In situ mulching of coffee using Cordia Abbysinica [ប្រទេសតង់សានី]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Bertha Munyaga
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យ Alexandra Gavilano
Kgutela igitutu ckimwani
technologies_1191 - ប្រទេសតង់សានី
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - ប្រទេសអ៊ីតាលីឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - ប្រទេសអ៊ីតាលី1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
11/02/2014
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
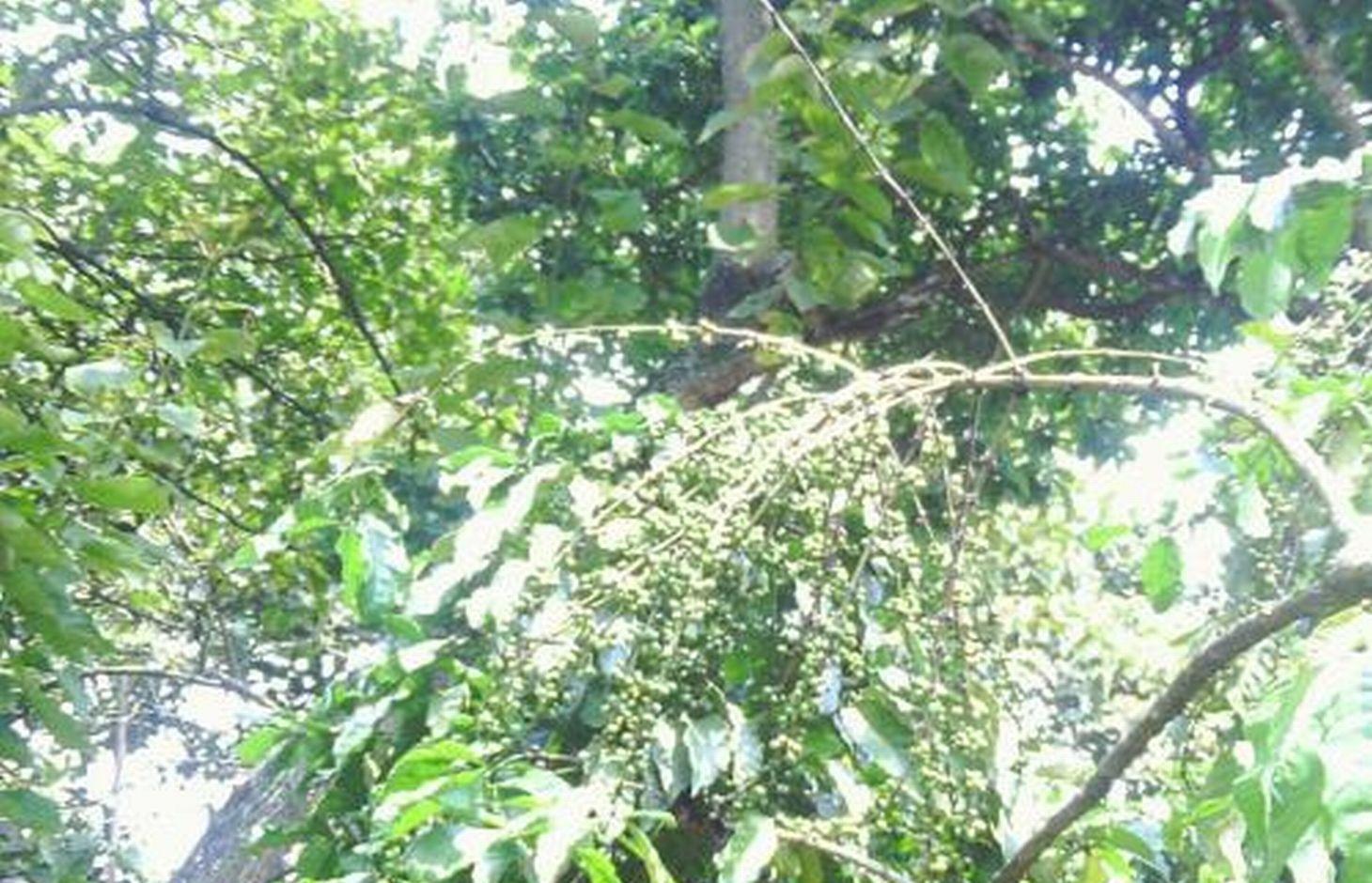
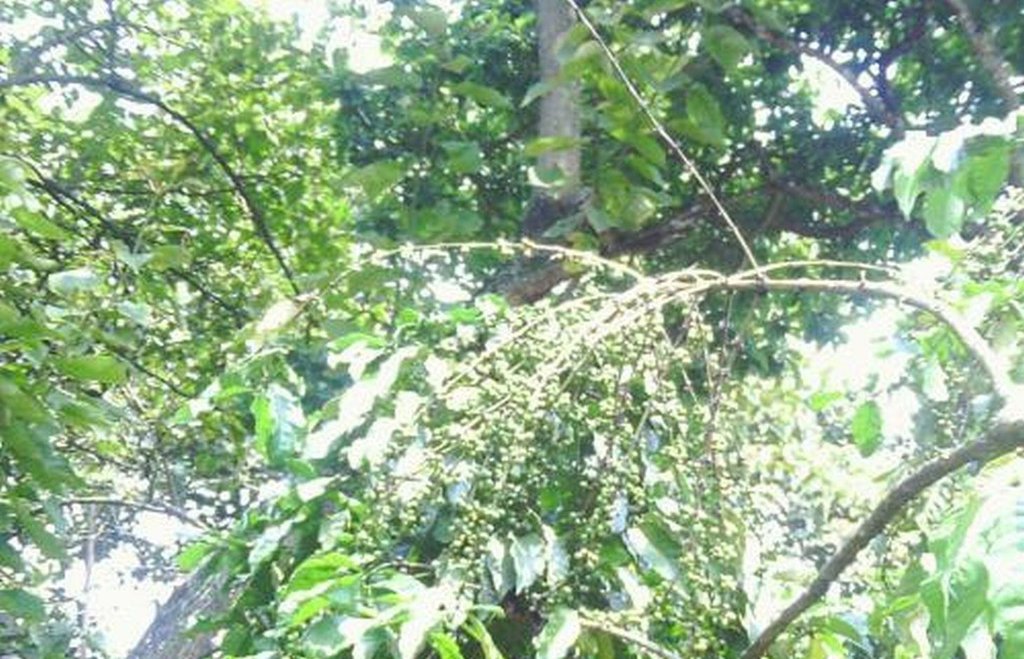
Use of indigenous trees to provide shade and leaves droppings as mulch for coffee production
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
Establishment of Robusta coffee farms by an individual,on a cropland by mixing indigenous tree spp which provide a shade and dropping leaves save as natural mulch.The technology has been developed through land user initiatives over 40 years ago. Establishment activities include land clearing and preparation,preparation of holes,seed collection and planting which involve family labor Seeds are collected from neighboring village from mature trees. Holes are prepared randomly about 4 meters apart. No inputs are applied at the establishment stage only hand tools are used (hand hoe, matchet)
Shade trees are planted after establishment of coffee which are randomly planted, tree spp dominating is Cordia abbysinica which has broader leaves and easy to decompose.Other tree spp included are Erythrina,Meosopsis eminii,Ficus thornngii,Makhamia lutea and Tephrosia vogelii.
Maintenance include weeding which is done by pulling weeds by hand or using hand hoe at early stage after establishment because few leaves have dropped. The farm is mainly meant for coffee production however,few crops which are cassava bananas, fruit trees Jack fruit, Mangoes, Citrus spp which are planted in the peripherals,and Dracaena sppplanted to demarcate the farm along road side.
Pruning of tree branches is done before the shade is heavy as to allow ventilation.Coffee pruning is done to an individual tree depending on number of branches it has at time of harvesting, normally 4 branches are left. Bending of coffee branches is practiced to avoid branch breaking during harvesting.
Settlement is within the farm with few livestock which are sheep, cattle and chicken.
Purpose of the Technology: To increase coffee production by mixing coffee with indigenous tree spp which drop / shed its leaves.Selected trees are those broad leaved which its leaves decompose easily hence improve soil fertility and due to high accumulation of dropped leaves there is an increase in soil moisture content.
Trees act as wind break hence no flower drop.Dracaena spp are planted very close along the road side to demarcate his plot from neighbors and public infrastructure and this helps to reduce land conflicts among neighbors and community as well.
Hand weeding is done as the technology suppress weeds to the big shade.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: A farmer bought a piece of land from the village government.Establishment activities include land clearance by removal of shrubs using a matchet.This is followed by land preparations and planting holes which are 30cm depth and 30cm width. These activities are done from May to July by family labor.Planting is normally done between September and October by collecting seedlings from mature trees in neighbors fields.Planting of indigenous tree spp is done randomly after coffee planting to allow ventilation 80 different spps are planted in 1.5 acres. Seeds and seedlings are obtained from neighbors farms.Maintenance includes weeding which is done using family labor who use hand hoe. This is done twice a year in May and December to January. Pruning and bending of coffee tree branches is done once per year after harvesting of coffee as well as trees in June and July using a matchet. Each coffee tree is treated individually only 4 branches are allowed per tree. Bending is done to avoid breaking of branches during coffee harvesting.
Gap filling is done few months after transplanting between February and March at the beginning of long rains. and this was followed pruning and bending of coffee branches.
Demarcation of coffee farm using Dracaena (shrub) done on one side of his farm along the road.
Natural / human environment: Land use type: Establishment of coffee has been done on crop land.
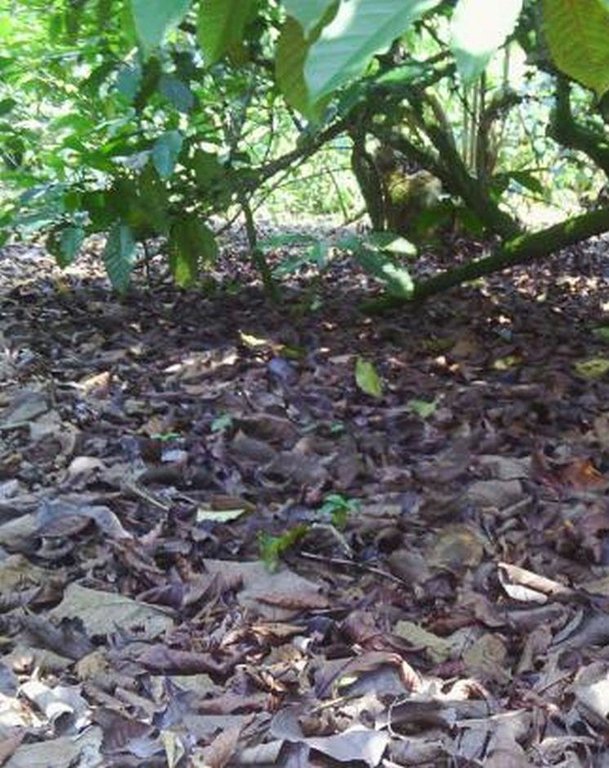
Agronomic: Natural mulch from leaves falling on ground.
Vegetative: Demarcation of boundary using Dracaena spp.
Climatic zone: Sub humid more than 269 growing days.
slope: 2-5% gentle slope
Soil type: Clay loam
Soil depth: Deep
Tools and inputs: Hand hoes,bush knife,axe, seeds and cuttings.
Land ownership: Individually owned.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសតង់សានី
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Tanzania
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Ngara District
មតិយោបល់:
Boundary points of the Technology area: 236229742E 236229740E 236229639E 236229639E
9726279N 9726387N 9726293N 9726392N
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- 10-50 ឆ្នាំ
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
The technology was adopted from Muleba district and adapted in Kirusya village
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ

ដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
- Tethering: rapid decline of land due to expansion of settlements and crop production
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion, water loss/moisture stress, loss of nutrients through leaching and flower drop which lead to reduced yield.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Poor soil fertility and water stress
3.3 ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 2
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: September-DecemberSecond longest growing period in days: 90Second longest growing period from month to month: March-May
ដង់ស៊ីតេនៃសត្វចិញ្ចឹម (បើពាក់ព័ន្ធ):
10-25 LU /km2
3.5 ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានសាយភាយពាសពេញតំបន់ណាមួយ សូមកំណត់ទំហំផ្ទៃដីអនុវត្តន៍:
- < 0.1 គម2 (10 ហិកតា)
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A1: ដំណាំ/គម្របដី
- A2: សារធាតុសរីរាង្គ/ជីជាតិដី

វិធានការរុក្ខជាតិ
- V1: ឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M3: ប្លង់យោងទៅតាមធម្មជាតិ និងបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ
មតិយោបល់:
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, manure / compost / residues, minimum tillage
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary, scattered / dispersed
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cn: ការថយចុះជីជាតិ និងកាត់បន្ថយបរិមាណសារធាតុសរីរាង្គ (មិនកើតឡើងដោយការហូរច្រោះទេ)

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bc: ការថយចុះនូវគម្របរុក្ខជាតិ
មតិយោបល់:
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (indigenous tree,fruits and coffee. (shrubs)), change in temperature (Loss of water due to evapo transpiration), labour availability (Vegetation degradation)
Secondary causes of degradation: change of seasonal rainfall (Change of seasonal rainfall), wind storms / dust storms (De flowering leading to production loss)
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
4.2 លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស/ ពណ៌នាពីគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស
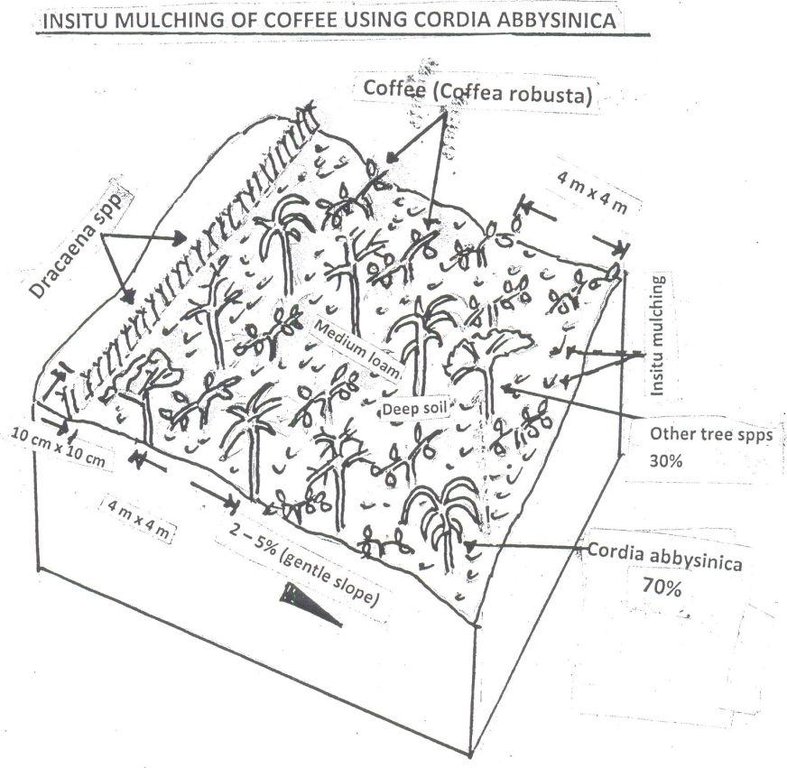
Indigenous tree are randomly planted and Cordia Abbysinica accounts for 70% of the indegenous tree spps. Demarcation of a coffee farm is done using Dracaena (shrub) done on one side of the farm along the road. Natural mulching is done by tree leaves/debris falling on ground. Slope category range from 2-5% gentle slope. Average spacing of Robusta coffee is 4m x 4m.
Location: Karushya Nyamigango. Ngara/Kagera/Tanzania
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: reduction in wind speed
Mulching
Material/ species: leavesof indigenous trees drop
Quantity/ density: 6 cm depth
Remarks: natural falling and irregular aligment
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: indigenous trees
Minimum tillage
Material/ species: Hand pulling sometimes use simple tools.
Aligned: -along boundary
Number of plants per (ha): 1,000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.1
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0
Scattered / dispersed
Number of plants per (ha): 375
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 60
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 60
Trees/ shrubs species: Cordia abbysinica, Ficus spp,Erythrina spp,Makhamia spp,Tephrosia spp Maesopsis spp (planted)
Fruit trees / shrubs species: avocado, mandarine,
Perennial crops species: Coffee
Other type of management: (Land protection and demarcation)
Planting Dracaena along the road side
4.3 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
Tanzanian shillings
កំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (បើទាក់ទង)៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
1600,0
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
3000.00
4.4 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Hole preparation | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | Nov. |
| 2. | Seed collection and preparation | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | Nov to Dec |
| 3. | Seedling planting | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | Dec |
| 4. | Demarcation and excavation of small trench | ការគ្រប់គ្រង | September-before long rains |
| 5. | Preparation of cuttings | ការគ្រប់គ្រង | September-December |
| 6. | Actual planting | ការគ្រប់គ្រង | September-December |
| 7. | labour | ការគ្រប់គ្រង | |
| 8. | pangas (matchet) | ការគ្រប់គ្រង | |
| 9. | handhole | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | |
| 10. | tree & coffee seedlings | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ |
4.5 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | labour | 1,0 | 2510,4 | 2510,4 | 100,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | tools | 1,0 | 21,88 | 21,88 | 100,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | seeds | 1,0 | 31,25 | 31,25 | 100,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | seedlings | 1,0 | 61,73 | 61,73 | 100,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 2625,26 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Duration of establishment phase: 6 month(s)
4.6 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pruning-Trees-Coffee | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | After harvesting, June-July |
| 2. | Weeding | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | after long rain season |
| 3. | Gap filling | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | March,during short rains |
| 4. | Bending and layering | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | Once after harvesting |
| 5. | Gap filling | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | before short rains |
| 6. | Prunning | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | Dry season |
4.7 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | labour | 1,0 | 63,63 | 63,63 | 100,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | seedlings | 1,0 | 33,05 | 33,05 | 100,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 96,68 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Machinery/ tools: Hand hoe, panga (matchet) and axe, Panga (Matchet), hand hoe and axe
The cost assesment was completed on 18 February 2014. The cost of labour can be reduced during the onset of rain when the soil is a bit workable.
4.8 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
Labour
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
Thermal climate class: tropics. All months above 18°C
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ខ្ពស់ (>3%)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
> 50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
ល្អ
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលមានគុណភាពល្អ
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម/ ទីផ្សារ
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
យេនឌ័រ:
- បុរស
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Tree and coffee pruning is done by men because it needs climbing
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
80% of the land users are average wealthy and own 80% of the land (He is getting income from coffee).
20% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Most of the residents are permanent farmers
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន ឬជួលគេដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតតូច
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មិនមានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
មតិយោបល់:
Water is accessed friendly, land is inherited.
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
16bags/ha
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
58 bags/ha
ផលិតកម្មចំណីសត្វ
ផលិតកម្មឈើ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
3cub.m/ha
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
12cub.m/ha
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ការចំណាយលើធាតុចូលកសិកម្ម
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
62 kg/ha
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
0 kgs/ha
បន្ទុកការងារ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
15 md/ha
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
2 md/ha
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
low
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
improved
ស្ថានភាពសុខភាព
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
little
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
inreased
ឱកាសវប្បធម៍
ឱកាសនៃការបង្កើតថ្មី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
none
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
available
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
ការកាត់បន្ថយជម្លោះ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
none
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
available
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
បរិមាណទឹក
គុណភាពទឹក
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
low
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
high
លំហូរទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
low
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
high
ដី
សំណើមដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
low
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
high
គម្របដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
low
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
high
ការបាត់បង់ដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
low
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
high
ដីប្រេះ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
low
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
medium
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ជីវម៉ាស/ កាបូនលើដី
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ហានិភ័យនៃភ្លើងឆេះព្រៃ
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ទឹកជំនន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
កំណកល្បាប់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
ខូចខាតដល់ស្រែអ្នកជិតខាង
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
low
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
medium
ខូចខាតដល់ហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធសាធារណៈ/ឯកជន
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | ប្រភេទនៃការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/ព្រឹត្តិការណ៍ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ព្យុះភ្លៀងតាមតំបន់ | ល្អ |
| ព្យុះកំបុតត្បូងតាមតំបន់ | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយទឹក
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ទឹកជំនន់ទូទៅ (ទន្លេ) | មិនស្គាល់ |
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| កាត់បន្ថយពេលដាំដុះ | មិនស្គាល់ |
មតិយោបល់:
Introduction of contour ridge
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
មតិយោបល់:
In 10 years he has obtained more money from sales of coffee and tree products
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
|
Increased production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote technology among other farmers |
|
Easy maintenance acctivities e.g. easy to keep weeds under control How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ditto |
|
Fuel wood availability How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ditto |
|
Availability of fruits How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ditto |
|
Improved kowlledge regarding SLM and soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ditto |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
|
This is cheap and affordable technology which can be used by smallholder farmers How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote technology among other farmers |
|
Large potential for increased income (higher coffee yields) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ditto |
|
Improve soil fertility How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote crop and livestock intergration (manure production) |
|
Increased soil moisture How can they be sustained / enhanced? Appropriate maintenance acttivities |
|
Erosion control How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintain sufficient soil cover |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Land competition with food crops | Promote technology among other farmers |
| High cost of tools, especially pruning scissors | Provide required tools |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Risk to fire during dry season | Introduce fire breaks |
| In areas where frost persist can lead to fungal diseases if not well pruned | Improve pruning |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Kagera TAMP project website
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល