Shelterbelts [ប្រទេសឥណ្ឌា]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Unknown User
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យ Fabian Ottiger
Line, Shelterbelts in Theri land
technologies_1473 - ប្រទេសឥណ្ឌា
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
03/08/2003
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
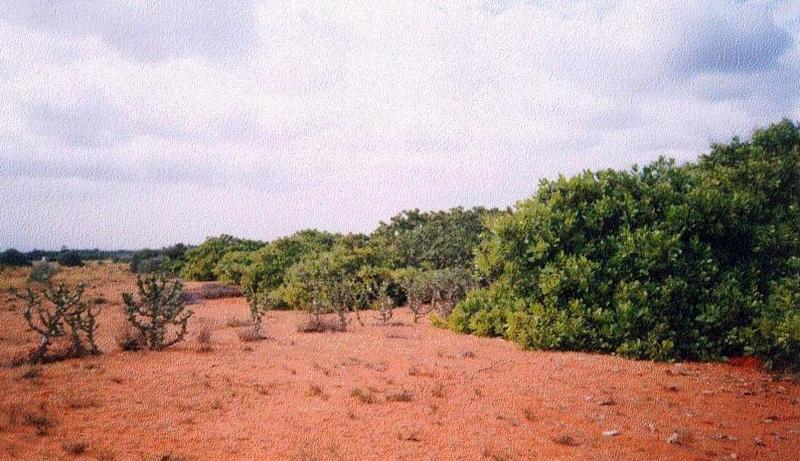
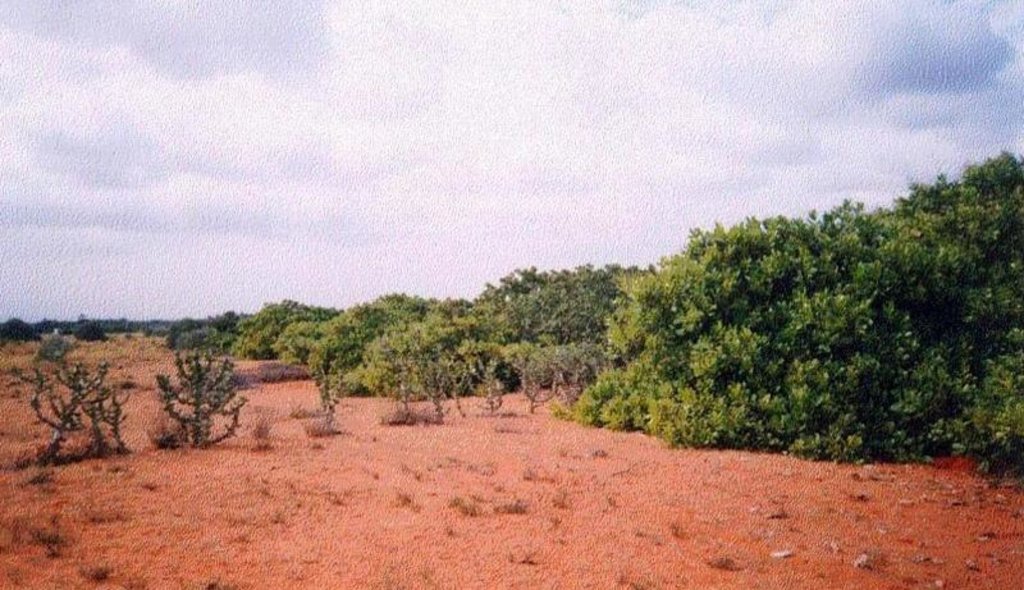
Cultivation of tree belts across the direction of wind at appropriate intervals in the deposition zone, with a view to arrest wind erosion and facilitate stabilisation of dunes through interbelt development.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
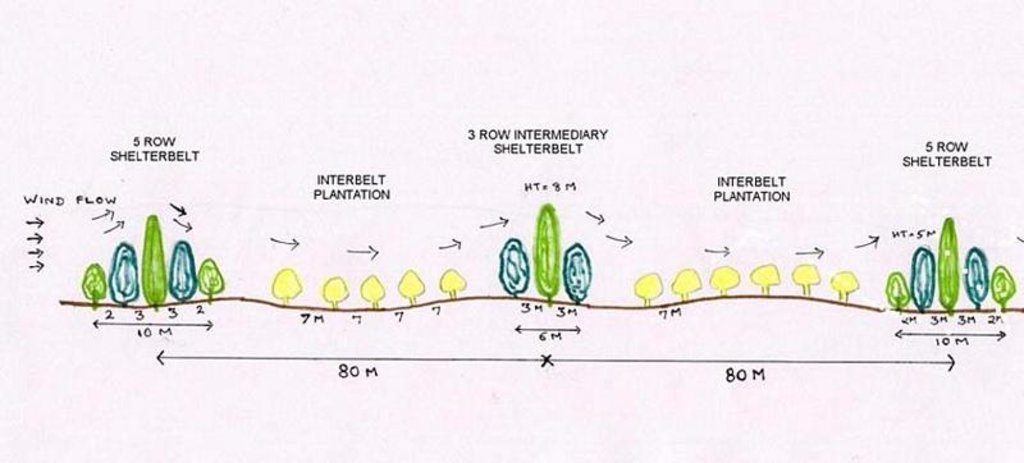
The technology comprises establishment of 5 row shelterbelts at 160 m intervals. 3 row intermediary shelterbelts are introduced in between existing shelterbelts at 80 m interval. Land owners are encouraged to cultivate tree crops in between the belts.
Purpose of the Technology: Shelterbelts are useful in reducing wind velocity, there by arresting shifting of sand dunes, deposition of sand on fields, habitation, wells, roads etc. Cultivation of area between tree belts is made possible leading to increase in productivity from these lands.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The shelterbelts comprise tree species of different heights planted in rows (5 and 3 row deep) in a straight line across the wind direction. Six month old seedlings are planted in pits of volume 1 cuft to 1.5 cuft, which are filled with tank silt. One borewell is provided for one km length for life saving irrigation.
Natural / human environment: The environment is arid and forms the deposition zone wherein sand lifted from the impact zone is deposited. Sand dunes cover the area.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសឥណ្ឌា
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Tirunelveli district, Tamil nadu state
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
The Department of Agriculture Engineering implemented shelterbelts since 1958 in neighbouring Madurai district. The technology was introduced to Tirunelveli district by the department in 1978 wherein 5 row shelterbelts were established.
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- អភិរក្សប្រព័ន្ធអេកូឡូស៊ី
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ចម្រុះ (ដំណាំ/ វាលស្មៅ/ ដើមឈើ)គិតទាំងកសិរុក្ខកម្ម
- ដីដាំដំណាំ និងចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Crops cannot be cultivated due to sand deposition. Grass cover cannot develop due to shifting of dunes. Hence the area is neglected and degrades further. Only hardy species (ef. Palymra) and coarse grasses survive. Predominant land use is open grazing.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Land cannot be cultivated economically due to arid conditions, shifting dunes and open grazing.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Cultivation is practiced only in years of good rainfall. Single crop of pulse (black gram ) is taken.
3.3 ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
មតិយោបល់:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated (ranked 2)
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 1
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Longest growing period in days: 100 Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Dec
3.4 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- របាំងខ្យល់
3.5 ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 100 m2.
The technology was implemented in the sand dune belt locally known as 'theri', located between the western mountain range and east coast of south India. The technology was initially implemented by the Government of Tamil nadu state in 1978 till 1985. The Danida supported project implemented by the department of Agricultural Engineering began activities to strengthen existing shelter belts, introduce inter belts and mass plantation from 1991 till 1999. The technology was initially implemented in an area much wider than the their lands, but experience showed that the shelterbelts was not the best methodology for low wind agricultural areas, so a shift to agro forestry and mass planting occurred.
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការបាត់ដីដោយសារខ្យល់
- Ed: អតិផរណា និង ការទម្លាក់
- Eo: ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាព
មតិយោបល់:
Main type of degradation addressed: Eo: offsite degradation effects
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Ed: deflation and deposition
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
4.2 លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស/ ពណ៌នាពីគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស
Technical Drawing - Shelterbelt
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: reduction in wind speed
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, arresting movement of sand
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 2.00%
4.3 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
Indian Rupee
កំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (បើទាក់ទង)៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
48,85
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
1.00
4.4 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Nursery raising | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | May-Nov |
| 2. | Pitting | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | Oct-Nov |
| 3. | Filling of pits | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | Nov-Dec at plantation |
| 4. | Life watering | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | Nov-Dec at plantation |
| 5. | Periodic watering | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | weekly during 1st year, except monsoon |
| 6. | Provision of shade to saplings | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | at planting |
4.5 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់:
Duration of establishment phase: 60 month(s)
4.6 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Watering | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | 2 & 3rd year after plantation /fortnightly, except monsoon |
| 2. | Casualty replacement | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | 2nd year /monsoon |
| 3. | Watch & ward | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | upto 5th year /full time watchman |
4.8 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
The above costs cover an establishment period of 5 years for 1 hectare (250 plants) of shelterbelt; year 1: pitting, planting, watering. Year 2 & 3: periodic watering, watch and ward, prunng, gap filling. Year 4 & 5: watch and ward, pruning. Of the total number of 391 mandays/ha. of shelterbelt, 288 mandays go towards periodic watering over the first 3 years. Watering of plants is essential due to the semi-arid climate and sandy soil. In addition, as supportive technology for provision of water, one borewell with handpump was established per kilometer of shelterbelt.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
កំណត់បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀង (បើដឹង) ជា មីលីម៉ែត្រ:
559,00
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
30 years average
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងតិចតួច
Since past few years, arid conditions prevail
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
មតិយោបល់ និងបញ្ចាក់បន្ថែមអំពីសណ្ឋានដី :
Landforms: Plateau/plains (undulating terrain)
Slopes on average: Gentle (undulating)
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ទាប (<1%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Soil depth on average: Very deep (due to deposition by wind)
Soil texture: Coarse/light (sandy soil),
Soil fertility: Very low (low organic matter)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (low vegetative cover)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (permeability is high)
Soil water storage capacity: Very low (sandy soil, low organic matter)
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- ច្រើនជាង 50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
38% of the land users are average wealthy (traders, labor).
42% of the land users are poor (small farmers, without water source).
20% of the land users are poor (small farmers, without water source).
Off-farm income specification: traders, employed in cashew processing plants, small industries, nearby towns, migration.
Level of mechanization: Manual work (in addition bullocks are used for ploughing)
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- អាស្រ័យផលសេរី (មិនមានការកំណត់)
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 0-10%
មតិយោបល់:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
5000 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Farmers are in favour of raising orchards to combat wind erosion and increase production in place of shelterbelts..
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Review Reports
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Chief Engineer, Agriculture Engineering Department, Anna Salai-439, Nandanam, Chennai-600035
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Project Implementation Plans, Project documents
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Programme Coordinator, WDCU, 11/1 Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi-110016.
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល