Use of household ponds for garden irrigation and fish production. [Cambodge]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Christoph Kaufmann
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
ការប្រើប្រាស់ស្រះគ្រួសារសំរាប់ស្រោចស្រពច្បារដំណំានឹងការចឹញ្ចឹមត្រី (Khmer)
technologies_1627 - Cambodge
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Khun Lean Hak
SOFDEC/LAREC
Cambodge
1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Ponds are used at household level to raise fish as well as to irrigate vegetable gardens and rice seedlings
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
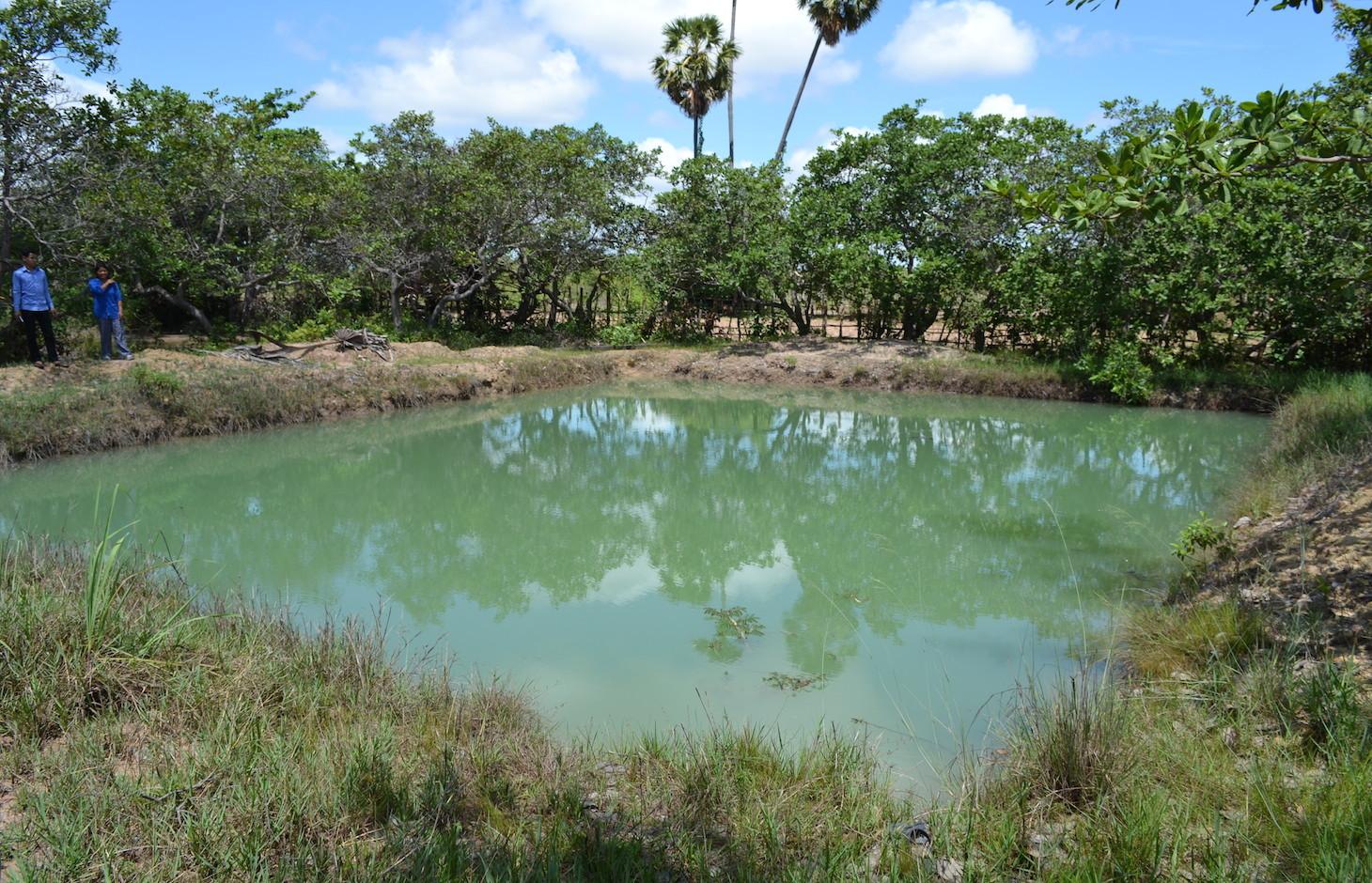
Wet-season rice is the predominantly grown crop in the area, but some land users also grow other crops (e.g. sweet potatoes, pumpkins, or peanuts). However, if droughts occur or if the rainfall patterns are erratic, the production can be harmed. Furthermore, due to the lack of water, the land users usually leave their fields bare during the dry season. This results in an increase of wind erosion and in negative impacts on the soil biota due to its exposure to the sun.
In order to tackle these challenges, ponds of 4 m depth (1 m deeper than the groundwater table during the dry season) are used at household level. By building ponds, some fields can be irrigated during the dry season, thus crops can be grown the whole year round. In this case study, sweet potatoes are the main cash crop grown on the irrigated fields during the dry season. The vines can be transplanted to the fields during the beginning of the rainy season, resulting in a better productivity of the crop. Peanuts and cucumbers are other cash crops grown on the irrigated fields.
Additionally, fish are introduced to the pond. These fish, which are caught during fishing for consumption in the flooded rice fields or nearby streams, increase the resilience of the land users: On one hand, they generate additional income and on the other hand, they allow the land users to eat fish the whole year round.
To build the ponds, the land users of this case study benefited from the road construction. The constructer needed soil, and offered to dig a pond for free if they could use the soil. They only dug 2 of the total 4 meters depth of the pond. The land users had to hire someone to dig deeper, as the groundwater level drops below 3 meters soil level during the dry season. The additional benefits from the pond, the fish are introduced as fingerlings when they are caught with the bigger fish. They are fed with termites (around 5 kg of termite nest each day) and with rice bran (1 kg every 3 days). As the pond is only 2 years old, the maintenance activities like digging out the mud did not have to be done yet.
The analysed area is flat (slope < 2%), tropic (dry and wet season), and the soils are mostly sandy or loamy. The soils contain little organic matter, the pH is sinking, the area has been deforested a long time ago and the groundwater table is rather high (1-2 m during the dry season, on the surface during wet season). and the groundwater table is rather high (3 m below soil level during the dry season, on the surface during the wet season).
Due to climate change, the rainfalls are more erratic, temperatures rise and droughts are more recurrent. Rice is the predominant crop grown in the area, since it serves as staple food (mix subsistence and commercial activities). Rice is often grown in monocultures and harvested once a year. Once the rice is harvested (dry season), some farmer release cattle to the paddy fields to eat the straw and weeds.
As an addition to rice, most land users grow vegetable and fruits in small home gardens (subsistence) and complement their income by producing handicrafts or through off farm income / remittances from family members working in other places. The increasing migration rate (the young generation leaves the villages to work in the cities, garment industry or abroad) results in a decrease of available labour force in the area which has detrimental effects on the agricultural activities. Furthermore, the civil war in the 1970s (Khmer Rouge) led to the loss of agricultural knowledge that different NGOs try to re-establish.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Cambodge
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Kampong Chhnang
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Roloer pha-er/Bantheay Preal/Tob Srauv (Village)
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Commentaires:
There are 4 ponds in the village. They are used to irrigate the rice seedlings if the rainy season starts with delay, or if there is a drought after the seeding. In the dry season they are used to irrigate vegetables. Total area of the irrigated fields is around 1 ha.
2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- grâce à l'innovation d'exploitants des terres
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The pond was built in 2012 by the land user.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- créer un impact économique positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- rice
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 210, Longest growing period from month to month: June to December

Voies d'eau, plans d'eau, zones humides
- Etangs, barrages, retenues d'eau
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Low soil fertility, lack of water during the dry season, more recurrent droughts due to climate change, leaving the fields bare after the rice is harvested which results in higher erosion and in the loss of soil biota, predominance of rice monocultures, low technical knowledge of the land users about land conservation measures.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Droughts, especially in the early rainy season. Rice seedlings need a reliable source of water.
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion de l'irrigation (incl. l'approvisionnement en eau, le drainage)
- gestion des eaux de surface (sources, rivières, lacs, mers)
- apiculture, aquaculture, élevage de volailles, de lapins, du ver à soie, etc.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S4: Fossés isohypses, trous
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation biologique
- Bq: baisse de la quantité/ biomasse

dégradation hydrique
- Ha: aridification
Commentaires:
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Mainly annuals with high water demand are planted.)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (Ploughing of soil, lack of water retention.), change in temperature (More hot days, drying up the soil.), change of seasonal rainfall (Beginning of rain season is unpredictable.), droughts (.Especially detrimental in the beginning of the monsoon.), education, access to knowledge and support services (A lot of agricultural knowledge was lost during the Khmer Rouge Regime.)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
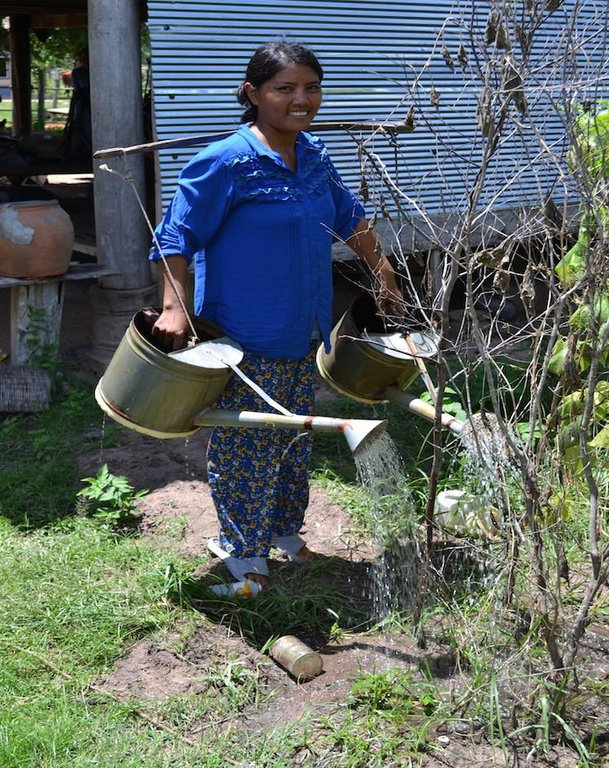
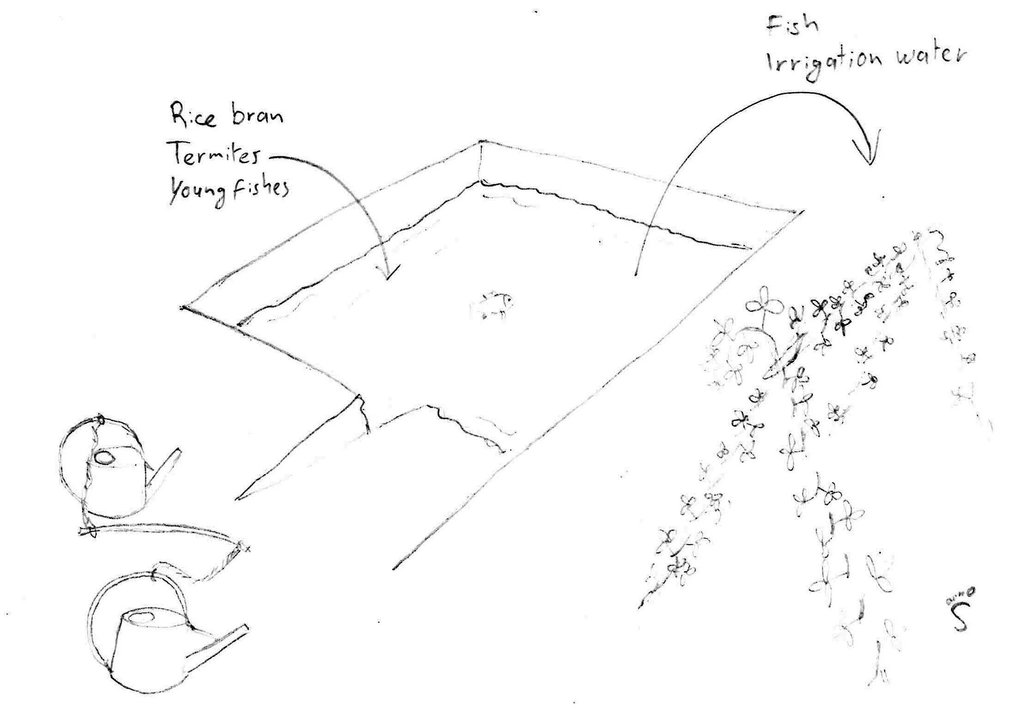
Pond used for irrigation as well as for fish production. In this case two watering cans are used, with a stick between them to transfer the weight to the shoulders.
Kampong Chhnang
Date: 2014
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (No field staff was involved.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Dam/ pan/ pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 4
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 12
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 18
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 800m3
Catchment area: ground waterm2
Auteur:
Stefan Graf, Switzerland
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
5.00
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Dig the first 2 m | Dry season |
| 2. | Dig the last 2 m | Dry season |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipements | machine use | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | 50,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 100,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 100,0 | |||||
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Catch and select fingerlings in the rice fields and canals. | Every year during wet season |
| 2. | Select fingerlings from catch in local streams to add in pond. | Every year during dry season. |
| 3. | Dig out the pond. Not yet done, as the pond is still new. | |
| 4. | Feed the fish with termites and rice bran. | Regularly. |
| 5. | Fertilize the pond | Yearly in the beginning of the wet season |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | labour | 1,0 | 134,5 | 134,5 | 100,0 | |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 134,5 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 134,5 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: Fishing traps. 1 costs around 1.2 US$. Fishing net, around 6.5 US$. They had them anyway to catch fish for consumption.
The costs were calculated for one pond, as the area is not relevant.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The most expensive factor is the availability of an excavator to dig the pond.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
1486.45 mm (2013) in Kampong Chhnang
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
Thermal climate class: tropics. 27-35°C
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
- faible (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
< 5 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
faible/ absente
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
faiblement potable (traitement nécessaire)
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Ground water table: during dry season
Availability of surface water: during dry season
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
- riche
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
Off-farm income specification: Handicraft, remittances, factory work
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- communauté/ village
- individu, sans titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- communautaire (organisé)
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- accès libre (non organisé)
Commentaires:
Land users have a title that is not recognized by the state.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
production animale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Fish
risque d'échec de la production
diversité des produits
surface de production
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
diversité des sources de revenus
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
contribution to human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Ponds allow the land user to grow crops the whole year round. Furthermore, there are fish in the pond which provide a reliable source of food.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
quantité d'eau
Sols
humidité du sol
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | bien |
| tempête de vent locale | bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- > 50%
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 0-10%
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
The farmer from this case study got a kind of subsidy: For the construction of the nearby road, the builders needed soil. They offered to dig a pond if they could get the soil. They only dug 2 of the 4 meters of the pond debt, the farmer had to hire somebody to dig out the rest. The other land users who have implemented the ponds also collaborated with construction workers to dig the pond. The lack of money hinders most of the farmers to implement the technology.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Water available in the dry season for cash crops. The rice fields can be used in the dry season instead of being left bare. |
| The rice seedlings can be irrigated during the early wet season in case of drought or erratic rainfall. |
| Diversification of diet and income: fish is available the whole year round. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| As parts of the rice fields are irrigated and planted during the dry season, there is less wind erosion and the soil is improving. |
| The fish feed (rice bran and termites) consists of local resources. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| If flooded the fish can go away. | Nets need to be put around the pond in the wet season. This farmer already does this. |
| Fingerlings are difficult to find. | Find a fish breeder, or breed fish by themselves. Creating niches in the ponds for the offspring, where the bigger fish do not eat it, could do the breeding. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Fingerlings of different sizes and species are put into the pond. The bigger eat the smaller. | Fence off areas for bigger fish, and move the big fish there so they cannot catch the smaller. Or build structures where the smaller fish can hide. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
07/07/2014
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Konhel Pith, Local Agricultural Research and Extension Centre LAREC in Kampong Chhnang; khonhel@gmail.com
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé