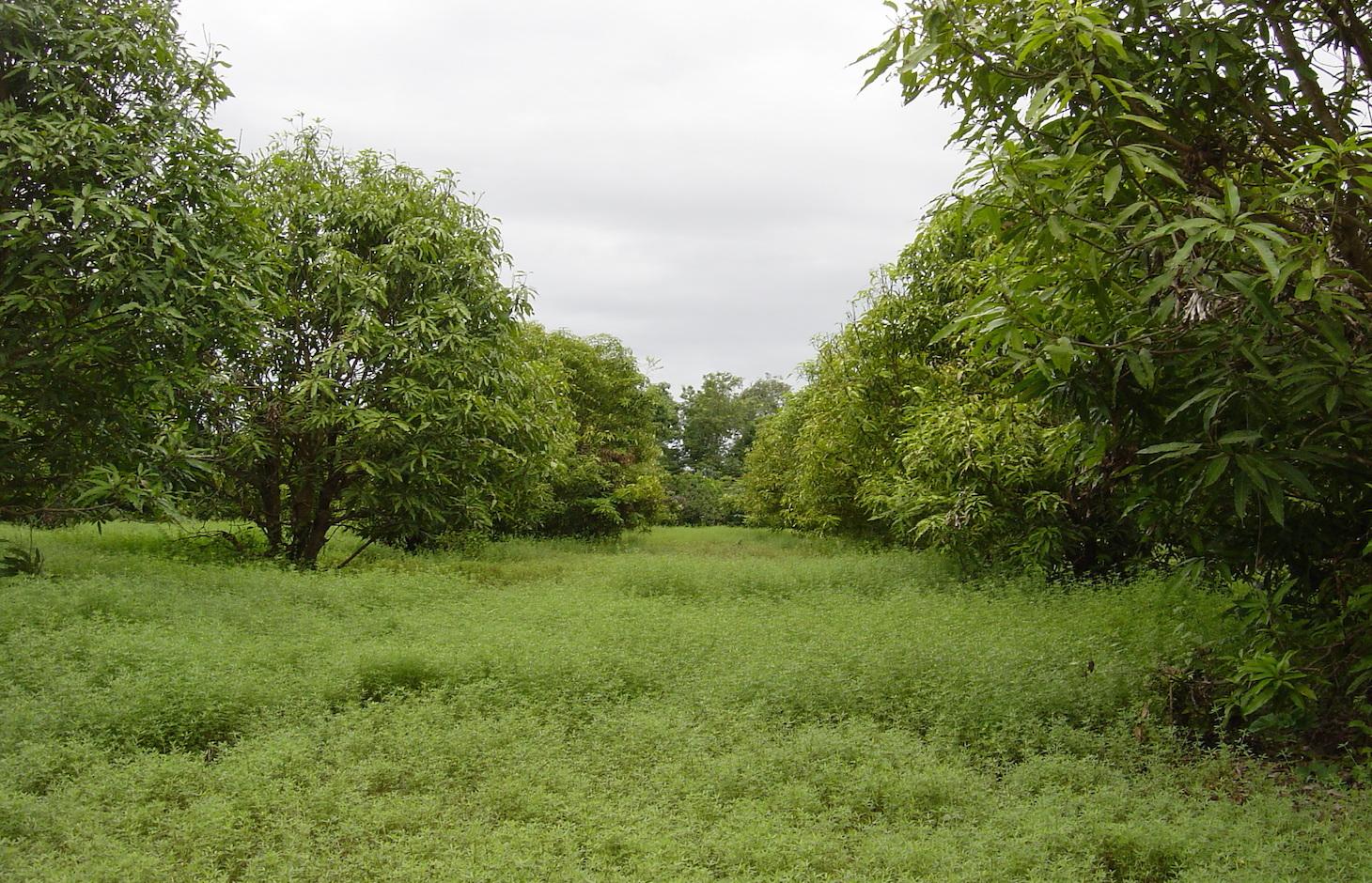
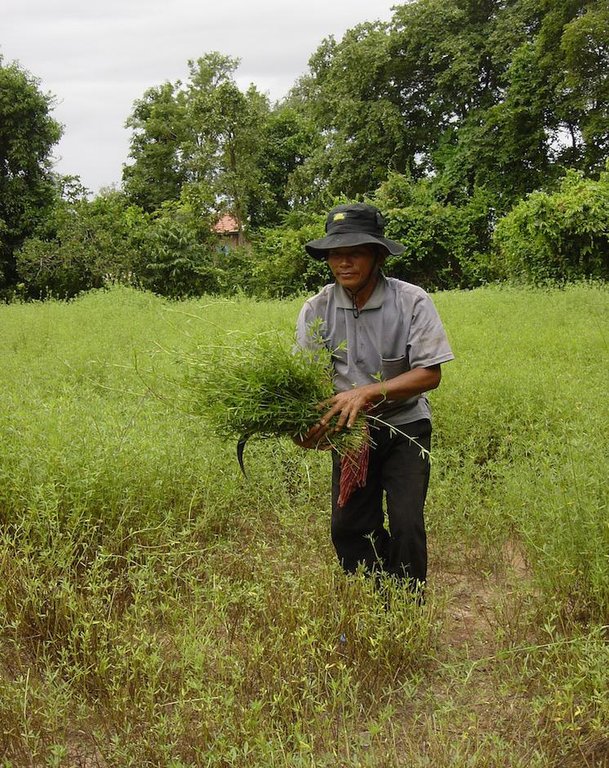
Growing stylo grass (Stylosanthes guianensis) as cattle fodder between and under mango trees. [ប្រទេសកម្ពុជា]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Christoph Kaufmann
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យ Deborah Niggli
ការដាំស្មៅជាចំណីសត្វ (Stylosanthes guianensis) ទៅតាមចន្លោះដើមស្វាយ (Khmer)
technologies_1642 - ប្រទេសកម្ពុជា
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
14/07/2014
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
Stylo grass (Stylosanthes guianensis) is grown under and between mango trees to be used as fodder for cattle.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
Stylo grass (Stylosanthes guianensis, CV. Stylo 184) is a leguminous shrub which is used in pastures and as fodder crop. It is drought tolerant and can be harvested during the whole year, though it grows only when sufficient water is available. Mangos (Mangifera indica) are grown mainly from seeds in the area, either as single trees in home gardens or as orchards. The farmer of this case study has a mango orchard of 0.6 ha with trees spaced 6 by 8 meters, and grows stylo grass as a cover crop under and between the trees. Each day a patch of stylo grass is harvested by hand, and around 40 kg of this fodder is fed to the cattle together with rice straw. This allows the farmer to keep more cattle than before, 11 heads instead of 5. The mangos are mainly sold on the market, and some are dried. This agroforestry system reduces erosion by wind and water, as the soil is covered the whole year and the trees slow down the wind. The cattle can be kept near the house, which is good for making compost and biogas.
In 2004, the farmer cleared a forest and planted mango seedling. Between the mangos, he grew pumpkins, watermelons and cucumbers, but even though he used compost the soil fertility deteriorated fast and the cucurbits did not produce anymore. A local NGO, LAREC (Local Agricultural Research and Extension Centre), was looking for farmers with enough cattle and land in the area to try stylo grass, which was unknown in the area. The farmer, first reluctant because his other crops were not producing, started to plant stylo grass seeds he got from the NGO in July 2013 (information for this documentation was collected one year after the start).To do so, he plouwed and harrowed the fields with the hand tractor, and broadcasted the seeds by hand. After the first 3 months, during which he needed to weed, he started harvesting the fodder, and he cut 40 kg a day, one patch after another, 20 cm from the soil. This allows the reproduction of this cover crop.
