Promoting farmer innovation [អ៊ូហ្គង់ដា]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Kithinji Mutunga
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យ Fabian Ottiger
approaches_2418 - អ៊ូហ្គង់ដា
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ (បើទាក់ទង)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - ប្រទេសអ៊ីតាលីឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ (បើទាក់ទង)
CIS-Centre for International Cooperation (CIS-Centre for International Cooperation) - ប្រទេសហូឡង់ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ (បើទាក់ទង)
Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock Development of Kenya (MoA) - ប្រទេសកេនយ៉ា1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 ការយោងមួយ (ច្រើន) ទៅលើ (កម្រង) បញ្ជីសំណួរនៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2. ការពណ៌នាអំពីវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM
2.1 ពណ៌នាសង្ខេបខ្លីពីវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
Identification of farmer innovators in SWC and water harvesting, and using them as focal points for visits from other farmers to spread the practices and stimulate the process of innovation.
2.2 ពណ៌នាលម្អិតពិវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
ពណ៌នាលម្អិតពិវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ:
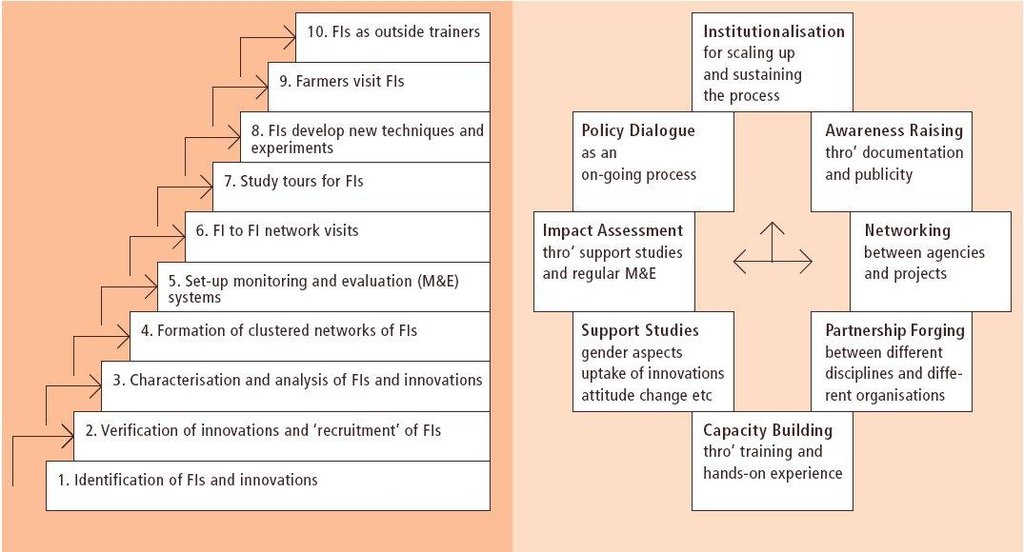
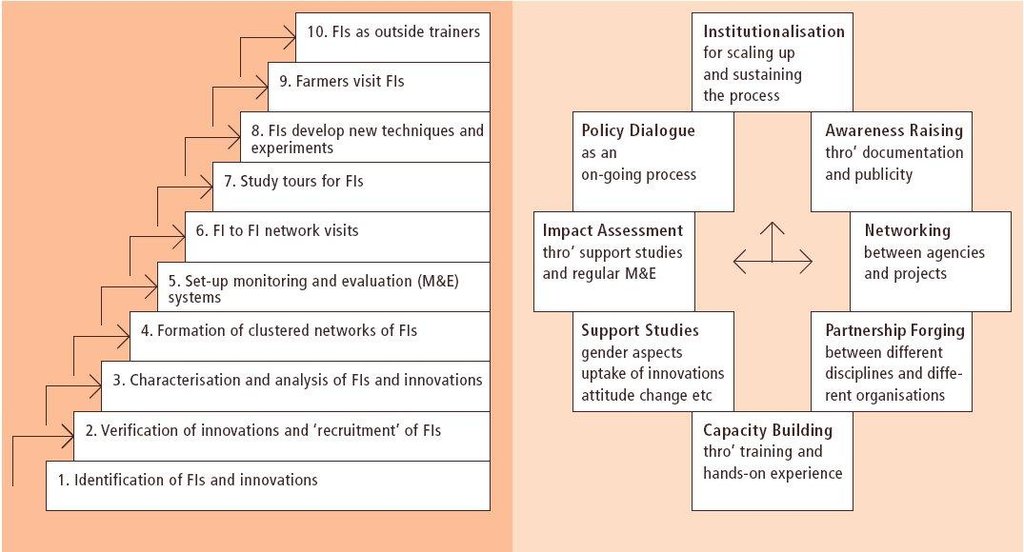
Aims / objectives: The Promoting Farmer Innovation (PFI) approach seeks to build on technical initiatives - innovations in the local context - developed by farmers themselves in dry/marginal areas where the conventional approach of transfer of technology from research to extension agents, and then on to farmers, has so often failed. The approach basically comprises identifying, validating and documenting local innovations/initiatives. Simple monitoring and evaluation systems are set up amongst those innovative farmers who are willing to co-operate. Through contact with researchers, extra value is added to these techniques where possible. Farmer innovators are brought together to share ideas. Finally, best-bet technologies, in other words those that are considered to be good enough to be shared, are disseminated through farmer-to-farmer extension. This takes two forms. First, farmers are brought to visit the innovators in their farms. Secondly farmer innovators are used as teachers/trainers to visit groups of farmers - including FAOs farmer field schools in some cases. Only in this second form of extension is an allowance payable to the innovator. A ten-step field activity methodology has been developed.
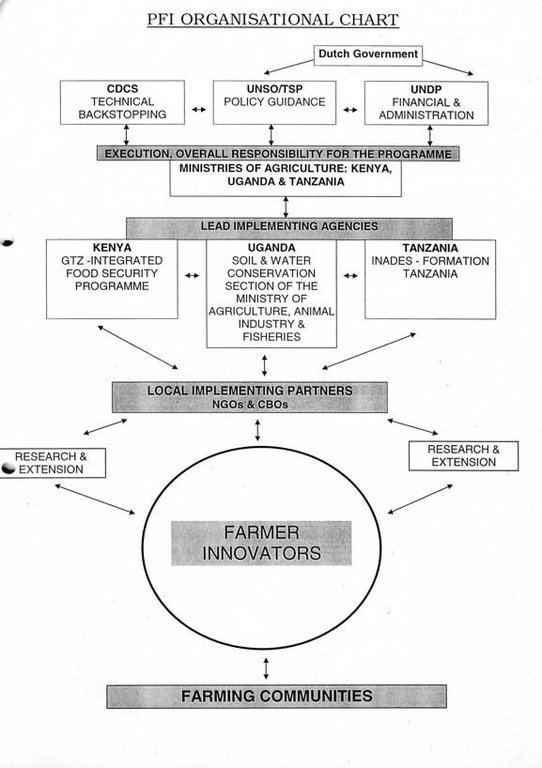
Methods: At programme level, there is capacity building of in-line extension and research staff, who are the main outside actors in the programme. In each of the countries the project has been implemented through a government ministry, which partners various NGOs in the field. The principle, and practice, is not to create separate project enclaves, but to work through existing personnel, sharing buildings and vehicles that are already operational in the area. A programme development process methodological framework shows how the ultimate goal of institutionalisation can be achieved. PFIs first phase, completed in 2000, was financed by the Government of The Netherlands, through UNDP, and was active in Kenya, Tanzania and Uganda.
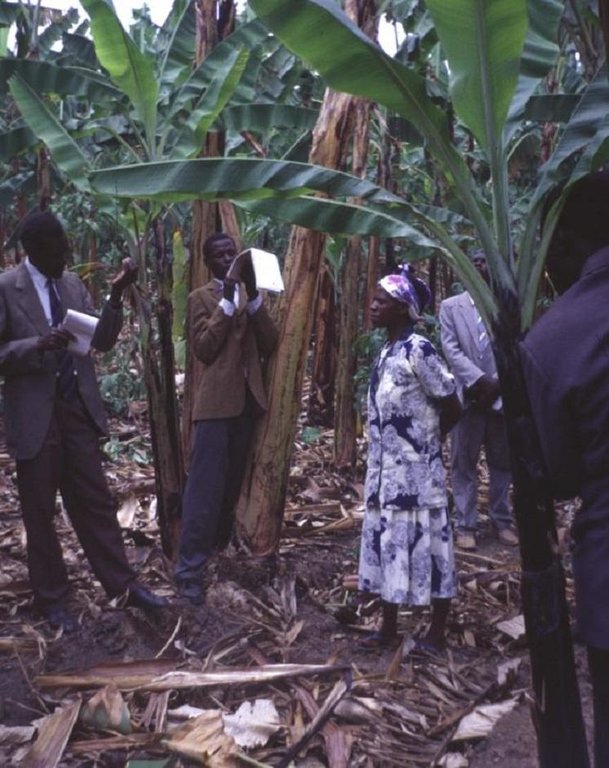
2.3 រូបភាពនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍
ប្រទេស:
អ៊ូហ្គង់ដា
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
East Africa (parts of Kenya, Tanzania and Uganda)
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការចាប់ផ្តើម និងបញ្ចប់នៃវិធីសាស្រ្តផ្សព្វផ្សាយនេះ
សូមបញ្ជាក់ឆ្នាំដែលបានបង្កើតឡើង:
1996
ឆ្នាំបញ្ចប់ (ប្រសិនបើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រូវបានឈប់ប្រើប្រាស់):
2000
2.7 ប្រភេទនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
- ផ្អែកលើគម្រោង/កម្មវិធី
2.8 គោលបំណង/ទិសដៅសំខាន់នៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (Better land husbandry practices (eg composting, crop selection))
Improve rural livelihoods through an increase in the rate of diffusion of appropriate SWC/water harvesting technologies based on farmer innovation, and through farmer-to-farmer exchange visits. At a higher level: to demonstrate the effectiveness of such an approach so that it can be institutionalised.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: - poor supply of relevant recommendations from research for small scale farmers in marginal areas - poor delivery of SWC technologies (where they exist) to farmers - lack of motivation of research and extension staff - isolation of promising ???innovative??? SWC/water harvesting ideas which address low crop yields, land degradation and poverty - lack of exchange of this knowledge
2.9 លក្ខខណ្ឌអនុញ្ញាត ឬរារាំងការអនុវត្តន៍បច្ចេកទេសដែលស្ថិតនៅក្រោមវិធីសាស្រ្តផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
សង្គម/វប្បធម៌/ និងតម្លៃនៃសាសនា
- រារាំង
Favoured farmer syndrome: where too much attention is given to particular innovative farmers and jealousy is aroused in others
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Avoid working with innovators who are so exceptional that they are outside society and others cannot relate to them. Rotate the farmers who are used as learning points: in other words once another farmer has adopted the technology, use him or her as the focal point.
ភាពអាចរកបាននៃធនធានហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ និងសេវាកម្ម
- រារាំង
Danger of identifying innovations that are good technically but too expensive for ordinary farmers to implement.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Linked to point (1) above: beware of farmers who are too exceptional/too rich.
បរិបទនៃស្ថាប័ន
- រារាំង
Lack of motivation of research and extension institutions
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Bringing them together with farmer innovatiors
ក្របខណ្ឌច្បាប់ (សិទ្ធិកាន់កាប់ដីធ្លី កម្មសិទ្ធីប្រើប្រាស់ដីនិងទឹក)
- រារាំង
Who gets the credit for the particular innovation?
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Important to make sure that an innovation is traced back within the locality to its roots, identifying the 'owner'. Especially important when a name is attached to an innovation.
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights hindered a little the approach implementation Farmers will only invest time and effort in innovation when they have secure land use rights (though not necessarily ownership), which is the case in all the areas where PFI has been operational. Access to land for women was a problem which inhibits women innovating.
ផ្សេងៗ
- រារាំង
Cultural: Gender imbalance in identification of innovators: women overlooked
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Gender sensitisation and training: bring together the identifiers with the farmers - male and female.
3. ការចូលរួម និងតួនាទីរបស់ភាគីពាក់ព័ន្ធ
3.1 អ្នកពាក់ព័ន្ធដែលបានចូលរួមក្នុងវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ និងតួនាទីរបស់ពួកគេ
- អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីក្នុងតំបន់/សហគមន៍
- អ្នកឯកទេសគ្រប់គ្រងដីប្រកបដោយចីរភាព/ទីប្រឹក្សាបច្ចេកទេសកសិកម្ម
- អង្គការក្រៅរដ្ឋាភិបាល
All involved et different levels: after implementation mainly government and NGO
- រដ្ឋាភិបាលថ្នាក់ជាតិ (អ្នករៀបចំផែនការ អ្នកសម្រេចចិត្ត)
All involved et different levels: after implementation mainly government and NGO
- អង្គការអន្តរជាតិ
All involved et different levels: after implementation mainly government and NGO
ប្រសិនមានភាគីពាក់ព័ន្ធច្រើនចូលរួមសូមចង្អុលបង្ហាញភ្នាក់ងារដែលនាំមុខគេ:
International specialists in collaboration with/after discussions with national specialists and land users
3.2 ការចូលរួមរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីក្នុងតំបន់/ សហគមន៍ក្នុងតំបន់ក្នុងដំណាក់កាលផ្សេងគ្នានៃវិធីសាស្រ្តផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
| ការចូលរួមរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីក្នុងតំបន់/សហគមន៍ក្នុងតំបន់ | សូមបញ្ជាក់នរណាត្រូវបានចូលរួម ព្រមទាំងពណ៌នាសកម្មភាពទាំងនោះ | |
|---|---|---|
| ការចាប់ផ្តើម/ការលើកទឹកចិត្ត | អសកម្ម | public meetings, interviews/questionnaires, workshops/seminars, rapid/participatory rural appraisal; interviews/Participatory Rural Appraisals etc |
| ការរៀបចំផែនការ | អសកម្ម | rapid/participatory rural appraisal, interviews/questionnaires, public meetings, workshops/seminars; interviews/Participatory Rural Appraisals etc |
| ការអនុវត្តន៍ | អន្តរកម្ម | Mainly: farmer-to-farmer exchange, responsibility for minor steps; partly: responsibility for major steps; interviews/Participatory Rural Appraisals etc |
| ការត្រួតពិនិត្យ និងវាយតម្លៃ | អន្តរកម្ម | Mainly: public meetings, measurements/observations; partly: workshop/seminars; monitoring, using forms designed mainly by specialists |
| Research | អន្តរកម្ម | on-farm |
3.3 គំនូសបំព្រួញ (ប្រសិនបើមាន)
ការពណ៌នា:
Farmer innovation methodology left: Field activities: the ten steps– from identification through to using innovators as trainers. (Critchley, 2000) right: Programme development processes: the framew
3.4 ការសម្រេចចិត្តលើការជ្រើសរើសបច្ចេកទេស SLM
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើអ្នកណាជាអ្នកបានសម្រេចចិត្តក្នុងការជ្រើសរើសបច្ចេកទេសដើម្បីយកមកអនុវត្តន៍:
- អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ដោយមានការគាំទ្រពីអ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM
ចូរពន្យល់:
???Best -bet??? technologies chosen by extension agents/researchers based on the selection of innovative farmers??? technologies identified in the field - but the farmers choose (develop) which technology to implement.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by by land users* alone (self-initiative / bottom-up)
4. ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស ការកសាងសមត្ថភាព និងការគ្រប់គ្រងចំណេះដឹង
4.1 ការកសាងសមត្ថភាព/ បណ្តុះបណ្តាល
តើវគ្គបណ្តុះបណ្តាលបានផ្តល់ឱ្យអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី/អ្នកពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងៗទៀតដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើអ្នកណាត្រូវបានបណ្តុះបណ្តាល:
- អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
- SWC specialists, extensionists/trainers
ទម្រង់នៃការបណ្តុះបណ្តាល:
- ការប្រជុំជាសាធារណៈ
- វគ្គបណ្តុះបណ្តាល
ទម្រង់នៃការបណ្តុះបណ្តាល:
- farm visits
ប្រធានបទបណ្តុះបណ្តាល:
Staff seconded from Ministries of Agriculture/NGOs provide: (1) methodology training for participating staff (2) presentational skill training for farmer innovators and (3) training in gender aspects.
4.2 សេវាផ្តល់ប្រឹក្សាយោបល់
តើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីបានទទួលនូវសេវាផ្តល់ប្រឹក្សាដែរ ឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
សូមបញ្ជាក់ប្រសិនបើសេវាកម្មប្រឹក្សាយោបល់ត្រូវបានផ្តល់ឱ្យ:
- នៅមជ្ឈមណ្ឌលជាអចិន្ត្រៃ
ពណ៌នា/ពន្យល់:
Name of method used for advisory service: Farmer innovator approach; Key elements: There are new roles for government/NGO extension staff under this methodology - as trainers and faci, Identify farmer innovators, form networks of farmer innovators, which meet, Bring farmers to se 'best bet' innovations; 1) Advisory service was carried out through: government's existing extension system, non-governmental agency; Extension staff: mainly government employees 3) Target groups for extension: land users
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities
4.3 ការពង្រឹងសមត្ថភាពស្ថាប័ន (ការអភិរឌ្ឍន៍អង្គភាព)
តើស្ថាប័នទាំងអស់ត្រូវបានបង្កើតឡើង ឬពង្រឹងសមត្ថភាពតាមរយៈវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយដែរ ឬទេ?
- បាទ/ច៎ា ជាមធ្យម
សូមបញ្ជាក់ថាតើស្ថាប័នត្រូវបានពង្រឹង ឬបង្កើតឡើងនៅត្រឹមកម្រិតណា(ច្រើន)?
- ថ្នាក់មូលដ្ឋាន
សូមបញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទនៃការគាំទ្រ:
- ការកសាងសមត្ថភាព/ បណ្តុះបណ្តាល
សូមផ្តល់ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមទៀតឱ្យបានលម្អិត:
training (see also Annex A3)
4.4 ការត្រួតពិនិត្យ និងវាយតម្លៃ
តើការត្រួតពិនិត្យ និងវាយតម្លៃគឺជាផ្នែកមួយនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
មតិយោបល់:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by 0 through observations; indicators: soils, moisture
technical aspects were regular monitored by 0 through observations; indicators: inputs
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored by 0 through measurements; indicators: number of men/women participating
economic / production aspects were regular monitored by 0 through observations; indicators: yields
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored by 0 through observations; indicators: None
no. of land users involved aspects were ad hoc monitored by 0 through observations; indicators: None
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Some changes, for example (a) increased numbers of women identified as innovators in response to gender sensitisation/training and (b) ???rotation??? of farmer innovators used for training - that is not using the same farmers all the time, as this can create envy. E.g. also better integration with government services/system for technical backstopping and extension
4.5 ការស្រាវជ្រាវ
តើការស្រាវជ្រាវ គឺជាផ្នែកមួយនៃវិធីសាស្រ្តដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
បញ្ជាក់ប្រធានបទ:
- បច្ចេកវិទ្យា
- socio-economics
សូមផ្តល់ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមទៀតឱ្យបានលម្អិត និងចង្អុលបង្ហាញនរណាដែលបានធ្វើការស្រាវជ្រាវ:
Theoretically, researchers should respond to the farmers??? research agenda, though this has proved difficult to achieve in practice. Apart from process monitoring of the methodology, which has led to improvements, technical research into the innovations has been relatively weak.
Research was carried out on-farm
5. ថវិកា និងសម្ភារៈឧបត្ថម្ភពីខាងក្រៅ
5.1 ថវិកាប្រចាំឆ្នាំសម្រាប់ផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM
ប្រសិនបើចំនួនពិតប្រាកដនៃថវិកាប្រចាំឆ្នាំមិនត្រូវបានដឹងច្បាស់ សូមប្រាប់ពីចន្លោះនៃថវិកានោះ:
- 100,000-1,000,000
មតិយោបល់ (ឧ. ប្រភពសំខាន់នៃមូលនិធិ/ម្ចាស់ជំនួយចំបង):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (national government): 20.0%; international (International agency): 60.0%; local community / land user(s) (-): 20.0%
5.2 ការគាំទ្រផ្នែកហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ / សម្ភារៈដែលបានផ្តល់ទៅឱ្យអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
តើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីបានទទួលការគាំទ្រផ្នែកហិរញ្ញវត្ថ/សម្ភារៈសម្រាប់ការអនុវត្តន៍បច្ចេកទេសដែរឬទេ:
ទេ
5.3 សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូលត្រូវបានផ្តល់បដិភាគ (រួមទាំងកម្លាំងពលកម្ម)
ប្រសិនបើកម្លាំងពលកម្មធ្វើដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី តើវាជាធាតុចូលដ៏សំខាន់មួយដែរ ឬទេ:
- ដោយស្ម័គ្រចិត្ត
មតិយោបល់:
done by the farmers themselves
plant materials - farmers often are given or collecting planting.
Support to institutions has been moderate: it has mainly taken the form of transporting existing groups (for example womens groups/church groups) to learn from farmer innovators.
5.4 ឥណទាន
តើឥណទានដែលបានផ្តល់នៅក្រោមវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយសម្រាប់សកម្មភាព SLM នេះយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច?
ទេ
6. ការវិភាគរកផលប៉ះពាល់ និងសេចក្តីសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
តើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយបានឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវបញ្ហាកាន់កាប់ដីធ្លី/សិទ្ធិអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដែលរារាំងដល់ការអនុវត្ត SLM?
- ទេ
- បាទ/ច៎ា បន្តិចបន្តួច
- បាទ/ច៎ា ជាមធ្យម
- បាទ/ច៎ា បានខ្លាំង
Gender sensitisation training may have helped. The problem is unlikely to be overcome in the near future.
6.3 សកម្មភាពផ្សព្វផ្សាយដែលប្រកបដោយចីរភាព
តើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីអាចធ្វើឱ្យមានចីរភាពនូវអ្វីដែលត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍តាមរយៈវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយដែរឬទេ(ដោយពុំមានការគាំទ្រពីអ្នកខាងក្រៅ)?
- មិនប្រាកដ
ប្រសិន ទេ ឬមិនប្រាកដសូមបញ្ជាក់ និងពន្យល់:
There are examples of spontaneous voluntary continuation of farmer innovator groups in all three countries - but on a reduced level after initial project support ended.
6.4 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Builds on local ideas (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue the approach and institutionalise.) |
| Revitalises the extension service (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Train and make use of existing Government extension agents.) |
| attractive to stakeholders at all levels (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Involve and inform stakeholders at all levels of plans and progress.) |
| Gives land users more confidence in their own abilities (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue to prioritise farmers and keep them at centre of activities.) |
| Offers new locally tested ideas/technologies which work (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Keep the focus on the farmers??? initiatives and use participatory technology development processes to improve these technologies.) |
6.5 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រ និងរកដំណោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យក្នុងទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Dependent on individual commitment and flexibility | Training in skills and methodologies. |
| Does not follow the conventional institutional chain of command | Considerable training in skills and methodologies required. |
| Sometime confers too much prestige on a particular group of ???favoured farmers??? | Rotate??? farmers who are the focus of attention. |
| Researchers reluctant to respond to farmers??? agenda | Effort needed to convince research staff of the need for, and potential benefits from, joint Critchley WRS (2000) Inquiry, Initiatives and Inventiveness: Farmer Innovators in East Africa. Phs Chem Earth (B), Vol 25, no 3, pp 285??¡§288Critchley WRS (2000) Inquiry, Initiatives and Inventiveness: Farmer Innovators in East Africa. Phs Chem Earth (B), Vol 25, no 3, pp 285??¡§288Critchley WRS (2000) Inquiry, Initiatives and Inventiveness: Farmer Innovators in East Africa. Phs Chem Earth (B), Vol 25, no 3, pp 285??¡§288Critchley WRS (2000) Inquiry, Initiatives and Inventiveness: Farmer Innovators in East Africa. Phs Chem Earth (B), Vol 25, no 3, pp 285??¡§288research with farmers. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Critchley WRS (2000) Inquiry, Initiatives and Inventiveness: Farmer Innovators in East Africa. Phs Chem Earth (B), Vol 25, no 3,Mutunga K and Critchley W (2001) Farmers??? initiatives in land husbandry. Regional Land Management Unit, Nairobi, KenyaCritchley W and Mutunga K (2003) Local innovation in a global context: documenting farmer initiatives in land husbandry through WOCAT.Critchley et al. (1999). Promoting farmer innovationPromoting farmer innovation VIDEO
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
RELMA, Nairobi (cost free)RELMA, Nairobi (cost free)
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Mutunga K and Critchley W (2001) Farmers initiatives in land husbandry. Regional Land Management Unit, Nairobi, Kenya
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Critchley W and Mutunga K (2003) Local innovation in a global context: documenting farmer initiatives in land husbandry through WOCAT.
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Critchley et al. (1999). Promoting farmer innovation
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
RELMA, Nairobi (cost free)
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Promoting farmer innovation VIDEO
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
RELMA, Nairobi (cost free)
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល