Stone wall [ប្រទេសអាហ្វហ្គានិស្ថាន]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Aqila Haidery
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យ David Streiff
Diwar Sangi (Dari)
technologies_1723 - ប្រទេសអាហ្វហ្គានិស្ថាន
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Burger Sieger
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Saadat Alemi
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Zainullah Hazem
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Hussein Muhammadi
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Zekrullah Ahmedi
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Reza Ahmedi
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Ershad Mustafa
mustafa.ershad@crs.org
Catholic Relief Service
ប្រទេសអាហ្វហ្គានិស្ថាន
ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Catholic Relief Services/East Africa (Catholic Relief Services/East Africa) - ប្រទេសកេនយ៉ា1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
14/09/2011
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.5 ការយោងទៅលើកម្រងបញ្ជីសំណួរនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM

Community-Based Watershed Management [ប្រទេសអាហ្វហ្គានិស្ថាន]
Sustainable implementation of watershed management through appropriate SLM technologies, formation of organizational structures and capacity building of stakeholders
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Aqila Haidery
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
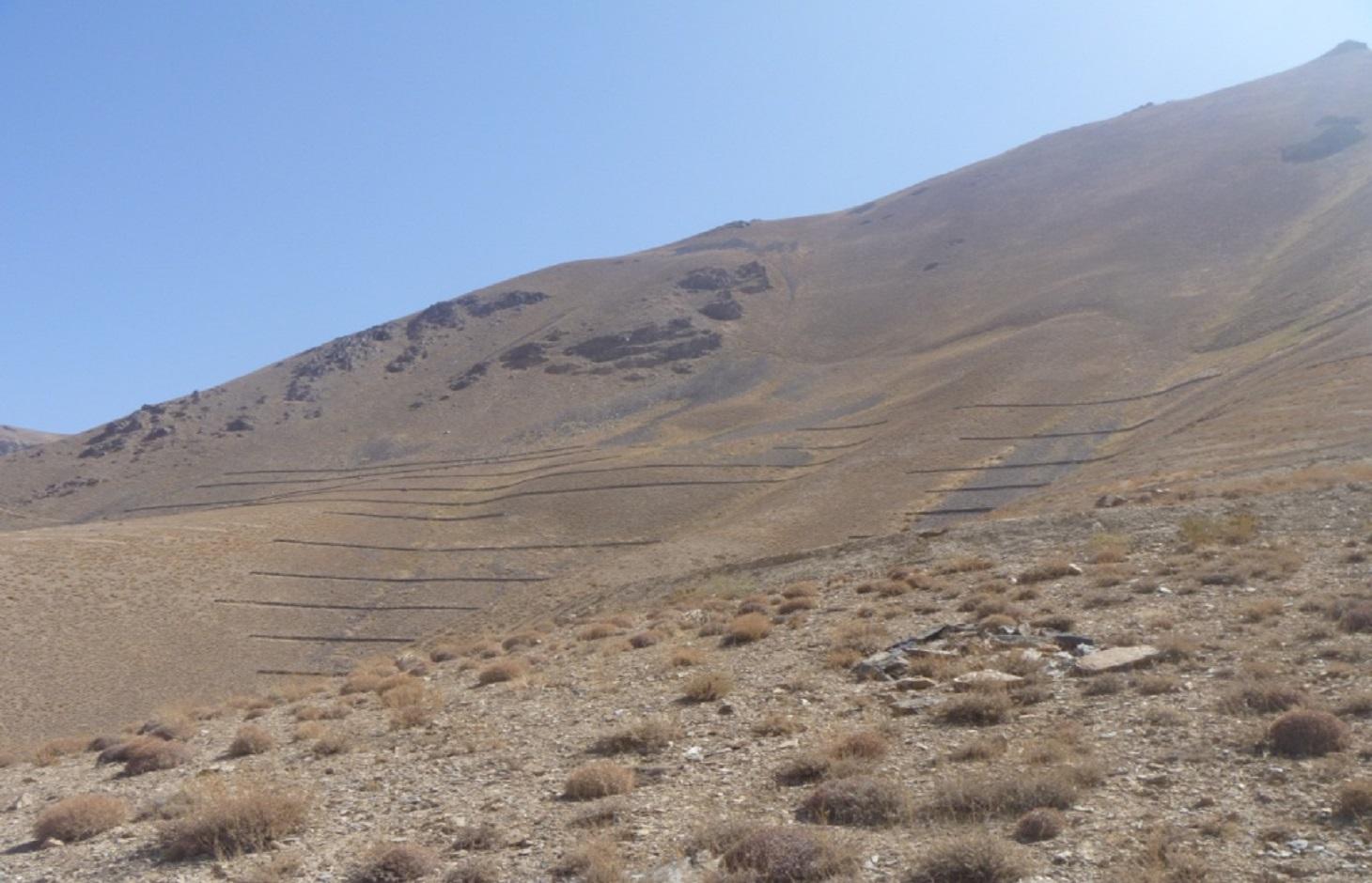
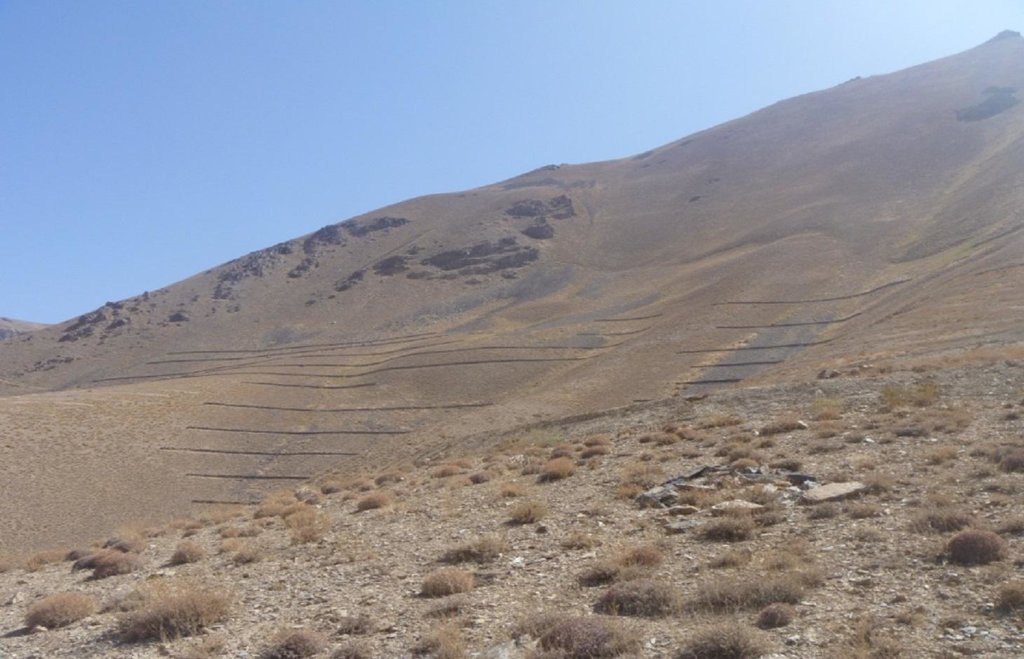
Contour stone walls constructed on moderate to steep slopes to retain water and sediments and trap snow.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
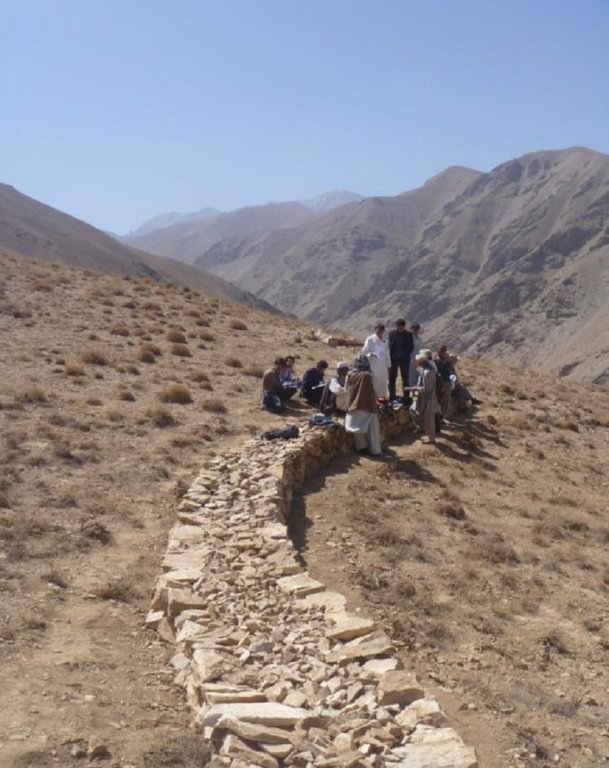
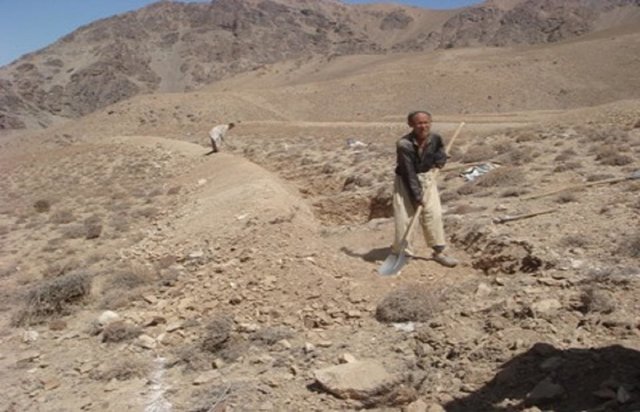
The Stone wall technology is documented by Sustainable Land Management Project/HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation with financial support of Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation(SDC) and close support and cooperation of the Catholic Relief Service (CRS). The technology was applied in community land in Sar e Ahangaran (Siakhar Toghai) watershed which drains into the main Bamyan valley forming part of the Kunduz watershed of the Amu Darya river basin. The project was initiated by CRS (Catholic Relief Services) in October 2009 and the participating families were involved in each stage of intervention, including surveys, design, and implementation and monitoring.
Purpose of the Technology: The main function of stone wall is to trap snow and control run-off. Through construction work, many families received income through cash for work. About 21,519 USD were spent on the technology, with 90% contribution from CRS and 10% from the participating community. The cost for implementing Stone Wall technology was about 2,390 USD/ha.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The technology was applied in extensive grazing land. The stone wall technology is not new to the farmers of Sar e Ahangaran (Siakhar Toghai) as they have applied it in their private croplands as well. CRS built on this traditional technology and improved it by applying it along contour lines demarcated with A-frame and establishing it a more technically sound manner. The technology is effective in reducing snow avalanches, surface run-off, sediments, and downstream flooding leading to more crop production and less destruction of property and crops. It is tolerant to increasing or decreasing temperature and droughts. If constructed properly along the contour, the technology is not impacted by heavy rainfall or severe flash floods.
Natural / human environment: The technology was applied on hill and mountain slopes at 3000-3500 m elevation. The average annual rainfall in the area is 250-500 mm. The longest growing period is 6 months, i.e. from April to September. Due to its proximity to the Koh-i-Baba mountains, the area experiences long, severe winters of around 6 months (Mid-October to mid-April).
The participating families are poor; 10-50 % of their income is from off-farm activities, e.g. labour, migration. The villagers have moderate access to health, education, technical assistance, drinking water and sanitation facilities. Accessibility to employment, markets, energy, good roads and financial services is poor. The production system is subsistence-oriented and non-subsidized.
The effectiveness of stone wall technology was strengthened through other SLM measures, including contour trench bund, gully plugs, shrub cutting and grazing control, planting trees below the walls, and re-sowing with improved fodder species.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសអាហ្វហ្គានិស្ថាន
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Sar-e-Ahangaran, Bamyan, Afghanistan
2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- 10-50 ឆ្នាំ
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- ពេលកំពុងពិសោធន៍
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- កាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
ដីវាលស្មៅធំៗ:
- ពនេចរ
ដីវាលស្មៅតូចៗ/ ផលិតកម្មចំណី:
- កាត់ និងជញ្ជូន/ គ្មានវាលស្មៅសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Degradation of slopes due to biotic pressures such as overgrazing, extraction of bushes for fuel and cultivation leading to snow avalanche, flash floods and decrease in spring water quantity. Lack of soil and water conservation measures on slopes contribute to low production from agriculture and pasture lands.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Grazing land: Gi: Intensive grazing/ fodder production
ប្រសិនបើដីមានការប្រែប្រួលបន្ទាប់ពីការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីការប្រើប្រាស់ដីមុនពេលអនុវត្តន៍បច្ចេកទេស:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង និងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Longest growing period in days: 180; Longest growing period from month to month: April to September
ដង់ស៊ីតេនៃសត្វចិញ្ចឹម (បើពាក់ព័ន្ធ):
25-50 LU /km2
3.4 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- វិធានការអនុវត្តកាត់ទទឹងទីជម្រាល
3.5 ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- អនុវត្តនៅកន្លែងជាក់លាក់មួយ/ ប្រមូលផ្តុំនៅតំបន់តូចៗ
មតិយោបល់:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.09 km2.
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S6: ជញ្ជាំង, របាំង, របងឈើខ្ពស់ៗ
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bc: ការថយចុះនូវគម្របរុក្ខជាតិ
មតិយោបល់:
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing, Contamination of water due to floods
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
4.2 លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស/ ពណ៌នាពីគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស
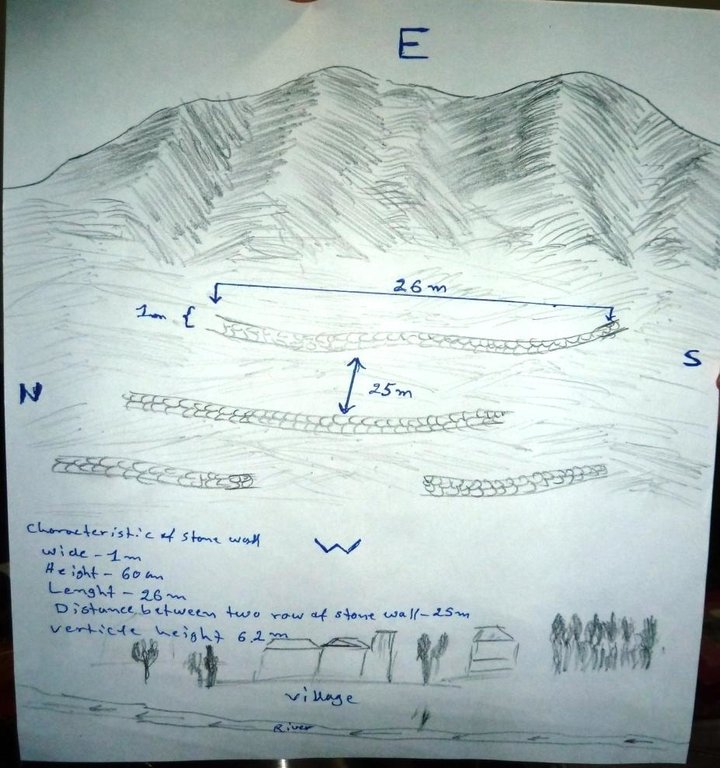
The hand drawing shows the dimensions of the technology, spacing, area’s borders and as well as the downstream area.
Stone wall dimensions are as follows:
length: 26 m; width: 1m; height: 60 cm; foundation: 30cm in depth.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope length, Reduction of snow avalanches
Secondary technical functions: Improvement of ground cover due to less soil erosion
Wall/ barrier
Spacing between structures (m): 25
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 26
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Construction material (stone): Dry stone masonry
4.3 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់រូបិយប័ណ្ណសម្រាប់ថ្លៃដើម:
- ដុល្លារអាមេរិក
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
6
4.4 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Excavation of the foundation | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | |
| 2. | Construction of the stone wall | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ |
4.5 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Excavation of the foundation | persons/day/ha | 13,75 | 6,0 | 82,5 | 10,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Construction of the stone wall (skilled labour) | persons/day/ha | 39,73 | 12,0 | 476,76 | 10,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Construction of the stone wall (unskilled labour) | persons/day/ha | 132,43 | 6,0 | 794,58 | 10,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Stone | m3 | 132,43 | 7,82 | 1035,6 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 2389,44 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Duration of establishment phase: 10 month(s)
4.6 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | No information on maintenance available. | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ |
4.8 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
Duration of the establishment phase in 0.9 square kilometer in 10 months.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
Bamyan has a very harsh 6 months winter with a heavy snow fall. Most of its villages face with scarcity of water during the summer
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងតិចតួច
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ទាប (<1%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Soil drainage / infiltration is good due to sandy soils
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
5-50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
មិនមាន/ គ្មាន
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- សម្រាប់ហូបក្នុងគ្រួសារ (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង)
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- 10-50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ជាក្រុម/ សហគមន៍
យេនឌ័រ:
- បុរស
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Women are not going to the site culturally.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន ឬជួលគេដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតមធ្យម
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- រដ្ឋ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- អាស្រ័យផលសេរី (មិនមានការកំណត់)
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មចំណីសត្វ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to better management measures
ហានិភ័យនៃភាពបរាជ័យរបស់ផលិតកម្ម
ផ្ទៃដីផលិតកម្ម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Decreased area for grazing and shrub cutting
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
បន្ទុកការងារ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
As it has decreased the requirement of cleaning the field after the floods
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
ស្ថាប័នសហគមន៍
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The project was implemented through watershed/NRM committee
ការកាត់បន្ថយជម្លោះ
ស្ថានភាពក្រុមដែលមានបញ្ហាក្នុងសង្គម និងសេដ្ឋកិច្ច
livelihood and human well-being
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Extra income from cash for work; less floods and hence more crop and fodder production, more spring discharge
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
លំហូរទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
And velocity
ដី
គម្របដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to reduced run off velocity
ការបាត់បង់ដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to less run off velocity
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃរុក្ខជាតិ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to better soil moisture and area protection
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ីផ្សេងៗ
soil disturbance
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
due to stone removal
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
In spring located downstream
ទឹកជំនន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
ទឹកក្រោមដី/ ការបំពុលទឹកទន្លេ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to less flash floods
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | ប្រភេទនៃការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/ព្រឹត្តិការណ៍ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ព្យុះភ្លៀងតាមតំបន់ | ល្អ |
| ព្យុះកំបុតត្បូងតាមតំបន់ | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយទឹក
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ទឹកជំនន់ទូទៅ (ទន្លេ) | មិនល្អ |
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| កាត់បន្ថយពេលដាំដុះ | ល្អ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
មតិយោបល់:
No more information is available in this regard.
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Appropriate information is not available.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Some of the involved farmers who have applied this technology have as well implemented this technology on their private annual croplands by their own initiative, not as technically precise as executed in the projects.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is a growing trend towards the adoption of the technology.
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
|
Reduces flash flood and sediments How can they be sustained / enhanced? combine the existing structural with vegetative measures |
|
Downstream spring water quantity improved How can they be sustained / enhanced? More vegetation around the spring catchment |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Less foundation of the structure | Combination of the structure with vegetation; foundation should be better |
| Stone avalanche if heavy rainfall happens | Combination of the structure with vegetation |
| In some areas, stones are not available, hence, the technology cannot be applied | Option for other measures |
| Compared with contour trench, stone wall cannot absorb much runoff | Combine with vegetative measures |
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់

Community-Based Watershed Management [ប្រទេសអាហ្វហ្គានិស្ថាន]
Sustainable implementation of watershed management through appropriate SLM technologies, formation of organizational structures and capacity building of stakeholders
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Aqila Haidery
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល