Participatory mapping, database building, and monitoring of rangeland resources [ប្រទេសកេនយ៉ា]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ IBRAHIM JARSO
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ Caroline King-Okumu
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ Hanspeter Liniger, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Donia Mühlematter, Joana Eichenberger
Resource Mapping
approaches_3439 - ប្រទេសកេនយ៉ា
- សង្ខេបជា PDF
- សេចក្តីសង្ខេបពេញលេញជាទម្រង់ PDF សម្រាប់បោះពុម្ព
- សេចក្តីសង្ខេបពេញលេញទម្រង់អ៊ីនធឺនេត
- សេចក្តីសង្ខេបពេញលេញ (មិនមានទម្រង់ជាក់លាក់)
- Participatory mapping, database building, and monitoring of rangeland resources: 5 ខែ កក្កដា ឆ្នាំ 2018 (inactive)
- Participatory mapping, database building, and monitoring of rangeland resources: 31 ខែ កក្កដា ឆ្នាំ 2018 (inactive)
- Participatory mapping, database building, and monitoring of rangeland resources: 5 ខែ កក្កដា ឆ្នាំ 2018 (inactive)
- Participatory mapping, database building, and monitoring of rangeland resources: 3 ខែ កញ្ញា ឆ្នាំ 2018 (inactive)
- Participatory mapping, database building, and monitoring of rangeland resources: 22 ខែ ឧសភា ឆ្នាំ 2018 (inactive)
- Participatory mapping, database building, and monitoring of rangeland resources: 13 ខែ ឧសភា ឆ្នាំ 2018 (inactive)
- Participatory mapping, database building, and monitoring of rangeland resources: 2 ខែ វិច្ឆិកា ឆ្នាំ 2021 (public)
- Participatory mapping, database building, and monitoring of rangeland resources: 19 ខែ ឧសភា ឆ្នាំ 2018 (inactive)
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Konsole Hussein
+254 728 064578
saritehussein@yahoo.com
Garbatulla Ward Adaptation Planning Committee
P.O. BOX 1Garbatulla
ប្រទេសកេនយ៉ា
Non-State Actor:
Abdullahi Shandey
+254 721109171
midp2003@gmail.com
Merti Integrated Development Program (MID-P)
Merti VillageIsiolo Kenya
ប្រទេសកេនយ៉ា
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ (បើទាក់ទង)
Strengthening Adaptation and Resilience to Climate Change in Kenya Plus (StARCK+)ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ (បើទាក់ទង)
Book project: Guidelines to Rangeland Management in Sub-Saharan Africa (Rangeland Management)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ (បើទាក់ទង)
Resource Advocacy Programme (RAP) - ប្រទេសកេនយ៉ា1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
16/01/2018
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
2. ការពណ៌នាអំពីវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM
2.1 ពណ៌នាសង្ខេបខ្លីពីវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
Participatory mapping and monitoring of vegetation types and other natural resources in the rangelands. This involves convening stakeholder groups, reviewing conditions of rangeland, water and other resources under changing climatic conditions.
2.2 ពណ៌នាលម្អិតពិវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
ពណ៌នាលម្អិតពិវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ:
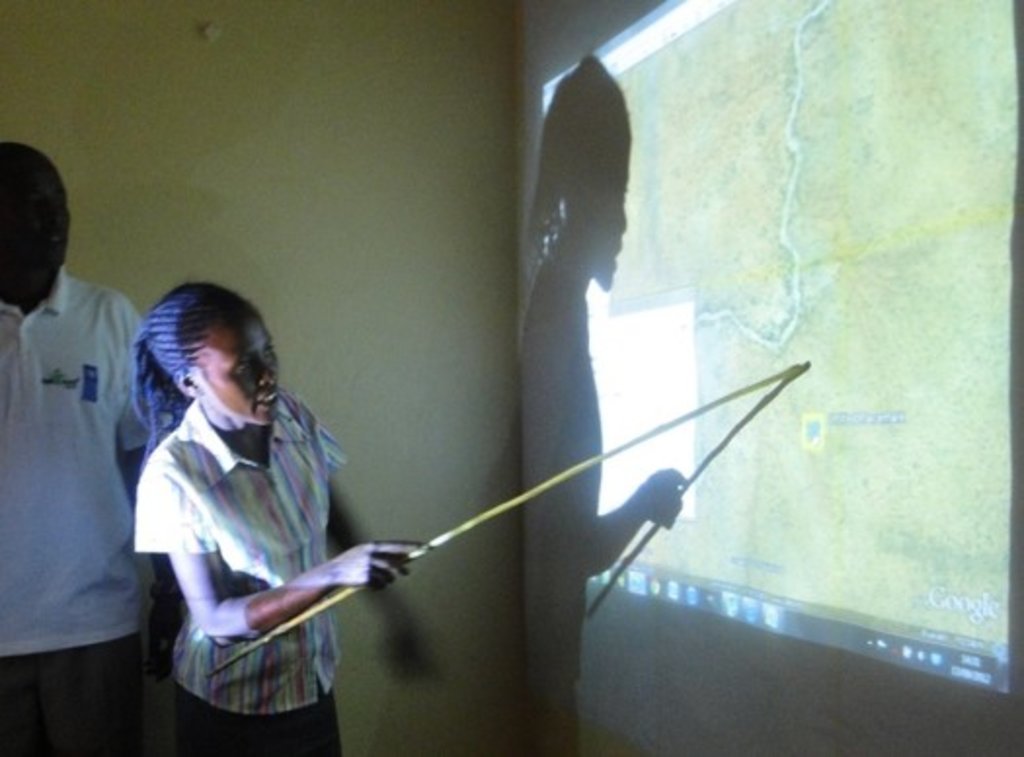
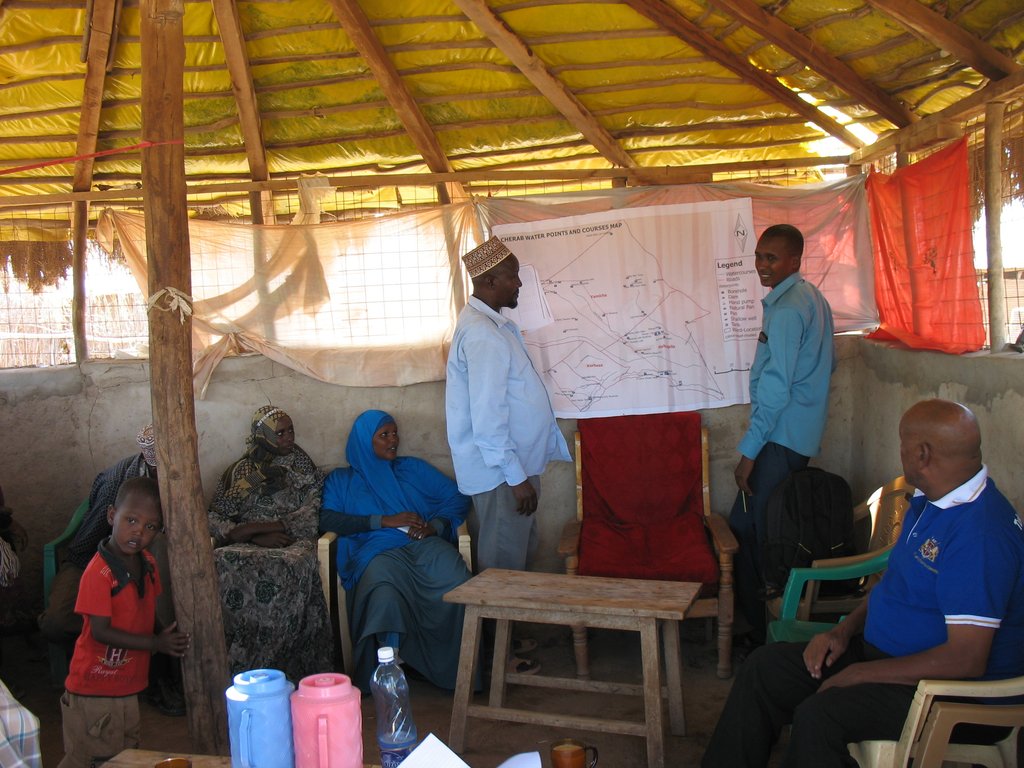
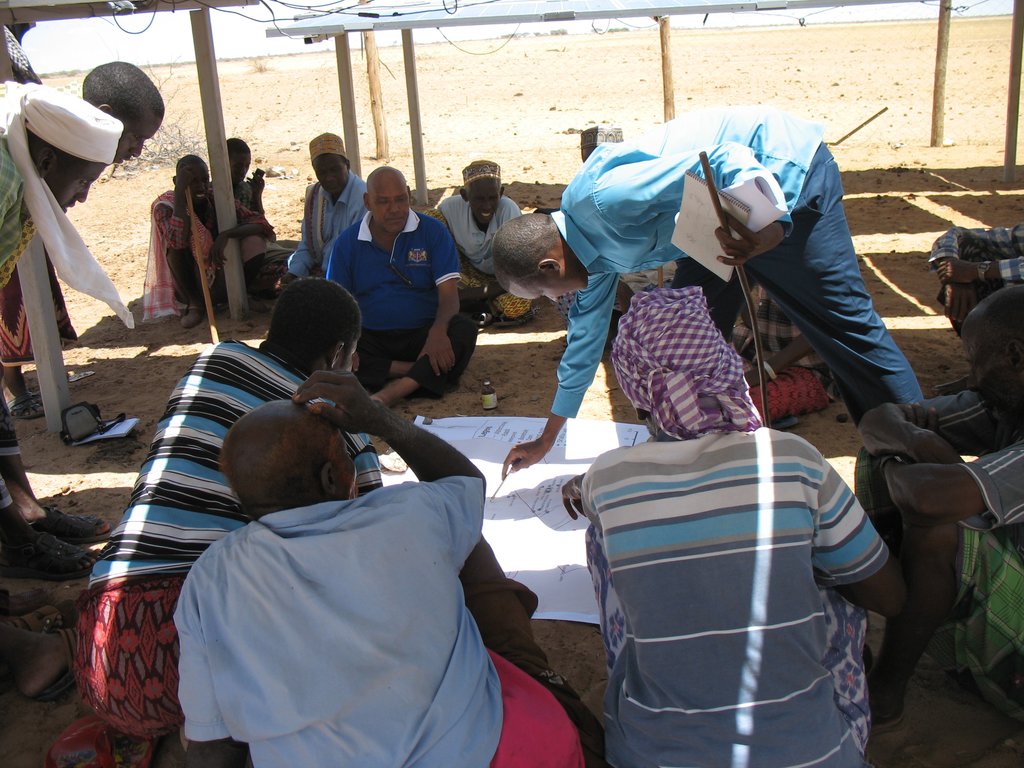
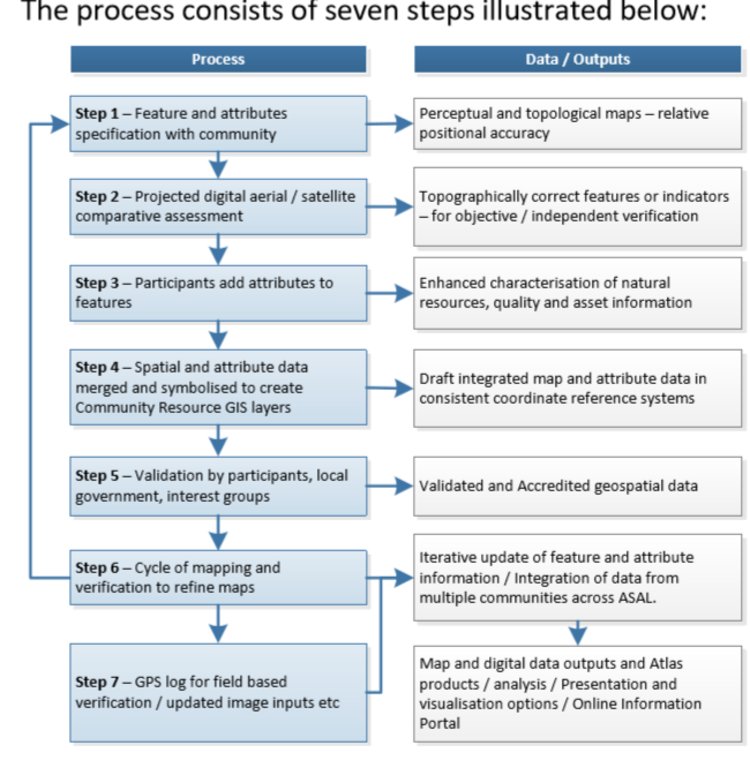
Participatory digital mapping using satellite imagery and digital earth and other open source Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is a practical tool that can bridge knowledge and communication gaps between pastoral communities and county government planners. It offers an effective ‘tool’ for participatory planning and decision-making in support of climate change adaptation efforts in the drylands of Kenya.The use of participatory mapping is not new in seeking to capture communities’ understanding and use of natural resources. These maps are typically drawn on the ground using stones, sticks and other locally available materials to depict key features such as schools, water points, and forest areas, etc. However the process used in Isiolo County combines digital mapping with community-drawn perception maps. This offers a number of extra benefits. While fully capturing the wealth of local knowledge, they contain an in-built coordinate system which corresponds to a global reference grid, enabling their linkage to maps used in formal systems. Furthermore, the coordinate system provides a geographically precise basis from which to discuss natural resource management, making outputs of participatory mapping more universally useable. These benefits, however, need to be carefully balanced to avoid the risk that through this process, pastoral resources – which are highly dynamic - are ‘frozen’ in time and space. Mapping processThe participatory mapping process has adopted GIS workflows within community workshops, enabling the creation of integrated, consistent and standardized geospatial information. The process follows seven steps:Step 1: Community level meetings to develop perception maps drawn on the ground and/or on paper. The product is a community perception map of those resources that are important for their livelihood systems. This map should be created in a community setting to enable the participation of a large group. Several maps may be produced by smaller sub-groups (women, the youth, elders etc) and then amalgamated. The final map is then copied onto paper. Step 2. Digital mapping is introduced. This step takes place in a workshop setting with a smaller group of key informants chosen by the community - as well as county government planners and technical staff. The presence of the latter is critical to the process of ‘legitimizing’ community knowledge. Following a quick explanation of satellite imagery, Google Earth is projected onto a wall alongside the perception maps developed under step 1. The use of Google Earth is only for orientation, and to enable participants to navigate the imagery and to cross-reference their paper-mapped key resources against the satellite imagery. Features that participants feel are important (e.g. water points, wet and dry season grazing areas, drought reserves, wildlife routes) are then captured digitally using open source applications: Quantum GIS (QGIS) and JOSM, the Open Street Map editing platform.This produces the coordinates that pinpoint the locations of natural resources in a manner that can be independently and objectively verified. The highly interactive process of geo-referencing local knowledge to a coordinate reference system allows resource maps to be produced to any scale, and in real-time, with the community. Step 3. Qualitative and quantitative attributes describing the key resources are collected. As participants add features to the map, they also describe their specified characteristics or attributes. Attribution data includes a fuller description of the physical characteristics of the resource (e.g. soil type, waterquantity and quality, pasture species) as well as issues concerning their management (e.g. under customary or modern management, land tenure status, negotiated or paid access, area of conflict). Updating this data on a regular basis adds temporal and trend data to the spatial database. This underlines the need to structure data systems well to manage time-based data and to record updates.Steps 4-6: Data verification cycles are integrated into the mapping process in order to capture community feedback and verify the records in the geospatial data and their attribute values against the specification. The mapping includes a series of validation, cross-checking and verification cycles, run with the community - and in a few instances on-the-ground verification termed ‘groundtruthing’. Step 7: Field validation. Field validation is carried out where the verification stages highlight gaps in information. Verification consists of targeted field visits to take GPS markers, or holding meetings with the local community to clarify particular issues.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសកេនយ៉ា
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Isiolo
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Pasturalist areas
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការចាប់ផ្តើម និងបញ្ចប់នៃវិធីសាស្រ្តផ្សព្វផ្សាយនេះ
សូមបញ្ជាក់ឆ្នាំដែលបានបង្កើតឡើង:
2012
ឆ្នាំបញ្ចប់ (ប្រសិនបើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រូវបានឈប់ប្រើប្រាស់):
2015
មតិយោបល់:
The mapping process needs to be continuous as new community resources are identified and added
2.7 ប្រភេទនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
- ផ្អែកលើគម្រោង/កម្មវិធី
2.8 គោលបំណង/ទិសដៅសំខាន់នៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
- To allow participation for community groups to inform planners.- To provide the necessary precision for planners to use local knowledge effectively.- To make a ‘bridge’ for information to flow between customary and formal institutions.- To better share ideas through communication tools using powerful visual language.- To demonstrate the depth of local knowledge about natural resources and with that, demonstrate the importance of these resources.- To identify gaps and risks in the system being mapped.- To compare one plan with another to see how complimentary/contradictory they are.
2.9 លក្ខខណ្ឌអនុញ្ញាត ឬរារាំងការអនុវត្តន៍បច្ចេកទេសដែលស្ថិតនៅក្រោមវិធីសាស្រ្តផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
សង្គម/វប្បធម៌/ និងតម្លៃនៃសាសនា
- អំណោយផល
Communities are awed by the technology that allows them to see their resources while seated in a single specific location. The approach doesn't conflict with any community social, cultural, religious norms and values.
- រារាំង
Minimal local capacity is required to use the technology.
ភាពអាចរកបាននៃធនធានហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ និងសេវាកម្ម
- អំណោយផល
A brief GIS training of four weeks can allow county government staff to develop, add and update the database.
- រារាំង
Short GIS training courses costs around $850 and facilitation of community engagement meetings may be costly to undertake.
បរិបទនៃស្ថាប័ន
- អំណោយផល
The approach helps in improving planning at community and government levels, and is accepted by all stakeholders.
- រារាំង
Poor capacity and financial resources can be a challenge.
ការសហការ/ការសម្របសម្រួលតួអង្គពាក់ព័ន្ធ
- អំណោយផល
The product of the participatory mapping process is beneficial to all actors and many are willing to engage in implementation of the approach.
- រារាំង
Different mapping initiatives are undertaken by actors with various objectives.
ក្របខណ្ឌច្បាប់ (សិទ្ធិកាន់កាប់ដីធ្លី កម្មសិទ្ធីប្រើប្រាស់ដីនិងទឹក)
- អំណោយផល
The approach helps in land use planning and supports regulations meant to improve land governance such as a customary natural resource management bill.
- រារាំង
County governments can develop their own spatial plans, but there are only few initiatives underway to map county resources
គោលនយោបាយ
- អំណោយផល
Many policies and laws (including the national constitution) support the mapping of resources to improve land use planning.
- រារាំង
Conflicts over land undermines political will.
អភិបាលកិច្ចដី (ការសម្រេចចិត្ត ការអនុវត្ត និងការរឹតបន្តឹង)
- អំណោយផល
The approach allows communities to develop their land use plans for resource utilisation, and digitize them - making the work of land governance easier.
- រារាំង
Competing claims over land and land-based resources in community lands means enforcement of the approach is often challenged. Resources along administrative boundaries are claimed by different communities.
ចំណេះដឹងស្តីពី SLM និងការទទួលបានការគាំទ្រផ្នែកបច្ចេកទេស
- អំណោយផល
New graduates in dryland resource management, and communities' reception of the new technologies, help in acceptance and implementation of the technology.
- រារាំង
58% of the residents of the county (according to the Kenya National Bureau of Statistics socio-economic survey report of 2016) are illiterate and may have difficulties engaging properly with the technology.
ទីផ្សារ (ទិញធាតុចូល លក់ផលិតផល) និងតម្លៃ
- អំណោយផល
Free open source programmes are available to digitize local knowledge to geo-referenced products.
- រារាំង
Good programmes for mapping are expensive.
ទំហំការងារ ភាពអាចរកបាននៃកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
- អំណោយផល
The technology makes the process simpler and reduces the workload.
- រារាំង
The processes can be tedious because of the paper maps involved, series of validation and verification of features.
3. ការចូលរួម និងតួនាទីរបស់ភាគីពាក់ព័ន្ធ
3.1 អ្នកពាក់ព័ន្ធដែលបានចូលរួមក្នុងវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ និងតួនាទីរបស់ពួកគេ
- អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីក្នុងតំបន់/សហគមន៍
Jarsa Dedha (customary natural resource management institutions) Community Members (i.e. pastoralists).
Jarsa Dedha identify the most knowledgeable elders from different grazing areas to help in identifying features and providing grazing land management plans that are in place. Community members identify features and contribute to the attributes of the features.
- អង្គការសហគមន៍មូលដ្ឋាន
Kinna Integrated community based initiative (KICBI)Ward Adaptation Planning Committees
They identify features and also contribute to attributes of the features
- អ្នកឯកទេសគ្រប់គ្រងដីប្រកបដោយចីរភាព/ទីប្រឹក្សាបច្ចេកទេសកសិកម្ម
Ibrahim Jarso
Support mapping process and also add new features supporting updates to the products.
- អង្គការក្រៅរដ្ឋាភិបាល
Resource Advocacy Program (RAP)Merti Integrated Development Program (MID-P)Adaptation Consortium
Support the mapping process and mobilize communities and stakeholders for the approach to be implemented properly.
- រដ្ឋាភិបាលថ្នាក់មូលដ្ឋាន
Isiolo County Government
Support the mapping process with intention to use product for planning purpose and own the product
- រដ្ឋាភិបាលថ្នាក់ជាតិ (អ្នករៀបចំផែនការ អ្នកសម្រេចចិត្ត)
Kenya's National Government
Support the planning process - also with the intention of using the product for planning.
- អង្គការអន្តរជាតិ
International Institute for Environment and Development (IIED) and theUniversity of Southampton (Geodata Institute)
Support with funding to implement the approach and also provide technical expertise to undertake GIS processing of data.
ប្រសិនមានភាគីពាក់ព័ន្ធច្រើនចូលរួមសូមចង្អុលបង្ហាញភ្នាក់ងារដែលនាំមុខគេ:
WAPC , ADA and IIED
3.2 ការចូលរួមរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីក្នុងតំបន់/ សហគមន៍ក្នុងតំបន់ក្នុងដំណាក់កាលផ្សេងគ្នានៃវិធីសាស្រ្តផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
| ការចូលរួមរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីក្នុងតំបន់/សហគមន៍ក្នុងតំបន់ | សូមបញ្ជាក់នរណាត្រូវបានចូលរួម ព្រមទាំងពណ៌នាសកម្មភាពទាំងនោះ | |
|---|---|---|
| ការចាប់ផ្តើម/ការលើកទឹកចិត្ត | អសកម្ម | Resource Advocacy Programme (RAP) undertook discussions with the local community and also with the county and national government in shaping the idea for the approach. |
| ការរៀបចំផែនការ | អន្តរកម្ម | All stakeholders (community, RAP, ADA, IIED, Geodata and Governments) were engaged in the planning for the implementation of the Approach. |
| ការអនុវត្តន៍ | អន្តរកម្ម | Community members and all stakeholders were involved in the implementation of the participatory mapping. |
| ការត្រួតពិនិត្យ និងវាយតម្លៃ | អសកម្ម | The county government and the actors (RAP, ADA and IIED) monitor the participatory mapping database and improves it. |
3.3 គំនូសបំព្រួញ (ប្រសិនបើមាន)
ការពណ៌នា:
Participatory mapping of community resources has seven steps, which can be summarised under the main groupings of: consultations with the community where key features are identified and mapped on paper; digitization of community identified points by GIS specialists; processing of the data where community identified attributes are incorporated into the data; and feedback sessions for community validation and verification.
អ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Ibrahim Jarso
3.4 ការសម្រេចចិត្តលើការជ្រើសរើសបច្ចេកទេស SLM
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើអ្នកណាជាអ្នកបានសម្រេចចិត្តក្នុងការជ្រើសរើសបច្ចេកទេសដើម្បីយកមកអនុវត្តន៍:
- គ្រប់ភាគីពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់ដែលជាផ្នែកនៃវិធីសាស្រ្តផ្សព្វផ្សាយដោយមានការចូលរួម
ចូរពន្យល់:
The process requires inputs from all the relevant stakeholders. The community provide local knowledge of the features, GIS specialists provide technical expertise and the other local stakeholders provide their knowledge and experience of working in the communities for many years.
សូមបញ្ជាក់ តើការសម្រេចធ្វើឡើងដោយផ្អែកលើអ្វីជាមូលដ្ឋាន:
- បទពិសោធន៍ និងគំនិតផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន(ពុំមានចងក្រងជាឯកសារ)
4. ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស ការកសាងសមត្ថភាព និងការគ្រប់គ្រងចំណេះដឹង
4.1 ការកសាងសមត្ថភាព/ បណ្តុះបណ្តាល
តើវគ្គបណ្តុះបណ្តាលបានផ្តល់ឱ្យអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី/អ្នកពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងៗទៀតដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើអ្នកណាត្រូវបានបណ្តុះបណ្តាល:
- អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
- បុគ្គលិកចុះទីវាល/អ្នកផ្តល់ប្រឹក្សាយោបល់
ប្រសិនទាក់ទង សូមបញ្ជាក់ ភេទ អាយុ ស្ថានភាពគ្រួសារ ជនជាតិដើមភាគតិច។ល។:
5 persons trained- One from County Government (Planning Unit), Two from National government (National Drought Management Authority and Kenya Meteorological Department (KMD)) and Two representative of Local NGOs (RAP and MID-P)
ទម្រង់នៃការបណ្តុះបណ្តាល:
- អនុវត្តន៍ជាមួយការងារ
- វគ្គបណ្តុះបណ្តាល
ប្រធានបទបណ្តុះបណ្តាល:
Participatory GIS mapping techniquesInput of data using different platformsUse of GPS devicesValidation of dataData management
មតិយោបល់:
The training was well done with seminars and practical sessions
4.2 សេវាផ្តល់ប្រឹក្សាយោបល់
តើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីបានទទួលនូវសេវាផ្តល់ប្រឹក្សាដែរ ឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
សូមបញ្ជាក់ប្រសិនបើសេវាកម្មប្រឹក្សាយោបល់ត្រូវបានផ្តល់ឱ្យ:
- នៅលើដីរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ពណ៌នា/ពន្យល់:
practical sessions were provided in the field and with communities
4.3 ការពង្រឹងសមត្ថភាពស្ថាប័ន (ការអភិរឌ្ឍន៍អង្គភាព)
តើស្ថាប័នទាំងអស់ត្រូវបានបង្កើតឡើង ឬពង្រឹងសមត្ថភាពតាមរយៈវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយដែរ ឬទេ?
- បាទ/ច៎ា ជាមធ្យម
សូមបញ្ជាក់ថាតើស្ថាប័នត្រូវបានពង្រឹង ឬបង្កើតឡើងនៅត្រឹមកម្រិតណា(ច្រើន)?
- ថ្នាក់មូលដ្ឋាន
ចូពណ៌នាពីស្ថាប័ន តួនាទី និងទំនួលខុសត្រូវ សមាជិក ។ល។:
Local institutions were able to use the maps to advocate for improved planning.
សូមបញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទនៃការគាំទ្រ:
- ការកសាងសមត្ថភាព/ បណ្តុះបណ្តាល
សូមផ្តល់ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមទៀតឱ្យបានលម្អិត:
Courses/trainings were provided
4.4 ការត្រួតពិនិត្យ និងវាយតម្លៃ
តើការត្រួតពិនិត្យ និងវាយតម្លៃគឺជាផ្នែកមួយនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
មតិយោបល់:
inputs were monitored
ប្រសិន បាទ/ច៎ា តើឯកសារនេះបានបង្កើតឡើងក្នុងគោលបំណងប្រើប្រាស់សម្រាប់ការត្រួតពិនិត្យ និងវាយតម្លៃដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
មតិយោបល់:
It was also used to mapped investments that were done to improve community livelihoods
4.5 ការស្រាវជ្រាវ
តើការស្រាវជ្រាវ គឺជាផ្នែកមួយនៃវិធីសាស្រ្តដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
បញ្ជាក់ប្រធានបទ:
- បរិស្ថានវិទ្យា
សូមផ្តល់ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមទៀតឱ្យបានលម្អិត និងចង្អុលបង្ហាញនរណាដែលបានធ្វើការស្រាវជ្រាវ:
Research on vegetation patterns in Isiolo’s rangelands were conducted by the University of Nairobi's Department of Land and Resource Management.
5. ថវិកា និងសម្ភារៈឧបត្ថម្ភពីខាងក្រៅ
5.1 ថវិកាប្រចាំឆ្នាំសម្រាប់ផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM
ប្រសិនបើចំនួនពិតប្រាកដនៃថវិកាប្រចាំឆ្នាំមិនត្រូវបានដឹងច្បាស់ សូមប្រាប់ពីចន្លោះនៃថវិកានោះ:
- 10,000-100,000
មតិយោបល់ (ឧ. ប្រភពសំខាន់នៃមូលនិធិ/ម្ចាស់ជំនួយចំបង):
The approach was supported by RAP and IIED under the Adaptation Consortium with funding from UK's Department for International Development (DfID). The budget is used to convene sub-county level meetings and trainings sessions. Many of the participants costs and preparation costs are not covered.
5.2 ការគាំទ្រផ្នែកហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ / សម្ភារៈដែលបានផ្តល់ទៅឱ្យអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
តើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីបានទទួលការគាំទ្រផ្នែកហិរញ្ញវត្ថ/សម្ភារៈសម្រាប់ការអនុវត្តន៍បច្ចេកទេសដែរឬទេ:
ទេ
5.3 សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូលត្រូវបានផ្តល់បដិភាគ (រួមទាំងកម្លាំងពលកម្ម)
- កម្លាំងពលកម្ម
| កម្រិតទំហំប៉ុណ្ណា | សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីការបដិភាគ |
|---|---|
| ផ្តល់ហិរញ្ញវត្ថុទាំងស្រុង | Community meetings were supported by the actors in the project (RAP, IIED and Adaptation Consortium). |
- សម្ភារៈ
| សូមបញ្ជាក់ ធាតុចូលណាខ្លះដែលបានផ្តល់បដិភាគ | កម្រិតទំហំប៉ុណ្ណា | សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីការបដិភាគ |
|---|---|---|
| ម៉ាស៊ីន | ផ្តល់ហិរញ្ញវត្ថុទាំងស្រុង | Machinery used in the approach was purchased by the actors involved. |
| ឧបករណ៍ | Tools used in the approach were purchased by the actors involved. | |
ប្រសិនបើកម្លាំងពលកម្មធ្វើដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី តើវាជាធាតុចូលដ៏សំខាន់មួយដែរ ឬទេ:
- ដោយស្ម័គ្រចិត្ត
មតិយោបល់:
Communities provided the local knowledge to support the approach.
5.4 ឥណទាន
តើឥណទានដែលបានផ្តល់នៅក្រោមវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយសម្រាប់សកម្មភាព SLM នេះយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច?
ទេ
6. ការវិភាគរកផលប៉ះពាល់ និងសេចក្តីសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
តើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយបានផ្តល់សិទ្ធិអំណាចដល់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវការចួលរួមអ្នកពាក់ព័ន្ធ?
- ទេ
- បាទ/ច៎ា បន្តិចបន្តួច
- បាទ/ច៎ា ជាមធ្យម
- បាទ/ច៎ា បានខ្លាំង
Yes, the approach strengthens community rights and management of resources.
តើវិធីសាស្រ្តផ្សព្វផ្សាយនេះអនុញ្ញាតឱ្យធ្វើការសម្រេចចិត្ដដោយផ្អែកលើភស្តុតាងជាមូលដ្ឋានដែរ ឬទេ?
- ទេ
- បាទ/ច៎ា បន្តិចបន្តួច
- បាទ/ច៎ា ជាមធ្យម
- បាទ/ច៎ា បានខ្លាំង
Yes greatly – provided databases that did not previously exist.
តើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយជួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដើម្បីអនុវត្តន៍ និងថែទាំបច្ចេកទេស SLM?
- ទេ
- បាទ/ច៎ា បន្តិចបន្តួច
- បាទ/ច៎ា ជាមធ្យម
- បាទ/ច៎ា បានខ្លាំង
Strengthened the traditional system of management of land.
តើវិធីសាស្រ្តផ្សព្វផ្សាយនេះធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវការសម្របសម្រួលនិងការអនុវត្តចំណាយរបស់ SLMមានប្រសិទ្ធិភាពបែបណា? :
- ទេ
- បាទ/ច៎ា បន្តិចបន្តួច
- បាទ/ច៎ា ជាមធ្យម
- បាទ/ច៎ា បានខ្លាំង
Improved coordination among the partners and enabled monitoring of resource conditions.
តើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយនេះធ្វើឱ្យចំណេះដឹងប្រសើឡើង និងសមត្ថភាពរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីក្នុងការអនុវត្តន៏ SLM?
- ទេ
- បាទ/ច៎ា បន្តិចបន្តួច
- បាទ/ច៎ា ជាមធ្យម
- បាទ/ច៎ា បានខ្លាំង
The technology provided digitized observation of resources, and communities realised their wealth of their resources.
តើវីធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយនេះពង្រឹងចំណេះដឹង និងកសាងសមត្ថភាពរបស់អ្នកពាក់ព័ន្ធឬទេ?
- ទេ
- បាទ/ច៎ា បន្តិចបន្តួច
- បាទ/ច៎ា ជាមធ្យម
- បាទ/ច៎ា បានខ្លាំង
The Community resource atlas of Isiolo County has been online since July 2015.
Yes greatly, the Approach made local institutions stronger and enhanced their collaboration and data sharing.
តើវីធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយនេះបានកាត់បន្ថយជំលោះឬទេ?
- ទេ
- បាទ/ច៎ា បន្តិចបន្តួច
- បាទ/ច៎ា ជាមធ្យម
- បាទ/ច៎ា បានខ្លាំង
The Approach mapped conflict hotspots and improved the process of conflict resolution and analysis.
តើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ បានធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងសមភាពយេនឌ័រ និងផ្តល់សិទិ្ធអំណាចដល់ស្ត្រី និងក្មេងស្រី?
- ទេ
- បាទ/ច៎ា បន្តិចបន្តួច
- បាទ/ច៎ា ជាមធ្យម
- បាទ/ច៎ា បានខ្លាំង
The process also engaged women in gathering local knowledge of resources and they made a very considerable contribution to the work.
តើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយបានលើកទឹកចិត្តដល់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលជាយុវជន/ក្មេងជំនាន់ក្រោយឱ្យចូលរួមក្នុង SLM ?
- ទេ
- បាទ/ច៎ា បន្តិចបន្តួច
- បាទ/ច៎ា ជាមធ្យម
- បាទ/ច៎ា បានខ្លាំង
The use of GIS fascinated young people and they felt attracted to the process.
តើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយបានឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវបញ្ហាកាន់កាប់ដីធ្លី/សិទ្ធិអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដែលរារាំងដល់ការអនុវត្ត SLM?
- ទេ
- បាទ/ច៎ា បន្តិចបន្តួច
- បាទ/ច៎ា ជាមធ្យម
- បាទ/ច៎ា បានខ្លាំង
The approach guided use of land and also strengthened communities ownership and rights over their land and their available resources.
តើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយនេះនាំឱ្យមានភាពប្រសើរឡើងក្នុងការទទួលបានទឹក និងអនាម័យ?
- ទេ
- បាទ/ច៎ា បន្តិចបន្តួច
- បាទ/ច៎ា ជាមធ្យម
- បាទ/ច៎ា បានខ្លាំង
The approach guided water investments in the community lands and improved placement of water infrastructure.
តើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយនេះនាំឱ្យមានកាប្រើប្រាស់ប្រកបដោយចីរភាព/ប្រភពនៃថាមពលកាន់តែប្រើសើរឡើង?
- ទេ
- បាទ/ច៎ា បន្តិចបន្តួច
- បាទ/ច៎ា ជាមធ្យម
- បាទ/ច៎ា បានខ្លាំង
The approach mapped boreholes, and the energy used to extract water from them, as well as encouraging use of clean and green energy.
តើវិធីសាស្ត្របានធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវការកសាងសមត្ថភាពរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដើម្បីបន្សុំាទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/អាកាសធាតុក្តៅហែង និងកាត់បន្ថាយគ្រោះមហន្តរាយទាក់ទឹងនឹងអាកាសធាតុ?
- ទេ
- បាទ/ច៎ា បន្តិចបន្តួច
- បាទ/ច៎ា ជាមធ្យម
- បាទ/ច៎ា បានខ្លាំង
The approach concretized the community land use plans and guided proper use of their pasture and water - enhancing the community's capacity to adapt to climate related disasters of drought and floods.
6.2 ការលើកទឹកចិត្តចម្បងៗរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីសម្រាប់ការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស SLM
- បង្កើនផលិតកម្ម
The Approach improved planning and management of resources leading to increased productivity
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
Mapping of Land use plans helped in reducing land degradation.Participatory Mapping Approach was used by International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) to map out degaraded lands in the County and targetted interventions were undertaken with Dedha elders.
- កាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ
The approach allowed the communities to plan and prepare before disasters happen by identifying fall back areas and mapping them.Flood prone areas, Drought reserves and Conflict hotspots were mapped and deliberate interventions undertaken on addressing this.
- ច្បាប់ និងបទបញ្ជា (ផាកពិន័យ)/ការប្រតិបត្តិ
The Approach developed Maps which guided the enforcement of the traditional rules and regulations of accessing pasture and water during specific seasons.
- ពង្រឹងស្មារតីផ្នែកបរិស្ថាន
The approach mapped key environmental resources like non-gazette forests with opportunity to enhance protection and conservation
- លើកកម្ពស់ចំណេះដឹង និងជំនាញ SLM
Supported the traditional systems of management of natural resources
- ការកាត់បន្ថយជម្លោះ
The approach mapped the conflict hotspots in the county with intention to resolve or mitigate conflicts
6.3 សកម្មភាពផ្សព្វផ្សាយដែលប្រកបដោយចីរភាព
តើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីអាចធ្វើឱ្យមានចីរភាពនូវអ្វីដែលត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍តាមរយៈវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយដែរឬទេ(ដោយពុំមានការគាំទ្រពីអ្នកខាងក្រៅ)?
- មិនប្រាកដ
ប្រសិន ទេ ឬមិនប្រាកដសូមបញ្ជាក់ និងពន្យល់:
The approach was implemented with support from donors and county government. Although in theory, it could be possible for resource users to auto-finance the Approach, this has not ever happened previously, and many of the resource users are not wealthy. Support is available for devolved development planning and mapping, but as yet this has not been assigned to participatory resource mapping.
6.4 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| It is a promising new approach that builds on the legitimacy of local/indigenous knowledge, and enables the county government to fulfil its mandate of undertaking participatory planning with communities. |
| GIS technology helps in the acceptance of the approach by many land users. |
| The mobililty of the technology can provide an opportunity for all community members to add features as they come up |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| It is a user friendly approach accepted and recognized by Isiolo pastoralists for mapping their rangeland resources. |
| It provides an opportunity to map all investments of development partners in the county and avoid duplication of projects. |
| It is a powerful tool for communication and advocacy for community land rights. |
6.5 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រ និងរកដំណោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| It requires time and commitment from community members and county officers. | Systematic use of media (e.g. radio, websites, etc) to publicize the approach and its importance to the community. |
| It is difficult for illiterate community members to fully engage with the approach and make meaningful contributions. | Provide local translations and interpretation as well as producing good visual maps. |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យក្នុងទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| There is a need for continuous updating | Engage local universities and students. |
| Observation of key features and resources are sometimes obscured by clouds and thus mapping precision is affected. | Ground truthing visits and observations need to be undertaken to improve precision. |
| Lack of legislation to support and enforce the use of the approach. | Formulate legislation to support enforcement. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
Made 2 field visits in Kinna and Garbatulla Wards, engaged 20 community members
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
20 community members and 3 community based organization representatives
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកជំនាញ/ ឯកទេស
Engaged 2 staff of MID-P and 2 staff of RAP
- ការចងក្រងពីរបាកការណ៍ និងឯកសារផ្សេងៗទៀតដែលមាន
used Community Resource Mapping and Validation reports and Isiolo Community Resource Atlas 2015
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Participatory Mapping using Digital Earth Tools, Imagery and Open Source GIS in the drylands of Kenya and Tanzania by Chris Hill, Tom Rowley, Homme Zwaagstra, Andrew Harfoot and Mike Clark
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Ada Consortium Website
7.3 ចូលទៅទាញយកឯកសារពាក់ព័ន្ធដែលមានលើបណ្តាញអ៊ិនធឺណែត
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Resource Atlas of Isiolo County, Kenya
វេបសាយ:
pubs.iied.org/pdfs/G03984.pdf
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល