Integrated watershed management for landslip and stream bank stabilisation [ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Dileep Kumar Karna
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យ Fabian Ottiger
Pahiro ra nadikinar katan roktham ka lagi ekikrit jaladhar byabasthapan (Nepali)
approaches_2354 - ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ (បើទាក់ទង)
G.B. Pant Institute of Himalayan Einvironment & Development (G.B. Pant Institute of Himalayan Einvironment & Development) - ប្រទេសឥណ្ឌាឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ (បើទាក់ទង)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ (បើទាក់ទង)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 ការយោងមួយ (ច្រើន) ទៅលើ (កម្រង) បញ្ជីសំណួរនៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2. ការពណ៌នាអំពីវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM
2.1 ពណ៌នាសង្ខេបខ្លីពីវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
Integrated watershed management as an example for landslip and stream bank stabilisation based on fostering a partnership between community institutions, line agencies, district authorities and consultants
2.2 ពណ៌នាលម្អិតពិវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
ពណ៌នាលម្អិតពិវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ:
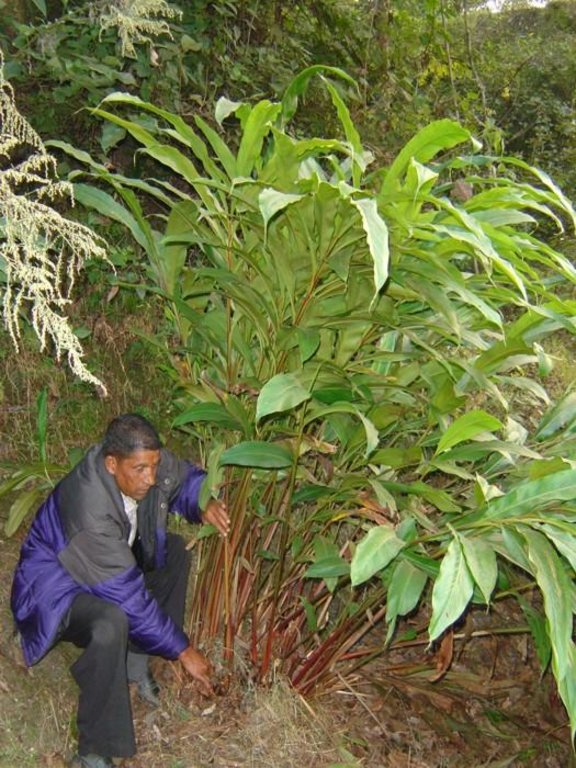
Aims / objectives: The sustainable management of mountain watersheds is a huge challenge for watershed management programmes due to the lack of collaboration between the various institutions involved. Building of synergies between these institutions is crucial for improved management. The Bagmati Integrated Watershed Management Programme (BIWMP) started in 1986, initiated, coordinated, and organised by the Department of Soil Conservation and Watershed Management with support from the European Commission. The programme aimed to help overcome natural resource degradation and thereby raise the standard of living of the rural population. The main causes of degradation and options to address the related problems were identified through participatory action research. Landslip and stream bank stabilisation was identified as one of the most promising and needed options to conserve soil and water, whilst providing direct livelihood benefits to local people, for example planting of large cardamom, later used as a cash crop, and reestablishment of damaged agricultural terrace above the landslip. The approach was to foster partnership between and among communities, district authorities, line agencies, and consultants. Key priorities were to ensure the equitable involvement of women and socially disadvantaged people and to promote local ownership, institutional capacity building, and sustainability.
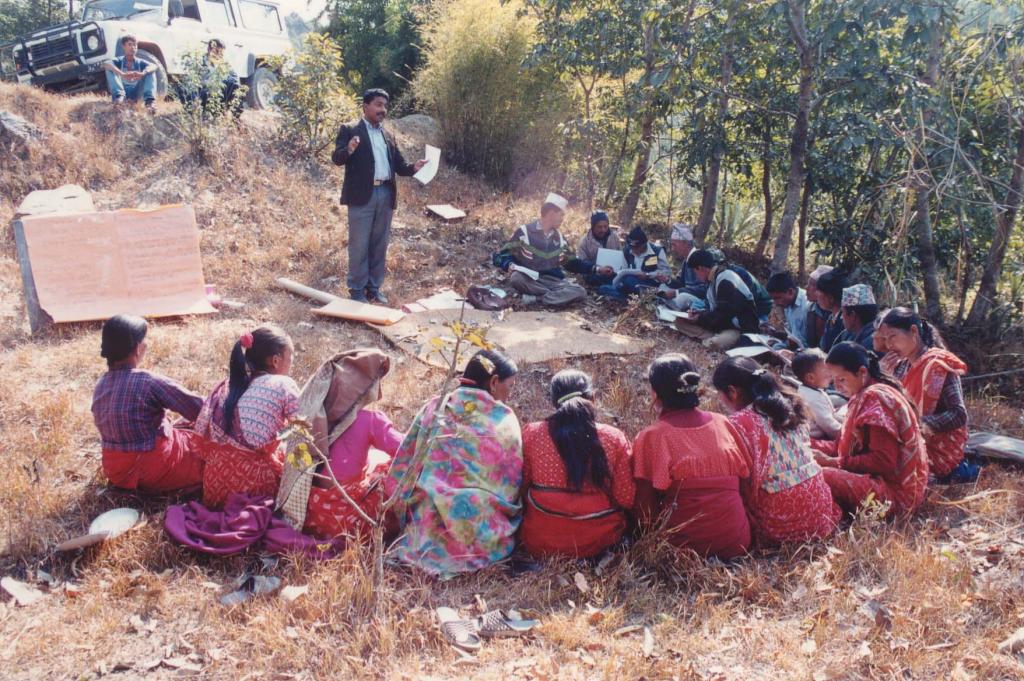
Methods: The programme used participatory extension methods such as farmer-to-farmer exchange, training workshops, and onsite demonstrations, with participatory approaches to planning, implementing, and monitoring. The activities were based on villager’s priorities and were implemented by individual households, farmer groups, and village institutions. The local village development committee, local NGOs, community forest user group, and individual households worked together on landslip and stream bank stabilisation. Involving a range of stakeholders was paramount for success.
Stages of implementation: The first phase began in 1986 and focused on developing technical packages which were implemented through user groups. The second phase focused on improvements to implementation procedures, especially community organisation, extension, and income generation activities. The capacity of community groups was developed by establishing communication facilities, building up community networks, and empowering women and disadvantaged groups. BIWMP ended in 2003 with much of its success attributed to the close involvement of all the main stakeholders, and especially the local people, in all the activities. It successfully helped land users to adopt improved livelihood options.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Bagmati Watershed
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការចាប់ផ្តើម និងបញ្ចប់នៃវិធីសាស្រ្តផ្សព្វផ្សាយនេះ
សូមបញ្ជាក់ឆ្នាំដែលបានបង្កើតឡើង:
1992
ឆ្នាំបញ្ចប់ (ប្រសិនបើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រូវបានឈប់ប្រើប្រាស់):
2003
2.7 ប្រភេទនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
- ផ្អែកលើគម្រោង/កម្មវិធី
2.8 គោលបំណង/ទិសដៅសំខាន់នៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (poverty reduction through sustained income generation, infrastructure improvement through equitable involvement of women and the socially disadvantaged.)
To overcome the constraints to effectively implementing a watershed management programme by building synergies between diverse stakeholder institutions. In the case of landslip and stream bank stabilisation work, the specific objective was to come up with a technology that conserved soil and water whilst also providing direct livelihood benefits to local people.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Lack of institutional capacity and collaboration for managing watershed resources
2.9 លក្ខខណ្ឌអនុញ្ញាត ឬរារាំងការអនុវត្តន៍បច្ចេកទេសដែលស្ថិតនៅក្រោមវិធីសាស្រ្តផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
សង្គម/វប្បធម៌/ និងតម្លៃនៃសាសនា
- រារាំង
Following conventional top-down approaches.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Introduction of improved methods with more participation/ involvement of land users.
បរិបទនៃស្ថាប័ន
- រារាំង
Lack of inter-institutional collaboration.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Building and ensuring collaboration.
ក្របខណ្ឌច្បាប់ (សិទ្ធិកាន់កាប់ដីធ្លី កម្មសិទ្ធីប្រើប្រាស់ដីនិងទឹក)
- អំណោយផល
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: The fact that the land was communal land (state property, use right with community) greatly helped smooth implementation of the approach as it was not necessary to deal with different land users.
ចំណេះដឹងស្តីពី SLM និងការទទួលបានការគាំទ្រផ្នែកបច្ចេកទេស
- រារាំង
Lack of new options.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Training about new technologies.
3. ការចូលរួម និងតួនាទីរបស់ភាគីពាក់ព័ន្ធ
3.1 អ្នកពាក់ព័ន្ធដែលបានចូលរួមក្នុងវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ និងតួនាទីរបស់ពួកគេ
- អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីក្នុងតំបន់/សហគមន៍
Men and women worked equally. existing groups of land users; men and women worked equally. BIWMP took a bottom-up approach to planning and implementation and encouraged the equitable involvement of women in its activities. The decisions about implementing the landslip and stream bank stabilisation technology were taken jointly by men and women
- អ្នកឯកទេសគ្រប់គ្រងដីប្រកបដោយចីរភាព/ទីប្រឹក្សាបច្ចេកទេសកសិកម្ម
- គ្រូបង្រៀន/សិស្សក្មេងៗ/សិស្ស-និស្សិត
- រដ្ឋាភិបាលថ្នាក់ជាតិ (អ្នករៀបចំផែនការ អ្នកសម្រេចចិត្ត)
- អង្គការអន្តរជាតិ
ប្រសិនមានភាគីពាក់ព័ន្ធច្រើនចូលរួមសូមចង្អុលបង្ហាញភ្នាក់ងារដែលនាំមុខគេ:
For the landslip and stream bank stabilisation technology, the approach was mainly designed by programme staff of the Kathmandu District Soil Conservation Office.
3.2 ការចូលរួមរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីក្នុងតំបន់/ សហគមន៍ក្នុងតំបន់ក្នុងដំណាក់កាលផ្សេងគ្នានៃវិធីសាស្រ្តផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
| ការចូលរួមរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីក្នុងតំបន់/សហគមន៍ក្នុងតំបន់ | សូមបញ្ជាក់នរណាត្រូវបានចូលរួម ព្រមទាំងពណ៌នាសកម្មភាពទាំងនោះ | |
|---|---|---|
| ការចាប់ផ្តើម/ការលើកទឹកចិត្ត | អន្តរកម្ម | rapid/participatory rural appraisal |
| ការរៀបចំផែនការ | អន្តរកម្ម | rapid/participatory rural appraisal; Share information from users right from planning period. |
| ការអនុវត្តន៍ | អន្តរកម្ម | responsible for major steps; Users were agreed to conserve soil by using SLM approaches. |
| ការត្រួតពិនិត្យ និងវាយតម្លៃ | អន្តរកម្ម | Mainly: reporting, public meetings, measurements/observations; partly: workshop/seminars; Regular monitoring and evaluation were successfully conducted by DSCO Office for the backstopping of the activities. |
| Research | អន្តរកម្ម | on-farm; This site is used as a Farmers School for extension of the technology on National and International level. |
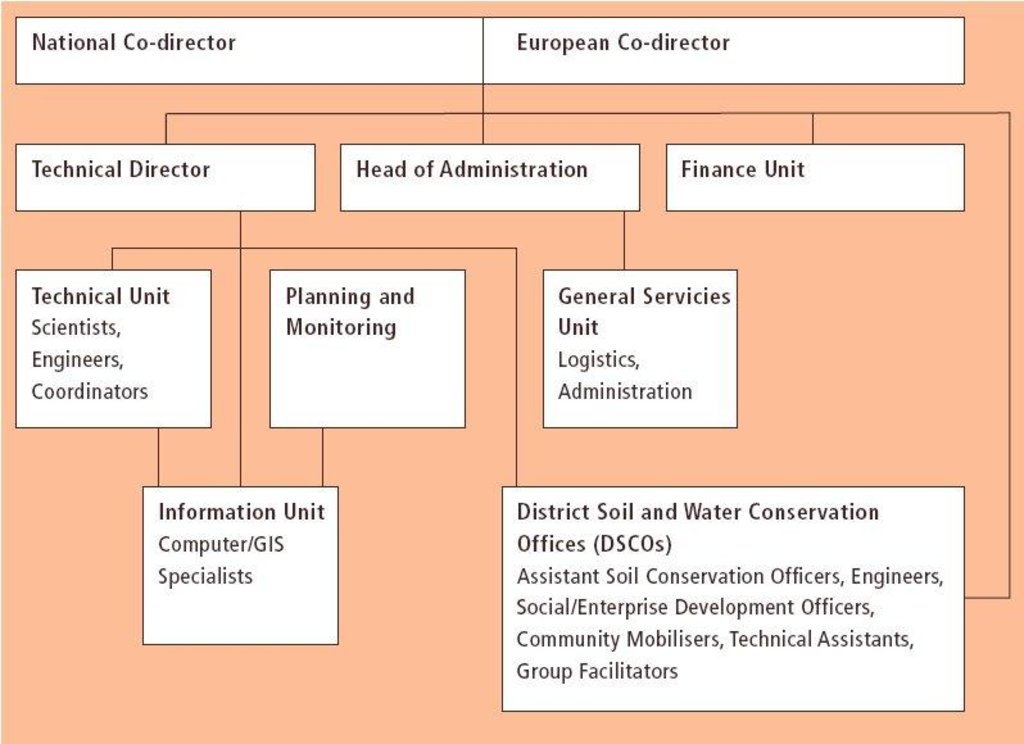
3.3 គំនូសបំព្រួញ (ប្រសិនបើមាន)
ការពណ៌នា:
Organogram of the Bagmati Integrated Watershed Management Programme (BIWMP). The landslip and stream bank stabilisation work was implemented by the Kathmandu District Soil Conservation Office supervi
3.4 ការសម្រេចចិត្តលើការជ្រើសរើសបច្ចេកទេស SLM
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើអ្នកណាជាអ្នកបានសម្រេចចិត្តក្នុងការជ្រើសរើសបច្ចេកទេសដើម្បីយកមកអនុវត្តន៍:
- អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM បន្ទាប់ពីបានប្រឹក្សាយោបល់ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ចូរពន្យល់:
The land users did not know about the technologies
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users. As measures required technical know-how
4. ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស ការកសាងសមត្ថភាព និងការគ្រប់គ្រងចំណេះដឹង
4.1 ការកសាងសមត្ថភាព/ បណ្តុះបណ្តាល
តើវគ្គបណ្តុះបណ្តាលបានផ្តល់ឱ្យអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី/អ្នកពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងៗទៀតដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើអ្នកណាត្រូវបានបណ្តុះបណ្តាល:
- អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ទម្រង់នៃការបណ្តុះបណ្តាល:
- ពីកសិករទីកសិករ
- ទីតាំងបង្ហាញ
- ការប្រជុំជាសាធារណៈ
ប្រធានបទបណ្តុះបណ្តាល:
On soil and water conservation
4.2 សេវាផ្តល់ប្រឹក្សាយោបល់
តើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីបានទទួលនូវសេវាផ្តល់ប្រឹក្សាដែរ ឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
សូមបញ្ជាក់ប្រសិនបើសេវាកម្មប្រឹក្សាយោបល់ត្រូវបានផ្តល់ឱ្យ:
- នៅលើដីរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ពណ៌នា/ពន្យល់:
Name of method used for advisory service: Integrated Watershed Management Programme; Key elements: Participatory Rural Appraisal, Trainings, Farmer to farmer exchange, workshops, seminars, On site Demnostration; 1) Advisory service was carried out through: government's existing extension system; Extension staff: mainly government employees 2) Target groups for extension: land users; Activities: Planning,Training, Awareness about SLM approaches
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; An extension workers is able to cover the areas where activities are implemented in small scale (i.e. subwatreshed or Micro subwatershed level programme).
4.3 ការពង្រឹងសមត្ថភាពស្ថាប័ន (ការអភិរឌ្ឍន៍អង្គភាព)
តើស្ថាប័នទាំងអស់ត្រូវបានបង្កើតឡើង ឬពង្រឹងសមត្ថភាពតាមរយៈវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយដែរ ឬទេ?
- បាទ/ច៎ា បានខ្លាំង
សូមបញ្ជាក់ថាតើស្ថាប័នត្រូវបានពង្រឹង ឬបង្កើតឡើងនៅត្រឹមកម្រិតណា(ច្រើន)?
- ថ្នាក់មូលដ្ឋាន
សូមបញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទនៃការគាំទ្រ:
- ការកសាងសមត្ថភាព/ បណ្តុះបណ្តាល
- សម្ភារៈ
4.4 ការត្រួតពិនិត្យ និងវាយតម្លៃ
តើការត្រួតពិនិត្យ និងវាយតម្លៃគឺជាផ្នែកមួយនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
មតិយោបល់:
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored through measurements
technical aspects were regular monitored through observations
socio-cultural aspects were regular monitored through observations
economic / production aspects were regular monitored through observations
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored through measurements
no. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored through observations
management of Approach aspects were regular monitored through observations
There were many changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: The approach described was designed on the basis of the results shown through monitoring and evaluating the first phase of BIWMP (1986-1992). In the second phase from 1992, more attention was focused on building up the capacity of community groups to plan, implement, and continue development activities. Capacity was built through (1) community-level training; (2) supporting the installation of com
4.5 ការស្រាវជ្រាវ
តើការស្រាវជ្រាវ គឺជាផ្នែកមួយនៃវិធីសាស្រ្តដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
បញ្ជាក់ប្រធានបទ:
- សង្គមវិទ្យា
- សេដ្ឋកិច្ច/ទីផ្សារ
- បរិស្ថានវិទ្យា
- បច្ចេកវិទ្យា
សូមផ្តល់ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមទៀតឱ្យបានលម្អិត និងចង្អុលបង្ហាញនរណាដែលបានធ្វើការស្រាវជ្រាវ:
see also further reading
5. ថវិកា និងសម្ភារៈឧបត្ថម្ភពីខាងក្រៅ
5.1 ថវិកាប្រចាំឆ្នាំសម្រាប់ផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM
ប្រសិនបើចំនួនពិតប្រាកដនៃថវិកាប្រចាំឆ្នាំមិនត្រូវបានដឹងច្បាស់ សូមប្រាប់ពីចន្លោះនៃថវិកានោះ:
- > 1,000,000
មតិយោបល់ (ឧ. ប្រភពសំខាន់នៃមូលនិធិ/ម្ចាស់ជំនួយចំបង):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (European Commission): 81.0%; government (national - His Majesty's Government (Nepal)): 4.0%; local community / land user(s) (Bagmati watershed): 15.0%
5.2 ការគាំទ្រផ្នែកហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ / សម្ភារៈដែលបានផ្តល់ទៅឱ្យអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
តើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីបានទទួលការគាំទ្រផ្នែកហិរញ្ញវត្ថ/សម្ភារៈសម្រាប់ការអនុវត្តន៍បច្ចេកទេសដែរឬទេ:
បាទ/ចា៎
5.3 សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូលត្រូវបានផ្តល់បដិភាគ (រួមទាំងកម្លាំងពលកម្ម)
- កសិកម្ម
| សូមបញ្ជាក់ ធាតុចូលណាខ្លះដែលបានផ្តល់បដិភាគ | កម្រិតទំហំប៉ុណ្ណា | សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីការបដិភាគ |
|---|---|---|
| គ្រាប់ពូជ | ||
| Seedlings and samples | ផ្តល់ហិរញ្ញវត្ថុមួយផ្នែក | |
- ការសាងសង
| សូមបញ្ជាក់ ធាតុចូលណាខ្លះដែលបានផ្តល់បដិភាគ | កម្រិតទំហំប៉ុណ្ណា | សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីការបដិភាគ |
|---|---|---|
| community infrastructure (cement, bricks, stones) | ផ្តល់ហិរញ្ញវត្ថុទាំងស្រុង | |
ប្រសិនបើកម្លាំងពលកម្មធ្វើដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី តើវាជាធាតុចូលដ៏សំខាន់មួយដែរ ឬទេ:
- ដោយស្ម័គ្រចិត្ត
មតិយោបល់:
About 75% of the labour for the landslip and stream bank stabilisation work was voluntar. The remainder was paid
5.4 ឥណទាន
តើឥណទានដែលបានផ្តល់នៅក្រោមវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយសម្រាប់សកម្មភាព SLM នេះយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច?
ទេ
6. ការវិភាគរកផលប៉ះពាល់ និងសេចក្តីសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
តើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយជួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដើម្បីអនុវត្តន៍ និងថែទាំបច្ចេកទេស SLM?
- ទេ
- បាទ/ច៎ា បន្តិចបន្តួច
- បាទ/ច៎ា ជាមធ្យម
- បាទ/ច៎ា បានខ្លាំង
The approach helped to improve soil and water management by promoting many activities related to agroforestry, water harvesting, landslip stabilisation, and community forestry. Many local land users adopted these technologies.
តើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយបានឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវបញ្ហាកាន់កាប់ដីធ្លី/សិទ្ធិអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដែលរារាំងដល់ការអនុវត្ត SLM?
- ទេ
- បាទ/ច៎ា បន្តិចបន្តួច
- បាទ/ច៎ា ជាមធ្យម
- បាទ/ច៎ា បានខ្លាំង
By influencing the forest department ot allocate forest to the people as community forest.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- ទេ
- បាទ/ច៎ា បន្តិចបន្តួច
- បាទ/ច៎ា ជាមធ្យម
- បាទ/ច៎ា បានខ្លាំង
It is not known whether this approach has been taken to address landslip and stream bank erosion problems in other areas by other projects.
6.3 សកម្មភាពផ្សព្វផ្សាយដែលប្រកបដោយចីរភាព
តើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីអាចធ្វើឱ្យមានចីរភាពនូវអ្វីដែលត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍តាមរយៈវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយដែរឬទេ(ដោយពុំមានការគាំទ្រពីអ្នកខាងក្រៅ)?
- មិនប្រាកដ
ប្រសិន ទេ ឬមិនប្រាកដសូមបញ្ជាក់ និងពន្យល់:
The land users were keen on maintaining the implemented technologies due to the benefits they could get from it. There has to be a strong driving force within the land users and the community to continue this approach.
6.4 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| Helped land users improve their livelihoods. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Similar approaches should be implemented by government and community programmes.) |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Involves all key actors in watershed management. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Institutionalise the approach.) |
| The approach encourages land users communities and local institutions to get involved in planning and decision making (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Involve them more in planning and decision making) |
| The implementation of technologies through this approach is cost-effective and socio-culturally acceptable. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Take into account local resources and knowledge) |
6.5 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រ និងរកដំណោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| No opinion. |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យក្នុងទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Some activities with high input requirements may not be spontaneously adopted by poor land users | Further research on how to reduce inputs or provide specifi c incentives for such disadvantaged groups. |
| The approach is 'project focussed' | Institutionalise the approach |
| The approach does not focus on landless families. | Implement watershed management activities that involve and benefit landless people |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Mallik, D.B. (2000) 'Working with Community'. In Jaladhar-QuarterlyBIWM (1998 to 2001) Annual Workplans for Project Years 1998 to 2002, prepared for Government of Nepal,MOFS,DSCWM and EU; Kathmandu, Nepal
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
BIWMPBIWMP email: biwmp@mos.com.np
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
BIWM (1998 to 2001) Annual Workplans for Project Years 1998 to 2002, prepared for Government of Nepal,MOFS,DSCWM and EU; Kathmandu, Nepal
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
BIWMP email: biwmp@mos.com.np
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល