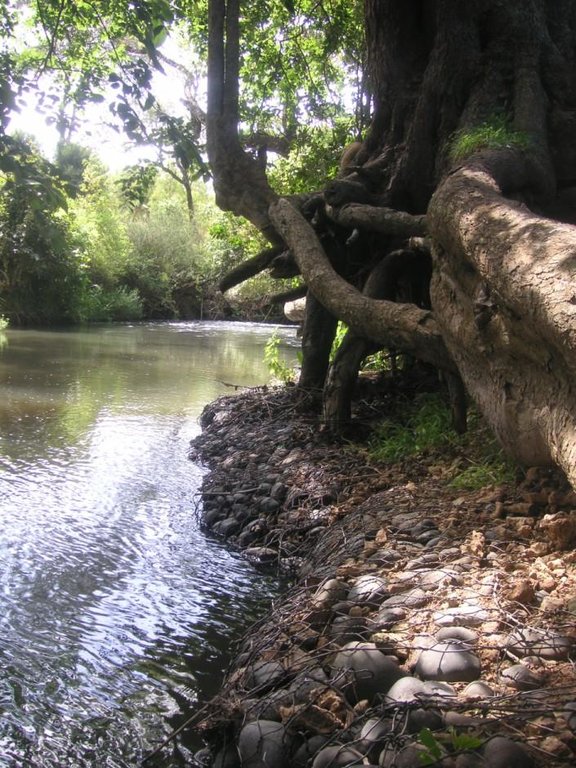
Structural riverbank protection by metal nets called gabion that are filled with stones
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
The studied land plot is situated in the semi-arid savannah zone of the Naro Moru sub-catchment at the foot of Mt. Kenya. A large-scale farmer owns a spacious land plot bordering Naro Moru River where he grows herbs and special plants to produce human care products. He rarely intervenes in the riparian area but is still interested in a good protection of water resources. Therefore, big stone control structures called gabions were installed to prevent big riparian trees from being undermined by water and destabilized by erosion. This method is cost intensive but can be applied locally for the protection of certain goods. The action was promoted by the Water Resource Users Association of the sub-catchment.
Purpose of the Technology: Despite semi-arid conditions, there is a high probability of flooding. Heavy rainfalls on upper slopes of Mt. Kenya lead to flood events in the semi-arid areas of Naro Moru River. These events have a destructive effect on the riverbanks, which have become instable by human induced activities such as overgrazing and deforestation. The instable riparian soils are eroded easily. The farmers lose their precious land and the water is polluted.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Big riparian trees are important for stabilizing the riverbed and riverbanks and for building a canopy that provides shade which enables the typical riparian conditions with its vast biodiversity. Thus, large metal nets (2x1x0.5 m) are filled with stones and placed in front of the roots to protect them from the direct current. These metal nets are called gabion and are placed at especially prone places. This structural measure contributes to mitigate or even stop riverbank degradation. High efforts are required to establish gabions. The costs for the metal net amount to 80 US-Dollar per net. Additionally, workforce must be found to fill the nets with stones from the river. Once installed, they ensure a good local protection. They are also used to protect bridge pillars. The life expectance of a gabion net is about 20 years if not destroyed by extreme events.
Natural / human environment: The plot is situated on a plateau at the western side of Mt. Kenya. There is not the same amount of precipitation as at the foot slopes of Mt. Kenya. However, the area still benefits from the runoff that is generated on the mountain. Precipitation in the so-called savannah zone ranges from 600mm to 900mm per year. Due to the high evaporation, rain-fed agriculture is only partly possible. Therefore most land users depend on irrigation using river water.
During the last decades, the region has experienced a still continuing population growth which increases population pressure in the area and removal and use of the vegetation along the rivers. The good accessibility and the moderate tourism allow even off-farm income-generation.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Kenya
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Kenya/Central Province
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Nyeri/Naro Moru
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, précisez la superficie couverte (en km2):
2,15
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Commentaires:
The riparian length as the crow flies is 2.15 km.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- au cours d'expérimentations / de recherches
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The WRUA talked to the farmer who introduced the technology
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire les risques de catastrophes
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 60 Longest growing period from month to month: april to may Second longest growing period in days: 60 Second longest growing period from month to month: october to november

Forêts/ bois
- Forêts (semi-)naturelles/ bois
Forêts (semi-)naturelles/ terres boisées: précisez le mode de gestion:
- Utilisation de la forêt non liée au bois
Produits et services:
- Pâturage/ broutage
- Conservation/ protection de la nature
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Due to the decreasing river flows, the riparian vegetation is being diminished.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Big riparian trees are threatened because of being undermined by water. The canopy and the roots of the trees are a vital component of the riparian habitat.
Other type of forest: Preservation
Forest products and services: grazing / browsing, nature conservation / protection
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion des eaux de surface (sources, rivières, lacs, mers)
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S6: Murs, barrières, palissades, clôtures

modes de gestion
- M2: Changement du niveau de gestion / d'intensification
Commentaires:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: management measures
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wr: érosion des berges

dégradation biologique
- Bh: perte d’habitats
- Bs: baisse de la qualité et de la composition/ diversité des espèces

dégradation hydrique
- Hp: baisse de la qualité des eaux de surface
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wr: riverbank erosion, Hp: decline of surface water quality
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bh: loss of habitats, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Main causes of degradation: over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.), floods, population pressure
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
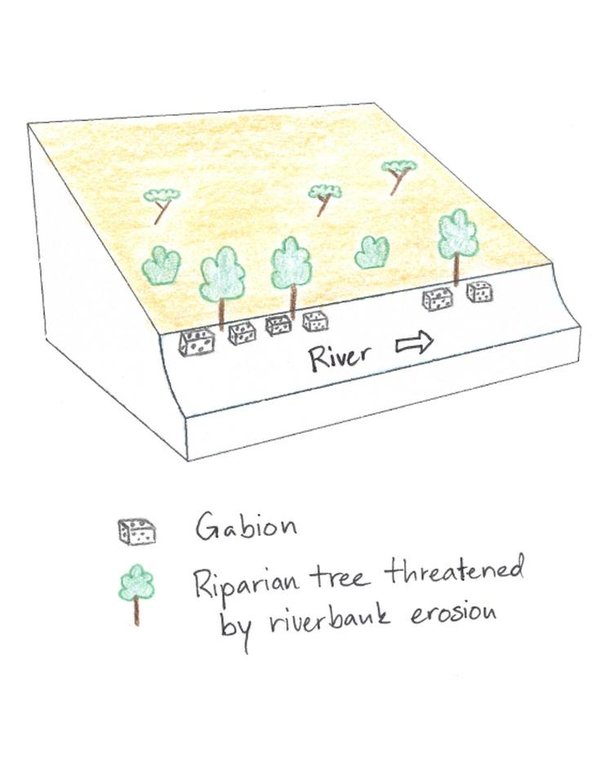
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
In the Savannah zone large riparian trees are threatened, thus gabions are used to protect them and to sustain the canopy. The gabions are applied at the roots of the riparian trees to protect them from the erosive power of the stream.
Location: Irioko. Nyeri / Central Province
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), stabilisation of riverbank
Secondary technical functions: sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Wall/ barrier
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Construction material (stone): Stones are collected directly in the riverbed.
Other type of management: The farmer protected his riparian zone with a fence.
Auteur:
Manuel Fischer
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par entité de la Technologie
Précisez l'unité:
Gabion
Précisez les dimensions de l'unité de terrain (le cas échéant):
2x1x0.5 m
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Kenyan Shilling
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
90,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
2.70
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Installing and filling the metal wire with stones | during dry season |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Installing and filling the metal wire with stones | Persons/day | 2,0 | 3,0 | 6,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Wire | piece | 1,0 | 80,0 | 80,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 86,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 0,96 | |||||
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Control of the gabion nets | |
| 2. | Control of fences |
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The price for the metal wire is the most cost determinant factor.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitudinal zone: 1870 m a.s.l.
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
< 5 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
bonne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
faiblement potable (traitement nécessaire)
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Availability of surface water: Just along the river, deeper ground water level 50-100m
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- élevé
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- commercial/ de marché
Revenus hors exploitation:
- > 50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- très riche
Individus ou groupes:
- employé (entreprise, gouvernement)
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
1% of the land users are very rich and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: The land owner has a company that produces oils and herbs for care products. The company produces in a organic way and preserves the environment.
Market orientation of production system: Conservation/Preservation (But company produces care products for worldwide shipping)
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- grande dimension
Commentaires:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Also 15-50 ha for cropland
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- entreprise
- individu, sans titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- accès libre (non organisé)
- communautaire (organisé)
Commentaires:
The land owner has a company that produces oils and herbs for care products. The company produces in a organic way and preserves the environment.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
surface de production
Impacts socioculturels
institutions communautaires
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
This was not mentioned by the interviewee, but seems to be the case
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Livelihood and human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The discussions about water conservation increase education. Also, the dialogue between farmers is improved.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
qualité de l'eau
ruissellement de surface
nappes phréatiques/ aquifères
Sols
humidité du sol
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
diversité végétale
diversité animale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
monkeys
diversité des habitats
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
impacts des inondations
Autres impacts écologiques
Riverbank degradation
Preservation of canopy
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
flux des cours d'eau fiables et stables en saison sèche
envasement en aval
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | bien |
| tempête de vent locale | bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
légèrement positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Commentaires:
The establishment costs are quite high.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- cas isolés/ expérimentaux
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
1 landowner
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 91-100%
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The costs are too high for an average farmer to adopt the technology.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Ensuring an intact environment to guarantee the organic origin of the company products. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Control that the riparian area is not being polluted or destroyed. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Conservation of the unique riparian habitat How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continue the protective measures and hinder negative intervention in the riparian area. |
|
Through the environmental activities, the acceptance of the company increases. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular interaction improve neighborly relations. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The implementation of the gabions is very cost-intensive. | Alternatives should be checked out. |
| The origin of the vegetation decline, the decreasing river flow, is not being combatted. | Water abstractions in the upper reaches should be diminished. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé