Improved Tree Nursery Bed [Ouganda]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Jalia Namakula
- Rédacteur : Kamugisha Rick Nelson
- Examinateurs : Drake Mubiru, Nicole Harari, Udo Höggel
Kayubu Kodi
technologies_2797 - Ouganda
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
exploitant des terres:
Oyet Julius
+256782165103 / +256752165103
Tudakatuba farmers group
Pajak village, Amuru District, Northern Uganda
Ouganda
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Uganda Landcare Network (ULN) - Ouganda1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
09/05/2017
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Improved fruit tree nursery is a technology comprising of grafted mangoes, grafted citrus, eucalyptus and pines, established with the aim of improving household income and promotion of agro-forestry farming systems within surrounding communities to achieve environmental conservation.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
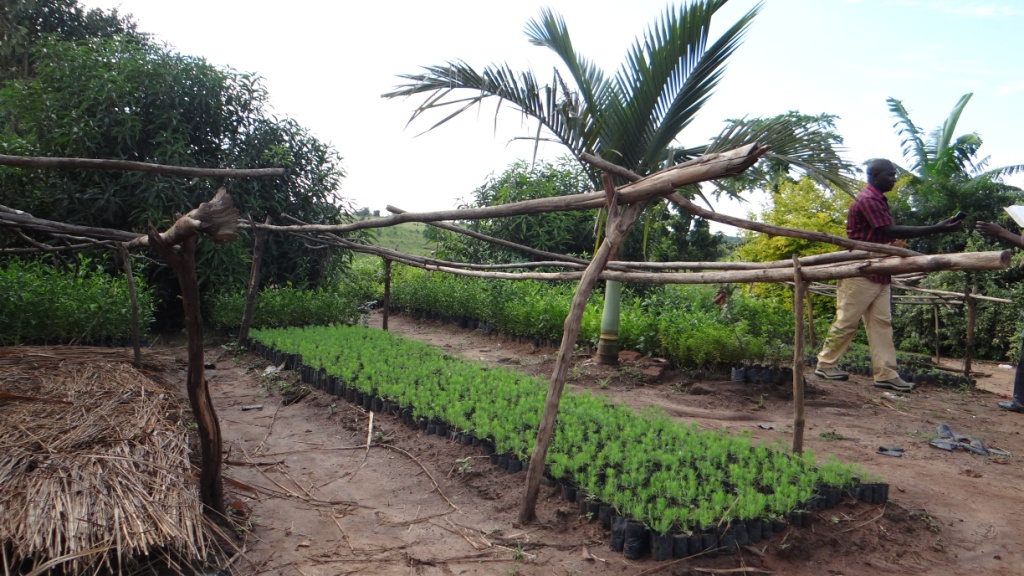
Tree nurseries are places where tree seedlings are propagated, managed, and grown to a transportable size. They are essential for producing quality seedlings in high quantities for rapid afforestation and sustainable land management.
In response to promoting this technology among farmers in Uganda, the Government of Uganda, through its initiatives such as Operation Wealth Creation (OWC), is promoting the growing of high value crops such as fruit trees to improve farmers’ incomes and food security. The technology is established on a gently sloping land lying on a plot of 1725 square meters, some 300 m away from a wetland used as a source of water for the nursery during the dry season. The soils here, on observation, have high clay content and are relatively deep.
The activities for establishing the nursery involved three stages:
1. clearing the bush on site, destroying all the termite mounds, ploughing the area, and levelling the mother beds established on flat or gentle rolling area to avoid water logging during the rainy season
2. preparation of the potting area and the potting medium which was done by mixing black soil with sand and manure in a ratio of 3-1-1 respectively. These activities took 2 person days to finish, followed by potting in 5cm × 12cm potting bags, taking 10 person days. The pots were then laid in a series of 1×10m long beds with paths of 0.75m between them. This activity took 2 persons days. Seeds were planted, watered and pots were covered with grass until germination after 14 days. After germination the seedlings are left for 4 months to mature until they are ready for grafting
3. grafting the then ready root stock with desired scion. The process involves cutting the root stock and scion at an angle and fitting the two together and holding them tightly with a wide plastic thread, the grafted seedlings are then placed in beds and placed in a closed housing unit with enough humidity only to be removed after 21 days. The seedlings are now placed again in rows where they are managed until ready for transportation
Maintenance activities included spraying fortnightly with pesticides and fungicides, watering with clean water twice every week, weeding and regular sorting of the seedlings to encourage proper growth. If any shade was put it is removed when the seedlings are well established to acclimatize them to open environmental conditions before they are transplanted or sold.
The tree varieties planted include improved mangoes, citrus, clonal eucalyptus and pines. Currently the nursery has over 10,000 citrus seedlings and 15,000 mango seedlings and a few seedlings of both pine and eucalyptus.
Tree nurseries are preferred by farmers because they use small land sizes, generate a lot of income, seedlings, when planted protect the environment and help in rapid production of genetically improved fruit trees in addition to offering employment to a wide spectrum of people including unskilled and skilled persons. There are notwithstanding, challenges such as lack of reliable water source and lack of skilled labor for grafting and high nursery establishment costs.
Limited market opportunities continue to be limiting factors to the tree nursery initiatives with the government being the only big buyer of tree seedlings in North Uganda.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.4 Vidéos de la Technologie
Date:
09/06/2017
Lieu:
Amuru District, Northern Uganda
Nom du vidéaste:
Isa Yiga
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Ouganda
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Northern Uganda
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Pajak village, Amuru District, Northern Uganda
Commentaires:
Coordinates: 2.812533 and 1.96157
The Nursery beds are s located in Pajak Village, Amuru District
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
2002
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
This practice was lean't from a fellow farmer in Mukono District, but technical support is provided by the Amuru local government.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- créer un impact économique positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres improductives
Précisez:
Bush surrounded by former brick making area
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
Commentaires:
The land user constructed a water reservoir close to a wetland to act as a water source especially during the dry season
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
The trees are planted once a year
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- tree nursery
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Commentaires:
The nursery is established on 69m2 × 25m2 of land
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface

érosion éolienne des sols
- Et: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
The nursery was established to improve production of the fruit trees and provide economic benefits to the landuser
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Auteur:
Prossy Kaheru
Date:
09/06/2017
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
The nursery is located on a 69m X 25 m (1725 m2) plot size
The nursery beds are a 1m x 10m, with a 75cm pathway between the beds
The beds contain 10,000 citrus seedlings 15,000 mango seedlings and a few clonal eucalyptus and pine trees
The pots used for growing mangoes are 5in x 7in, whereas citrus , eucalyptus and clonal are 4in X 7in
The rivets used to construct the shades are between 2m and1.5cm high. grass is used to shield the young seedlings from direct sunshine
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par superficie de la Technologie
Indiquez la taille et l'unité de surface:
1725 m2
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
UGX
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
3818,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
3000/=
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Determine water source | Modes de gestion | June and July |
| 2. | Mix soils with manure | Agronomique | June and July |
| 3. | Buy planting material (seeds and potting bags) and poles for constructing shelter shelter | Modes de gestion | June and July |
| 4. | Potting and planting seeds | Agronomique | June and July |
| 5. | Cover pots with grass | Agronomique | June and July |
| 6. | Put under shade | Modes de gestion | June and July |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Potting and Planting | People | 4,0 | 12000,0 | 48000,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Arranging pots | People | 1,0 | 50000,0 | 50000,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Preparing mango seeds | people | 4,0 | 10000,0 | 40000,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | 100,0 | |||||
| Equipements | Water pump | Piece | 1,0 | 1000000,0 | 1000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Wheel barrow | Piece | 2,0 | 80000,0 | 160000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Watering can | Piece | 9,0 | 7500,0 | 67500,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Potting bags | Roll | 12,0 | 6000,0 | 72000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Water storage drum | Piece | 1,0 | 70000,0 | 70000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds (Eucalyptus) | Kg | 5,0 | 30000,0 | 150000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds (Pine) | Kg | 10,0 | 10000,0 | 100000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds (citrus) | Kg | 4,0 | 60000,0 | 240000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds (mangoes) | Bag | 50,0 | 15000,0 | 750000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Cyons (mangoes) | Piece | 15000,0 | 100,0 | 1500000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Cyons (citrus) | Piece | 10000,0 | 20,0 | 200000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Soil | Truck | 2,0 | 50000,0 | 100000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Sand | Truck | 1,0 | 50000,0 | 50000,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | DAP | Kg | 5,0 | 3500,0 | 17500,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Liquid fertilisers | Litre | 1,0 | 18000,0 | 18000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Construction poles | piece | 50,0 | 3000,0 | 150000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Grass | piece | 50,0 | 2500,0 | 125000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Nails | kg | 3,0 | 1000,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Polythene bags (6inch) | kg | 100,0 | 6500,0 | 650000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Polythene bags | kg | 120,0 | 6500,0 | 780000,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 6341000,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
The land user takes this as a major source of income
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Watering | Agronomique | 2/week |
| 2. | Pesticides application | Agronomique | 2/season |
| 3. | Sorting of seedlings | Agronomique | 2/season |
| 4. | Construction of shades | Structurel | 1/season |
Commentaires:
Sorting of seedlings happens continuously every season
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Watering | People | 5,0 | 3000,0 | 15000,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Weeding | People | 5,0 | 15000,0 | 75000,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Sorting | People | 5,0 | 1000,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Strings | People | 2,0 | 8000,0 | 16000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Poles | Piece | 50,0 | 1500,0 | 75000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Grass | Bundle | 25,0 | 2500,0 | 62500,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 248500,0 | |||||
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Accessibility to quality seed, transportation of materials, drought
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Rainfall started late. First season rains started in April instead of late March, and second season started in September instead of late August
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
Gulu meteorology station
Zone agro-climatique
- humide
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- fin/ lourd (argile)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
< 5 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
bonne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Non
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
The nursery borders with a wetland therefore, water availability is not a challenge
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
Diversité des habitats:
- faible
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
Only a few tree species planted
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- commercial/ de marché
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- riche
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- personnes d'âge moyen
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
The nursery owner also operates a small maize mill
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
The technology lies on less than an acre of land. The average land holding of this area is 2ha.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- communauté/ village
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- communautaire (organisé)
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The farmer sold 25,000 seedlings and earned over UGX 37,500,000 ( USD 9,868)
Impacts écologiques
Sols
humidité du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
continuous watering of the seedlings, maintains soil moisture
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
disponibilité de l'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The water used in the dry season is drawn from the pond constructed in a wetland close. However this is affecting the water flow to other neighbours using this water.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Type de changements/ extrêmes climatiques | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien | |
| précipitations annuelles | décroît | bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
Tree nurseries are very expensive to establish and take close to a year for the seedlings to be sold. Therefore, establishment costs surpass benefits in the short run, however when the trees are sold they fetch a lot of income. Maintenance costs, both in the short and long term are positve.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- 1-10%
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 90-100%
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Non
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Optimal space utilisation |
| Maintenance costs are low |
| Nurseries generate high value crops |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Nurseries rehabilitate degraded land |
| Environmental improvements |
| They are used for aesthetic benefits |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Establishment costs are high | Bulk purchases of inputs |
| Grafting needs technical skills | Hire skilled labour |
| Markets are inaccessible | Register company with the district and sub-county |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Labour intensive | |
| Markets are highly seasonal | Sourcing from other buyers for examples NGOs promoting agro- forestry |
| Trees do not grow at the same rate | Application of fertilizers |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
one
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
one
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Improving Sustainable Productivity in Farming systems and Enhanced livelihoods through Adoption of Evergreen Agriculture in Eastern Africa. Joy Buyinza and Vicent I Opolot
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
https://www.cgiar.org/research/publication/improving-sustainable-productivity-in-farming-systems-and-enhanced-livelihoods-through-adoption-of-evergreen-agriculture-in-eastern-africa-shortened-as-trees-for-food-security-project/
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes disponibles en ligne
Titre/ description:
Improving Sustainable Productivity in Farming systems and Enhanced livelihoods through Adoption of evergreen Agriculture in Eastern Africa
URL:
https://www.worldagroforestry.org
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé