Comprehensive Development & Management of a Small Watershed [Chine]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Unknown User
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Intergraded development of a small watershed
technologies_971 - Chine
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)

Comprehensive Development & Management of a Small Watershed [Chine]
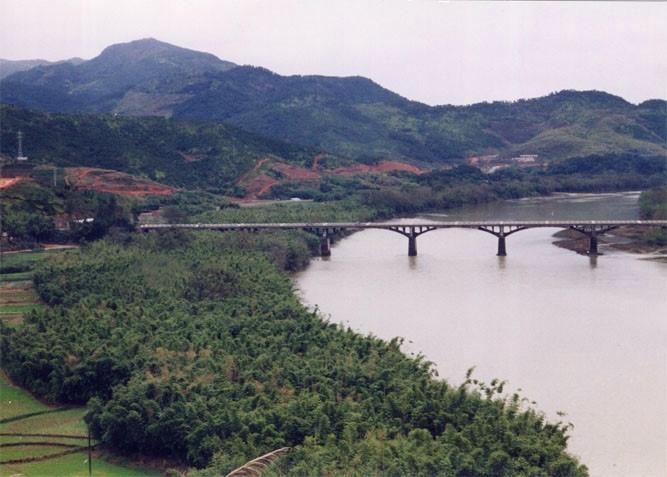
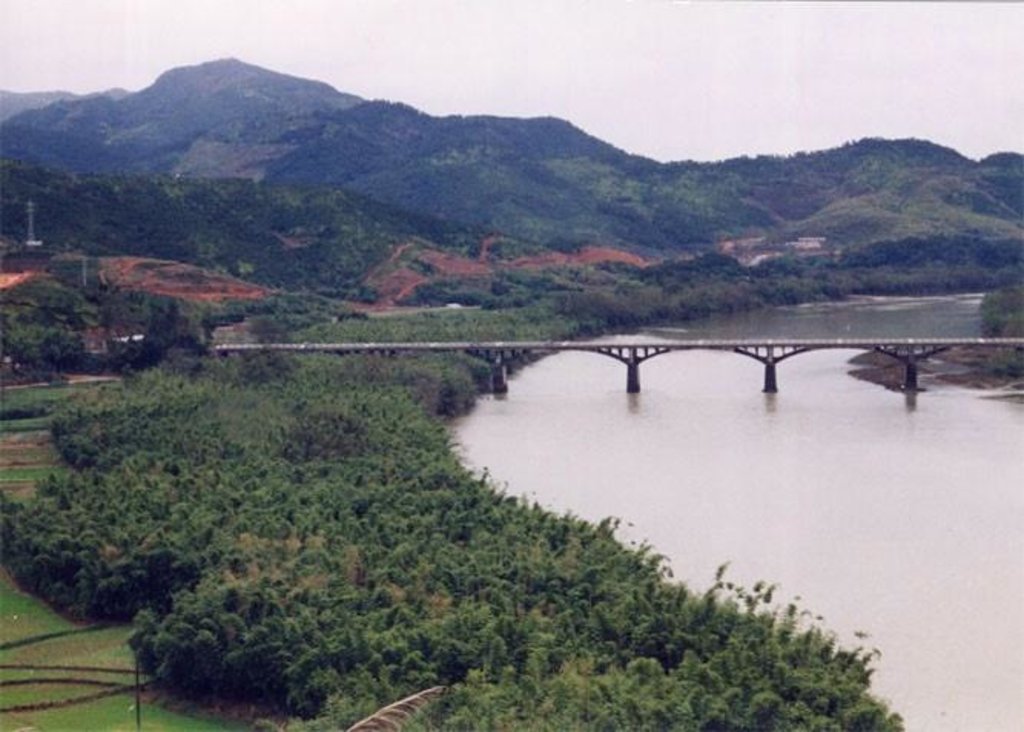
The comprehensive measures including interplanting & intercropping are applied in the small watershed to control soil and water loss and improve land production and farmers' income.
- Compilateur : Unknown User

Interplanting fruit trees of Longan, Peach, Plum etc. [Chine]
Interplanting plum, peach and other fruit trees in longan orchard on level terraces in order to prevent soil and water loss and improve production of the fruit trees.
- Compilateur : zhangsheng LIU
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
The comprehensive measures including interplanting & intercropping are applied in the small watershed to control soil and water loss and improve integrated production.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
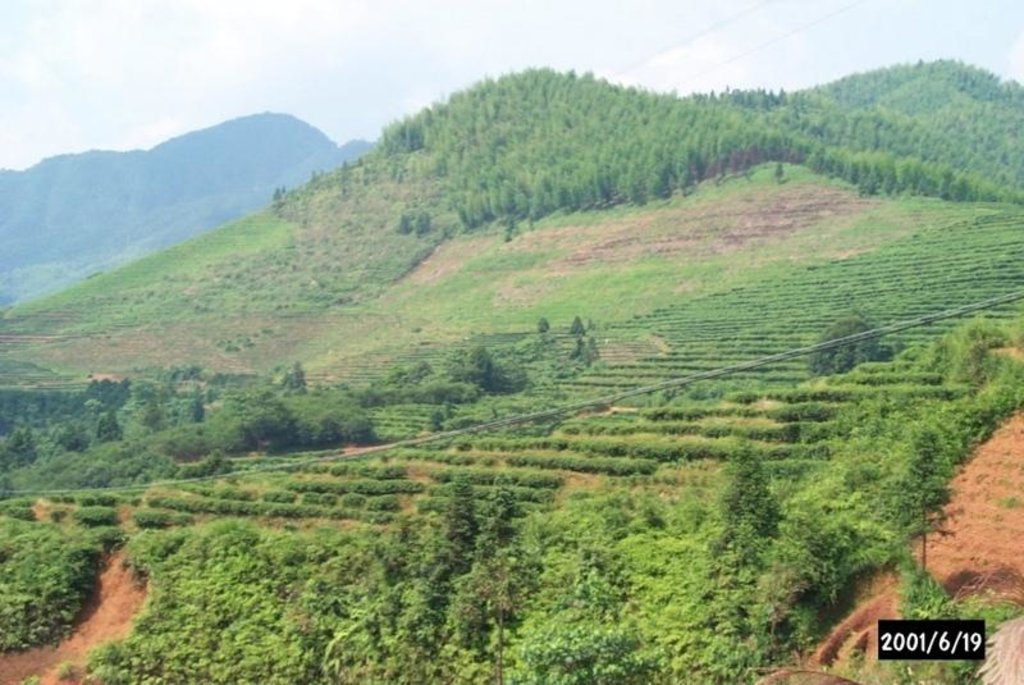
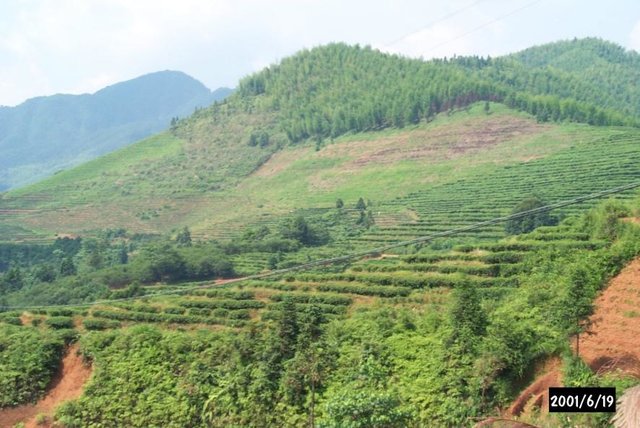
Based on the national conditions and soil and water loss in the area, the corresponding SWC measures were adopted to pursue the targets including: 1. Closing the hilly and mountain area of 224ha for the timber forest and grass growing as well as preventing soil and water loss; 2. Adjusting the land use structure so as to strengthen the comprehensive development of the hilly land as well as crop land irrigation; 3. Changing the area of W & S loss to economic vegetation land; 4. Constructing reservoirs and roads.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Chine
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Fujian Province
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, précisez la superficie couverte (en km2):
5,93
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- 1-10 km2
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 5.93 km2.
Xinxili small watershed is located in southern Zhenghe county. It belongs to administration of Jiefang village of Xiongshan town including three villages. The area of the watershed is about 606 ha. The weather in the region is sub-tropical monsoon climate with artificial vegetation. The soil type is red soil.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Based on the long term experiences of the mass's practice in SWC, the SWC specialists innovated through guidance, design and implementation of local water & soil conservation.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- protéger un bassin versant/ des zones situées en aval - en combinaison avec d'autres technologies
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agro-sylvo-pastoralisme

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
- rice
Plantations d'arbres et d'arbustes - Précisez les cultures:
- raisins
- thé
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 365Longest growing period from month to month: Jan - Dec
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Oui

Pâturages
Type d'animal:
- volailles

Forêts/ bois
Type d’arbres:
- Espèces d'Abies (sapin)
- Bambou commun
- Espèces de Pinus (pin)
Produits et services:
- Bois d'œuvre (de construction)
- Pâturage/ broutage
- Conservation/ protection de la nature
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The layout of vegetation is not rational. The traffic is not convenient.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Lack of new species and SWC technique. Hopefully more funds could be supported from government.
Grazingland comments: Reclaiming fish pools area of 5.6 ha, stall breeding chicken, duck etc.
Problems / comments regarding forest use: Planting young bamboo in the sparse woodland (about 135 ha) in the western watershed and planting lotus after deforesting the woodland (36.7 ha) in the southwestern watershed as well as changing the adult tea gardens to afforest in the northeast watershed.
Forest products and services: timber, grazing / browsing, nature conservation / protection
Type of grazing system comments: Reclaiming fish pools area of 5.6 ha, stall breeding chicken, duck etc.
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Commentaires:
Water supply also mixed rainfed-irrigated
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion des eaux de surface (sources, rivières, lacs, mers)
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A1: Couverture végétale/ du sol

structures physiques
- S7: Collecte de l'eau/ approvisionnent en eau/ équipement d'irrigation

modes de gestion
- M1: Changement du type d’utilisation des terres
Commentaires:
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, mulching, minimum tillage, contour tillage
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines

érosion éolienne des sols
- Et: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)

dégradation hydrique
- Ha: aridification
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Et: loss of topsoil, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (population increasing and lack of fuel), poverty / wealth (Lack of captial: Low living standard of the local people and lack of funds.)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (neglecting ecological benefit, overfelling forest), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Sandy and loose red soil.)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, Improvement of soil structure
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Remarks: Intercropping/mixed cropping
Mulching
Material/ species: Straw
Quantity/ density: all crop a
Remarks: strips
Trees/ shrubs species: fir, bamboo, horsetail pine,
Fruit trees / shrubs species: pear, loquat, peach, greengage
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 25.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 20.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 20.00%
Construction material (earth): With some stone
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 35.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 25.00%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 60.00%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:10.00
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars américains
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
1.44
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | closing mountain to afforest | 1990 |
| 2. | planting bamboo | 1990 |
| 3. | bamboo forest cultivated | 1990 |
| 4. | changing farmland to forest | 1990 |
| 5. | planting fruit trees | 1990 |
| 6. | Building sluice dams | 1990 |
| 7. | road constructing | 1990 |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 72 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | fertilizing | 1990-1999 /3 |
| 2. | cleaning out ruderal | 1990-1999 /2 |
| 3. | Preventing and curing illness and insect pests | 1990-1999 /3 |
| 4. | Broadening road | 1995/timely |
| 5. | highway maintenance | 1995/timely |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Commentaires:
Size of the variable structural measures and areas of grass planting.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Because mechanic machines are not available, more labor forces are needed costing much. In addition, the expense for seeding, fertilizer, flagstone used in building dams take most of the total fees.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
1609,00
Zone agro-climatique
- humide
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- abondant (>3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
soil texture: granite and fiber rock
Soil fertility: medium
Soil drainage / infiltration: good
Soil water storage capacity: high
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- traction animale
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
and own 2% of the land.
and own 2% of the land.
and own 72% of the land.
and own 10% of the land.
and own 8% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: The benefit of SWC implementation is about 1.03 million US dollars. Among them, 257,289 US Dollars from the agricultural production, 145,301 USD from the forest industry and 286,746 USD from others.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Quantité avant la GDT:
40
Quantité après la GDT:
30
Sols
perte en sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
25
Quantité après la GDT:
5
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- > 50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
510 households
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 11-50%
Commentaires:
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
410 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
100 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Even without fund support, rich land users could gain added income from the implementation of SWC technique.
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Comprehensive Development & Management of a Small Watershed [Chine]
The comprehensive measures including interplanting & intercropping are applied in the small watershed to control soil and water loss and improve land production and farmers' income.
- Compilateur : Unknown User

Interplanting fruit trees of Longan, Peach, Plum etc. [Chine]
Interplanting plum, peach and other fruit trees in longan orchard on level terraces in order to prevent soil and water loss and improve production of the fruit trees.
- Compilateur : zhangsheng LIU
Modules
Aucun module trouvé