The land user wants to expand his stylo grass to his other mango orchard, and is collecting seeds for this. Other farmers in the area are also interested in this technology; and the land user of this case-study starts to sell them stylo grass seeds but does not produce enough for all yet.
The analysed area is mostly flat (slope < 2%), tropic (dry and wet season), and the soils are mostly sandy or loamy. The soils contain little organic matter (low soil fertility, acidification, small amount of cattle, area has been deforested) and the groundwater table is rather high (3 m below soil level during the dry season, on the surface during the wet season).
Due to climate change, the rainfalls are more erratic, temperatures rise and droughts are more recurrent. Rice is the predominant crop grown in the area, since it serves as staple food (mix subsistence and commercial activities). Rice is often grown in monocultures and harvested once a year. Once the rice is harvested (dry season), some farmer release cattle to the paddy fields to eat the straw and weeds.
As an addition to rice, most land users grow vegetable and fruits in small home gardens (subsistence) and complement their income by producing handicrafts or through off farm income / remittances from family members working in other places. The increasing migration rate (the young generation leaves the villages to work in the cities, garment industry or abroad) results in a decrease of available labour force in the area which has detrimental effects on the agricultural activities. Furthermore, the civil war in the 1970s (Khmer Rouge) led to the loss of agricultural knowledge which different NGOs try to re-establish.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសកម្ពុជា
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Kampong Chhnang
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Sre Ouk Samlor Sap/Taing Krasaing/Rolear Pha,er
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
It started in July 2013 when SOFDEC gave stylo grass seeds to farmers with enough cattle and land
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ចម្រុះ (ដំណាំ/ វាលស្មៅ/ ដើមឈើ)គិតទាំងកសិរុក្ខកម្ម
- កសិរុក្ខកម្ម
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Lack of organic matter, lack of water retention in soil, irregularity of rainfall, low soil fertility (sandy soil), monocultures, bare soil during dry season.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low soil fertility, lack of water, soil erosion by water on the slope.
ប្រសិនបើដីមានការប្រែប្រួលបន្ទាប់ពីការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីការប្រើប្រាស់ដីមុនពេលអនុវត្តន៍បច្ចេកទេស:
Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
3.3 ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 1
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Longest growing period in days: 210Longest growing period from month to month: June-December
3.4 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- កសិរុក្ខកម្ម
3.5 ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានសាយភាយពាសពេញតំបន់ណាមួយ សូមកំណត់ទំហំផ្ទៃដីអនុវត្តន៍:
- < 0.1 គម2 (10 ហិកតា)
មតិយោបល់:
0.6 ha
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការរុក្ខជាតិ
- V2: ស្មៅនិងរុក្ខជាតិៗដែលដុះមានអាយុមិនលើសពី 2ឆ្នាំ

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M1: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់
មតិយោបល់:
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cn: ការថយចុះជីជាតិ និងកាត់បន្ថយបរិមាណសារធាតុសរីរាង្គ (មិនកើតឡើងដោយការហូរច្រោះទេ)

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bc: ការថយចុះនូវគម្របរុក្ខជាតិ
- Bq: ការថយចុះនូវជីវម៉ាស/ បរិមាណ
មតិយោបល់:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Soil left bare during the dry season.), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Deforestation in 2004)
Secondary causes of degradation: population pressure (.New areas are deforested, and are degraded after a few years.), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Lack of irrigation.)
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការជួសជុល/ ស្តារឡើងវិញនៃឱនភាពដីធ្ងន់ធ្ងរ
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
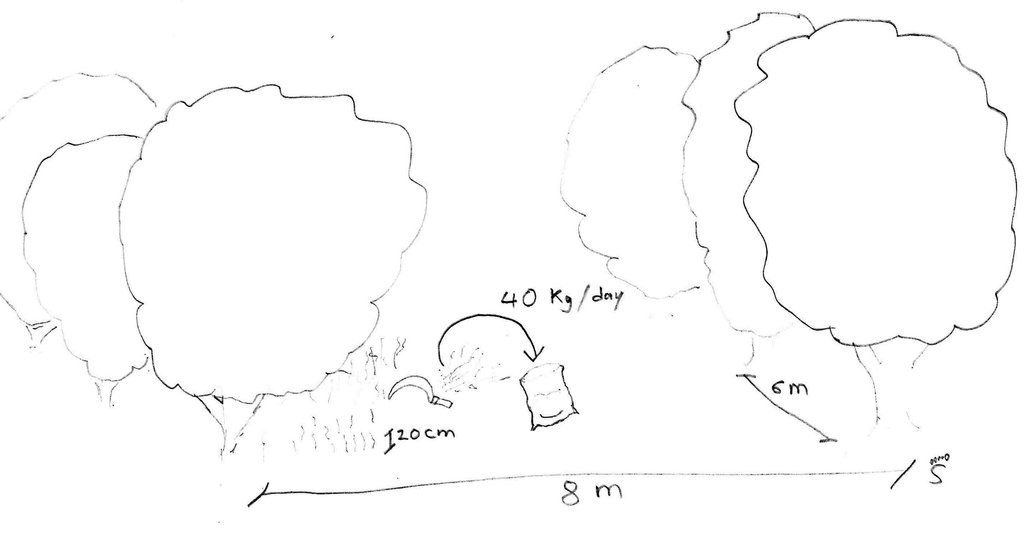
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
4.2 លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស/ ពណ៌នាពីគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស
Stylo grass is harvested daily between the mango trees, one patch after another. This allows different stages of growth.
Kampong Chhnang
Date: 2014
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 200
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 8
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
Vegetative measure: Covering the soil
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Trees/ shrubs species: Mangoes, Mangifera indica. Planted.
Grass species: Stylo grass, Stylosanthes guianensis. Seeded.
4.3 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
5.00
4.4 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plow the field, dig holes and plant mango seedlings. | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | Once at the beginning of the wet season (May-June) |
| 2. | Sow stylo grass. | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | Once in July. |
| 3. | Weeding | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | first 3 months |
4.5 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 21,25 | 21,25 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | machine use | ha | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | seeds | ha | 1,0 | 8,0 | 8,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 28,0 | 28,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 357,25 | |||||
4.6 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Harvest 40 kg of stylo grass. | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | 1h/d |
| 2. | Harvest mangoes | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | April-May |
| 3. | Maintain the stylo grass, sowing bare spots | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | 2 person days per month |
4.7 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 590,0 | 590,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 590,0 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
The costs were calculated in 2014 for an area of 0.6 ha. The farmer got 100’000 riel (25US$) for the 800 – 1000 kg mangoes produced, and a bag of fodder (40 kg, that he harvests each day on 0.6 ha) can be sold for around 5000 riel (1.25) on the market.
4.8 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
The costs were calculated as if he hired someone, and bought mango seedlings. As he did all of the work by himself, it was much cheaper. The most expensive is the harvesting of the fodder, but it should be taken into account that it is less labour intensive than harvesting wild grasses and cheaper than buying them.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
1486.45 mm 2013 in Kampong Chhnang
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
27° to 35°C
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
- ទាប (<1%)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
< 5 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
មិនមាន/ គ្មាន
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលគ្មានគុណភាព (តម្រូវឱ្យមានការសំអាត)
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងៗទៀតលើគុណភាព និងបរិមាណទឹក :
availability of surface water poor durin dry seasons
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- ទាប
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- 10-50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មាន
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
យេនឌ័រ:
- បុរស
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Only one man is applying the technology, his wife works in the garment industry.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
Off-farm income specification: His wife works in a factory.
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន ឬជួលគេដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតមធ្យម
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ភូមិ
- ឯកជន មិនមានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
- ឯកជន
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- អាស្រ័យផលសេរី (មិនមានការកំណត់)
មតិយោបល់:
Land ownership is very complex. Most of the land belongs officially to the government, yet many land users hold a paper confirming they applied for a land title – but de iure, this paper is worthless.
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មចំណីសត្វ
គុណភាពចំណីសត្វ
ផលិតកម្មសត្វ
ផ្ទៃដីផលិតកម្ម
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ភាពសម្បូរបែបប្រភពប្រាក់ចំណូល
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
Contribution to human well-being
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Less time needs to be invested in harvesting wild grasses.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
ដី
គម្របដី
ការបាត់បង់ដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
No wind erosion because of the soil cover, less water erosion.
វដ្តនៃសារធាតុចិញ្ចឹម/ការទទួលបាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Stylo gras is a leguminous, thus fixes nitrogen.
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គដី/ការបូនក្រោមដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The mango leaves fall to the soil and increase the organic content.
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ជីវម៉ាស/ កាបូនលើដី
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ល្បឿនខ្យល់
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The mango trees slow down the wind
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
កំណកល្បាប់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
ខ្យល់នាំយកនូវធូរលី
Fields need to be fenced because of the neighbour's cattle
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The living fence was already planted before.
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | ប្រភេទនៃការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/ព្រឹត្តិការណ៍ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | មិនស្គាល់ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ព្យុះភ្លៀងតាមតំបន់ | ល្អ |
| ព្យុះកំបុតត្បូងតាមតំបន់ | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយទឹក
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ទឹកជំនន់ទូទៅ (ទន្លេ) | មិនស្គាល់ |
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| កាត់បន្ថយពេលដាំដុះ | ល្អ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
មតិយោបល់:
The maintenance costs consist mainly of harvesting, which is very positive.
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- ច្រើនជាង 50%
បើអាច សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីបរិមាណ (ចំនួនគ្រួសារ និង/ ឬតំបន់គ្របដណ្តប់):
100% or 1 land user family
មតិយោបល់:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Other farmers in this village want to grow stylo grass, but cannot get seeds. This farmer starts to sell seeds to other farmers.
Other farmers in this village want to grow stylo grass, but cannot get seeds. This farmer starts to sell seeds to other farmers.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Other farmers in the village showed strong interest to start applying this technology. The farmer of this case study started to sell seeds to 3 of them, and 7 others in the area showed interest as well but there were not enough seeds available.
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| As a leguminous, stylo grass could be plowed into the soil to improve the soil fertility. |
| Less time is needed to harvest fodder for the cattle, as he does not need to collect it from the wild anymore. |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
|
As a leguminous, stylo grass has a high protein content, which makes it valuable as fodder. |
|
The soil is covered, trees slow down the wind, inducing a good micro-climate and stopping wind erosion. |
| Water erosion on slopes is reduced as the stylo grass covers the soil. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| The land has to be fenced off, as neighbours cattle otherwise graze in his fodder. | Living fence (currently used by the land users), needs only little maintenance. |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Productivity of the mangoes is mostly low as seedlings were used. | Learn how to graft, with improved varieties or selected individuals from the farm. The use of seedlings allows a selection of new varieties; the grafting can take place at any tree size. |
| The cultivar Stylo 184 has only a single-gene resistance to anthracnose (tropicalforage.info). In case of breakdown all the fodder is lost. | Mixed cropping with another fodder, or mixed cropping of different cultivars of Stylosanthes guianensis |
| Stylo grass is not considered shade tolerant (tropicalforages.info), when the mangoes will grow higher could become unproductive. | Use dwarf rootstocks for the mangoes, space them further apart, or use different species of fodder. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Tropical forage info website. Stylosanthes guianensis
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
http://www.tropicalforages.info/key/Forages/Media/Html/Stylosanthes_guianensis_var._guianensis.htm
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Feedipedia Website. Stylo (Stylosanthes guianensis)
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
http://www.feedipedia.org/node/251
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល