Selective forest clearing to prevent large forest fires [Espagne]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Nina Lauterburg
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Alexandra Gavilano, Deborah Niggli, Hanspeter Liniger
Clareo selectivo para la prevención de incendios (tratamientos selvícolas) (Spanish)
technologies_1586 - Espagne
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Valdecantos Alejandro
Fundación Centro de Estudios Ambientales del Mediterráneo (CEAM)
Espagne
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Catastrophic shifts in drylands (EU-CASCADE)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Centro de Estudios Ambientales del Mediterraneo (CEAM) - Espagne1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
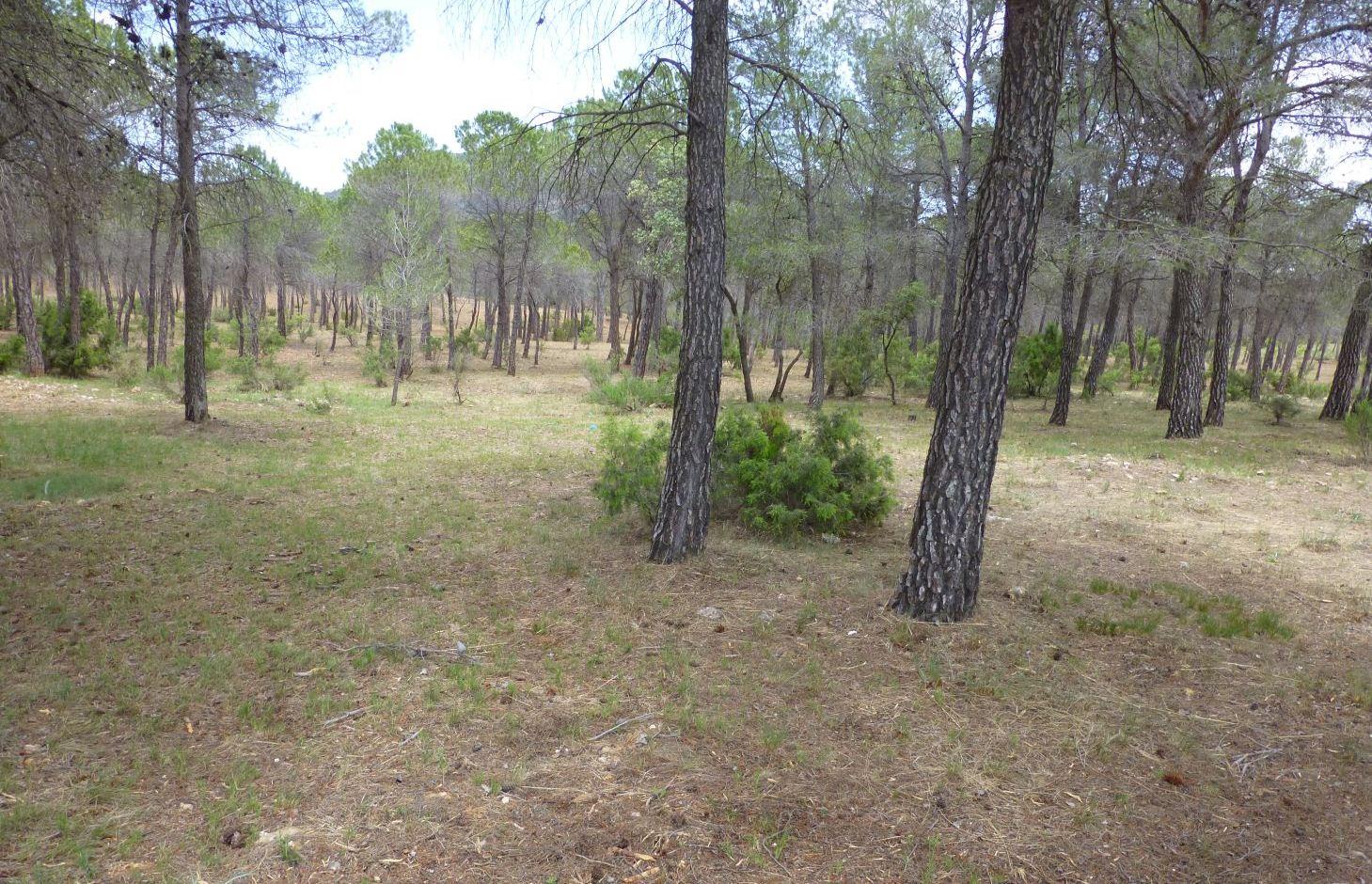
Selective forest clearing aims in reducing the connectivity and the amount of (dead standing) fuel, as well as reducing the competition between regenerating pines, in order to prevent forest fires and to ensure the growth of a healthy forest.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
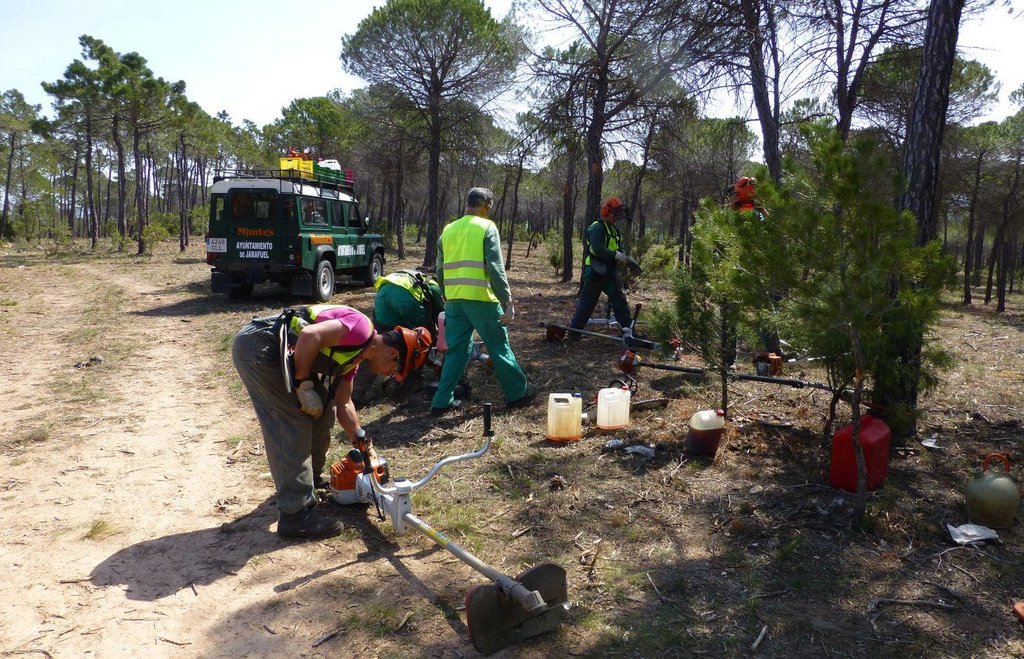
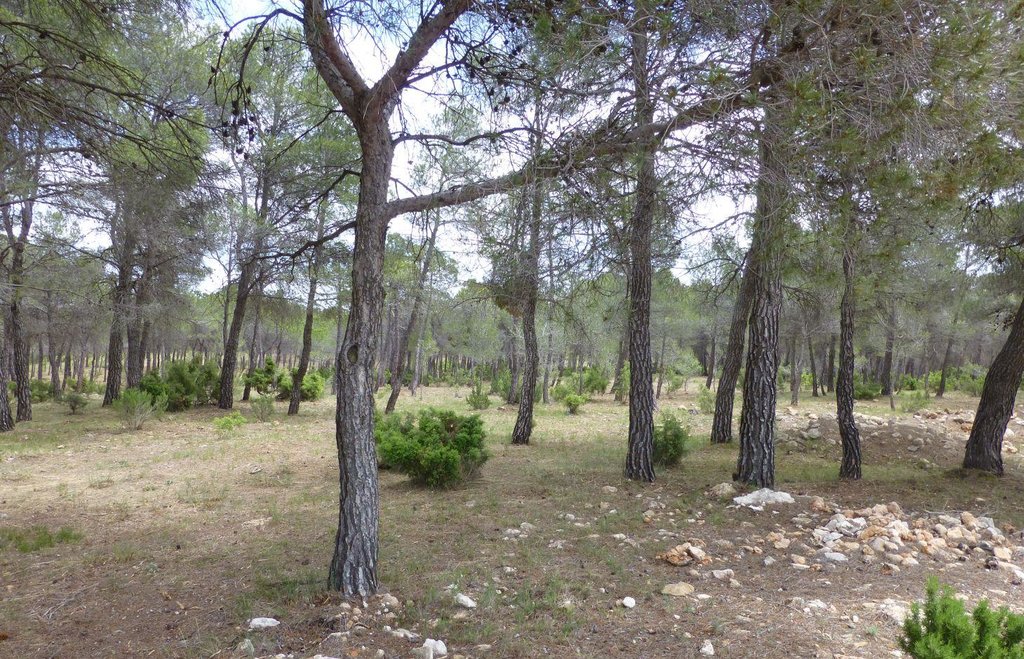
The forests in the Ayora region experienced a huge disturbance in the past, such as deforestations, removal of key species, land abandonment, dense growth of fire-prone seeder species (high continuity of dead standing fuel), missing management, wildfires and dense afforestations. These disturbances resulted in the degradation of the vegetation, the reduction of the resilience of the ecosystem against fires and thus an increasing risk of wildfires. After fires, many landscapes regenerated with a high and continuous fuel accumulation with few native resprouter species, which made it extremely difficult to control forest fires. The dense growth not only increased the risk of wildfires but also the competition between different species (nutrients, light, space). Therefore appropriate vegetation management to increase the resilience of the ecosystem to fires and to reduce competition is crucial.
These problems are approached by selective forest clearing. The main purposes of thinning dense pine forests are the prevention of fires by reducing the fuel load and its continuity, and to improve pine regeneration by eliminating the competition between different species. As a result, the quality of the plants is improved and the amount of dead or sick plants is reduced, which is essential to ensure a healthy forest. This also leads to a higher resistance to pests which in turn again decreases the risk of fire (less dead plants). Vegetation removal produces fresh vegetation growth, therefore more diverse and nutritious fodder is provided to animals (game and livestock) in the cleared areas which is a benefit for herders. Also wild animals use this fodder supply which in turn hinders them to destroy cultivated fields of the farmers. Furthermore, honey producers make use of the enhanced growth of shrubs and the additional space created by selective clearing to place their beehives and to increase honey production.
Especially during the current economic crisis forest management is an important source for jobs - most of the workers were unemployed before working in the selective clearing. Through the clearings, fuelwood is gained and offered to retired people for free for cooking and heating, allowing them to save money. Additionally, almost all villagers like to have a cleared forest due to its high aesthetic and recreational value.
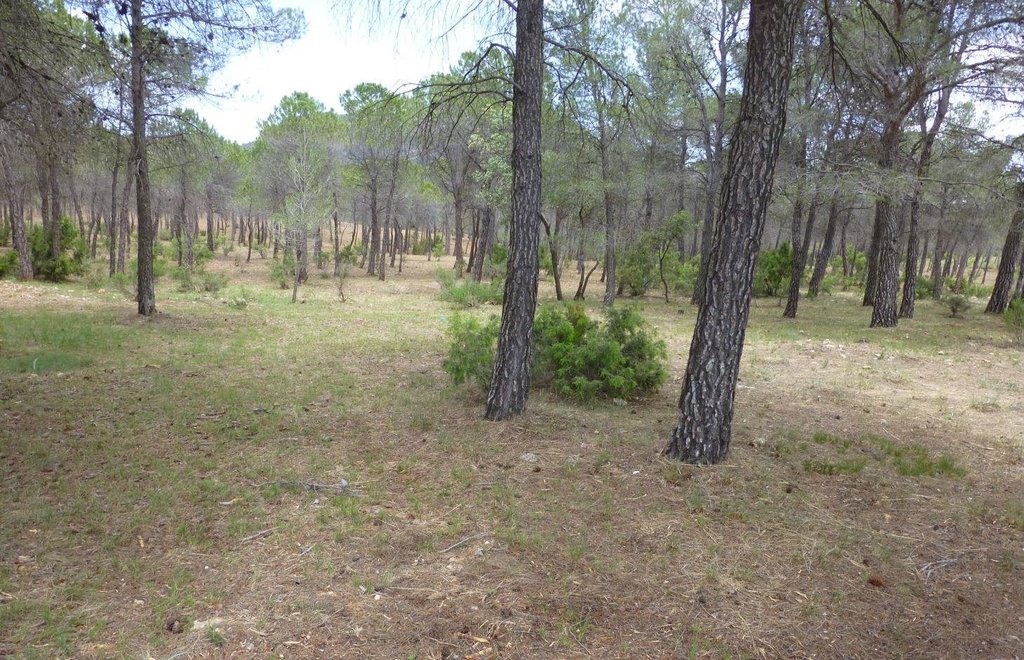
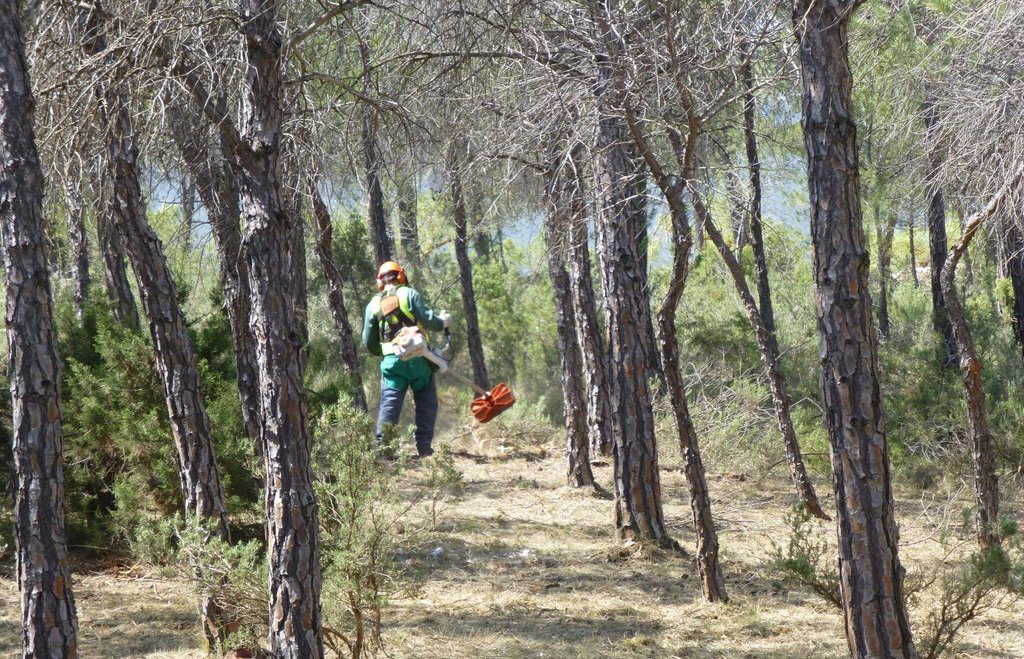
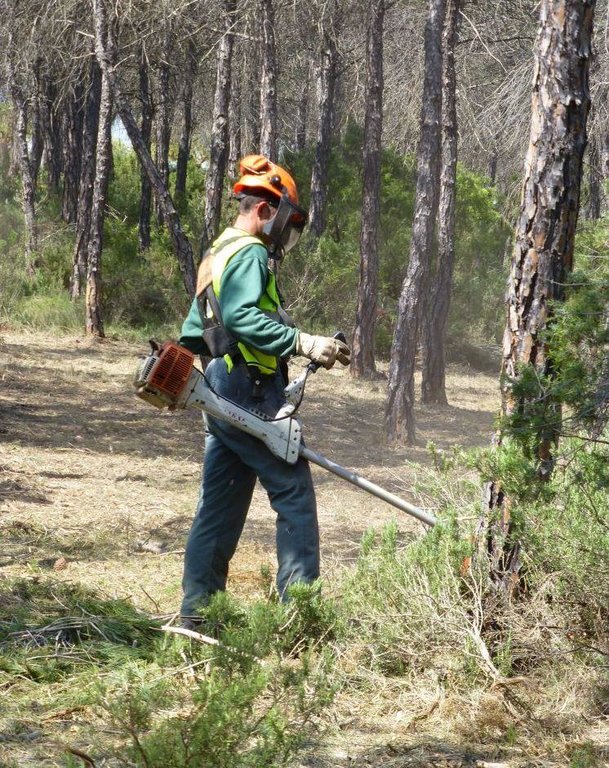
In order to be selective and to preserve desired species, the clearing is done with small machines such as brushcutters and chainsaws. On average the forest is thinned until reaching a density of 800-1200 trees/ha. Species such as Juniperus, Rhamnus al., Quercus rotundifolia, Quercus faginea or Fraxinus ornus are not removed which increases the probability to have a more fire-resistant vegetation composition in future. Dead or sick plants and also a part of fire-prone shrubs such as Ulex parv. and Cistus alb. are removed. If there are both Pinus pinaster and Pinus halepensis. Pinus halepensis is cleared because they compete with each other. The roots are not removed which ensures the stability and productivity of the soil. The remaining species are pruned (“poda”) until a maximum height of 2.5m to improve the conditions of the species. Around each tree they should clear an area of 2m.
After felling trees and shrubs a part of the residues is chipped in-situ and covers the soil as mulch, which results in ecological benefits (e.g. increase in soil moisture, prevention from erosion, enhancement of nutrient cycling, reduction of the soil surface temperature).
If the slope is steep, it takes more time to do the clearing and it might also increase the risk of erosion afterwards. Under the best conditions (e.g. good access and terrain), 0.8ha per day are cleared (calculated for a group of 9 persons working 7 hours). In this case the costs are paid by the municipal council, which receives a part of the money from the rental fee paid by the wind mill company. The cleared areas have to be maintained depending on the speed of the vegetation growth (which amongst others depends on the soil, slope and humidity). If the clearings are done regularly, it takes less time and it is cheaper than the first clearing. It should be noted that recurrent maintenance is crucial to ensure the effectiveness of the technology.
The region of Ayora is mountainous with a dry subhumid climate (~380 mm annual rainfall). The risk of fire incidence is at its highest from June to September when there are adverse conditions like drought, high temperatures and strong winds (mainly the winds coming from central Spain, called “poniente”). The population density is very low and there are only few job opportunities (e.g. marginal agriculture, grazing, hunting, beekeeping). Most of the inhabitants work in the nuclear power plant. Forest management could be a source for jobs.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Espagne
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Spain, Valencia
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Ayora/Jarafuel
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- 0,1-1 km2
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.5 km2.
The forest agent told me that during this project they are clearing some 50 ha of forest. But in total (including the clearings in the past) they cleared more than 1000 ha in Jarafuel.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The clearings documented here were done in the years 2012 and 2013, mandated by the state and executed by the municipal council of Jarafuel. But already in 1990 clearings (with machines) were applied. At that time they were called “ayuda regeneración” which means regeneration help.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire les risques de catastrophes
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Forêts/ bois
- Forêts (semi-)naturelles/ bois
Type d’arbres:
- Espèces de Pinus (pin)
Produits et services:
- Bois d'œuvre (de construction)
- Bois de chauffage
- Fruits et noix
- Autres produits forestiers
- Pâturage/ broutage
- Conservation/ protection de la nature
- Loisirs/ tourisme
- Protection contre les aléas naturels
- wind mill parc, hunting
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The prevalent dense shrublands (dominated by seeder species), which resulted from past agricultural land use (changes of the vegetation composition, e.g. removal of key species), land abandonment/rural depopulation and fire occurrence, contain a high fire risk because of both the high fuel loads and their continuity. Also dense forests (either afforestations or natural regeneration) show a high risk for fires. Through the modifications of the vegetation composition in the past (removal of more fire resistant resprouter species, whereas fire-prone seeder species are abundant), the resilience of the ecosystem to fires has decreased. Today a higher fire recurrence can be observed which could still be worsen by future climate change impacts, undermining more and more the ecosystem’s capacity to buffer such shocks. Furthermore, the high density of the forest results in a competition between different species which increases the amount of dead or thin material.
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: As a management practice. The forest should be cleared more frequently since there is a huge amount of fuel.
Plantation forestry: Almost the whole forest in this region was planted.
Trees/ shrubs species: Trees and shrubs are cleared (e.g. Ulex parviflorus, Cistus albidus, some pines)
Other species: Not removed species: e.g. Juniperus, Rhamnus alaternus, Quercus rotundifolia, Quercus faginea
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Oui (Veuillez remplir les questions ci-après au regard de l’utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie)
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Non

Forêts/ bois
- Forêts (semi-)naturelles/ bois
Forêts (semi-)naturelles/ terres boisées: précisez le mode de gestion:
- Coupes sélectives
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- réduction des risques de catastrophe fondée sur les écosystèmes
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques végétales
- V3: Défrichement de la végétation
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation biologique
- Bh: perte d’habitats
- Bf: effets néfastes des feux
- Bs: baisse de la qualité et de la composition/ diversité des espèces
- Bp: augmentation des insectes nuisibles (ravageurs)/ maladies, baisse des prédateurs
Commentaires:
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Deforestation in the past (removal of resprouter species), land abandonment, uncontrolled growth of fire prone vegetation, afforestations, forest fires), population pressure (Vast areas were deforested in the past for agriculture, important key species were removed. After land abandonment there was a lack of management strategies.), poverty / wealth (The current economic crisis in Spain leads to a lack of investment in forest management, therefore only a minor part of forests is managed by selective clearing.), labour availability (In the past there was outmigration from the region to the big cities and therefore there was a lack of management.)
Secondary causes of degradation: change of seasonal rainfall (More variability in precipitation leads to a higher risk of fires.), droughts (more fires during droughts), land tenure (The state is only allowed to apply management practices in public forest. The private forest is often not managed which increases the risk of fires and the resulting degradation.), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (There were big fires in the past because of the lack of fire extinction media like water ponds, streets, transport media (this has been improved now).), education, access to knowledge and support services (Loss of knowledge, important for today’s fires: People (especially from the cities) are not aware anymore of the risk of fire. In the past people lived with the risk and knew how to prevent fires.), governance / institutional (Law to induce implementation of conservation interventions (ley forestal 3/1993) and “plan de selvicultura preventiva de incendios en los sistemas forestales de Valencia (1996)”. Before less practices)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
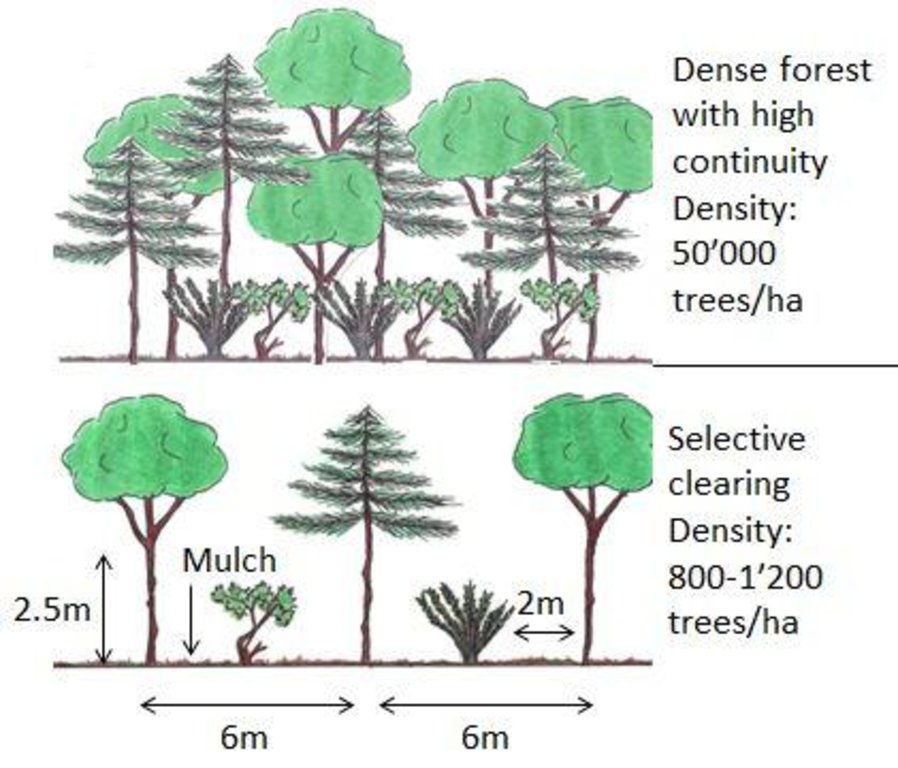
The main purposes of thinning dense forests (some 50’000 individuals per ha) are the prevention of fires by reducing the fuel load and its continuity (both vertical and horizontal), and to improve regeneration by eliminating the competition between different species. On average the forest is thinned until reaching a density of 800-1200 trees/ha. Species such as Juniperus, Rhamnus al., Quercus rotundifolia, Quercus faginea or Fraxinus ornus are not removed which increases the probability to have a more fire-resistant vegetation composition in future. Dead or sick plants and also a part of fire-prone shrubs such as Ulex parv. and Cistus alb. are removed.
The remaining species are pruned (“poda”) until a maximum height of 2.5m to improve the conditions of the species. Around each tree they should clear an area of at least 2m but ideally there should be a distance of 6m between different individuals.
After felling trees and shrubs a part of the residues is chipped in-situ and covers the soil as mulch, which results in ecological benefits and provides fodder to livestock and game.
Location: Ayora/Jarafuel. Valencia, Spain
Date: 08-12-2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (The forest agent needs a high technical knowledge. He acts as a link between engineer and forest brigade and controls if the brigade executes what the engineer dictates. He also provides assistance.)
Technical knowledge required for forest engineer: high (The forest engineer works for the state and plans the clearing project, therefore he needs a high technical knowledge.)
Technical knowledge required for forest workers/brigade: low (The forest workers only execute what the engineer and the forest agent tell them. They need to know how to handle the machines but don’t have to judge which trees and shrubs need to be cleared.)
Main technical functions: control of fires, reduction of dry material (fuel for wildfires), reduction of fire-prone species
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Vegetative measure: selective vegetation clearing
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Trees/ shrubs species: Trees and shrubs are cleared (e.g. Ulex parviflorus, Cistus albidus, some pines)
Other species: Not removed species: e.g. Juniperus, Rhamnus alaternus, Quercus rotundifolia, Quercus faginea,
Auteur:
Nina Lauterburg
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Euro
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
0,74
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
47.00
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cutting and chipping (in-situ) of trees and shrubs (selective clearing) | autumn/winter, in this case late spring (end of may) |
| 2. | Transport of wood (fuel wood) | after clearing |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | labour | ha | 1,0 | 404,0 | 404,0 | |
| Equipements | machine use | ha | 1,0 | 2024,0 | 2024,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 2428,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 3281,08 | |||||
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cutting and chipping (in-situ) of trees and shrubs (selective clearing) | autumn/winter, in this case late spring (end of may) |
| 2. | Transport of wood (fuelwood) | after clearing |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipements | machine use | ha | 1,0 | 446,0 | 446,0 | |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 446,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 602,7 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: brushcutters, chainsaws, tractors
The costs were calculated for the application of the technology (selective clearing) on one hectare. In this case, 9 people are working as a team. If the site is accessible and if the terrain is good for clearing work they can clear 0.8 ha per day. It should be noted that clearing with small machines such as brushcutters and chainsaws is much more expensive than clearing with tractors, but often it is only possible to clear with small machines (e.g. removal of trees is not possible with tractors). A tractor costs more or less 500 Euro per ha (674 Dollar per ha). A clearing of a pine forest with manual machines costs around 1800 Euro per ha (2428 Dollar per ha). The costs of the maintenance activities (e.g. second clearing) are much lower because the area was cleared already some years before. Therefore more ha per day can be cleared.
In Jarafuel, a part of the costs are covered by the rental fee paid by the windmill company.
The currency rate (Euro-Dollar) was calculated on November 16th, 2013.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The costs of selective forest clearing can be affected by numerous factors, such as slope (if the slope is steep, the work is much more difficult and takes more time), vegetation density (it takes more time to clear a dense area) and vegetation type (pine forest or shrubland), distance from a street (people can work less in a day if they have to walk far to clear). Important to note is that maintenance costs could increase with an increase in rainfall because the vegetation will grow faster.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Ayora, Jarafuel (Ayora: 383mm)
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
> 50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
faible/ absente
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Individus ou groupes:
- employé (entreprise, gouvernement)
Genre:
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Yes, the work is mainly done by men, because it is heavy work and it is not usual that women are working in the forest.
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative
Off-farm income specification: The forest brigade is only working when there is money and a project. If there is no money they have no work and need to look for another job.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
- public/open access but organised (e.g. wood, hunting)
- public/open access but organised (e.g. wood, hunting)
Commentaires:
There is some public land, controlled by the state. But there is also some private land. The access to the public land is open but organized. Permission is needed from the government to cut trees, to build a house or to hunt. There are some private hunting areas for which the hunting association has to pay a fee.
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production fourragère
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Vegetation removal produces fresh growth. More grasses available for animals (game and livestock) in the cleared areas.
qualité des fourrages
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The new growth provides more diverse and nutritious fodder Animals (especially goats) eat everything but they like more young grasses than shrubs
production animale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Game/wildlife and livestock are better because there is an increase in fodder quantity and quality
production de bois
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Production increases because there is less competition between species (nutrients,light,space). The wood/timber generated by the clearing can be used for biomass, fertilizers, pellets, firewood. A part of the wood is chipped in-situ and applied as mulch.
diversité des produits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Honey (bees can fly better), hunting, wood/timber
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
There are more opportunities to place the beehives
production d'énergie
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
A part of the cleared vegetation is used for bioenergy (biomass).
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Less damage on the cultivated fields because the wild animals do not destroy the fields anymore and stay in the forest (because there is more grass available due to clearings).
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
A cleared forest has a higher value–e.g. a “finca” with an exclusive right for hunting earns more because there are more animals (more fodder), or because it is easier to shoot animals (less possibilities to hide). Each killed animal has to be paid.
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The establishment and the maintenance is expensive because the work has to be done manually (manual machines)
Autres impacts socio-économiques
fuelwood
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Villagers of Jarafuel receive fuelwood gained by clearings for free (from municipal council).
job uncertainty
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
If there is no money provided by the state the clearings cannot be executed. This constitutes a high risk for forest workers because they never know if they will loose their jobs
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Forest workers earn money to buy food, otherwise they would depend on unemployment pay and thus put pressure on the state.
situation sanitaire
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Improved air quality by reducing forest fires
opportunités culturelles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
People appreciate the visual impact of a cleared forest. It has a high aesthetic value and offers recreational opportunities.
possibilités de loisirs
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
People appreciate the visual impact of a cleared forest. It has a high aesthetic value and offers recreational opportunities.
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Local people know about the importance of conservation of the area and really like to have the forest protected of wildfires
apaisement des conflits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Less fires result in a decrease of the destroyed area, less money will have to be invested in restoration or fire extinction. Farmers, hunters,honey producers will experience fewer losses. Wild animals remain in the forest (more grasses after clearing).
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
More jobs for unemployed, this is especially important during the current economic crisis
contribution to human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Through the clearings it is easier to control fires and protect people. Furthermore it created jobs for the unemployed. In general forest management is not something people want to do, they work in this sector only if there are no other job opportunities. Forest management means a hard job and this kind of work is not well-respected in society.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
évaporation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to the mulch layer more moisture is stored in the soil and less water is lost by evaporation (the soil is covered)
Sols
humidité du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
More soil moisture because of less dense forest/shrubland and mulch cover after clearing
couverture du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Mulch layer
encroûtement/ battance du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Mulch layer protects the soil from crusting
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
diversité végétale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
By clearing the competition between species is reduced but the forest agent told me that there are not more species, the same species grow again. But maybe there is more space for dispersal of seeds by birds.
diversité animale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
There might be more animals because of the fodder supply
contrôle des animaux nuisibles/ maladies
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Mono-plantations are bad for the propagation of a pest. After clearing there is a decrease in competition, plants are in healthier conditions,less prone to diseases.Weak plants are eliminated which reduces the risk of pests (always weak plants affected)
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
émissions de carbone et de gaz à effet de serre
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
less emissions because there is less burnt vegetation
risques d'incendies
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
By clearing the forest the vertical and horizontal connectivity of the vegetation is interrupted and the amount of fuel is reduced.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
inondations en aval
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
When fire removes less vegetation then the soil is less prone to flooding
envasement en aval
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
When fire removes less vegetation then the soil is less vulnerable to erosion
dommages sur les infrastructures publiques/ privées
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Forest fire frequency and intensity and the associated damages are reduced
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | bien |
| tempête de vent locale | bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | pas connu |
Commentaires:
The technology was not modified but it is important to add some notes to the above stated reactions to climatic extremes. The cleared areas are quite resistant against climate change or weather extremes. Only if there will be more rainfall the vegetation might grow faster and the maintenance costs could increase.
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
Both the short-term and the long-term benefits are very positive assuming that maintenance is done. It contributes to prevent devastating fires and to guarantee a healthy forest. Together with the creation of jobs, directly after clearing there is firewood and timber available and a reduced risk of wildfires. But it should also be considered that the establishment costs are high. If maintenance is not done the long-term returns will be very negative because an increase in the risk of fire will occur again (without management, there will also be no firewood, no timber and no jobs). The maintenance costs increase the longer you wait because the vegetation will grow again densely.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Commentaires:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The clearing is financed by the state (indirectly the clearings are partly paid by the local wind mill company through their rental fee).
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Clearings are only done when the state has money. Selective clearing is also applied in other countries/regions, e.g. in California.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| There are both social and economic benefits for local people. The selective clearings provide jobs for rural people, which allows them to increase their livelihood conditions. People do not depend on unemployment pays and are therefore more accepted in society. A part of the extracted wood is used for biomass, fertilizers, pellets, or firewood. Furthermore there would be improved conditions for grazing. Therefore forest management contributes to rural development. |
| There are also off-site benefits. Fewer fires will result in a reduction of downstream flooding, downstream siltation and damage on neighbours’ fields. When fire removes less vegetation the soil is less vulnerable to erosion. |
| In Jarafuel where most of the land is public retired people receive the firewood gained by forest clearings for free. They can use the wood for cooking and heating and save a lot of money. |
| Almost all villagers like to see a cleared forest. It has a high aesthetic and recreational value (it is possible to walk through the forest). They are also aware that the risk of wildfires is reduced through this technology. |
| Shepherds, hunters and farmers benefit from forest clearings. Vegetation removal produces fresh vegetation growth, therefore more diverse and nutritious fodder is available for animals (game and livestock) in the cleared areas. Game/wildlife and livestock are better because there is an increase in fodder quantity and quality. Wild animals benefit from this food source which in turn hinders them to destroy cultivated fields of the farmers. Also honey producers benefit from the cleared areas since bees can fly better and there is more place to put the beehives, furthermore the growth of shrubs is enhanced. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Through selective forest clearing the fuel amount and connectivity (vertical/horizontal) is reduced which is crucial for preventing the occurrence and spread of large forest fires. |
| There is a reduction of competition between plants which is essential to ensure a healthy forest (more nutrients, light, space). This also leads to a higher resistance against pests which in turn again decreases the fire risk (less dead or sick plants). |
| Fuel management through vegetation clearing presents some positive aspects with respect to other techniques, e.g. the possibility of being selective in order to preserve desired species or individuals. Furthermore, after felling trees and shrubs a part of the vegetation is chipped in-situ and covers the soil as mulch. This results in ecological benefits (e.g. increase in soil moisture, prevention from erosion, enhancement of nutrient cycling, reduction of the soil surface temperature and evaporation loss). |
| The trees/shrubs are cut but the roots are not removed. This ensures the stability and productivity of the soil. |
| Fewer fires result in a decrease of the destroyed area, less money will have to be invested in restoration or fire extinction. Furthermore, farmers, hunters and honey producers will experience fewer losses. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The establishment and the maintenance activities are expensive and labour-intensive. Without management the technology is not effective anymore. It would be necessary to extract biomass from the forest to decrease the continuity of the trees and shrubs. In case of a lack of management the risk of fires increases. | Management is crucial. Prevention measures are often less expensive than rehabilitation activities after a fire. The state should therefore invest more money in forest management and fire prevention. Managing the forest would not only decrease the risk of fire but also generate benefits (e.g. wood, biomass, fuelwood). Instead of getting unemployment pay people could get jobs in forest management. Stakeholders mentioned that it would be important to promote the forest as a sustainable economic resource and that the relation between the villagers and the forest should be enhanced. Furthermore it was mentioned that traditional activities (such as grazing, agriculture, wood gathering) should be reactivated and that the villagers should get economic compensation to maintain the forest in a good state. Especially the promotion of grazing was stressed many times. Also planting of more fire-resistant species (late successional stages) in some spots as suggested by CEAM could increase the resilience of the ecosystem and decrease management costs. |
| The clearing of forests has potential to prevent fires and therefore degradation. But there are also a lot of highly connected shrublands with a high fuel load which are not addressed by this management practice. | Shrublands need to be cleared as well since they constitute a huge risk for wildfires. |
| If there is more space after clearing the first shrubs which will grow will be fire-prone early successional species, such as Cistus albidus and Ulex parviflorus. Without management, they will increase the risk of fires. | Recurrent maintenance is crucial to ensure the effectiveness of the technology. Management through grazing could be a simple way to reduce the costs and the risk. By planting resprouter species really densely seeders would not grow anymore in those spots which would also decrease the fire risk and the management costs. |
| When the clearing is done on extremely steep slopes there might be an increase in erosion. | Before clearing the soil erosion risk should be calculated. |
| In some areas there will be less shade which could harm some species. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
11/05/2013
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé